Open Journal of Statistics
Vol.04 No.08(2014), Article ID:50106,8 pages
10.4236/ojs.2014.48060
Estimation of the Mean of the Exponential Distribution Using Maximum Ranked Set Sampling with Unequal Samples
B. S. Biradar1, C. D. Santosha2
1Department of Studies in Statistics, University of Mysore, Mysore, India
2All India Institute of Speech and Hearing, Mysore, India
Email: biradarbs@statistics.uni-mysore.ac.in, getsanthoshcd@gmail.com
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 24 July 2014; revised 8 August 2014; accepted 19 August 2014
ABSTRACT
In this paper maximum ranked set sampling procedure with unequal samples (MRSSU) is proposed. Maximum likelihood estimator and modified maximum likelihood estimator are obtained and their properties are studied under exponential distribution. These methods are studied under both perfect and imperfect ranking (with errors in ranking). These estimators are then compared with estimators based on simple random sampling (SRS) and ranked set sampling (RSS) procedures. It is shown that relative efficiencies of the estimators based on MRSSU are better than those of the estimator based on SRS. Simulation results show that efficiency of proposed estimator is better than estimator based on RSS under ranking error.
Keywords:
Efficiency, Error in Ranking, Maximum Likelihood Estimator, Modified Maximum Likelihood Estimator, Ranked Set Sampling

1. Introduction
In many studies where sampling is used, such as environmental managements, ecology, sociology and agriculture, exact measurement of a selected unit is either difficult or costly and time-consuming. However, the ranking of a small set of selected units can be carried out easily either by visual inspection with respect to the study variable or on the basis of auxiliary variable. McIntyre [1] proposed a method, later called ranked set sampling (RSS), for estimating mean pasture and forage yields when measurement is costly. In RSS one first draws m2 units at random from the population and partitions them into m sets of m units. The m units in each set are ranked without making actual measurements. From the first set of m units the unit ranked lowest is chosen for actual quantification. From the second set of m units the unit ranked second lowest is measured. This process is continued until the unit ranked largest is measured from the m-th set of m units. If a large sample is required then the procedure can be repeated r times to obtain a sample of size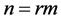 . These chosen elements are called ranked set sample. Dell and Clutter [2] and Takahasi and Wakimoto [3] studied theoretical aspects of this technique on the assumption of perfect judgment ranking and imperfect judgment ranking, respectively. Dell and Clutter [2] showed that the variance of the ranked set sample mean is never larger than the variance of the random sample mean, whether or not judgment ranking is perfect (for more research work on parametric methods for RSS, see for example, Lam et al. [4] , Stokes [5] ). Samwi et al. [6] used extreme ranked set sample (ERSS) which is easier to use than RSS procedure to estimate the population mean in case of symmetric distributions. Al-Odat and Al-Saleh [7] introduced concept of varied set size RSS which they called moving extreme ranked set sampling (MERSS).
. These chosen elements are called ranked set sample. Dell and Clutter [2] and Takahasi and Wakimoto [3] studied theoretical aspects of this technique on the assumption of perfect judgment ranking and imperfect judgment ranking, respectively. Dell and Clutter [2] showed that the variance of the ranked set sample mean is never larger than the variance of the random sample mean, whether or not judgment ranking is perfect (for more research work on parametric methods for RSS, see for example, Lam et al. [4] , Stokes [5] ). Samwi et al. [6] used extreme ranked set sample (ERSS) which is easier to use than RSS procedure to estimate the population mean in case of symmetric distributions. Al-Odat and Al-Saleh [7] introduced concept of varied set size RSS which they called moving extreme ranked set sampling (MERSS).
Al-Saleh and Al-Hadhrami [8] studied the MLE of location distributions based on MERSS. Abu-Dayyeh and Al-Sawi [9] have obtained modified MLE of the mean of exponential distribution using MERSS. The MERSS requires identification of 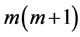 sample units and 2m of these are actually measured, thus making a comparison of this sampling procedure with RSS of size m is meaningless. In the next section we introduce a maximum ranked set sampling procedure with unequal samples. The existence of MLE for scale parameter of exponential distribution is demonstrated and properties are studied in Section 3. Since under some regularity conditions the asymptotic efficiency of the MLE can be obtained from the inverse of the Fisher information number, we compute Fisher information number for scale parameter in Section 4. The asymptotic efficiency of the MLE using proposed sampling scheme w.r.t. that using SRS and RSS is compared numerically for the scale parameter of the exponential distribution in this section. In order to get a closed form expression of the approximate MLE of
sample units and 2m of these are actually measured, thus making a comparison of this sampling procedure with RSS of size m is meaningless. In the next section we introduce a maximum ranked set sampling procedure with unequal samples. The existence of MLE for scale parameter of exponential distribution is demonstrated and properties are studied in Section 3. Since under some regularity conditions the asymptotic efficiency of the MLE can be obtained from the inverse of the Fisher information number, we compute Fisher information number for scale parameter in Section 4. The asymptotic efficiency of the MLE using proposed sampling scheme w.r.t. that using SRS and RSS is compared numerically for the scale parameter of the exponential distribution in this section. In order to get a closed form expression of the approximate MLE of , some terms of the likelihood equation will be replaced by their expectations. This technique was used by Mehrotra and Nanda [10] for studying MLE based on censored data, Zheng and Al-Saleh [11] for MLE with RSS data, and Al-Saleh and Al-Hadhrami [8] [12] and Abu-Dayyeh and Al-Sawi [9] for MLE using MERSS data. In Section 5 we study a modified MLE for estimating the scale parameter of exponential distribution assuming perfect ranking. Numerical comparison of these estimators is given here. Errors in ranking are studied in Section 6.
, some terms of the likelihood equation will be replaced by their expectations. This technique was used by Mehrotra and Nanda [10] for studying MLE based on censored data, Zheng and Al-Saleh [11] for MLE with RSS data, and Al-Saleh and Al-Hadhrami [8] [12] and Abu-Dayyeh and Al-Sawi [9] for MLE using MERSS data. In Section 5 we study a modified MLE for estimating the scale parameter of exponential distribution assuming perfect ranking. Numerical comparison of these estimators is given here. Errors in ranking are studied in Section 6.
2. Maximum Ranked Set Sampling with Unequal Samples (MRSSU)
In the maximum ranked set sampling with unequal samples (MRSSU), we draw m simple random samples, where the size of the i-th sample is i,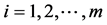 . The procedure of MRSSU is described as follows
. The procedure of MRSSU is described as follows
1) Select m SRS of size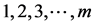 , respectively.
, respectively.
2) Order the element of each set by visual inspection or other relatively inexpensive methods, without actual measurement of the characteristic of interest.
3) Measure accurately the maximum ordered observation from each set.
4) Repeat the above steps r times until the desired sample size 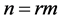 is obtained.
is obtained.
In MRSSU, we measure accurately only m maximum order statistics out of 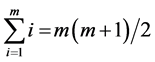 ranked units.
ranked units.
Since it is not difficult to identify maximum in each set. MRSSU is a very useful modification of RSS. It allows for an increase in set size without introducing too many ranking errors.
3. The Maximum Likelihood Estimator
Assume that the characteristic of interest X has a probability density function 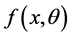 and distribution function
and distribution function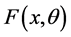 , where the form of F is known, our interest is to estimate
, where the form of F is known, our interest is to estimate 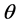 based on MRSSU. Let
based on MRSSU. Let ,
,  be m sets of random samples from X, and they are independent. Denote
be m sets of random samples from X, and they are independent. Denote  ,
, . Then
. Then  is a MRSSU from X. Note that the elements of this sample are independent. If the judgment ranking is perfect then
is a MRSSU from X. Note that the elements of this sample are independent. If the judgment ranking is perfect then 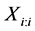 has the same density as the i-th order statistic (maximum) of an SRS of size i from
has the same density as the i-th order statistic (maximum) of an SRS of size i from

The likelihood function based on MRSSU can be written as
The log-likelihood function is
where C is a constant. Let a MRSSU be drawn from an exponential distribution with pdf





If the MLE of 




Now, taking second derivative we have

Note that the first term of Equation (3) is always negative and the second term is zero at any solution 






Thus the solution 


Theorem 1. Assume that we are sampling from an exponential distribution using MRSSU then for any real number “a” satisfies
1)
2)
Proof. Proof of this theorem is similar to Theorem 1 of Chen et al. [13] .
4. The Fisher Information Number
We denote the MLE’s based on SRS by 




If 
We give the Fisher information number based on MRSSU in the following theorem.
Theorem 2. With 


Proof. From Equation (1), we have
Note that

After simplification Equation (5) reduces to Equation (4).
We compare the ML estimator from the SRS which is

from the RSS which is obtained from Equation (2.6) of [5] denoted by 

where 


From [5] Fisher information number about 

Asymptotic efficiency of MLE using MRSSU w.r.t. that of using SRS is defined as

Similarly, we have

The numerical results are shown in Table 1. ARE of 





5. Modified MLE (MMLE)
In order to obtain closed form approximate MLE of
Taking the expectation of third term of LHS of (2), we obtain
After simplification, we get likelihood Equation (2) as
Solving for

where


Table 1. The information numbers and asymptotic efficiencies of 



Theorem 3.
a) 

b)
where d is defined as in Equation (11).
Proof a). From Equation (11), we have
i.e.,

It is well known that under some regularity conditions (see Lehmann [14] (pp. 440-441)),

Using Equation (13) and Equation (14), the expectation of Equation (2) reduces to

Hence the proof of a).
Proof b). Since 



Now

Thus using Equation (17), we obtain Equation (12).
We compare MMLE based on MRSSU relative to MLE using SRS and MMLE using RSS with the same size. From Equation (2.6) of Zheng and Al-Saleh [11] we can obtain MMLE of scale parameter of exponential distribution using RSS and is given by
where 
We can easily derive the variance of 
Let 


Similarly, efficiency of 
The efficiencies were computed for 






6. Errors in Ranking
In this section we study the situation where there are ranking errors. For MRSSU the ranking may not always be perfect, i.e., i-th largest observation in the i-th set measured by MRSSU method may not be the actual i-th largest order statistics in the set of size i. The errors in ranking may have an effect on the estimates.
To gain some insight of the effect of ranking errors on the efficiencies of the estimators, various simulation
Table 2. The efficiency of 



trails were conducted. We use the simulation method considered by David and Lavine [15] and Dell and Clutter [2] . In the first stage we generate m sets of simple random samples





where Xij and eij are independent. Then we can obtain MRSSU’s of Xij’s and Zij’s (










We repeat this procedure for 10,000 times. The estimate for 




It is observed from Table 3 that bias in the modified ML estimator 



Table 3. The expectation values of 

Table 4. The efficiencies of 


Table 5. The efficiencies of 


decreases with 





References
- McIntyre, G.A. (1952) A Method for Unbiased Selective Sampling Using Ranked Sets. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 3, 385-390. http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/AR9520385
- Dell, T.R. and Clutter, J.L. (1972) Ranked Set Sampling Theory with Order Statistics Background. Biometrics, 28, 545-555. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2556166
- Takahasi, K. and Wakimoto, K. (1968) On Unbiased Estimates of the Population Mean Based on the Sample Stratified by Means of Ordering. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 20, 1-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02911622
- Lam, K., Sinha, B.K. and Wu, Z. (1994) Estimation of Parameters in Two-Parameter Exponential Distribution Using Ranked Set Sampling. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 46, 723-736. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00773478
- Stokes, L. (1995) Parametric Ranked Set Sampling. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 47, 465-482.
- Samwi, H., Ahmad, M. and Abu-Dayyeh, W. (1996) Estimating the Population Mean Using Extreme Ranked Set Sampling. Biometrical Journal, 38, 577-586. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bimj.4710380506
- Al-Odat, M.T. and Al-Saleh, M.F. (2001) A Variation of Ranked Set Sampling. Journal of Applied Statistical Science, 10, 137-146.
- Al-Saleh, M.F. and Al-Hadrami, S. (2003a) Parametric Estimation for the Location Parameter for Symmetric Distributions Using Moving Extremes Ranked Set Sampling with Application to Trees Data. Environmetrics, 14, 651-664. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/env.610
- Abu-Dayyeh, W. and Al Sawi, E. (2009) Modified Inference about the Mean of the Exponential Distribution Using Moving Extreme Ranked Set Sampling. Statistical Papers, 50, 249-259. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00362-007-0072-5
- Mehrotra, K.G. and Nanda, P. (1974) Unbiased Estimator of Parameter by Order Statistics in the Case of Censored Samples. Biometrika, 61, 601-606. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/biomet/61.3.601
- Zheng, G. and Al-Saleh, M.F. (2002) Modified Maximum Likelihood Estimators Based on RSS. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 54, 641-658. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/A:1022475413950
- Al-Saleh, M.F. and Al-Hadrami, S. (2003b) Estimation of the Mean of the Exponential Distribution Using Moving Extremes Ranked Set Sampling. Statistical Papers, 44, 367-382. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00362-003-0161-z
- Chen, W.X., Xie, M.Y. and Wu, M. (2013) Parametric Estimation for the Scale Parameter for Scale Distributions Using Moving Extremes Ranked Set Sampling. Statistics and Probability Letters, 83, 2060-2066. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.spl.2013.05.015
- Lehmann, E.L. (1983) Theory of Point Estimation. John Willey and Sons Inc., New York. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-2769-2
- David, H.A. and Levine, D.N. (1972) Ranked Set Sampling in the Presence of Judgment Ranking Error. Biometrics, 28, 553-555.



















