Journal of Modern Physics
Vol.05 No.16(2014), Article ID:50644,11 pages
10.4236/jmp.2014.516164
The Relativistic Time-Dependent Aharonov-Bohm Effect
Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Email: athan.petridis@drake.edu
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 28 July 2014; revised 23 August 2014; accepted 18 September 2014
ABSTRACT
The relativistic Aharonov-Bohm (AB) effect is studied using the time-dependent
Keywords:
Aharonov-Bohm Effect,

1. Introduction
The Aharonov-Bohm (AB) effect [1] , consisting of wave function phase shifts due to minimal coupling with four-vector potentials, observable by means of interference patterns, has been a cornerstone of gauge field theories. In its original magnetic version, electrons propagate around an impenetrable, very long solenoid, thus experiencing no
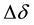 , introduced by a closed path C encircling the solenoid in the vector field, A, is equal to the magnetic flux:
, introduced by a closed path C encircling the solenoid in the vector field, A, is equal to the magnetic flux:
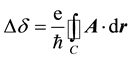 . (1)
. (1)
A similar effect arises from interactions with a scalar potential. There is experimental evidence for the existence of the AB effect [2] [3] and it has become stronger over the years [4] . Recently the existence of the effect has been demonstrated even during quantum tunneling [5] .
The AB effect has its roots in the topology of the electromagnetic (EM) vacuum [6] which is not simply- connected since the first homotopy group, 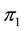 of the compact, gauge group
of the compact, gauge group 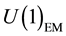 is isomorphic to the group of integers Z. In the Standard-Model, however, the
is isomorphic to the group of integers Z. In the Standard-Model, however, the 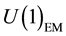 subgroup is irregularly embedded into the
subgroup is irregularly embedded into the 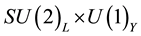 electro-weak symmetry group and it is non-compact leading to a trivial EM vacuum topology.
electro-weak symmetry group and it is non-compact leading to a trivial EM vacuum topology.
The plane-wave solution in the asymptotic limit has been obtained in the case electrons interacting with cosmic strings [7] . Also some theoretical models for dark matter predict the formation of dark cosmic strings that can interact with the Standard Model charged particles via the AB effect [8] . The AB effect is relevant to magnetic-field vortices in superconductors. One interesting result is macroscopic parity violation leading to a spontaneous Hall effect [9] . There has been substantial progress in mathematically solving the Schrӧdinger equation with wave-packets with AB interactions [10] . The effects of spin have been addressed in terms of the non-rela- tivistic
There are questions, though, pertaining to the role of dipole-like fields due to the finite-longitudinal-size of physical solenoids and the influence of induced Coulomb charges in the conductors that make up the solenoids. Furthermore, a complete relativistic treatment of the problem can allow for the investigation of the very high energy range and, in this way, of the limits of applicability of the multiply-connected EM vacuum topology.
To this end, the AB effect is studied by means of the time-dependent relativistic
2. Numerical Algorithm and the
The numerical algorithm to be employed in this work is the staggered-leap-frog method. It is applied on a spatial grid of bin-size 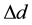 with a time-step
with a time-step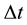 . At every grid point, r, the 4-dimentional spinor,
. At every grid point, r, the 4-dimentional spinor, 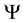 , describing a spin-1/2 fermion, at time
, describing a spin-1/2 fermion, at time 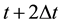 is computed using the spinor at time t and the Hamiltonian,
is computed using the spinor at time t and the Hamiltonian, 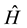 , operating on the spinor at time
, operating on the spinor at time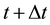 :
:
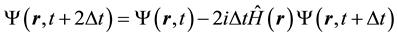 . (2)
. (2)
The spatial derivatives are calculated symmetrically to avoid false propagation of the spinor, biased in one direction. Totally reflecting boundary conditions are chosen to ensure that there is no loss in the probability density. Reflections off the grid boundaries are avoided by stopping the algorithm at their onset. Due to the relativistic covariance of the
The
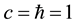 and
and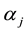 ,
, 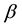 are 4 × 4
are 4 × 4
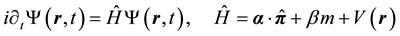
where V is a scalar potential and the canonical momentum operator is given by the minimal coupling scheme as
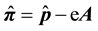
where 
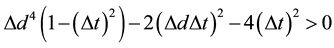
Since the equation is usually coupled, a numerical way to safeguard stability is needed. To this end, evaluating the norm of the spinor at each time step and checking for deviations from unity proved very effective. When instability ensues the norm starts deviating from unity very rapidly and/or it oscillates wildly. Stability is achieved by selecting an appropriately small time step. Since the algorithm requires information on the spinor from two previous time-steps, the first step is taken using a simple linear approximation. To further increase stability, a predictor-corrector step is inserted but proved unnecessary in the cases presented here.
In order to calculate the time dependence of the probability distributions, the initial spinor is chosen to be a wave packet with group momentum 

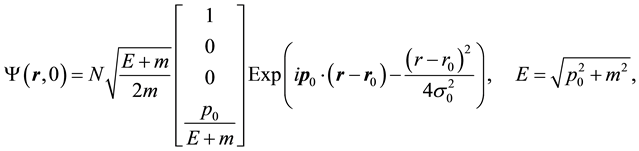
where N is an overall normalization factor and the spinor structure is in the matrix. When
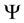
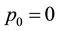
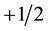
3. One-Dimensional Test Studies
Studies of the numerical solutions to the time-dependent
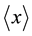
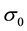
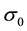

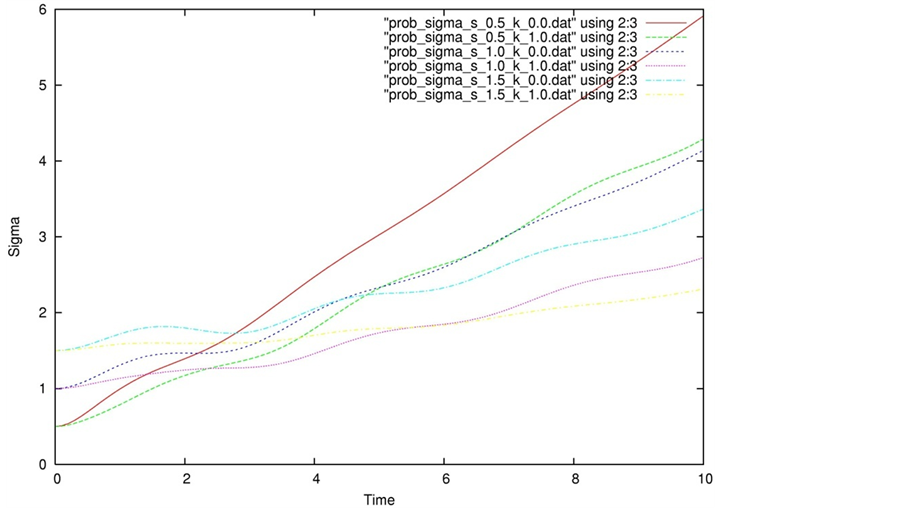
In Figure 2 the standard deviation, 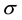
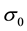
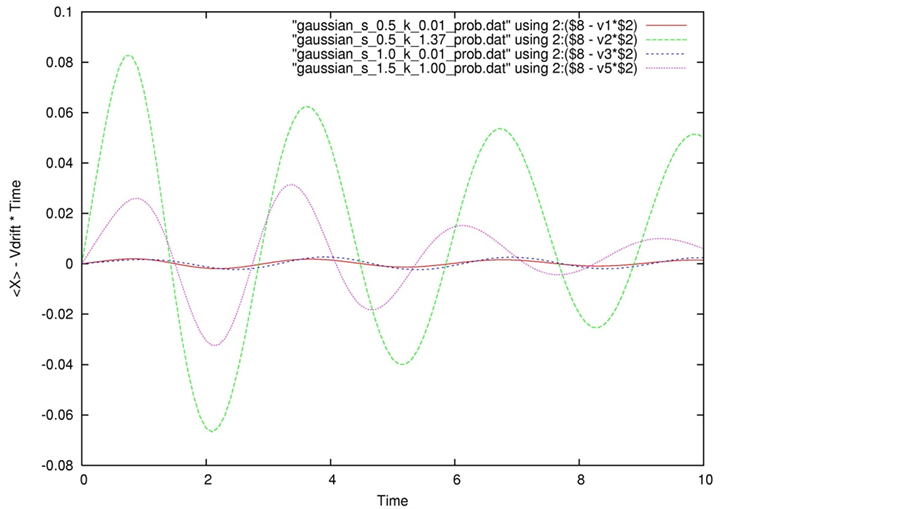
Figure 1. The position expectation value, 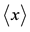
Figure 2. The position standard deviation, σ, versus time (red: σ0 = 0.5, p0 = 0; green: σ0 = 0.5, p0 = 1.0; blue: σ0 = 1.0, p0 = 0; purple: σ0 = 1.0, p0 = 1.0; light blue: σ0 = 1.5, p0 = 0; yellow: σ0 = 1.5, p0 = 1.0). An initially narrower or slower wave packet spreads out faster with time. The jitter is more pronounced at 2σ0 = λC and dies out with time.
slower initial wave packet spreads out faster with time. The jitter decays away with time and is more pronounced at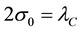
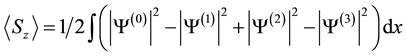
is plotted versus time where, 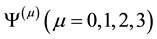
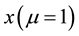
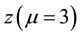
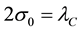
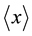
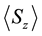
Su, and
4. Infinite-Solenoid and Dipole Fields
In this section numerical results on the time-dependent relativistic AB effect are presented. The
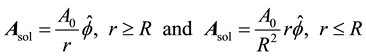
where r is the distance from the center and A0 is the potential strength (it depends linearly on the current in the solenoid). If the solenoid is finite in length a dipole component is also generated. It is assumed that small magnetic
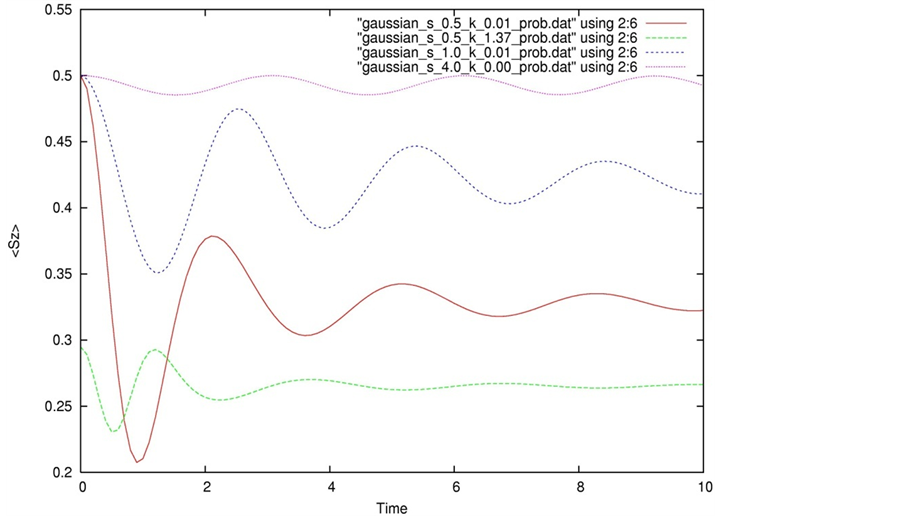
Figure 3. The expectation value of the spin component perpendicular to the propagation direction versus time (red: σ0 = 0.5, p0 = 0.01; green: σ0 = 0.5, p0 = 1.37; blue: σ0 = 1.0, p0 = 0.01; purple: σ0 = 4.0, p0 = 0.0). The jitter is present even when p0 = 0.0, is more pronounced at 2σ0 = λC and dies out with time.
fields produced around individual wires of the solenoid can be neglected due to the presence of the effectively impenetrable, smooth wall around the structure. The vector potential due to a simple, ideal dipole placed perpendicularly to the x-y plane at the origin is
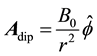
where B0 is its strength. Unlike the solenoid potential this corresponds to a non-zero magnetic field for r > R. In the calculations to be presented in this article the initial wave packet has group momentum p0 = 1.134 with initial standard deviation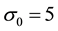
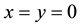
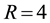
First, a pure solenoid field is examined with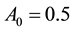
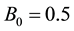
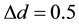
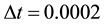
5. Characteristic Signals
The time-dependent asymmetry of the diffraction pattern can be exploited in order to identify the type of potential that produces it. Since the effect is typically measured by inductively-coupled devices, sensitive to the local current density fluctuations and placed around the solenoid, a good measure would be the difference between the integrated densities left and right of the initial propagation direction. Specifically the probability density can be separately integrated in the upper-left and the lower-right quadrants (Figure 4 and Figure 5) and the (Left-Right) signal (a function of time) can be defined as
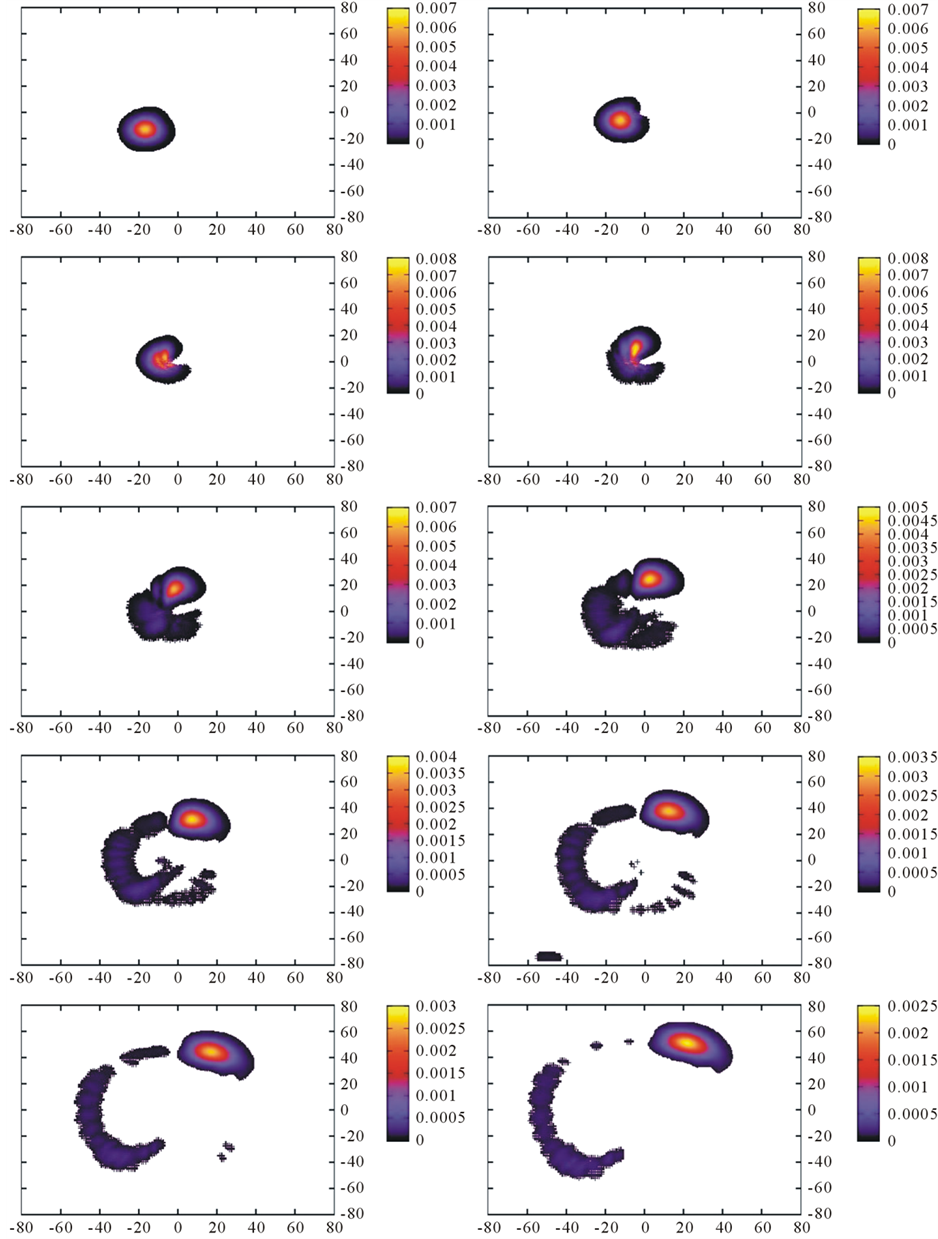
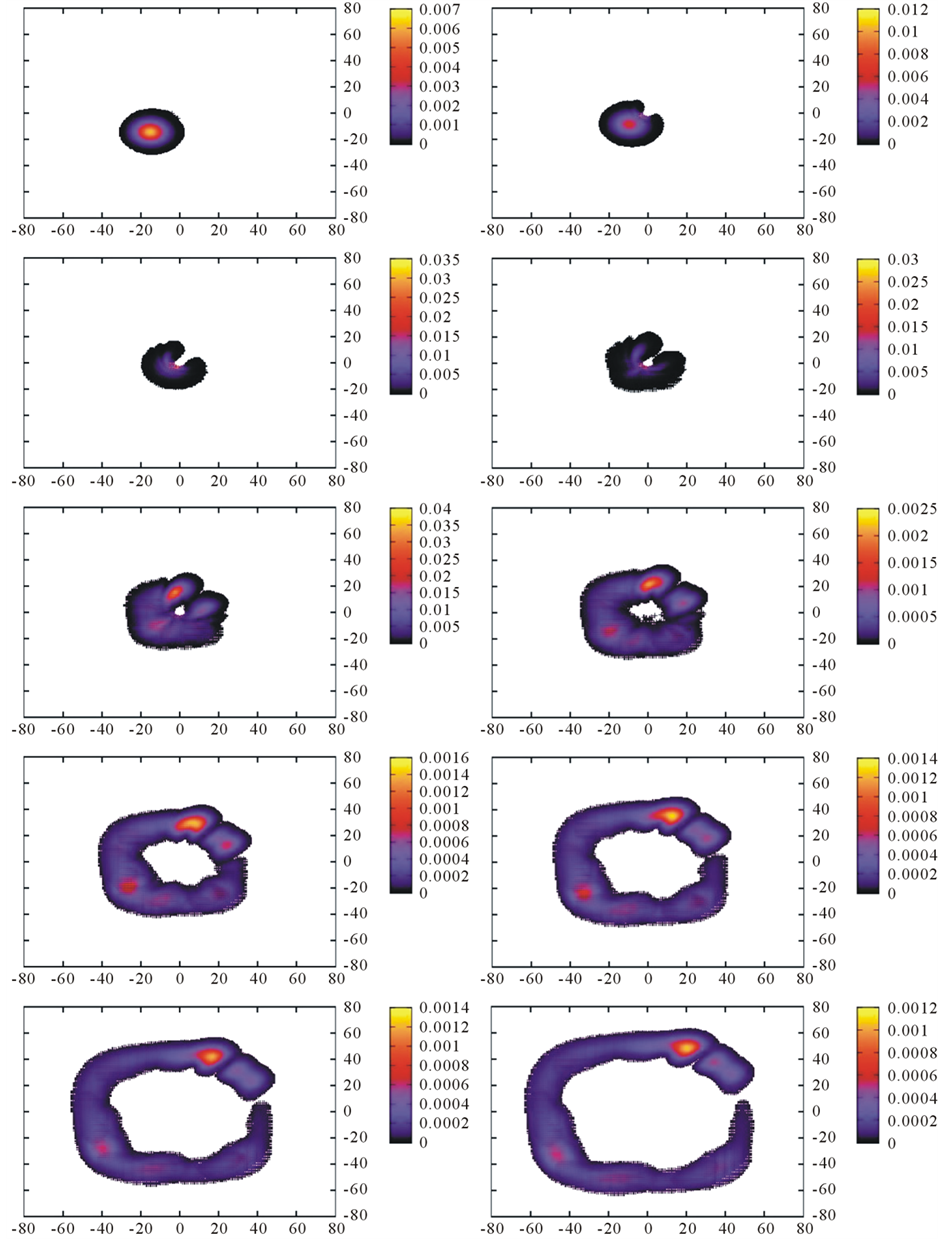
Figure 4. Probability density distribution for diffraction off a solenoid field with strength A0 = 0.5. The initial spinor has p0 = 1.134 and σ0 = 5 and moves diagonally. The solenoid is at the center and has radius R = 4. The time sequence is left to right and, then, upper to lower panel: t = 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120.
Figure 5. Probability density distribution for diffraction off a dipole field with strength B0 = 0.5. The initial spinor has p0 = 1.134 and σ0 = 5 and moves diagonally. The solenoid is at the center and has radius R = 4. The time sequence is left to right and, then, upper to lower panel: t = 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120.
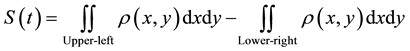
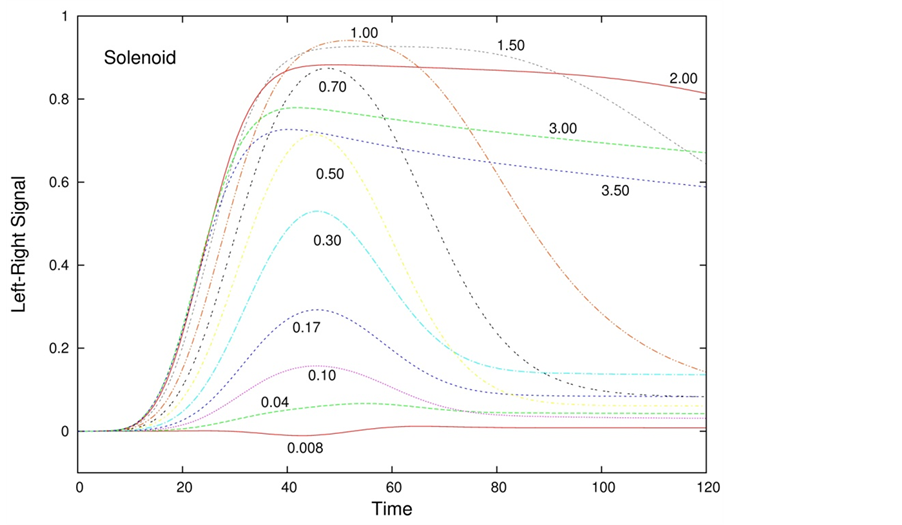
The signal obtained with a pure solenoid field is presented in Figure 6 as a function of time for increasing values of the potential strength A0, indicated beside each curve. The signal has the form of a pulse that becomes broader as A0 increases. It is important to note that the signal-peak dependence on A0 is non-monotonic. It is maximized around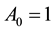
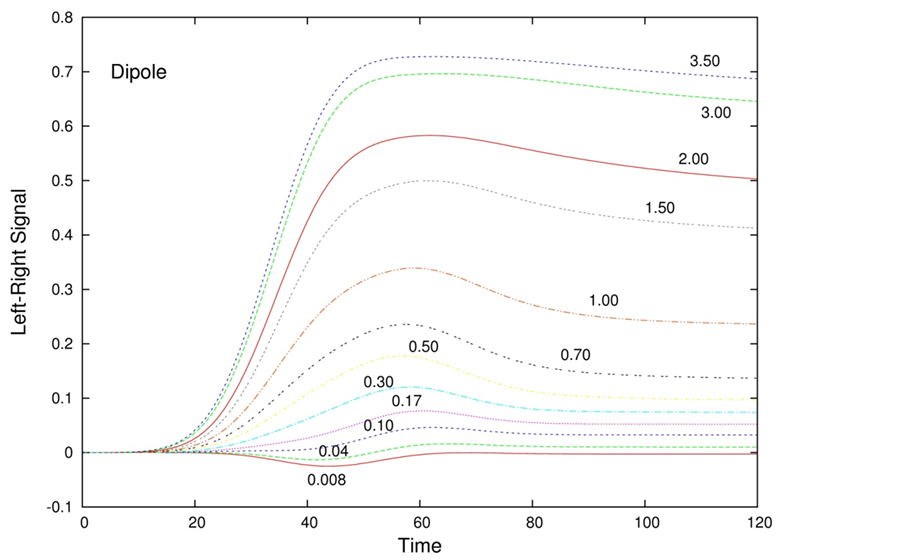
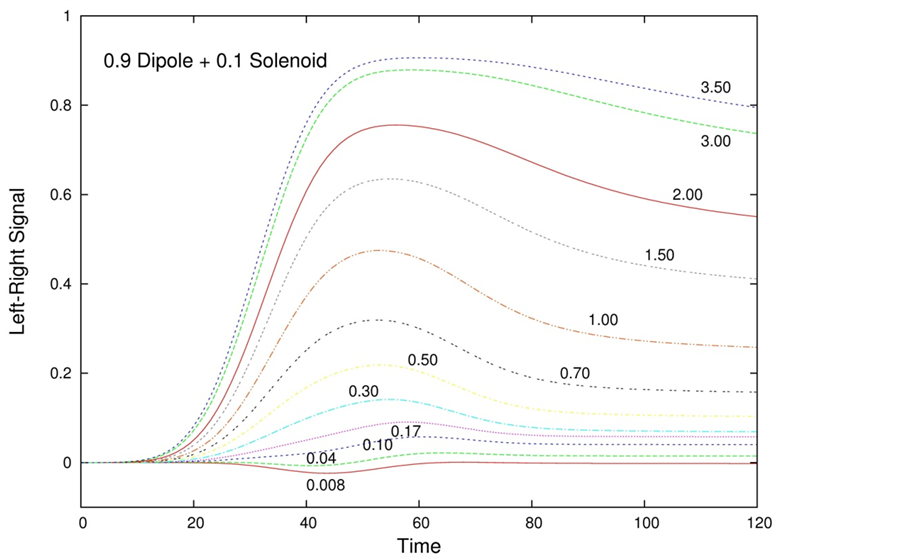
The signal obtained with a pure dipole field is presented in Figure 7 as a function of time for increasing values of the potential strength B0, indicated beside each curve. The signal has the form of a pulse that becomes broader as B0 increases. In the range of potential strengths investigated, the peak signal is monotonic in B0. In this range the effect of the probability density swinging around the solenoid is not as large as in the case of the pure solenoid field because the dipole field dies out faster with the distance from the center.
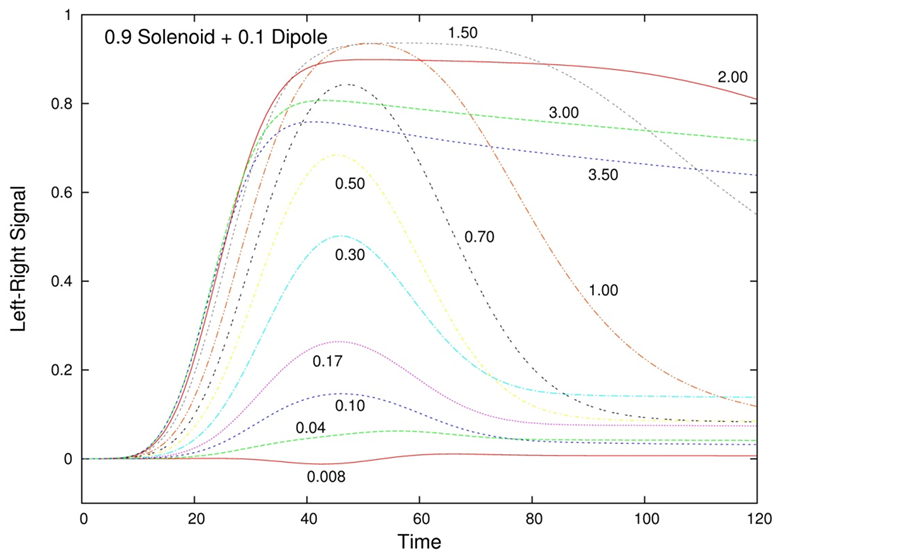
For comparison the signal for a solenoid field of strength A0 superimposed with a dipole field of strength 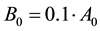
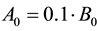
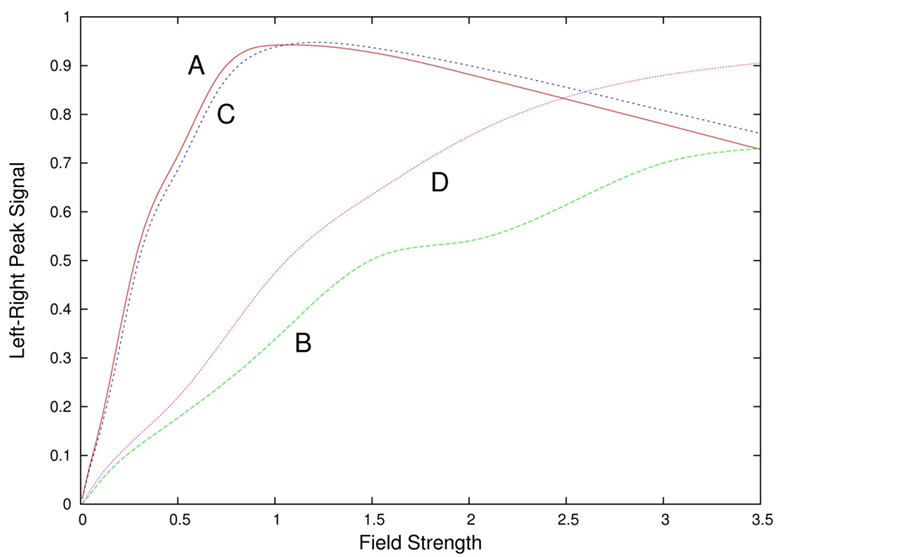
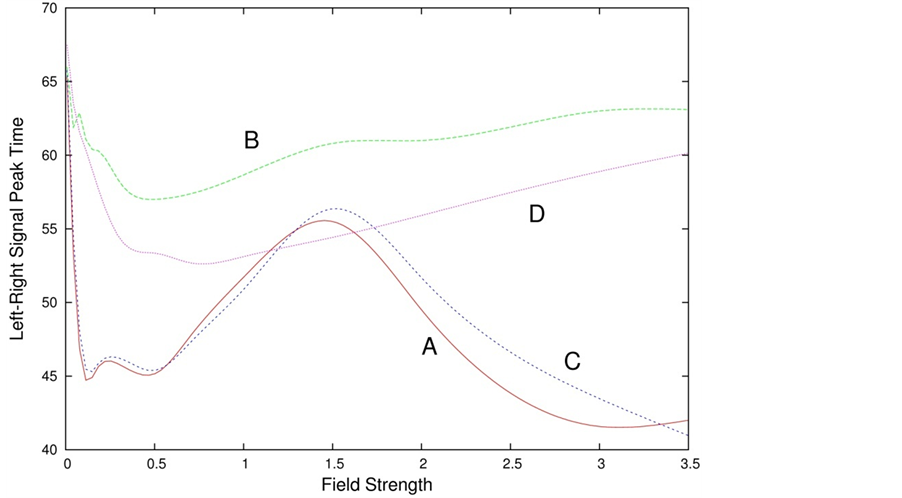
The results obtained can be further elucidated by examining the dependence of the peak signal, i.e., the maximal value of the Left-Right signal, on the total field strength, A0 + B0 (Figure 10). When the solenoid field dominates the non-monotonic behavior is clear. Another observable that provides a very clear distinction between solenoid and dipole fields is the time at which the Left-Right signal peak occurs. This is plotted in Figure 11 versus the total field strength. In the case of solenoid-dominated fields a maximum appears at intermediate values of A0 + B0.
A pulsed experiment may, therefore, be designed. An oscilloscope can easily produce the Left-Right signal captured by induction detectors. The experiment can be repeated for various field strengths and the signal shapes
Figure 6. Left-Right signal versus time for increasing values of a pure solenoid field whose strength, A0, is indicated beside each curve. The pulse becomes broader as A0 increases. The peak value is a non-monotonic function of A0.
Figure 7. Left-Right signal versus time for increasing values of a pure dipole field whose strength, B0, is indicated beside each curve. The pulse becomes broader as B0 increases. In this field-strength range, the peak value is a monotonic function of B0.
Figure 8. Left-Right signal versus time for increasing values of a 0.91 solenoid + 0.09 dipole field whose total strength is indicated beside each curve. The pulse becomes broader as the field increases. The peak value is a non-monotonic function of the field strength. The overall behavior is solenoid- like.
Figure 9. Left-Right signal versus time for increasing values of a 0.91 dipole + 0.09 solenoid field whose total strength is indicated beside each curve. The pulse becomes broader as the field increases. The peak value is a monotonic function of the field strength in this range. The overall behavior is dipole-like.
Figure 10. Left-Right signal peak value versus the total field strength, A0 + B0. A: solenoid, B: dipole, C: 0.91 solenoid + 0.09 dipole, D: 0.91 dipole + 0.09 solenoid. The behavior distinctly shows the presence of the solenoid field contribution.
Figure 11. Left-Right signal peak time versus the total field strength, A0 + B0. A: solenoid, B: dipole, C: 0.91 solenoid + 0.09 dipole, D: 0.91 dipole + 0.09 solenoid. The maximum at intermediate field strengths (curves A and C) distinctly shows the presence of the solenoid field contribution.
versus time and field strength can confirm the existence of the AB effect even in the presence of a residual dipole field.
6. Induced Coulomb Charges
The initial physical size of the electron pulses described in the previous section has been chosen to have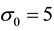
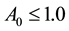
It is known [13] [14] that the time-development of induced charges and the establishment of potentials between them and the outside (inducing) charges placed or moving in front of conductors involve phenomena at the atto-second (10−18 s) up to femto-second (10−15 s) scales. The details depend on the intrinsic plasma frequencies of conduction electrons in the specific material. The induced Coulomb potentials oscillate about their “infinite-time” (static) values with periods of several atto-seconds and converge to them in femto-seconds. The convergence is faster and the amplitude of those oscillations is smaller when the outside charges are closer to the surface of the conductor. Thus, fast moving pulses of electrons approaching small solenoids may produce AB effect signals that develop at time scales that are shorter than the induced potential formation times, minimizing the effect of the latter on the measurements. A simple extrapolation of the results obtained in the previous section shows that for a weak 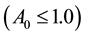
7. Conclusion
The time-development of the relativistic AB effect has been investigated using the
Acknowledgements
Z. K. and
References
- Aharonov, Y. and Bohm, D. (1959) Physical Review, 115, 485-491. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.115.485
- Tonomura, A., et al. (1982) Physical Review Letters, 48, 1443-1446. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.48.1443
- Tonomura, A., et al. (1986) Physical Review Letters, 56, 792-795. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.792
- Caprez, A.P., et al. (2007) Physical Review Letters, 99, Article ID: 210401 (4).
- Noguchi, A., et al. (2014) Nature Communications, 5, Article No. 3868.
- Ryder, L.H. (1996) Quantum Field Theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511813900
- Alford, M.G. and Wilczek, F. (1989) Physical Review Letters, 62, 1071-1074. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.62.1071
- Vachaspati, T. (2009) Physical Review D, 80, Article ID: 063502 (5).
- Emparan, R. and Valle Basagoti, M.A. (1994) Physical Review B, 49, 14460-14465. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.49.14460
- Ballesteros, M. and Weder, R. (2009) Journal of Mathematical Physics, 50, 122108-122162. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3266176
- Khalikov, V.R. and Ho, C.-L. (2008) Annals of Physics, 323, 1280-1293. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aop.2007.08.007
- Brawn, J.W., Su, Q. and Grobe, R. (1999) Physical Review A, 59, 604-612. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.59.604
- Alducin, M., Díez Muiño, R. and Juaristi, J.I. (2003) Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 129, 105-109. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0368-2048(03)00057-4
- Díez Muiño, R., Sánchez-Portal, D., Silkin, V.M., Chulkov, E.V. and Echenique, P.M. (2011) Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 108, 971-976.