Open Journal of Business and Management
Vol.04 No.03(2016), Article ID:68610,7 pages
10.4236/ojbm.2016.43049
Corporate Social Responsibility and Family Enterprise
Fengjiao Zhang
Management School, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China

Copyright © 2016 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 18 April 2016; accepted 16 July 2016; published 19 July 2016
ABSTRACT
As one of important characteristics of the economic development and social progress, fulfilling corporation social responsibility has attracted wide attention from all sectors of society. We empirically test the influence of family enterprise on the behavior characteristics of corporate social responsibility. We find that the family enterprises fulfill more social responsibility to shareholders, but less social responsibility to employees, suppliers, and the environment than non-family enterprises. Now family enterprise has gradually become a part of China economy booming. The government should strengthen the guidance to family enterprise to promote its development. Chinese family enterprises will make greater contribution to the social responsibility in future.
Keywords:
Corporation Social Responsibility, Family Enterprise, Non-Family Enterprise, Fulfill Responsibility

1. Introduction
Since the reform and opening up, Chinese enterprises have continued to be booming and fruitful. But at the same time, many public events, such as food safety issues, environmental pollution issues, labor dispute issues, which make Chinese economy shame of, occur frequently. This not only reflects a series of problems in the country economic transformation, but also exposes the general lack of social responsibility of domestic enterprises. As fullfilling corporate social responsibility (CSR) becomes a powerful proof that the enterprise is responsible for itself and its stakeholders, enterprises of our country gradually start to pay more attention to corporate social responsibility. In fact, now all sectors of society have paid great attention to the corporate social responsibility. So the academic research on corporate social responsibility has become more important.
Although scholars have done a lot of research on corporate social responsibility, but research on family enterprises social responsibility is less involved. Zekiene, Aurelija (2011) points out that socially responsible investment is a new trend of socially responsible activity [1] . Lixin Zhou (2012) believes that family business is a complex system that family is involved in the enterprise. Family, as unique social organization and the main ultimate controller of the enterprise, may have important influence on social responsibility behavior [2] . Zhijun Chen (2015) argues that as a combination of family units and enterprise units, the pursuit of both interests for “family” and “enterprise” is one of the important characteristics of family enterprise, which means that the family business not only pursues the main economic goal, but also pursues social goals, resulting in the diversity of business objectives. Therefore, social responsibility of the family enterprises and non-family enterprises will be different [3] . So, what are the characteristics of family enterprises social responsibility? Compared with the non- family enterprises, do family enterprises have any effect on social responsibility? The study of these issues has a positive significance for us to deeply understand the social responsibility of family listing corporation in China.
2. Theoretical Basis and Research Hypothesis
2.1. The Definition of Social Responsibility and the Social Responsibility of Family Enterprises
As one of important characteristics of the economic development and social progress, fulfilling corporation social responsibility has attracted wide attention from all sectors of society. But so far the definition of corporate social responsibility hasn’t been received a consensus. At present, the concept of corporate social responsibility that is the most widely accepted is “corporate social responsibility pyramid model” proposed by Carroll (1991). Carroll believes that corporate social responsibility is a Pyramid type structure, in which economic responsibility is the foundation, followed by law, ethics and voluntary responsibility. Therefore, the complete corporate social responsibility should include the economic responsibility, legal responsibility, moral responsibility and charitable responsibility [4] .
As one of the most popular forms of organization, family enterprise has played an important role in the global economic activities. According to Forbes Chinese network statistics, by the year of 2014, there have been 747 listed family enterprises in China.
There have been two basic points about the family enterprise and social responsibility. Some think that the family enterprises will better fulfill their social responsibilities than non-family enterprise. Others believe that compared with non-family enterprise, family enterprise is irresponsible for the social responsibility.
The research on the social responsibility of family enterprises has not yet reached a unanimous conclusion. In this paper, the listing corporation whose ultimate control power is attributed to the individual or family members is defined as a family listing enterprise. Through the research on the relationship between family enterprises, non-family enterprises and social responsibility, we analyze and summarize the characteristics of family enterprise social responsibility, and the difference between family enterprises and non-family enterprises.
2.2. Stakeholder Theory and Social Responsibility of Family Enterprise
Although Pyramid model of corporate social responsibility is generally accepted, it still has its shortcomings. It do not define clearly who is responsible for the enterprise. Stakeholder theory is a negation of traditional concept of “shareholders first”. That is, the company is owned by individuals and institutions and company managers should be responsible for the whole company, not only for the individual members. In his book, “strategic management: stakeholder management analysis method”, Freeman clearly put forward the stakeholder theory. Stakeholder theory refers to the management activities of the enterprise managers to balance the interests of all stakeholders. Compared to the traditional theory “shareholder supremacy”, this theory points out that enterprise’s survival and development depend on the support of the stakeholder. Therefore, enterprises also have an obligation to meet the requirements of these stakeholders. Freeman also points out that any organization or individual that affected the company’s target of the completion or was affected by the company’s target should be included in the group of stakeholders. Under the framework of stakeholder theory, the objects of corporate social responsibility behavior are clearly defined as stakeholders in the enterprise. And then the corporate social responsibility objects are segmented for five types, including the shareholders responsibility, employees responsibility, suppliers, clients and consumers rights responsibility, environment responsibility, government responsibility. Xiatong Fei’s “difference preface pattern” points out that Chinese society takes the pattern of difference sequence. Chinese people treat everyone differently according to the affinity degree of their relationship. In the same way, because of the organizational characteristics of Chinese enterprises, enterprise will take different actions for different stakeholders.
For the family enterprise, the shareholders are the most closely related to the enterprise. The vast majority of family members are the controlling shareholders. So in order to seek the survival and development of enterprises, it is necessary to pursue the maximization of the interests of shareholders. From the perspective of employees, family employees in family enterprise generally enjoy faster promotion opportunities, better working conditions and higher status than non-family employees. Bassanini (2011) pointed out that, although the possibility of layoffs in the family business is smaller, the average wage of employees in the family business is lower [5] . From the point of view of supplier, customer and consumer, for a long time, Chinese family enterprises have been subject to the credit crunch, such as the production and sale of counterfeit goods, “mountain fastness goods”. Libo Ma (2009) believes that due to the information asymmetry, which may lead to the moral hazard behavior, there may be conflicts between the enterprise and suppliers, customers and consumers [6] . From the perspective of environmental protection, the western society is a contractual society, the contradiction between the interests of the shareholders and the environmental responsibility has been tempered by the relatively perfect legal system. But in China, the corporate manager is easy to ignore environmental responsibility, regardless of the survival and development of future generations. From the view of government responsibility, Dyer (2006) believes that if enterprises meet the expectations of the external stakeholders, they will not necessarily be able to improve their economic performance, but they can get their positive evaluation, which is the basis of good corporate reputation. To the Chinese family business still in the primary stage, the good reputation can improve the social legitimacy of enterprises and help enterprises to survive and develop [7] .
By analyzing the relationship between five different stakeholders and family enterprise, this paper puts forward the following assumptions:
Hypothesis 1: compared to the non-family enterprises, family enterprises fulfill more social responsibility.
Hypothesis 2: compared to non-family enterprises, family enterprises fulfill more responsibility to shareholders.
Hypothesis 3: compared to non-family enterprises, family enterprises is less responsible for employee performance.
Assumption 4: compared to non-family enterprises, family enterprises fulfill less responsibility to suppliers, customers and consumers.
Hypothesis 5: compared to non-family enterprises, family enterprises is less responsible for the environmental performance.
Hypothesis 6: compared to non-family enterprises, family enterprises fulfill more responsibility of public welfare donations.
3. Data and Research Methods
3.1. Sample and Data Sources
In order to ensure the effective control of the controlling shareholders, this paper defines at least 20% or more share as the criteria of family control. According to the above mentioned standards, the sample selection process is as follows: (1) excluding listing corporation belonging to the financial industry samples; (2) excluding ST listing corporation; (3) for the period of 2010 to 2014, the previous year’s data of sample corporations is available. After the screening, we finally get 5809 samples. The related data about social responsibility of the sample enterprises is from hexun.com and other relevant financial data from the CSMAR database.
3.2. Variable Definition
Dependent variable: Corporation Social responsibility (CSR) is taken from the analysis report issued by professional evaluation system of hexun.com. Professional evaluation system sets up secondary and tertiary indexes to make comprehensive evaluation of the social responsibility, which involves 13secondary indexes and 37 tertiary indexes.
Independent variables: The nature of enterprise (FOWN). According to the definition of family enterprise standards, all samples will be divided into the family enterprise and non-family enterprise. The dummy variable for family enterprise is 1; the dummy variable for non-family enterprise is 0.
Control variables: Personal characteristics of enterprise managers, corporate characteristics and institutional environment are the influencing factors of corporate social responsibility. Therefore, we select the enterprise manager’s age (OLD) and the educational level (EDU) to control the influence of the individual characteristics enterprise managers. Select of company size (Lnasset), listed years (AGE) and industry variables (INDU) to control the impact of corporate characteristics. In addition, we use the “China market index” by Fan Gang and Wang Xiaolu et al. (2011) to measure environmental governance level of the area. We use the local market index (MKT), government intervention index (Gov) and the level of the rule of law index (Law) to measure the institutional environment of different regions.
The specific definition of variables is presented in Table 1.
3.3. Study Design
In order to test the influence of family control on social responsibility, the model1 was designed.
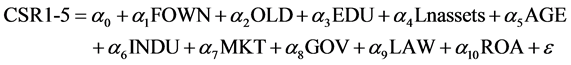 (1)
(1)
4. Empirical Results and Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
As shown in Table 2, for 5809 sample observations, the mean value of Corporation Social Responsibility (CSR) is 27.5, which suggest that our country enterprises need to be encouraged to fulfill social responsibility better. Also, its standard deviation is 18.01 and the gap between the lowest and the highest value is large, suggesting that there exist great differences of behavioral effects between different enterprises. In the descriptive statistics, the analysis of five indicators, CRS1-5, is consistent with that of the total social responsibility, CRS. The average value of the five indicators is very low. In addition, the average value of FOWN is 0.46, suggesting that family enterprises and non-family enterprises almost have equal shares in the sample of listed companies.
Table 1. Study variables description.
Table 2. Descriptive statistics of all variables.
As for the control variables, the average age of enterprise manager is 52 years old. The youngest is 34 years old and the most elderly is 70 years old, which suggest that now most China’s listed companies are controlled by the 60’s and the 70’s whose sense of social responsibility is quite different from the 80’s and the 90’s. The average value of level of education of enterprise managers is 0.85, which indicates that the education level for the majority of managers of the listing corporation is bachelor degree or above, with a higher degree of education. The mean value of Industry variables (INDU) is 0.66, which shows that about 66% of the listing corporations are in the manufacturing sector. The standard deviations of the marketization index (MKT), government intervention index (Gov) and the index of legal level (Law) show that there are great differences about the external institutional environment within the different regions.
4.2. Multiple Regression Analysis
In this paper, multiple regression is carried out. The results are shown in Table 3. In the model (1), the nature of the enterprise and the total social responsibility showed a significant negative correlation on the 1% level, which suggests that the family enterprises fulfill less social responsibility than non-family enterprises. This is contrary to hypothesis 1. The cause may be that the time of the development of Chinese family enterprises only last for a few decades and family enterprises are still in the early stage of survival. Therefore, the economic strength of family enterprises are still weak and rarely take the initiative to undertake economic responsibilities or non-
Table 3. Multivariate regression results.
t-statistics in parentheses; ***p < 0.01, **p < 0.05, *p < 0.1.
mandatory social responsibility. Also, the private enterprises in our country, compared with the state-owned enterprises, have difficulties in financing. In the face of financial difficulties, the family enterprise is difficult to retain more funds to fulfill the social responsibility. And more, in general, the quality of managers of family enterprise is relatively lower than that of non-family enterprise. The legal awareness and the sense of social responsibility of the manager of family enterprise is also relatively weaker. In addition, China’s social responsibility mechanism is not perfect, which lack of government guidance for family enterprise. In short, the characteristics of the development of China’s local family enterprise, may make the family enterprises fulfill less social responsibility than non-family enterprises.
In model (2)-(6) of the display, the family enterprises fulfill more social responsibility to shareholders, and less social responsibility to employees, suppliers, and the environment than non-family enterprises, which are consistent with the hypothesis 2-5. Although the responsibility for public welfare donations is positively correlated with Fown, the results are not significant. It indicates that family enterprises are contributing more to public welfare donations. This is consistent with the analysis of the development stage of the local family enterprise and the macro-environment in our country.
5. Conclusions
Family business is a combination of family system and enterprise system. Due to the dual influence of family factors and enterprise factors, social responsibility behavior of family enterprise is significantly different from that of non-family enterprise. In this paper, based on relevant data of the listing corporation, we empirically test the influence of family enterprise on corporate social responsibility behavior characteristics. The results show that Chinese family enterprises are still in the primary development stage. Because of the characteristics of development of Chinese family enterprises, social responsibility performance of family enterprises also has the corresponding features, such as the financial difficulties, nepotism, credit crisis and so on, which restrict the fulfillment of social responsibility of family business. In addition, the family enterprise has gradually played an important role in Chinese economy. And its contribution to economic and social development is also growing with each passing day. Although the legal system and credit system of the macro environment is not perfect, with the improvement of the economic strength of the family enterprise, Chinese family enterprises will make greater contribution to the social responsibility. The government should strengthen the guidance to family enterprise to promote its development.
It should be noted that this study is still insufficient. We only use the “dichotomy”. The sample is divided into family and non-family enterprises. In fact, family enterprises can be further divided into family involvement, family control and other segments. And the impact of these segments on corporate social responsibility is uncertain. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out further research on the above problems in future.
Cite this paper
Fengjiao Zhang, (2016) Corporate Social Responsibility and Family Enterprise. Open Journal of Business and Management,04,476-482. doi: 10.4236/ojbm.2016.43049
References
- 1. Aurelija, Z. and Juozas, R. (2011) Socially Responsible Investment as a Part of Corporate Social Responsibility. Economics & Management, 16, 628-636.
- 2. Zhou, L.X. (2010) Family Corporate Social Responsibility: Research Trends. Business Economics and Management, 229, 47-52.
- 3. Chen, Z.J. and Min, Y.J. (2015) Family Control and Corporate Social Responsibility: An Explanation Based on the Theory of Social Emotional Wealth. Economic Management, 532, 42-50.
- 4. Carroll, A.B. (1991) The Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility: Toward the Moral Management of Organizational Stakeholders. Business Horizons, 34, 39-48. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0007-6813(91)90005-G
- 5. Andrea, B., Thomas, B., Eve, C. and Antoine, R. (2013) Working in Family Firms: Paid Less But More Secure? Evidence from French Matched Employer-Employee Data. Industrial & Labor Relations Review, 66, 433-466.
- 6. Ma, L.B., Zhang, J.M. and Lv, Y.J. (2009) The Life Cycle of Social Responsibility and Family Enterprise. Research on Financial and Economic Problems, 3, 56-63.
- 7. Dyer, G.W. and Whetten, D.A. (2006) Family Firms and Social Responsibility: Preliminary Evidence from the S&P500. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 30, 785-802.


