Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 Psychology 2011. Vol.2, No.8, 781-791 Copyright © 2011 SciRes. DOI:10.4236/psych.2011.28120 781 Identity Salience and Its Dynamics in Palestinians Adolescents Ibrahim A. Kira1, Abdul Wahhab Nasser Alawneh2, Sharifa Aboumediane1, Jamal Mohanesh3, Bulent Ozkan4, Hala Alamia1 1Center of Cumulative Trauma Studies, Stone Mountain, USA; 2Arab and Middle East Resource Center, Dearborn, USA; 3ACCESS Community Health and Research Center, Dearborn, USA; 4Wayne State University, Detroit, USA. Email: kiraaref@aol.com Received May 8th, 2011; revised August 29th, 2011; accepted October 2nd, 2011. The goal is to build and test a measure for identity salience and use it to explore the validity of some assump- tions of the identity trauma theory (ITT). ITT suggests that the salience of identity concerns, personal, and col- lective enhances or negatively affect agency and self-efficacy and explain suicidality and militancy. Using sam- ples of 880 Palestinian adolescents, we developed in the first study a measure for identity salience that included sub-scales for identity commitment and militancy. In the second study we used the measure along with measures for fear of death, mental health variables, and trauma types. Personal identity traumas were associated with de- crease in fear of death; increase in mental health problems and in clinical suicide. Collective identity traumas were associated with increase in identity commitment and militancy. Militancy was found to be associated with decreased PTSD which suggests that militancy acts as anxiety buffer. Identity commitment was associated with decrease in militancy. The implications of the results were discussed. Keywords: Identity Salience, Mortality Salience, Suicidality, Militancy, Identity Trauma Theory Introduction Identity develops through life from attachment to parents (Bowlby, 1969, 1988) to autonomy and independence to the stage of interdependence and being part of the networks of the society. An impressive body of research focused on the early development and related attachment dynamics. Individuation and identity development did not attract, so far, an equal atten- tion of research. Identity development of the individual is con- nected to the individuation process in early adolescence and adulthood (e.g., Erikson, 1963; Gross, 1987; Rasmussen, & Eri- kson, 1964). In adolescence and early adulthood. The individ- ual develops, at this stage, increased self awareness and in- creasingly complex identity to grow with him over his/her life span. The acquired identity, at this stage of development, be- came central to personal and interpersonal dynamics. Accord- ing to developmental theories, self-definition that determines identity comprises of, at least, two fundamental self-represen- tations or self-schemata: Personal self representations and so- cial or group self representations that connect the individual to his status in the global interdependent network. The second is derived from membership in larger, more impersonal collec- tives or social categories (e.g. Tajfel, & Turner, 1986). Based on this developmental framework, (ITT) differentiates between at least two different kinds of identity traumas that can chal- lenge the existence of either: personal identity Trauma (PIT) (e.g., violation of self autonomy by rape, sexual or physical abuse, and involve fears of loss of autonomy and independent identity that the individual develops), and collective or social identity trauma (CIT) (e.g., targeted genocide, holocaust, slav- ery, discrimination, and different kinds of social structural vio- lence that may triggers fears of the group subjugation or anni- hilation), (e.g., Kira, 2001; Kira, 2010, Kira et al., 2008). CIT that may overwhelm individuals can be socio-political, histori- cal or social structural traumas (SST). SSTs are those traumas associated with perceived relative deprivation and/or social structural violence. Examples of social structural violence are extreme poverty (e.g., Cassiman, 2005, Smith, Spears, & Ham- stra, 1999; Walker, & Pettigrew, 1984), and extreme gender discrimination. (e.g., Kira et al., 2010) PITs and CITs are main causal factors for identity terror and fear of losing the developmentally acquired identities. Each identity trauma type may challenge the respective identity sheer existence, causing identity annihilation terror, and may nega- tively affects physical and mental health as well as related per- sonal, social and political dynamics. Further, collective Identity is increasingly conceptualized as fundamental to the mainte- nance and reproduction of political conflict (Kira, 2002, 2006). According to this theory, self-efficacy feelings, as contrasted to self-esteem, buffer against fear of loss of identities that the individual develops across life (Bandura, 1997). Acquired iden- tities are nested in hierarchical dynamic structure. Identity nested hierarchy is a dynamic coherent whole, that is derived by a governing self-agency that is associated with feelings of self-efficacy and/or collective agency and control beliefs (cf, e.g., Bandura, 1997, Kira, 2002, 2006, 2010). Identity traumas, within this development-based trauma frame work, are contrasted to other trauma types, for example, attachment traumas (e.g., abandonment by mother of her infant) that involve fears of security loss that negatively activates secu- rity salience, and survival traumas (e.g., attacks by weapons, or natural disasters) and involve fears of death that triggers mor- tality salience (Kira et al., 2008, Kira, 2010). On the other hand, identity traumas can cause fears and terror of identity loss/ identity annihilation or subjugation and/or return to the state of dependency, threatening the salience of personal or collective identity. Identity salience or dormancy refers to the status of one iden- tity in the hierarchy of nested identities, whether it is central, or peripheral. Individuals process stimuli according to their as-  I. A. KIRA ET AL. 782 signed negative or positive value as relevant and important and their potential threat to their salient identities (Kira, 1987, 1997). More salient, relevant, super-ordinate, or central identi- ties are more likely to be activated and act as lens through which individuals appraise and process relevant situational information. Identities higher in the salience/dormancy hierar- chy will take precedence over identities lower in the salience/ dormancy hierarchy and will direct/bias individual perceptions, emotions and actions and establish situational priorities. (c.f., e.g., Stryker, & Burke, 2000, Stryker, & Serpe, 1982, McCall, & Simmons, 1978; Ashmore, Deaux, & McLaughlin-Volpe., 2004; Kira, 2010). Nested identities hierarchy is mostly dynamic and is modifi- able by different types of identity traumatic events. Serious threats to one’s dormant identity can move it to be more salient and rearrange the centrality and salience of identities in the dynamic nested identities’ hierarchy. Realigning the nested identity hierarchy can be ongoing process. Several assumptions were deduced from trauma identity theory framework: 1) Collective identity traumas, (e.g., the holocaust, Septem- ber 11, or Pearl Harbor attack) kindle this national or group collective identity to be more salient and push personal or physical identity to be more dormant decreasing fear of physi- cal death, and increasing fear of group or collective annihila- tion/ extinction or subjugation. The opposite will happen if the event is related to personal identity, for example rape attack or domestic violence, which may rearrange the salience hierarchy. 2) Collective identity, when became salient, increases the level of commitment, for example ethnic group solidarity, and militancy to protect such identity (cf., e.g., Ibn Khaldûn, 1968). Identities with higher levels of commitment and militancy will take precedence over those with lower levels of commitment and/or militancy, when action is called for. 3) Identity traumas, personal, and collective, activate differ- ent type of primal fears that deactivate fear of death. When personal identity is seriously threatened, self-annihilation panic can erupt and deactivate the salience of collective identity as well as individual’s mortality and may trigger suicidal thoughts and actions. Conversely, serious collective identity threats, for example in a struggle against domination or oppression, can activate collective annihilation, sub-ordination or subjugation fears and deactivate personal identity concerns as well as mor- tality salience and may trigger militancy and/or extremism. In each case, mortality concerns become dormant. 4) Persons who reach such level of militancy to one’s own salient identity may be ready to ignore or even sacrifice the existence of other less salient identities. An example is commit- ting suicide (eliminating the physical entity); to regain personal autonomy and control that they perceive they lost by rape, in- cest or betrayal. Another example is the readiness to die for the country in a war to promote or achieve the collective national identity goals (Kira, 2002, 2006). The Goals of the First Study The goal of the first study is to develop a measure for collec- tive identity commitment and militancy (identity salience) and explore its reliability, and test its construct validity. We will test its predictive validity through testing basic predictions of trauma developmental theory in the second study. Testing the measure on samples of Palestinian adolescents may allow us to further test some of assumptions of this theory in adolescents that are subjected to high collective identity trauma load and are developing highly politicized collective identity. The First Study Hypotheses Hypothesis 1: Identity salience scale (ISS) developed in this study has adequate reliability. Hypothesis 2: ISS has adequate construct validity in the population under study. The First Study: Method Participants Participants were 880 adolescents, high school students from Gaza and West Bank in Palestine (438 from West bank, and 442 from Gaza). While we used Gaza data to conduct confir- matory factor analysis of identity salience scale, the focus of this paper will be on West Bank participants (N = 438). Family size seemed to be higher in Gaza compare to West Bank samples. West Bank participants included 54.6% males, and 45.4% females. Age ranged from 12 - 19, mean age was 15.66, SD of 1.43. Family size ranged from 2 - 22 with mean of 7.99, SD 2.69. 40% of the participants were from middle school and 60% from high school. Gaza’s Participants included 442 adolescents, 47.5% males and 52.5% females. Participants included 5% from villages’ residents, 50.3% from Gaza city residents, and 44.7% from refugee camps’ residents. Age ranged between11 and 19, with mean of 15.89 and SD of 2.86. Family size average was 9.77 and SD of 2.79. Family size seemed to be higher in Gaza com- pare to West Bank samples. In the sample 99% are Muslims and 1% is Christians. Procedure A focus group discussion of five professionals developed a pool of fifty items that focus on person’s group identity com- mitment and militancy according to the theory. The fifty items scale tested in small convenient sample of 30 Arab refugee adolescents in USA. Based on item analysis and the least num- ber of items criteria, research team chose 10 items that repre- sent the concept of identity salience. Research team decided to make the items non-specific to a group, we added other ques- tions that ask about which groups of belonging are more im- portant and relevant at the time as separate probe questions. The study was approved by Palestinian Authority. Partici- pants were recruited through West Bank and Gaza School sys- tems and covered 7 schools in each region. The seven schools were randomly selected and included schools from refugee camps. Participation was completely voluntary and fully in- formed. Research participants told that they may withdraw from the study at any time. Parents were informed of the nature of the research that target understanding the effects of different traumas on their children health and mental health; active in- formed parental consent and written adolescents’ ascent were obtained or offered by participating schools and research team. Some parents approved verbally but chose not to sign due the political situation at the time or for other reasons. No identify- ing information was recorded that can link the subjects to the data. The disclosure of the data could not reasonably place the subjects at any risk or any liability according to federal and local human subjects’ guidelines. Interviews were conducted face-to-face in Arabic by trained Palestinian teachers and local research team and took between 45 - 60 minutes as it included 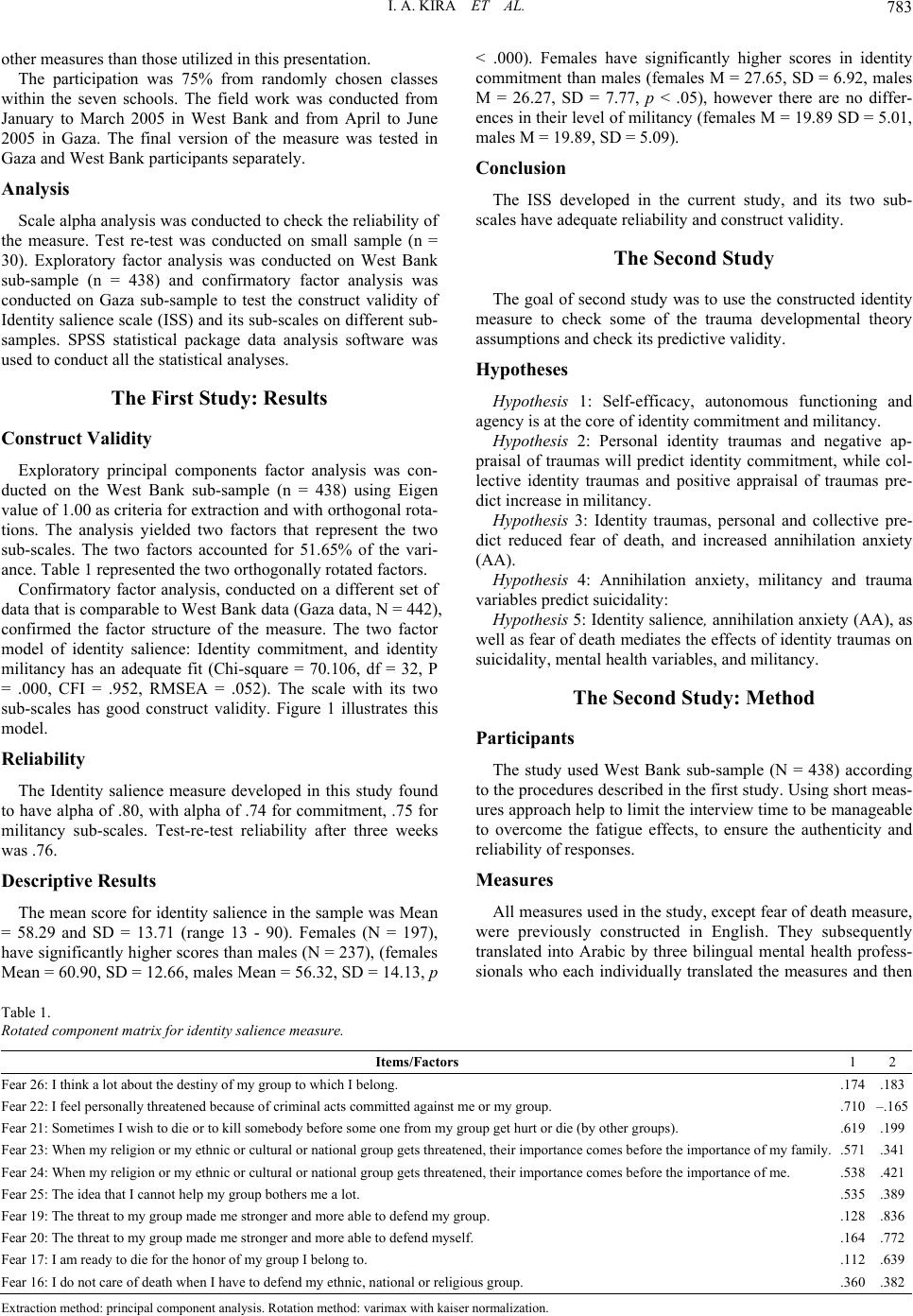 I. A. KIRA ET AL. 783 other measures than those utilized in this presentation. The participation was 75% from randomly chosen classes within the seven schools. The field work was conducted from January to March 2005 in West Bank and from April to June 2005 in Gaza. The final version of the measure was tested in Gaza and West Bank participants separately. Analysis Scale alpha analysis was conducted to check the reliability of the measure. Test re-test was conducted on small sample (n = 30). Exploratory factor analysis was conducted on West Bank sub-sample (n = 438) and confirmatory factor analysis was conducted on Gaza sub-sample to test the construct validity of Identity salience scale (ISS) and its sub-scales on different sub- samples. SPSS statistical package data analysis software was used to conduct all the statistical analyses. The First Study: Results Construct Validity Exploratory principal components factor analysis was con- ducted on the West Bank sub-sample (n = 438) using Eigen value of 1.00 as criteria for extraction and with orthogonal rota- tions. The analysis yielded two factors that represent the two sub-scales. The two factors accounted for 51.65% of the vari- ance. Table 1 represented the two orthogonally rotated factors. Confirmatory factor analysis, conducted on a different set of data that is comparable to West Bank data (Gaza data, N = 442), confirmed the factor structure of the measure. The two factor model of identity salience: Identity commitment, and identity militancy has an adequate fit (Chi-square = 70.106, df = 32, P = .000, CFI = .952, RMSEA = .052). The scale with its two sub-scales has good construct validity. Figure 1 illustrates this model. Reliability The Identity salience measure developed in this study found to have alpha of .80, with alpha of .74 for commitment, .75 for militancy sub-scales. Test-re-test reliability after three weeks was .76. Descriptive Results The mean score for identity salience in the sample was Mean = 58.29 and SD = 13.71 (range 13 - 90). Females (N = 197), have significantly higher scores than males (N = 237), (females Mean = 60.90, SD = 12.66, males Mean = 56.32, SD = 14.13, p < .000). Females have significantly higher scores in identity commitment than males (females M = 27.65, SD = 6.92, males M = 26.27, SD = 7.77, p < .05), however there are no differ- ences in their level of militancy (females M = 19.89 SD = 5.01, males M = 19.89, SD = 5.09). Conclusion The ISS developed in the current study, and its two sub- scales have adequate reliability and construct validity. The Second Study The goal of second study was to use the constructed identity measure to check some of the trauma developmental theory assumptions and check its predictive validity. Hypotheses Hypothesis 1: Self-efficacy, autonomous functioning and agency is at the core of identity commitment and militancy. Hypothesis 2: Personal identity traumas and negative ap- praisal of traumas will predict identity commitment, while col- lective identity traumas and positive appraisal of traumas pre- dict increase in militancy. Hypothesis 3: Identity traumas, personal and collective pre- dict reduced fear of death, and increased annihilation anxiety (AA). Hypothesis 4: Annihilation anxiety, militancy and trauma variables predict suicidality: Hypothesis 5: Identity salience, annihilation anxiety (AA), as well as fear of death mediates the effects of identity traumas on suicidality, mental health variables, and militancy. The Second Study: Method Participants The study used West Bank sub-sample (N = 438) according to the procedures described in the first study. Using short meas- ures approach help to limit the interview time to be manageable to overcome the fatigue effects, to ensure the authenticity and reliability of responses. Measures All measures used in the study, except fear of death measure, were previously constructed in English. They subsequently translated into Arabic by three bilingual mental health profess- sionals who each individually translated the measures and then Table 1. Rotated component matrix for identity salience measure. Items/Factors 1 2 Fear 26: I think a lot about the destiny of my group to which I belong. .174 .183 Fear 22: I feel personally threatened because of criminal acts committed against me or my group. .710 –.165 Fear 21: Sometimes I wish to die or to kill somebody before some one from my group get hurt or die (by other groups). .619 .199 Fear 23: When my religion or my ethnic or cultural or national group gets threatened, their importance comes before the importance of my family..571 .341 Fear 24: When my religion or my ethnic or cultural or national group gets threatened, their importance comes before the importance of me. .538 .421 Fear 25: The idea that I cannot help my group bothers me a lot. .535 .389 Fear 19: The threat to my group made me stronger and more able to defend my group. .128 .836 Fear 20: The threat to my group made me stronger and more able to defend myself. .164 .772 Fear 17: I am ready to die for the honor of my group I belong to. .112 .639 Fear 16: I do not care of death when I have to defend my ethnic, national or religious group. .360 .382 Extraction method: principal component analysis. Rotation method: varimax with kaiser normalization. 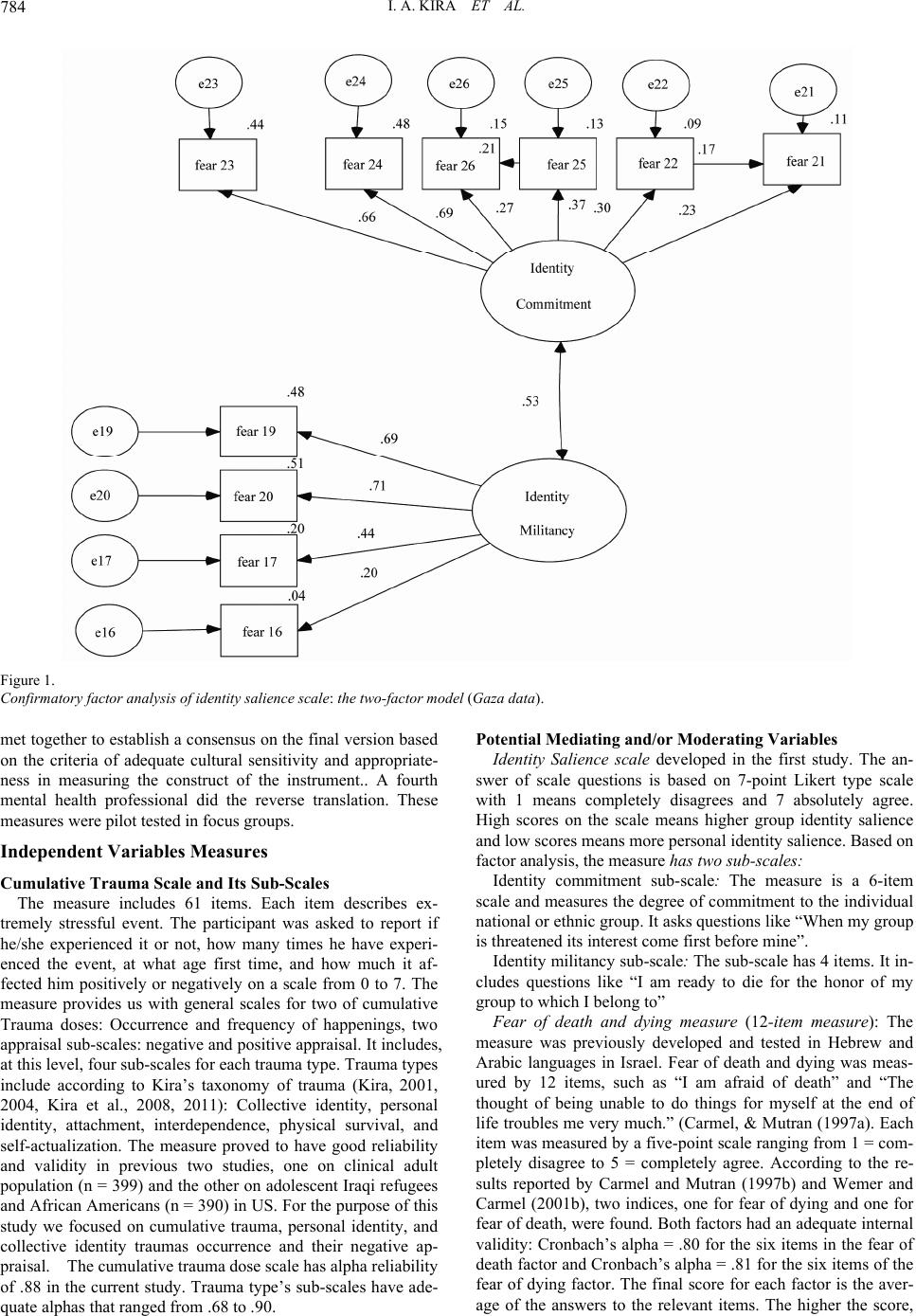 I. A. KIRA ET AL. 784 Figure 1. Confirmatory factor analysis of identity salience scale: the two-factor model (Gaza data). met together to establish a consensus on the final version based on the criteria of adequate cultural sensitivity and appropriate- ness in measuring the construct of the instrument.. A fourth mental health professional did the reverse translation. These measures were pilot tested in focus groups. Independent V ar iables Measures Cumulative Trauma Scale and Its Sub-Scales The measure includes 61 items. Each item describes ex- tremely stressful event. The participant was asked to report if he/she experienced it or not, how many times he have experi- enced the event, at what age first time, and how much it af- fected him positively or negatively on a scale from 0 to 7. The measure provides us with general scales for two of cumulative Trauma doses: Occurrence and frequency of happenings, two appraisal sub-scales: negative and positive appraisal. It includes, at this level, four sub-scales for each trauma type. Trauma types include according to Kira’s taxonomy of trauma (Kira, 2001, 2004, Kira et al., 2008, 2011): Collective identity, personal identity, attachment, interdependence, physical survival, and self-actualization. The measure proved to have good reliability and validity in previous two studies, one on clinical adult population (n = 399) and the other on adolescent Iraqi refugees and African Americans (n = 390) in US. For the purpose of this study we focused on cumulative trauma, personal identity, and collective identity traumas occurrence and their negative ap- praisal. The cumulative trauma dose scale has alpha reliability of .88 in the current study. Trauma type’s sub-scales have ade- quate alphas that ranged from .68 to .90. Potential Mediating and/or Moderating Var i able s Identity Salience scale developed in the first study. The an- swer of scale questions is based on 7-point Likert type scale with 1 means completely disagrees and 7 absolutely agree. High scores on the scale means higher group identity salience and low scores means more personal identity salience. Based on factor analysis, the measure has two sub-scales: Identity commitment sub-scale: The measure is a 6-item scale and measures the degree of commitment to the individual national or ethnic group. It asks questions like “When my group is threatened its interest come first before mine”. Identity militancy sub-scale: The sub-scale has 4 items. It in- cludes questions like “I am ready to die for the honor of my group to which I belong to” Fear of death and dying measure (12-item measure): The measure was previously developed and tested in Hebrew and Arabic languages in Israel. Fear of death and dying was meas- ured by 12 items, such as “I am afraid of death” and “The thought of being unable to do things for myself at the end of life troubles me very much.” (Carmel, & Mutran (1997a). Each item was measured by a five-point scale ranging from 1 = com- pletely disagree to 5 = completely agree. According to the re- sults reported by Carmel and Mutran (1997b) and Wemer and Carmel (2001b), two indices, one for fear of dying and one for fear of death, were found. Both factors had an adequate internal validity: Cronbach’s alpha = .80 for the six items in the fear of death factor and Cronbach’s alpha = .81 for the six items of the fear of dying factor. The final score for each factor is the aver- age of the answers to the relevant items. The higher the score,  I. A. KIRA ET AL. 785 the greater is the participant's fear of death or/and dying. In our study we find the same two factors, however, to accurately describe what the scale is measuring we decided to re-label the fear of dying as fear of loss of functioning and independence in old age, while the first scale accurately describe the fear of actual death. It has alpha of .80 in current study. Dependent Variable Measures Annihilation anxiety measure: The measure is based on the assumption that there are two main sources of the emergence of annihilation anxiety, personal identity and collective identity survival threats (traumas). The 3-item scale have been used before on Iraqi refugees in Michigan and found to have good reliability (alpha. 93), divergent and predictive validity (Tem- plin, Kira et al., 2006). It has an alpha of .87 in the current study. PTSD Measure (CAPS-2) (18 items): This measure was de- veloped by Blacke and his colleagues (Blacke et. al., 1990). It is widely used to assess PTSD. It is a structured clinical inter- view that assesses 17 symptoms rated on frequency and sever- ity on a 5-point scale. CAPS demonstrated high reliability with a range from 0.92 - 0.99 and showed good convergent and dis- criminant validity (Weathers, Keane, & Davidson, 2001). In this study, we used the frequency sub-scale of CAPS-2 that is currently widely used in psychiatric literature. It has alpha of .91 in the current study. CES-D Depression Measure: Center for Epidemiologic stud- ies-Depression mood scale is a 20 item scale (Radloff, 1977). Each item is assessed on a 4-point scale and reflects the fre- quency that each symptom is experienced (0 = none of the time, 3 = all of the time). Adequate reliability and validity have been reported for the CES-D (Orme, Reis, & Herz, 1986). A cutoff score of ≥16 is commonly used for the CES-D to indicate a need for further assessment of the presence of MDD (Radloff, 1977). High internal consistency reliability results (ranging from .85 to .92) have been found for the CES-D among various age, sex, geographic, and racial-ethnic subgroups. Validation studies have found that the CES-D has good convergent valid- ity, discriminant validity (Himmelfarb, & Murrell, 1983), and sensitivity and specificity (Mulrow et al., 1995). The Arabic version of the measure has been used previously on Iraqi refu- gees in Michigan, and found to have good reliability (alpha = .92), and predictive validity. It has alpha of .89 in the current study (e.g., Kira et al., 2011). DASS-A General Anxiety DASS-A: Anxiety Measure (14 items): DASS is a 42-item scale developed by Lovibond and Lovibond, 1995, and includes three sub-scales that measure depression, anxiety, and stress. According to Antony, Bieling, Cox, Enns, and Swinson, 1998, DASS may hold more promise for distinguishing between anxiety and depression as well as between physical arousal and symptoms of generalized anxiety. DASS-A sub-scale measures anxiety, which is increasingly used in different clinical and research settings. Different studies suggest that DASS-A possess adequate convergent validity, with reliability of .84 in non-clinical samples and .89, and 91 in clinical samples (e.g., Lovibond, & Lovibond, 1995). Its au- thors reported alpha reliability of .89 in clinical sample. ). The Arabic version of the measure has been used previously on Iraqi refugees in Michigan, and found to have good reliability (alpha = .89), and predictive validity. It has alpha of .86 in the current study. CTD (Cumulative Trauma disorder) Cumulative Trauma Disorders Measure CTD: The 15-item measure was developed by Kira and associates in three studies on Iraqi refugees: Kira. (2004), Kira, Clifford, & Al-haider, (2002), Kira, Clifford & Al-Haider, (2003). It proved to have high reliability (ranged from .85 and .98), construct, and convergent, divergent and predictive validity. Test-retest reliability in a 6 week-interval is .76. Different kinds of traumas, torture, and severity of tor- ture, number of divorces and remarriage, and cumulative trauma in general accounted for significant variance as predic- tors of CTD symptoms. Exploratory factor analysis found that the measure has four factors and four sub-scales: Executive function deficits, suicidality, dissociation, and depression/ anxiety interface. Confirmatory factor analysis confirmed this structure with comparative fit index of .99. The suicidality sub- scale will be used especially to test some of our hypothesis. Analysis Multiple regressions was utilized to test predictors of sui- cidality, fear of death, militancy and annihilation anxiety con- trolling for age, gender, family size, and grades. Different plausible path models were tested to explore the direct, and indirect effects of the independent variables using structural equation model SEM (AMOS 7 software), (Arbuckle, 2006). Model fit indices were selected in accordance with sev- eral recommendations and included the normed χ2 test statistic (χ2/df), the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) and the comparative fit index (CFI). χ2/df values < 5.0 are con- sidered acceptable; RMSEA values ≤0.05 indicate close fit, values 0.05 to 0.08 indicate reasonable fit, and values >0.10 indicate poor fit . CFI values >0.95 indicate good fit (e.g., Kline, 2005; Hu, & Bentler, 1999). We used bootstrap (N = 200) with bias-corrected confidence intervals to test the significance of the direct and indirect effects of each variable in the model. Bootstrapping is a computer-intensive re-sampling technique. It involves generating bootstrap samples based on the original observations. Bootstrapping is often used to get a better ap- proximation of sampling distribution of a statistic than its theo- retical distribution provides, especially when assumption of normality may be violated. Bootstrapping is more robust mod- ern statistics that are used to generate and to create a sampling distribution, and this bootstrapped distribution is used to com- pute p values, test hypotheses and generate confidence intervals for direct and indirect effects (e.g., Erceg-Hurn, & Mirosevich, 2008). The Second Study: Results Hypothesis 1: Self-efficacy, autonomous functioning and agency is at the core of identity commitment and militancy; Fear of death, attachment trauma (e.g., abandonment by mother) and achievement trauma (e.g., school failure) did not predict either of the collective identity salience variables, how- ever, fear of loss of functioning (fear of loss of autonomy, and loss of efficacy and independence in old age) was the highest predictor of both (Beta = .398. for CIC, and CIM, beta = .328). Self-efficacy, autonomous functioning and agency concerns seem to be at the core of identity commitment and militancy, which confirm one of identity theory theory’s assumptions. Hypothesis 2: Personal identity traumas predict identity commitment, while collective identity traumas predict increase in militancy. Cumulative trauma dose, cumulative negative appraisal, per- sonal identity traumas, Interdependence or secondary trauma and its negative appraisal, and annihilation anxiety predicted  I. A. KIRA ET AL. 786 increase in identity commitment but not militancy. The Cumu- lative positive appraisal of traumas and collective identity traumas, family and survival traumas, PTSD, anxiety, and de- pression predicted increase in both identity commitment and militancy. However, positive appraisal of collective identity trauma, and of survival traumas, predicted militancy, but did not predict identity commitment (see Table 2). Hypothesis 3 and 4: Predictors of Suicidality fear of death and Annihilation Anxiety Fear of death with its two sub-scales was not significant pre- dictor of suicidality. Annihilation anxiety was the strong pre- dictor (beta = .30). Collective identity commitment was not significant predictor of suicidality, however, collective identity militancy (beta = .11) was. Cumulative trauma variables pre- dicted suicidality (beta = .27). Attachment traumas (beta = .13), personal identity trauma (beta = .18), collective identity trau- mas (.17), family traumas (beta = .17), survival traumas (beta = 20), interdependence trauma (beta = .25), and cumulative stress trauma (beta = .26) all predicted suicidality. Identity traumas, personal and collective predicted reduced fear of death, and increased annihilation anxiety (AA). Hypothesis 5: Identity salience, annihilation anxiety (AA) (fear of identity annihilation), as well as fear of death mediates the effects of identity traumas on suicidality and militancy and mental health variables. Using Path analysis we tested the model of identity salience in two conditions. The first condition was when the personal identity trauma is the independent variable in the model. The second condition was when the collective identity trauma is the independent variable in the model. In the first model, increased personal identity traumas predict direct increased in identity commitment (identity salience) and decrease in fear of death (mortality salience). Such traumas predict indirect increase in AA, depression and suicidality. Increased identity salience predicts directly an increase in AA and decrease in militancy. It predicts indirectly an increase in general anxiety, depression, PTSD, and suicidality. Increased AA predicts, directly, in- creased mortality salience, and predicts both direct and indirect increase in militancy, general anxiety, depression and suicide. It predicts indirect increase in PTSD. Increased mortality salience Table 2. Multiple Regression of the effects of different variables on Identity Commitment and Militancy. Collective Identity Commitment Collective Identity Militancy Dependent variables (a) B SE Beta P B SE Beta P PTSD Scale .063 .020 .164 .002 .049 .014 .185 .000 CTD Scale .079 .033 .127 .016 .032 .023 .074 .164 CTD Depression/anxiety syndrome .323 .122 .140 .009 .183 .086 .115 .033 CTD Suicidality sub-scale (items 10, 12) .309 .156 .102 .047 .042 .109 .020 .699 CTD Executive function deficits sub–scale .517 .163 .164 .002 .248 .114 .115 .031 CTD Dissociation/psychoses sub-scale .271 .118 .118 .023 .026 .083 .017 .754 Fear of death sub-scale .344 .357 .052 .335 .170 .249 .037 .495 Fear of loss of functioning (autonomy and efficacy) at old age b sub-scale2.644.329 .398 .000 1.493 .236 .328 .000 DASS-Anxiety Scale .137 .059 .121 .020 .099 .041 .127 .016 Psychological anxiety-Sub-scale .571 .353 .084 .106 .235 .247 .050 .342 Physical anxiety sub-scale .869 .340 .131 .011 .595 .237 .130 .012 CES-D Depression Scale .073 .033 .116 .027 .057 .023 .132 .013 Annihilation anxiety scale .351 .126 .142 .006 –.001 .089 –.001.989 Cumulative dose of trauma occurrence .282 .069 .208 .000 .096 .049 .103 .052 The negative appraisal of trauma dose .131 .055 .123 .016 .066 .038 .089 .086 The positive appraisal of trauma dose .490 .210 .119 .020 .420 .146 .149 .004 Attachment traumas occurrence sub-scale 1.116.626 .091 .076 .150 .438 .018 .732 Personal identity trauma occurrence .981 .391 .130 .013 .331 .274 .064 .229 Negative appraisal of personal identity traumas .598 .297 .103 .044 .134 .208 .034 .520 Positive appraisal of personal identity traumas 2.017.869 .119 .021 1.312 .607 .112 .031 The frequency of collective identity traumatic events .514 .156 .170 .001 .231 .110 .111 .036 Negative appraisal of collective identity traumatic stressors .575 .213 .141 .007 .343 .149 .122 .022 Positive appraisal of collective identity traumatic events 1.068.973 .056 .273 1.667 .674 .128 .014 the occurrence of family traumatic stressors 1.555.356 .219 .000 .525 .253 .108 .039 the occurrence of survival traumas .635 .177 .188 .000 .281 .124 .121 .025 The negative appraisal of survival traumatic stressors .391 .127 .157 .002 .153 .089 .090 .086 The positive appraisal of survival traumatic events .674 .468 .074 .150 .644 .325 .103 .048 Interdependence or secondary trauma occurrence .630 .183 .175 .001 .205 .129 .083 .112 The negative appraisal of secondary trauma events .431 .143 .153 .003 .136 .101 .070 .179 The positive appraisal of secondary traumas .774 .467 .084 .099 .969 .323 .154 .003 Achievement trauma occurrence (School failures) 1.4052.718.027 .605 –.562 1.895 –.016.767 (a) The results have been obtained after age, gender, education; income and family size have been controlled statistically. 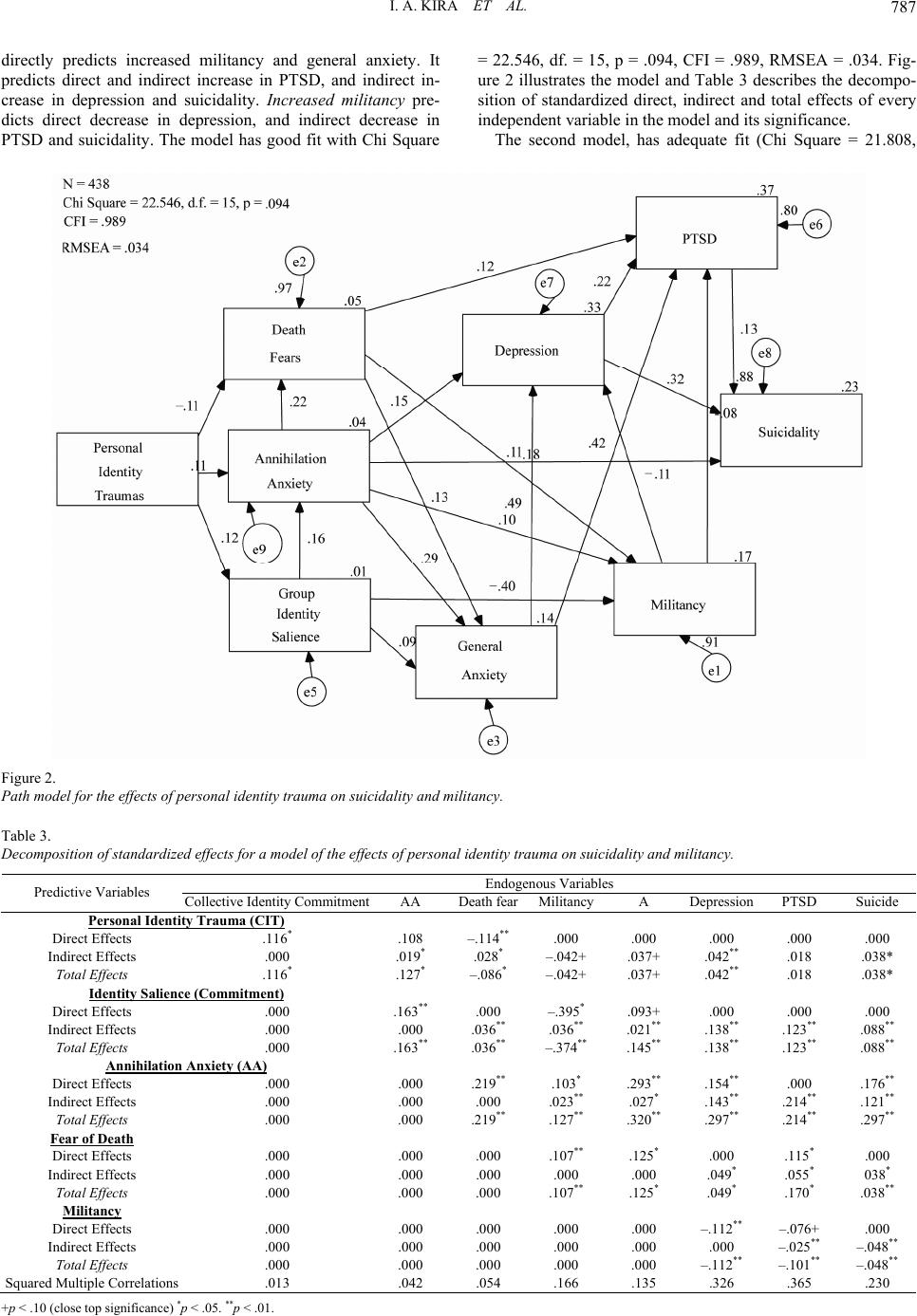 I. A. KIRA ET AL. 787 directly predicts increased militancy and general anxiety. It predicts direct and indirect increase in PTSD, and indirect in- crease in depression and suicidality. Increased militancy pre- dicts direct decrease in depression, and indirect decrease in PTSD and suicidality. The model has good fit with Chi Square = 22.546, df. = 15, p = .094, CFI = .989, RMSEA = .034. Fig- ure 2 illustrates the model and Table 3 describes the decompo- sition of standardized direct, indirect and total effects of every independent variable in the model and its significance. The second model, has adequate fit (Chi Square = 21.808, Figure 2. Path model for the effects of personal identity trauma on suicidality and militancy. Table 3. Decomposition of standardized effects for a model of the effects of personal identity trauma on suicidality and militancy. Endogenous Variables Predictive Variables Collective Identity CommitmentAA Death fearMilitancyA Depression PTSD Suicide Personal Iden tity Traum a (CIT) Direct Effects .116* .108 –.114** .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 Indirect Effects .000 .019* .028* –.042+ .037+ .042** .018 .038* Total Effects .116* .127* –.086* –.042+ .037+ .042** .018 .038* Identity Salience (Commitment) Direct Effects .000 .163** .000 –.395* .093+ .000 .000 .000 Indirect Effects .000 .000 .036** .036** .021** .138** .123** .088** Total Effects .000 .163** .036** –.374** .145** .138** .123** .088** Annihilation Anxiety (A A) Direct Effects .000 .000 .219** .103* .293** .154** .000 .176** Indirect Effects .000 .000 .000 .023** .027* .143** .214** .121** Total Effects .000 .000 .219** .127** .320** .297** .214** .297** Fear of Death Direct Effects .000 .000 .000 .107** .125* .000 .115* .000 Indirect Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .049* .055* 038* Total Effects .000 .000 .000 .107** .125* .049* .170* .038** Militancy Direct Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 –.112** –.076+ .000 Indirect Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 –.025** –.048** Total Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 –.112** –.101** –.048** Squared Multiple Correlations .013 .042 .054 .166 .135 .326 .365 .230 +p < .10 (close top significance) *p < .05. **p < .01.  I. A. KIRA ET AL. 788 df. = 16, p = .149, CFI = .992, RMSEA = .029), In the second model increased collective identity traumatic events predict, directly, increased identity commitment (identity salience) and increased AA, and predict, indirectly, increase in fear of death (mortality salience), general anxiety, depression, PTSD, and suicidality. Increased identity salience, in this model, directly predicts increased AA, and predicts, indirectly, increased mor- tality salience. It also predicts decrease in militancy, and indi- rectly, predict increase in general anxiety, depression, PTSD and suicidality. Increased AA predicts direct increase in fear of death (mortality salience), and predict direct and indirect in- crease in militancy, general anxiety, depression and suicidality. It predicts, indirectly, PTSD. Increased fear of death (mortality salience) predicts direct increase in militancy and general anxi- ety. It predicts directly and indirectly PTSD. It predicts indi- rectly increased depression and suicidality. Increased militancy, as in the first model, predicts direct decrease in depression, and indirect decrease in PTSD and suicidality. Militancy plays an effective role as a coping mechanism to lower increased PTSD, depression and anxiety resulting from high traumatic events, personal and collective, as it predicts decrease in such symp- toms. In both path models, increased general anxiety predicts direct increase in depression and direct and indirect increase in PTSD, and indirect increase in suicidality. Increased depression pre- dicts direct increase in PTSD, and direct and indirect increase in suicidality. Increased PTSD directly predicts suicidality. Table 4 describes the decomposition of standardized direct, indirect and total effects of every variable and its significance in the model. Alternative models: Care must be taken when making causal inferences from cross-sectional data. The theoretical argument for the proposed models is strong and the model fitted the data well; however, there are always alternative models (MacCallum, & Austin, 2000). We considered several alternative models in which we changed the order of the, mediators, and eliminate identity salience and fear of death alternatively. In the alterna- tive models (AM), with PIT as predictor we eliminate fear of death from the mediator variables, the model fit improved, when identity salience was removed, the model fit get worse, when we replaced interchangeably AA with PTSD, Depression and anxiety, as a mediating variables, the model fit get worse. In the alternative models with CIT as predictor, we eliminate fear of death from the mediator variables, the model fit stayed almost the same, when identity salience was removed, the model fit get worse, when we replaced interchangeably AA with PTSD, Depression and anxiety, as a mediating variables, the model fit get worse (see Table 5). The results highlighted the importance of adding identity salience as mediating variable to explain suicidality and militancy. Discussion The results generally indicate adequate reliability, construct and predictive validity for the identity salience measure and its two sub-scales that have been developed. The reliability of the other measures used was adequate in the current data. It seems that identity commitment and identity militancy represent re- lated but unique concepts. Identity commitment is more rele- vant to personal identity salience, while identity militancy is another important identity dimension that is more relevant to group and political dynamics. The findings generally suggest that identity salience, per- sonal and collective, are important and can be strong explana- tory variable that contribute to explaining the dynamics of iden- tity and its development. Identity salience, personal and collec- tive is another dimension of adolescent and adult development. The results generally fit the predictions of TDT which gives the scale an adequate predictive validity. Identity traumas are strong causal variables in predicting identity fears, commitment and militancy. Identity trauma, personal and collective pre- dicted increased identity commitment (identity salience), and increased suicidality. Personal identity trauma activated identity salience and deactivated mortality salience (decreased fear of death) increasing the suicidality and to some degree militancy. However, contrary to the TDT theory’s predictions, AA did not decrease fear of death; it actually increased it in both models. Fear of identity loss increased fear of death. However, personal Table 4. Decomposition of standardized effects for the model of collective identity trauma on suicidality and militancy. Endogenous Variables Predictive Variables Identity Salience AA Death fearMilitancy A Depression PTSD Suicide Collective Identity Trauma (CIT) Direct Effects .191** .352** .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 Indirect Effects .000 .021* .076** –.029 .136** .128** .096** .118** Total Effects .191** .373** .076** –.029 .136** .128** .096** .118** Identity Salience (Commitment) Direct Effects .000 .108* .000 –.395* .093+ .000 .000 .000 Indirect Effects .000 .000 .022* .014* .034* .122** .111** .072** Total Effects .000 .108* .022* –.382* .127* .122** .111** .072** Annihilation Anxiety (A A) Direct Effects .000 .000 .204** .104* .293** .154** .000 .176** Indirect Effects .000 .000 .000 .022** .026* .142** .212** .121** Total Effects .000 .000 .204** .125** .318** .296** .212** .297** Fear of Death Direct Effects .000 .000 .000 .107** .125* .000 .115* .000 Indirect Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .049* .055* .038* Total Effects .000 .000 .000 .107** .125* .049* .170* .038* Militancy Direct Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 –.112** –.076 .000 Indirect Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 –.025** –.048** Total Effects .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 –.112** –.101** –.048** Squared Multiple Correlations .036 .150 .042 .166 .135 .326 .365 .230  I. A. KIRA ET AL. 789 Table 5. Alternative models (AM) for the effects on Personal Identity Traumas (PIT), and Collective Identity Traumas (CIT), on suicidality and militancy. Predictor variable(s) Mediating variables Outcome variables Model Fit AM1 PIT Identity salience and fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, anxietyχ2 = 22.546, df = 15, p = .094, CFI = .989, RMSEA = .034 (Chosen) AM2 PIT Identity, salience variables Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, anxietyχ2 = 16.547, df. = 12, p = .167, RMSEA = .029 (BEST FIT) AM3 PIT Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, anxietyχ2 = 27.564, df = 7, p = .000, CFI = .957, RMSEA = .082 AM4 PIT General anxiety Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, AAχ2 = 107.147, df. = 15, p = .000., CFI = .861, RMSEA = .119 AM5 PIT PTSD Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy AA depression, Anxietyχ2 = 30.777, df. = 15, p = .009, CFI = .976, RMSEA = .049 AM6 PIT Depression Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, AA χ2 = 61.795, df. = 15, p = .000, CFI = .930, RMSEA = .084 AM1 CIT Identity salience and fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, anxietyχ2 = 21.808, df. = 16, p = .149, CFI = .992, RMSEA = .029 (Chosen) AM2 CIT Identity salience variables Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, anxietyχ2 = 18.972, df. = 12, p=.089, CFI = .990, RMSEA = .036 AM3 CIT Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, anxietyχ2 = 14.949, df = 6, p = .021,CFI = .981, RMSEA = .058 AM4 CIT General anxiety Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, depression, AAχ2 = 153.402, df. = 16, p = .000, CFI = .809, RMSEA = .140 AM5 CIT PTSD Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy AA depression, Anxietyχ2 = 85.737, df. = 16, p = .000, CFI = .903, RMSEA = .100 AM6 CIT Depression Fear of death Suicidality, Militancy PTSD, AA χ2 = 119.380, df. = 16, p = .000, CFI = .856, RMSEA = .122 identity trauma directly reduced fear of death. Further, as the theory anticipated, AA (fear of identity loss) predicted directly an increase in militancy and suicidality, while fear of death indirectly predicted suicidality, but not militancy. Clinical suicidality is separate syndrome different from readiness to die for the group (militancy) and is more present in the case of personal identity trauma. Suicidality is mediated by AA (fear of identity loss) and associated with depression, anxi- ety and PTSD. One of the important findings is that increased militancy, in both models, predicted direct decrease in depression, and indi- rect decrease in PTSD and suicidality. Militancy seems to play a positive role as a coping mechanism to lower increased PTSD, depression and anxiety resulting from high personal and collective identity trauma load. In other words, militancy plays as a buffer against increase in AA, in fear of death and associ- ated mental health syndromes. Militancy, ready to die for the group, seems to be opposite to clinical suicidality. Another important finding is that while both AA (fear of identity loss) and fear of death predicted increased militancy, identity com- mitment predicted decreased militancy. Identity commitment, in political conflicts, may act as positive factor after all. Another important findings is that fear of loss of functioning, (fear of loss of independence and loss of self-efficacy, i.e., due to age) was the strongest predictor of identity salience, con- firming, at least partly, the assumption that self-efficacy and agency, that have been acquired through the individuation de- velopmental processes, buffers against fear of identity loss. Fear of identity loss (annihilation anxiety) predicted identity commitment, and decreased militancy Why people, who usually fear death and strive to live, com- mit suicide or sacrifice their lives for their groups? Our findings derived from developmental theories, provide some answers and more questions. Alternative theories, other than TDT, pro- vide different explanations and hypotheses. One of the other strong theories proposed to explain the terror originated in the core of the existential condition of the individual’s inherent death threats, is Terror Management Theory (TMT). According to (TMT) (e.g., Becker, 1962, 1973; Pyszczynski, Greenberg, & Solomon, 1999), a great deal of human behavior can be under- stood as attempts to gain psychological equanimity in the face of awareness of inevitability of death. In recent development of the theory (e.g., Kruglanski, Chen, Dechesne, Fishman, & Orneck, 2009), TMT added that humans struggle for a sense of identity and significance in the world, (partly), as a way to pro- tect themselves against death and its anxieties. This search for validation and value, sometimes, takes the form of expanding oneself in a larger beyond, such as one’s group or nation. These serve as avenues for the person to find meaning and value in a vaster scheme that will not be shattered by one’s own death. As such, the pursuit of symbolic immortality can assuage fear of death. Mortality reminders, under certain conditions, found to make participants express greater willingness to sacrifice their selves for their country (Routledge, & Arndt, 2008). Navarrete, Kurzban, Fessler, and Kirkpatrick, 2004, provide different evolutionary-based argument as well as experimental evidence that question the primacy of mortality salience causal- ity hypotheses. Marshaling social support was a reliably adap- tive need to deal with adversities in human evolutionary path by forming social network and coalitions to improve group sur- vival potential. In-group affliliative sentiments are necessary to obtain needed social support and can have strong explanatory power for the same behaviors that are believed to be due to mortality reminders (see also, Kirkpatrick, & Navarrete, 2006). While developmentally based TDT assumptions, as well as evolutionary-based coalition psychology assumptions can be reconciled theoretically within the robust TMT framework, the primacy of identity salience contrasted with the primacy of mortality salience, or the primacy of affliliative sentiments salience, should be resolved in subsequent controlled or longi-  I. A. KIRA ET AL. 790 tudinal studies. Implications of the Results While the results have theoretical implications for individua- tion and identity development in social and political context, we need to brainstorm and utilize the current findings to develop different ways to reduce suffering in ways other than becoming a militant with increased violence and terrorist suicide, or com- mitting clinical suicide. The finding about the role of militancy in alleviating mental health suffering in those traumatized ado- lescents is important. Providing effective multi-systemic and ecological interventions and supports to children, adolescents and adults, in addition to conflict resolution and reconciliation efforts, may reduce militancy as well as clinical suicide. Further, the finding that identity commitment actually reduces militancy is equally important. Interventions that enhance positive iden- tity development in youth should prevent increased militancy and suicidality. Identity commitment, in itself can be positive indicator; fear of identity loss due to different events can be alleviated by focusing on positive identity development for those affected. Reducing collective traumatic events and pre- venting its cross-generational transmission can reduce suffering and enhance future peace and conflict resolution. Devising interventions that interrupt and stop the cycle of cross-genera- tional transmission of such intractable collective identity trau- mas is another important task. Such brainstorming can yield some successful strategies to alleviate pain and suffering of the groups. Current study can be a one step toward such scientific analysis that can set progress toward peace and identity conflict resolution and reduce or eliminate terror. Limitations This pilot study has its definite limitations. The current cross-sectional study does not explicitly draw causality from the results. We realize the limitation of causal analysis with SEM (e.g., Bullock, Harlow, & Mulaik, 1994; Rosenbaum, 2002). Unobserved confounding variables can distort statistical causal inference. These may be impossible to eliminate their effects in observational studies. However, there are cases where only observational data are available and one cannot conduct any experimental studies. Experimental studies, e.g., using death reminders, may not simulate the real effects of actual personal and collective identity traumas for such populations. For these cases, SEM is powerful tools for causal statistical causal inference, although one has to pay very careful attention to confounding variables. One caution should be made here. We must not assert that causation is established based solely on the results derived from SEM but should make substantive arguments as well. Future replications on different populations and longitudinal studies could reach such inference of causality. Nevertheless, the findings of our study provide preliminary evidence of the important associations between identity variables and increased or reduced distress and symptom clusters of PTSD, depression, anxiety, suicidality and militancy. References Antony, M. M., Bieling, P. J., Cox, B. J., Enns, M. W., & Swinson, R. P. (1998). Psychometric properties of the 42-item and 21-item ver- sions of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales in clinical groups and a community sample. Psychological Assessment, 10, 176-181. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.10.2.176 Arbuckle, J. L. (2006). Amos 7.0 User’s Guide. Chicago: SPSS. Ashmore, R. D., Deaux, K., & McLaughlin-Volpe, T. (2004). An orga- nizing framework for collective identity: Articulation and signifi- cance of multidimensionality. Psychological Bulletin, 130, 80-114. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.130.1.80 Bandura, A. (1997), Self-efficacy: The exercise of control, New York: Freeman. Becker, E. (1962). The birth and death of meaning. New York: Free Press. Becker, E. (1973). The denial of death. New York: Free Press. Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment and loss. Vol. 1: Attachment. New York: Basic Books. Bowlby, J. (1988). A secure base (2nd ed.). New York: Basic Books. Blake, D. D., Weathers, F. W., Nagy, L. M., Kaloupek, D. G., Klau- minzer, G., Charney, D. S., & Keane, T. M. (1990). A clinician rat- ing scale for assessing current and lifetime PTSD: The CAPS-1. The Behavior Therapist, 13, 187-188. Bullock, H. E., Harlow, L.L., Mulaik, S. A., (1994). Causal issues in structural equation modeling research. Structural Equation Modeling, 1, 253-267. doi:10.1080/10705519409539977 Carmel, S. & Mutran, E. (1997a). Wishes regarding the use of life- sustaining treatments among elderly persons in Israel: An explana- tory model. Social Science and Medicine, 45, 1715-1727. doi:10.1016/S0277-9536(97)00104-4 Carmel, S., & Mutran, E. (1997b). Preferences for different life-sus- taining treatments among elderly persons in Israel. Journal of Ger- ontology, 52B, S97-S102. doi:10.1093/geronb/52B.2.S97 Cassiman, S. A. (2005). Toward more inclusive poverty knowledge: Traumatological contributions to the poverty discourse. The Social Policy Journal, and: Cutting Edge of Social Policy Research, 4, 93- 106. Erceg-Hurn, D. & Mirosevich, V. (2008). Modern robust statistical methods: An easy way to maximize the accuracy and power of your research. American Psychologist, 63, 591-601. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.63.7.591 Erikson, E. H. (1963). Childhood and society (2nd ed.). New York: Norton. Erikson, E. H. (1980). Identity and the life cycle. (2nd ed.). New York: Norton. Gross, F. L. (1987). Introducing Erik Erikson: An invitation to his thinking. Lanham, MD: University Press of America. Hu, L., Bentler, & P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in co- variance structure analysis: conventional versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1-55. doi:10.1080/10705519909540118 Ibn Khaldûn. (1968). Al-Muqaddima (Discours sur l’histoire univer- selle), Tome 1. Paris: Sindbad. (Original work published 1377). Kira, I. (2010). Etiology and Treatments of post-cumulative traumatic Stress disorders in Different Cultures. Traumatology: An Interna- tional Journal, 16, 128-141. Kira, I. (2006). Collective identity terror in the Israeli-Palestinian con- flict and potential solutions. In J. Kuriansky (Ed.), Terror in the Holy land, inside the anguish of Israeli-Palestinian Conflict (pp. 125-130). New York: Praeger. Kira, I. (2002, August). Suicide terror and collective trauma: A collec- tive terror management paradigm. Chicago, Illinois: American Psy- chological Association Annual Convention. Kira, I. (2004). Cumulative Trauma Disorder: A new scale for complex PTSD. Proceeding of the XXVIII International Congress of Psy- chology, Beijing. Kira, I. (2001). Taxonomy of trauma and trauma assessment. Trauma- tology, 2, 1-14. Kira, I. (1997). Value Processing: A clinical cross-cultural model (an empirical study). Ph.D. Dissertation, Columbia: Columbia Univer- sity. Kira, I. (1987). Human values: A conceptual model for the dynamics of value processing. Master Thesis, Hayward: California State Univer- sity. Kira, I., Templin, T., Lewandowski, L., Ramaswamy, V., Bulent, O., Abu-Mediane, S., Mohanesh, J., & Alamia, H. (2011). Cumulative Tertiary appraisal of traumatic events across cultures: Two studies. Journal of Loss and Trauma: International Perspectives on Stress & Coping, 16, 43-66. Kira, I., Lewandowski, L., Templin, T., Ramaswamy, V., Ozkan, B., &  I. A. KIRA ET AL. 791 Mohanesh, J. (2008). Measuring cumulative trauma dose, types and profiles using a development-based taxonomy of trauma, Trauma- tology, 14, 62-87. doi:10.1177/1534765608319324 Kira, I., Clifford, D. & Al-haider (2003). Assessing and treating cumu- lative trauma disorders (CTD) in Iraqi refugees. In American Psy- chological Association Annual Convention, Toronto. Kira, I., Clifford, D., & Al-Haidar, A. (2002). Cumulative Trauma Disorder in Iraqi refugees in Michigan: A Preliminary data. In Sec- ond Annual Symposium on Refugee, Dearborn, Michigan. Kirkpatrick, L. A., & Navarrete, C. D. (2006). Reports of my death anxiety have been greatly exaggerated: A critique of terror manage- ment theory from an evolutionary perspective. Psychological Inquiry, 17, 288-298. doi:10.1080/10478400701366969 Kline R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation mod- eling (2nd ed.). New York: The Guilford Press. Kruglanski, A. W., Chen, X.,Dechesne, M., Fishman, S., & Orehek, E. (2009). Fully Committed Suicide bombers’ motivations and the quest for personal significance. Political Psychology, 30, 331-357. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9221.2009.00698.x Lovibond, P. F., & Lovibond, S. H. (1995). The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the Depression Anxiety and Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories, Behavior Research and Therapy, 33, 335-342. doi:10.1016/0005-7967(94)00075-U McCall, G. J., & Simmons, J. L. (1978). Identities and interactions (Rev. ed.). New York, NY: Free Press. Mulrow C., Williams J. W., Gerety, M. B., Ramirez, G., Montiel, O. M., & Kerber, C. L.: Case-finding instruments for depression in primary care settings. Annals of Internal Medicine, 122, 913-921. Orme, J. G.; Reis, J, & Herz, E. J. (1986). Factorial and discriminant validity of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression (CES- D) scale. Journal of Clinical-Psychology, 42, 28-33. doi:10.1002/1097-4679(198601)42:1<28::AID-JCLP2270420104>3. 0.CO;2-T MacCallum, R. C., & Austin, J. T. (2000). Applications of structural equation modeling in psychological research. Annual Review of Psy- chology, 51, 201-226. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.51.1.201 McGregor, Η. Α., Lieberman, J. D., Greenberg, J., Solomon, S., Aradt, J., Simon, L,. & Pyszczynski, T. (1998). Terror management and ag- gression: Evidence that mortality salience motivates aggression a- gainst worldview-threatening others. Journal of Personality and So- cial Psychology, 74, 590-605. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.74.3.590 Pyszczynski, T., Greenberg, J., & Solomon, S. (1999). A dual-process model of defense against conscious and unconscious death-related thoughts: An extension of terror management theory. Psychological Review, 106, 835-845. doi:10.1037/0033-295X.106.4.835 Navarrete, C. D., Kurzban, R.; Fessler, D. & Kirkpatrick, L. (2004). Anxiety and Intergroup Bias: Terror Management or Coalitional Psychology? Group Processes Intergroup Relations, 7, 370-397. doi:10.1177/1368430204046144 Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population, Applied Psychological Meas- urement, 1, 385-401. doi:10.1177/014662167700100306 Rasmussen, J., & Erikson, E. E. (1963). Childhood and society (2nd ed.). New York: Norton. Rosenbaum, P. R., (2002) Observational Studies (2nd ed.). New York: Springer. Routledge, C., & Arndt, J. (2008). Self-sacrifice as self-defense: Mor- tality salience increases efforts to affirm a symbolic immortal self at the expense of the physical self. European Journal of Social Psy- chology, 38, 531-541. doi:10.1002/ejsp.442 Smith, H. J., Spears, R., & Hamstra, I. J. (1999). Social identity and the context of relative deprivation. In N. Ellemers, & R. Spears (Eds.), Social identity: Context, commitment, content (pp. 205-229). Oxford, England: Basil Blackwell. Stryker, S., & Burke, P. J. (2000). The past, present, and future of an identity theory. Social Psychology Quarterly, 63, 284-297. doi:10.2307/2695840 Stryker, S., & Serpe, R. T. (1982). Commitment, identity salience, and role behavior: A theory and research example. In W. Ickes, & E. S. Knowles (Eds.), Personality, roles, and social behavior (pp. 199- 218). New York: Springer-Verlag. Tajfel, H., & Turner, J. C. (1986). The social identity theory of inter- group behavior. In S. Worchen & W. G. Austin (Eds.), Psychology of intergroup relations (pp. 7-24). Chicago: Nelson Hall. Templin, T., Kira, A., Lewandowski, L., Hammad, A., Mohanesh, J., & Abdulkhaleq, H. (2006). Annihilation Anxiety, trauma dose, and trauma negative appraisal: A new measure for annihilation anxiety. In American Psychological Association Annual Convention, New Orleans, Louisiana. Walker, I., & Pettigrew, T. F. (1984). Relative deprivation theory: An overview and conceptual critique. British Journal of Social Psychol- ogy, 23, 301-310. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8309.1984.tb00645.x Weathers, F., Keane, T., & Davidson, J. (2001). The Clinician-Admin- istered PTSD scale: A review of the first ten years of research. De- pression and Anxiety. 13, 132-156. doi:10.1002/da.1029 Werner, P., & Carmel, S. (2001b). Life-sustaining treatment decisions: Health care social workers’ attitudes and their correlates. Journal of Gerontological Social Work, 34, 83-97. doi:10.1300/J083v34n04_07 |

