Frequent Episodic Vertigo Is an Unexpected Side Effect of Flutamide339
cerebral flow volume was 760 mL/min, which was the
sum of bilateral internal carotid arterial volumes and bi-
lateral vertebral arterial volumes (Table 1). Twenty-four
hours’ Holter showed that heart rate was averaged 68
beats/min with highest 114 beats/min (8:00 am) and low-
est 42 beats/min (4:00 AM). T1, T2, fluid-attenuated
inversion recovery and diffusion weighted image mag-
netic resonance imaging (1.5 Tesla system, Picker Edge
Eclipse, Picker 98 International, USA) did not find any
lesion, but time of flight magnetic resonance angiogram
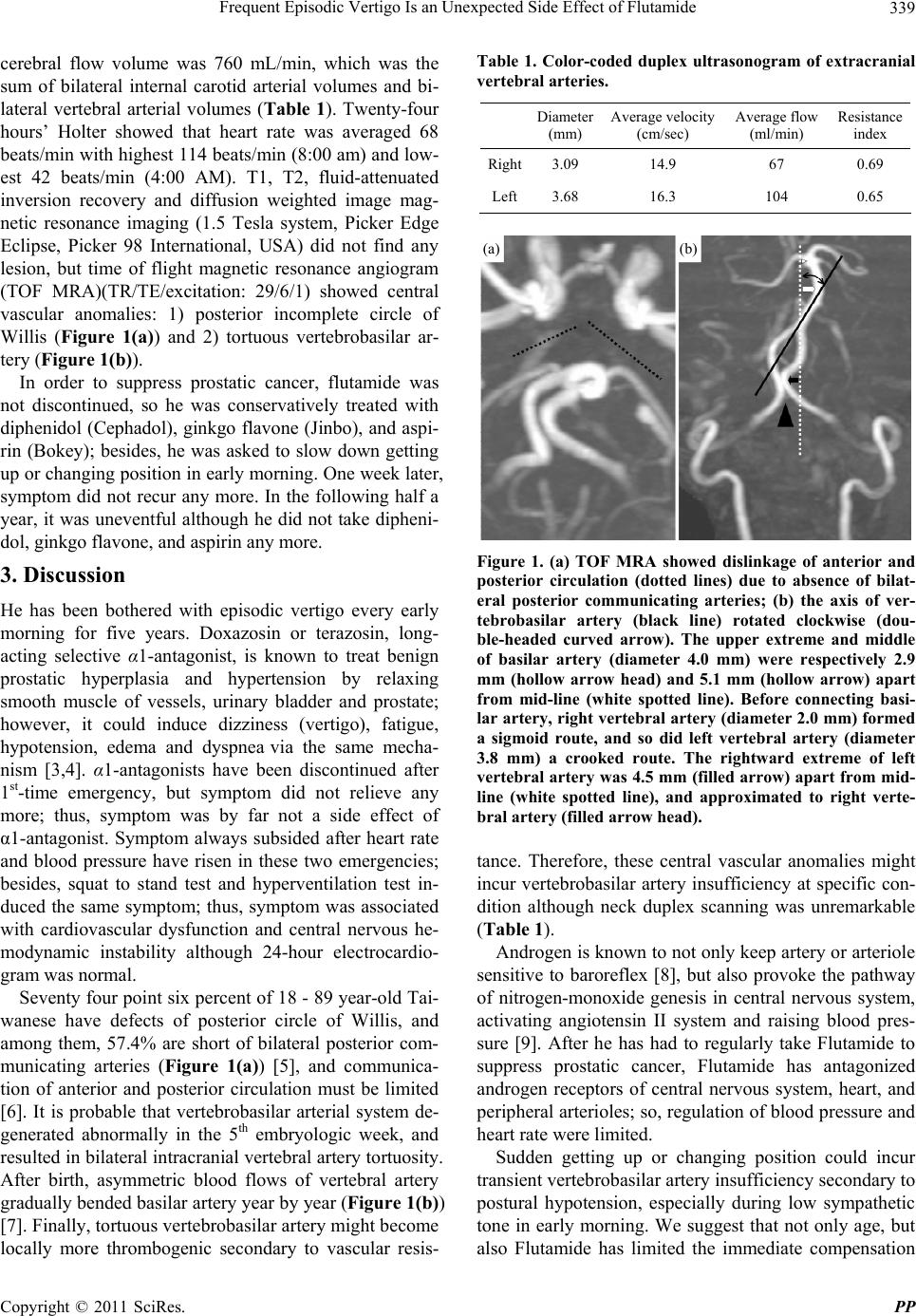
(TOF MRA)(TR/TE/excitation: 29/6/1) showed central
vascular anomalies: 1) posterior incomplete circle of
Willis (Figure 1(a)) and 2) tortuous vertebrobasilar ar-
tery (Figure 1(b)).
In order to suppress prostatic cancer, flutamide was
not discontinued, so he was conservatively treated with
diphenidol (Cephadol), ginkgo flavone (Jinbo), and aspi-
rin (Bokey); besides, he was asked to slow down getting
up or changing position in early morning. One week later,
symptom did not recur any more. In the following half a
year, it was uneventful although he did not take dipheni-
dol, ginkgo flavone, and aspirin any more.
3. Discussion
He has been bothered with episodic vertigo every early
morning for five years. Doxazosin or terazosin, long-
acting selective α1-antagonist, is known to treat benign
prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension by relaxing
smooth muscle of vessels, urinary bladder and prostate;
however, it could induce dizziness (vertigo), fatigue,
hypotension, edema and dyspnea via the same mecha-
nism [3,4]. α1-antagonists have been discontinued after
1st-time emergency, but symptom did not relieve any
more; thus, symptom was by far not a side effect of
α1-antagonist. Symptom always subsided after heart rate
and blood pressure have risen in these two emergencies;
besides, squat to stand test and hyperventilation test in-
duced the same symptom; thus, symptom was associated
with cardiovascular dysfunction and central nervous he-
modynamic instability although 24-hour electrocardio-
gram was normal.
Seventy four point six percent of 18 - 89 year-old Tai-
wanese have defects of posterior circle of Willis, and
among them, 57.4% are short of bilateral posterior com-
municating arteries (Figure 1(a)) [5], and communica-
tion of anterior and posterior circulation must be limited
[6]. It is probable that vertebrobasilar arterial system de-
generated abnormally in the 5th embryologic week, and
resulted in bilateral intracranial vertebral artery tortuosity.
After birth, asymmetric blood flows of vertebral artery
gradually bended basilar artery year by year (Figure 1(b))
[7]. Finally, tortuous vertebrobasilar artery might become
locally more thrombogenic secondary to vascular resis-
Table 1. Color-coded duplex ultrasonogram of extracranial
vertebral arteries.
Diameter
(mm)
Average velocity
(cm/sec)
Average flow
(ml/min)
Resistance
index
Right3.09 14.9 67 0.69
Left3.68 16.3 104 0.65
(a) (b)
Figure 1. (a) TOF MRA showed dislinkage of anterior and
posterior circulation (dotted lines) due to absence of bilat-
eral posterior communicating arteries; (b) the axis of ver-
tebrobasilar artery (black line) rotated clockwise (dou-
ble-headed curved arrow). The upper extreme and middle
of basilar artery (diameter 4.0 mm) were respectively 2.9
mm (hollow arrow head) and 5.1 mm (hollow arrow) apart
from mid-line (white spotted line). Before connecting basi-
lar artery, right vertebral artery (diameter 2.0 mm) formed
a sigmoid route, and so did left vertebral artery (diameter
3.8 mm) a crooked route. The rightward extreme of left
vertebral artery was 4.5 mm (filled arrow) apart from mid-
line (white spotted line), and approximated to right verte-
bral artery (filled arrow head).
tance. Therefore, these central vascular anomalies might
incur vertebrobasilar artery insufficiency at specific con-
dition although neck duplex scanning was unremarkable
(Table 1).
Androgen is known to not only keep artery or arteriole
sensitive to baroreflex [8], but also provoke the pathway
of nitrogen-monoxide genesis in central nervous system,
activating angiotensin II system and raising blood pres-
sure [9]. After he has had to regularly take Flutamide to
suppress prostatic cancer, Flutamide has antagonized
androgen receptors of central nervous system, heart, and
peripheral arterioles; so, regulation of blood pressure and
heart rate were limited.
Sudden getting up or changing position could incur
transient vertebrobasilar artery insufficiency secondary to
postural hypotension, especially during low sympathetic
tone in early morning. We suggest that not only age, but
also Flutamide has limited the immediate compensation
Copyright © 2011 SciRes. PP