Open Access Library Journal
Vol.04 No.11(2017), Article ID:80708,9 pages
10.4236/oalib.1104109
Investigation of TCM Constitution in 138 Patients with Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
Xinxin Wang1, Weiping Zhu2
1Institute of Integrative Medicine, Qingdao University Medical College, Qingdao, China
2Qingdao Haici Hospital, Qingdao, China

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Open Access Library Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: November 1, 2017; Accepted: November 26, 2017; Published: November 29, 2017
ABSTRACT
Objective: To analyze the distribution and characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Constitution in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). Methods: Divide the PBC patients who met the inclusion criteria into 3 groups according to the stage of disease development, including group A (group of basic normal), group B (group of symptom stage) and group C (group of decompensation stage). Each group collected 46 cases, and every patient done investgations, including blood routine examination, live function
test, image ultrasound examination, autoantibody examination and immunoglobulin test, and counted their clinical symptoms and judged all patients’ constitution of TCM. Results: 1) For 138 patients with PBC, the constitution of TCM is characterized by biased constitution, among which constitution of qi stagnation (19.57%) was the most, followed by constitution of qi asthenia (15.94%), constitution of yin asthenia (15.94%) and constitution of damp-heat (14.49%). There was no significant correlation between the type of constitution and the age of onset (P > 0.05). 2) The constitution types of A and B two groups were mainly constitution of qi stagnation, constitution of qi asthenia and constitution of damp-heat, while group C was mainly composed of constitution of blood stasis, constitution of yin asthenia and constitution of yang asthenia. And there was a correlation between the type of constitution and clinical stage (P < 0.05). 3) The highest positive rate of autoantibodies was constitution of qi stagnation, followed by constitution of damp-heat, constitution of qi asthenia and constitution of yin asthenia. The most abnormal liver function and immunoglobulin were constitution of qi stagnation, followed by constitution of qi asthenia, constitution of yin asthenia, constitution of damp- heat. Conclusion: Constitution of qi stagnation, constitution of qi asthenia, constitution of damp-heat and constitution of yin asthenia are the susceptible constitutions of PBC patients.
Subject Areas:
Clinical Trials
Keywords:
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC), Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Constitution Type, Clinical Stage

1. Background
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic cholestatic liver disease with specific intrahepatic bile ducts. Its pathological features are progressive and non suppurative intrahepatic cholangitis, which can eventually develop into cirrhosis. Primary biliary cirrhosis was renamed as primary biliary cholangitis in 2015, and still retained the acronym for PBC [1] . There is no record of name, etiology and pathogenesis of PBC, whose clinical symptoms are diversified in traditional Chinese medicine. Modern medicine believes that the factors of immune damage and genetic susceptibility are related to its pathogenesis, which has something to do with the constitution theory of TCM. The discussion of TCM constitution was first seen in Huangdi’s Canon of internal medicine. After a long period of exploration and research, the Chinese Medical Association published the criteria for determining the constitution of Chinese medicine in April 9, 2009, which made the classification of TCM constitution more standardized and scientific [2] . It is found that there is almost no investigation on the TCM constitution of PBC patients after referring to the literature. PBC is an autoimmune disease, which is closely related to the constitution, so the study has guiding value for clinical prevention of disease.
2. Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria: patients who met the diagnostic criteria of PBC were able to successfully cooperate with the clinical investigation. Exclusion criteria: exclude pregnant or lactating women and those who do not cooperate with the survey, and AMA positive other diseases, such as acute functional failure (lead to AMA transient positive), chronic hepatitis C, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pulmonary tuberculosis, etc.
2.2. Diagnostic Criteria
Referring to the consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (also referred to as primary biliary cholangitis) published in 2015 by the Chinese Medical Association and Hepatology branch [1] . In accordance with the following three standards in two can be diagnosed as PBC. 1) Biochemical indicators such as elevated ALP reflect cholestasis. 2) Serum AMA or AMA-M2 positive. 3) The histopathology of liver was consistent with PBC. Grouping criteria is according to the development stage of PBC natural history [3] . Divided into three groups, which is Group A, Group B, and Group A. Group A (group of basic normal) consisted of preclinical stage and asymptomatic phase, and the former was positive for AMA, but there was no obvious abnormality in biochemical indexes, while the latter was mainly characterized by abnormal biochemical indexes, but no obvious clinical symptoms. Group B is the symptom stage, which appeared fatigue, pruritus and other clinical symptoms. Group C is the decompensation stage, which appeared gastrointestinal bleeding, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy and other clinical manifestations.
2.3. Determination of Constitution Type of Chinese Medicine
According to the classification method of 9 kinds of constitutions by Professor Wang Qi of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, the utioconstitn is divided into constitution of yang asthenia, constitution of yin asthenia, constitution of qi stagnation, constitution of phlegm-dampness, constitution of damp-heat, constitution of blood stasis, allergic constitution, constitution of qi asthenia [4] . Then, determine the patient’s constitution type of TCM, and summarize the survey results. The type of constitution is investigated and determined by trained personnel.
2.4. Research Method
The cases, which accepted treatment in Qingdao Haici hospital and Sixth People’s Hospital during January 2013 and June 2017, met the inclusion criteria and diagnostic criteria of PBC. All the patients(A total of 240 cases), do some routine examination, which mainly are liver function tests [including aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), r-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)], auto antibody test [including antinuclear antibody(ANA), anti mitochondrial antibody(AMA), Anti mitochondrial antibody type II(AMA-M2)], serum immunoglobulin M (IgM) detection and imaging of ultrasound examination. The results and clinical information of patients were collected. According to the development stage of PBC disease, patients with PBC were divided into group A (group of basic normal), group B (group of symptom stage) and group C (group of decompensation stage). Each group was randomly selected from 46 patients. The data of 138 patients were investigated as follows: There were 118 females (85.51%) and 22 males (15.94%), which the ratio of two was 5.36:1, and an average age (58.32 ± 10.14). The patients of positive ANA were found in 121 cases (87.68%), AMA positive were 115 cases (83.33%), and AMA-M2 positive were 81 cases (58.70%). There were 78 cases (56.52%) with elevated AST, 84 cases (60.87%) with elevated AST, 108 cases (78.26%) with elevated ALP, 86 cases (62.31%) with elevated GGT, and 81 cases (58.70%) with elevated IgM. Then, according to Professor Wang Qi’s 9 kinds of physical classification method, each group of patients with a pre designed questionnaire for physical investigation. That is to answer all the questions in constitution classification and decision table of Chinese medicine [5] . Each problem is calculated according to 5 grades, and the original score and conversion score are calculated, and then, determine the type of constitution, and summarize the results of physical fitness. Finally, observe the abnormal situation of ALT, AST, ALP, GGT, IgM, and the positive rates of autoantibodies ANA, AMA and AMA-M2 in PBC patients with different constitutional types.
2.5. Statistical Methods
Use SPSS 21.0 to do statistical analysis. Measurement data were compared with analysis of variance, express in ( ); count data were compared with χ2 analysis, and use the available frequency or rate of description; use descriptive statistical analysis of clinical feature and etiology characteristics of all cases. The correlation analysis of two categories, using rank sum test; the association analysis of multi group and multi classification need to be Fisher accurate test, and take P < 0.05 as the inspection level.
3. Results
Figure 1 shows that 138 patients with PBC were more likely to have biased constitution, including constitution of qi stagnation (19.57%), followed by constitution of qi asthenia (15.94%), constitution of yin asthenia (15.94%), and constitution of damp-heat (14.49%).
Table 1 shows that there was no significant correlation between the type of constitution and the age of onset (P > 0.05), and the difference was not statistically significant.
Excluding constitution of yin-yang harmony and allergic constitution of sample with less content, and sample size remained in 132 cases. Table 2 shows that the constitution types of A and B two groups were mainly constitution of qi stagnation, constitution of qi asthenia and constitution of damp-heat, while C
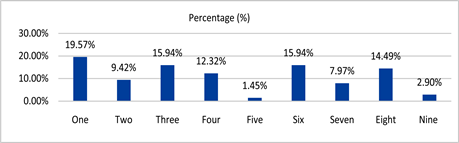
Figure 1. Distribution of TCM Constitution Types in 138 cases of patients with PBC.
Table 1. The relationship between constitutional types and age of onset of 138 cases.
Note: By rank sum test, P > 0.05 indicated that there was no significant correlation between the type of constitution and the age of onset.
Table 2. The relationship between constitutional types and clinical stages of 132 cases.
Note: by Fisher accurate test, P < 0.05 indicated that there was correlation between constitutional type and clinical stage.
group was mainly composed of constitution of blood stasis, constitution of y in asthenia and constitution of yang asthenia. The Fisher test showed that there was a correlation between the type of constitution and clinical stage (P < 0.05). It is found that the distribution of body constitution is different in the course of disease progression. The changes are roughly as follows: there was a downward trend in the number of patients with constitution of qi stagnation and constitution of damp-heat; the number of patients with constitution of qi asthenia was unchanged at first and then decreased; The number of patients with constitution of yin asthenia, constitution of blood stasis and constitution of yang asthenia showed an increasing trend, and reached the highest level in the decompensation period; while, the number of patients with phlegm dampness is at a similar level. Because of the small sample size of PBC patients, the results have certain clinical significance, which can increase the clinical sample size, and further explore the study.
Table 3 shows that ANA positive patients were found in 121 cases (87.68%), AMA positive patients in 115 cases (83.33%), and AMA-M2 positive patients in 81 cases (58.70%). The highest positive rate of autoantibodies was constitution of qi stagnation (59 cases), followed by constitution of damp-heat (53 cases), constitution of qi asthenia (51 cases) and constitution of yin asthenia (48 cases).
Table 4 shows that 78 patients (56.52%) with elevated AST, 84 patients (60.87%) with elevated AST, 108 patients (78.26%)with elevated ALP, 86 patients (62.31%)with elevated GGT, and 81 patients (58.70%) with elevated IgM. The most abnormal liver function and immunoglobulin in PBC patients were constitution of qi stagnation (92 cases), followed by constitution of qi asthenia (74
Table 3. Autoantibodies in 138 cases of PBC patients with different constitutional types.
Table 4. Abnormal liver function and serum immunoglobulin in 138 cases of PBC patients with different constitutional types.
cases), constitution of yin asthenia (73 cases), and constitution of damp-heat (63 cases). And the abnormal distribution of AST, ALT, ALP, GGT and IgM in different constitutions were different.
4. Discuss
The clinical symptoms of PBC are complex and changeable. Traditional Chinese medicine can be classified as “jaundice”, “hypochondriac pain”, “skin itching”, “asthenia labor” and other disease syndromes [6] . Modern medicine thinks that physique can reflect the particularity of organism function, and the characteristics of body Yin and Yang and Qi and blood rise and fall. At the same time, it also determines the susceptibility to pathogenic factors, as well as the propensity to produce lesions type [7] .
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic progressive autoimmune disease, which is closely related to the constitution of Tradition Chinese Medicine (TCM). This study was carried out to investigate 138 cases of patients with PBC type of constitution. It found that the constitution type of TCM was mainly constitution of qi stagnation, followed by constitution of qi asthenia, constitution of yin asthenia, and constitution of damp-heat. It is speculated that these constitutions may be the susceptible constitution of PBC patients. Therefore, we should pay attention to the targeted methods to improve the Constitution and combine with the clinical treatment. Many studies have shown that PBC patients are mostly perimenopausal or amenorrhea elderly women, just as “plain questions” described in the middle-aged woman in Ren deficiency, liver and kidney function decline stage. The asthenia of Ren will block the virtual physiological function of Spleen governing transportation and transformation, Liver storing blood, Kidney dominating water and storing essence disorder, which could cause deficiency of Qi, Blood and Yin essence. Li Hongyu and others think that liver plays the most important role in women’ physiological function, and the Yin essence and Yin blood of liver and kidney gradually wear away after their middle age, which can ease to cause eficiency of vital qi [8] . At this time, if the improper diet, overstrain, or feelings of evils, easily lead to positive imaginary evil sheng. But, further research finds that there was no significant correlation between the physical type of PBC patients and their age. Therefore, this may be due to the inclusion of PBC patients aged more than 49 to 72 years old, their physical type has become mature and stable. In addition, statistics showed that the constitution of type of patients with PBC who stay in the preclinical stage and asymptomatic phase were mainly constitution of qi stagnation, constitution of qi asthenia, and constitution of damp-heat. However, the patients of decompensation stage were mainly constitution of blood stasis, constitution of yin asthenia and constitution of yang asthenia. The Fisher exact test suggests that there is a correlation between the constitution types and clinical staging (P < 0.05). With the progress of disease, the distribution of constitutional types of patients with PBC varies, which may be related to the clinical pathological changes of patients.
This study uses the academic thought of “preventive treatment of disease” in TCM, emphasizes the adjustability of constitution, and provides a theoretical basis and method for the prevention of PBC from the point of view of improving physique. Traditional Chinese Medicine Constitution can treat individual patients with different constitution from the diet, daily life, medicine and other aspects of the development of individualized treatment and nursed back to health program PBC. The clinical research of TCM Constitution can better guide the clinical treatment and nursing of PBC patients. At present western medicine in the treatment of PBC with drug ursodeoxycholic acid (ursodeoxycholic acid, UDCA) and Ocaliva (obeticholic acid), which is the second FDA approved drugs in the United States for the treatment of adult with PBC. There are more than 50% of the primary biliary cholangitis patients effectively for UDCA, but nearly as many as 40% of the patients with inadequate response to UDCA, and 5% to 10% of patients on UDCA intolerance. On the other hand, Ocaliva has side effects, such as a variety of skin itching, severe fatigue, joint pain, rash, and so on. The study found that the safety and the effect of Chinese medicine in the treatment of PBC disease significantly. Traditional Chinese medicine has obvious advantages in preventing and treating disease. The physical research of PBC has some practical value. On the one hand, it can take care of the diet and daily life of the patients in the preclinical and asymptomatic periods, and make reasonable plans to prevent the disease from progressing to symptomatic period. On the other hand, the symptoms of the period can be combined with the daily physical health care and clinical drug treatment, to eliminate the symptoms of patients with discomfort, slow down the development of disease. On decompensated patients, make the physical type combined with TCM syndrome differentiation, and the treatment method for the clinical use of traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine combined to improve the patient’s expectations of diet and sleep, improve their quality of life, increase the confidence to resist the disease. Hope that the future can be based on the patient’s physical type and clinical symptoms to achieve individualized diagnosis and treatment program, which in order to reflect the “people-oriented” and “person” thought.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, the results of TCM Constitution identification suggested that constitution of qi stagnation, constitution of qi asthenia, constitution of damp-heat and constitution of yin asthenia are the susceptible constitutions of PBC patients. The qi stagnation is caused by emotional discomfort, anxiety and rage. Emotional internal injury is the main cause of qi depression, but it is easy to suffer from qi stagnation, and often has internal factors of Zang Qi weakness. Qi deficienc mostly dues to the pressure of working life form, eating cold or greasy, lack of exercise and exercise, unhealthy lifestyle. And, yin deficiency is because of acquired dystrophy formation, such as excessive sexual indulgence, consumption, or work and life stress, living without the law, exhaustion and so on. Damp heat mainly has the reason of smoking and drinking, staying up late, nourishing improper or mood is not smooth. The specific etiology research needs combined with clinic. This study only physically surveys of Qingdao Haici medical group and the Sixth People’s Hospital of Qingdao city in PBC, has certain limitations. It hopes that could further expand the scope of investigation in the future research. A large sample of research can be carried out, the use of modern diagnosis and treatment technology, in order to further analyze the distribution characteristics and clinical practical value of TCM Constitution in patients with PBC.
Cite this paper
Wang, X.X. and Zhu, W.P. (2017) Investigation of TCM Constitution in 138 Patients with Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC). Open Access Library Journal, 4: e4109. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1104109
References
- 1. Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (Also Referred to as Primary Biliary Cholangitis) (2015). Liver, 12, 960-968.
- 2. Wang, J. (2015) Study on Individual Health Management Using the Criteria of Constitution Classification of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chinese Sanatorium, 24, 239.
- 3. Mayo, M.J. (2008) Natural History of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Clinics in Liver Disease, 12, 277-288.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2008.02.012 - 4. Wang, Q. (2005) Medicine. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, 79-82.
- 5. Chinese Medicine Association (2009) Classification and Determination of Constitution of Chinese Medicine. World Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 4, 303.
- 6. Zhang, N., Zhang, S.Q. and Gong, M. (2011) The Status of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Chinese Modern Medicine, 11, 172-173.
- 7. Wang, Q. and Ye, J.N. (2006) Phlegm Dampness Constitution of the Criteria of Chinese. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 21, 73-75.
- 8. Li, H.Y. and Xue, B.Y. (2014) Literature Study on TCM Syndrome Differentiation and Treatment Regularity of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Journal of Chinese Experimental Prescription Science, 3, 209-213.


