Journal of Service Science and Management
Vol.09 No.01(2016), Article ID:63465,10 pages
10.4236/jssm.2016.91008
Study on Nature of Property Right, Shareholding of Institutional Investor and Enterprise Value
Lehua Huang
College of Economics, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China

Copyright © 2016 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 19 January 2016; accepted 14 February 2016; published 17 February 2016
ABSTRACT
Based on 2688 groups of data during 2012-2014 of A-share market of Shenzhen and Shanghai Composite as the study sample, this article explores the influence of institutional investor on enterprise financial value and market value under the property differences. The study result shows that: The shareholding ratio of institutional investor and enterprise financial value are positively correlated; the shareholding ratio of institutional investor and enterprise market value are also positively correlated. Furthermore, this article, based on property right factors, explores the functional mechanism of the shareholding of institutional investors, finding that: Value of shareholding of institutional investors and market value in private enterprises are improved more than in SOE, indicating that governmental factors aggravate the subject of agency in SOE, and weaken the role of shareholding of institutional investors in improving the value of SOE.
Keywords:
Shareholding of Institutional Investors, Nature of Property Right, Financial Value, Market Value

1. Introduction
From the end of 1980s, institutional investors became important investors in security market of the UK and the US, etc. Particularly in the recent 30 years, institutional investor has become a strong force in capital market as the institutional investors holding ratio increases and professional level improves continually. Institutional investors can not only transform the structure of stock rights in mature capital market, but also play an increasingly important role in enterprise governance. Compared with personal investor, institutional investor possesses more excellent ability to collect information and analyze richer experience in investment, and more affluent manpower. These advantages enable institutional investor to intervene enterprise governance though supervising the business and operation of management people in listed companies so as to make the business of listed companies more standard and efficient thereby decreasing the agency cost and enhancing the enterprise value.
In China, with the rising of trust and investment company and fund management company in 1996, the subject of institutional investor became richer and richer. However, the institutional investor achieved rapid development with the dividend policy, along with the emerging of strategy of “extraordinary development of institutional investor” initiated by CSRC in 2000. According to the statistics, by the end of 2006, the shareholding ratio of institutional investor in China reached 30%, becoming a significant group in our security market. Meanwhile, World Bank (2001) reported that only shareholding ratio of institutional investor reached a certain critical value (generally speaking, 20% of the stock market), can the investor has the enthusiasm in participating the enterprise governance. Therefore, we can conclude that our institutional investor has the motivation to supervise the behavior of listed companies, to involve in the governance of companies and improve the enterprise value.
However, state-owned business and private enterprise coexist because of the diversity of our economic system and the specificity in economic transformation period. As the pillar of the national economy, SOE’s historical specificity and the nature of property right decide its special political relation with government: On one hand, the special relation can make SOE get more governmental resources; on the other hand, SOE also faces political pressure such as increasing the financial income, political promotion, and finding solution to unemployment, provision for the old and social instability, leading to short-time target, and the low efficiency of enterprise governance. Meanwhile, with development over last 30 years, the private economy has achieved rapid development, and become an important part of socialist market economy little by little, brick by brick. However, the lack of special political bond with government cannot provide private enterprise with more securities, so that the private enterprise can live under great market pressure, and enjoy high governance efficiency.
Obviously, the difference between SOE and private enterprise can be seen not only in their connection with government, but also in their investment behavior, business efficiency and social value, etc. And, these differences will influence institutional investors’ enterprise governance, and enterprise value at large. Because of this, this article studies the influence of shareholding of institutional investor on enterprise value, particularly different effects brought by enterprise’s nature of property right.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Shareholding of Institutional Investor and Enterprise Value
Institutional investor has two participation modes to participate in company governance: One is to undersell the shares, the investor can retreat from the invested enterprises by taking the method of “Voting with Feet”; The other is to have the long-term investment, the investor can positively participate in enterprise governance and protect its investment rights and interests, which is “the activism of institutional investor”. As a lot of studies show, compared with the great loss caused by declining of stock prices brought by “Voting with Feet”, that institutional investors positively participate in enterprise governance so as to improve the performance of enterprise, and market value is a better choice.
Although there are differences on the conclusions about the influence of shareholding of institutional investor on enterprise market, most scholars believe that institutional investor can improve enterprise governance and enterprise value. According to the study from scholars Shleifer and Vishny (1986), institutional investor, as the big holder of share rights, had the motivation to supervise agency behaviors, participate in enterprise governance, thereby improving enterprise value [1] ; Shleifer and Vishny (1997) pointed out that the institutional investor in the US lessened agency problems and promoted managers to improve enterprise performance [2] . With the flourish of domestic institutional investors, the studies on value of institutional investor and enterprise are gradually conducted. According to the study of Li Weian, etc. (2008), institutional investor helps improve the enterprise governance level, decrease the agency cost of listed companies, remarkable positive correlation can be seen between the shareholding ratio of institutional investor and enterprise performance, market value [3] . Ruan Ziping, Wang Rui (2008) took 102 listed companies under SME board of Shenzhen stock exchange as samples and concluded that EPS, Tobin’s Q and shareholding ratio of institutional investor had the positive correlation. That means the increase of ratio of shareholding of institutional investor can be conductive to the improvement of enterprise performance [4] .
2.2. Nature of Property Right, Shareholding of Institutional Investor and Enterprise Value
According to the theory of property, SOEs suffer low efficiency compared with private enterprises, privatization is the fundamental direction for reform of SOE. Study from Bo Xianhui, Wu Liansheng (2009) showed that: State-owned shares and institutional investors could create positive effects for enterprise governance, but state-owned sharing caped this effect [5] . With 722 state-owned sharing listed companies and 324 private-owned sharing listed companies in Shenzhen and Shanghai stock market during 2008-2012 as the study objects, Xiao Yan, Su Yaqin (2013) concluded that compared with SOE, private enterprises are more conductive to institutional investors’ playing its role in positive governance [6] .
Because of the diversity of our economic systems and the characteristics of the special period in our history, few scholars in foreign countries studied the role of the shareholding of institutional investor in improving enterprise value. And we are also lack of studies like this. This article tries to provide theoretical basis for the promotion of reform on property right, the adjustment of economic structure, the proper distribution of resources, the improvement of resource use efficiency.
3. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
3.1. Shareholding of Institutional Investor and Enterprise Value
The principal pursues capital gain and maximization of enterprise profit; but for the agent, maximization of enterprise is not fundamental, the agent aims to pursue the maximization of interests, that means maximization of personal income including salary, bonus, subsidy and allowance and a comfortable and gorgeous working environment, etc. Meanwhile, information asymmetry still exists between principal and agent. Although principal owns the right to be informed about enterprise financial condition, the right to vote about big events such as investment and work distribution. But they are just a part of information in daily operation and management, most of information in enterprise is under control of agents.
The situation is likely to make agent pursue the maximization of its own interest in cost of the interest of principal, ethical risk of opportunistic behavior is led by this.
We can conclude that, because of the information asymmetry and the speciality of “agent”, agent is likely to have the agency problems of ethical risk and adverse selection; to pursue the maximization of enterprise interests and avoid problems like this, principal will conduct supervision and management for the behavior of agent, thereby producing agency cost. Generally speaking, agency cost includes the supervision evaluation cost from principal and the guaranteed cost of agent. Information asymmetry, responsibility asymmetry, and the contradiction of objective function between principal and agent aggravates; the principal costs become higher, the subsequent enterprise profits decreases; the rights and interests are hard to guarantee.
With the perfection of security market, our institutional investors are becoming more and more. To pursue the maximization of personal interest, institutional investor has the motivation to involve itself into internal governance through stockholders’ meeting, board of directors and board of supervisors. This internal involvement can mainly be seen the following 2 aspects: On one hand, compared with personal investor, institutional investor is more professional, and owns stronger ability to control the risk. Institutional investor can take advantage of these advantages to make listed companies more standard and effective thereby weakening the opportunism of agent and improving the governance of companies; On the other hand institutional investors’ stronger ability to get external information and deal with these information can enable institutional investor send the message to listed companies in a suggested manner so as to improve the information symmetry level and improve enterprise performance. With the shareholding ratio of institutional investor becoming larger, institutional investor’s motivation to improve enterprise performance through looking for information, supervising managers and improving enterprises’ governance level is becoming stronger.
Based on above analysis, the article puts forward the following hypothesis:
H1: Shareholding ratio of institutional investor and enterprise financial value have the positive correlation.
Meanwhile, the developmental experience and system arrangement in international capital market show that with the professionalism and great ability to deal with information, institutional investor can accurately judge the stock value of listed companies, justify the quality of listed companies, and price the stocks according to the real value of enterprise, so that it can effectively distribute resources, decrease stock market bubble, and increase the market stability. Therefore, the shareholding ration of institutional investor in listed companies can reflect institutional investor’s recognition degree of enterprise. A higher shareholding ratio of institutional investor can send the information about effective internal governance of enterprise, sound sate of business to external investors, thereby improving the market value of enterprise.
Based on above analysis, the article puts forward the following hypothesis:
H2: Shareholding ratio of institutional investor and enterprise market value have the positive correlation.
3.2. Shareholding of Institutional Investor and Enterprise Market Value Based on Differences of Nature of Property Right
(1) Shareholding of institutional investor and value of private enterprise
Private enterprise is a unique economic concept in China, its counterpart is SOE. Private enterprise here is equal to private business, its property right belongs to its legal person or natural person, and the control right is not at the hand of our state, either directly, or indirectly. Private enterprise is under control of private property right, shows the value appeal of shareholders, closely connect personal pursuit of stall with the maximization of enterprise interests so as to achieve enterprise economic goals to the largest degree, such as “military culture” and “wolf spirit” of Huawei. Meanwhile, the property right of private enterprise belongs to private person, its administrative participation degree is low, which can seen that enterprise managers are strictly selected through market requirement, so that compared with “government administrative leadership system” in SOE, private enjoys flexible operating system and a sound market reaction mechanism, which enables it to have a quick response to changes of market.
Principal-agent relationship in private enterprise has generality, which can be seen first grade principal-agent relationship, that means shareholder-manger (board of directors and managers). Although principal-agent problems still exist in private enterprises. The private enterprise pose a positive effect on the supervision of agent because of the residual claim right of enterprise owners. Then, owners of enterprise can have conduct effective supervision over agents in a more positive and direct manner, thus weakening agent problems such as ethical risk and adverse selection. So in private enterprise, while the shareholding ratio of institutional investor increases, the nature of property rights in private enterprises and the mutual interaction among institutional investors can promote the improvement of company governance mechanism. Base on interest as the first priority, more value can be created for enterprises. Meanwhile, because of the lack of resource and support from government, signaling effect will be more obvious, thereby improving market value of private enterprise when institutional investors vigorously invest in private enterprise.
Based on above analysis, the article puts forward the following hypothesis:
H3: Shareholding ratio of institutional investor and financial value of private enterprise have the positive correlation.
H4: Shareholding ratio of institutional investor and market value of private enterprise have the positive correlation.
(2) Shareholding of institutional investor and value of SOE
SOE is a lawful, business-based economic organization most or all of whose capital are invested by the state. SOE includes government enterprise, special legal person enterprise, and joint-stock company. The article studies on joint-stock company. State-owned joint-stock company differs from private enterprise as for its nature of state-owned capital holding and government involvement. Therefore, SOE must embody the state's will-power, and closely connect its mission and spiritual idea with national development, therefore achieving social requirement for national development. So while improving enterprise value, SOE also takes social responsibilities. The profit maximization is not our only objective of business activities. Meanwhile, the nature of property right in SOE decides its weak administration and enforcement in its leadership system.
As for principal-agent relation, excessive decentralization of property rights leads to the omission of owners of property rights in SOE. To find solution to this problem, government officials possess the operation and management rights of state-owned assets acting as the agent of people. However, as the administrative personnel, government officials don’t have the ability to operate and manage, so they entrust the operation and management rights of enterprise to professional agent, producing double principal-agent relationship. Process can be showed in “state-owned property rights-government officials-professional agents”.
Compared with private enterprises, the chain of principal-agent becomes longer owning to the government officials’ involvement in SOE, which is also the fundamental reason why the principal-agent problem in SOE is different from that in private enterprise. But, the nature of property right in SOE decides that government officials don’t have remaining assets claims right. Under such condition of inequity of right and interest, government officials are more likely to seek for personal interests in cost of enterprise interests. Actually, government officials face political pressures such as political promotion, increase of fiscal revenue, finding solution to unemployment, social stability and social pension. So, SOE burdens political pressure besides pursuing maximization of interest because the government officials’ involvement. In addition, most of managers in SOE are entrusted and recommended by government officials. Because of the omission of property right owners, it is very difficult for the initial principal to supervise the final receiver.
Government officials are both principal and supervisor, and government officials seek for long cooperation with SOE managers. So SOE lags behind private enterprise as for the supervision, which, to a large degree intensifies the adverse selection and ethnic risk of agent, leading to very obvious agent problems. SOE has long been serving as political tools of politician, and tools for entrepreneurs to pursue interests, with the increase of its state ownership, this “Grabbing Hand” will pose more negative effects.
Although after rapid development over several decades, institutional investor has become a strong dominating force in capital market. The institutional investor can involve in company governance, improve supervision mechanism inside enterprise, decrease agent cost, and improve enterprise performance. However, because of the special nature of proper rights in SOE, compared with private enterprise, value enhancement of institutional investor is weakened to some degree. Meanwhile, capital market experiences the conflicts between the state- owned holding and shareholding of institutional investor, and SOE’ role in improving enterprise market value will also be weakened compared with private enterprise.
Based on above analysis, the article puts forward the following hypothesis:
H5: Shareholding ratio of institutional investor and financial value of SOE have the positive correlation.
H6: Shareholding ratio of institutional investor and market value of SOE have the positive correlation.
H7: Compared with SOE, the financial value of shareholding of institutional investor in private enterprise can be enhanced to a larger degree.
H8: Compared with SOE, the market value of shareholding of institutional investor in private enterprise can be enhanced to a larger degree.
4. Study Design
4.1. Selection of Samples and Data Source
Owning to the fact that the financial accounting, information disclosure and inner management etc. of listed companies is more standard and sound than unlisted companies, the article studies the listed companies. Data of this article mainly comes from wind database, CSMAR database. It selects A-share listed companies in Shenzhen and Shanghai stock market and selects samples according to the following principles: 1) reject ST-type and PT-type listed companies; 2) reject listed companies with missing value and abnormal value; 3) reject financial and insurance companies. In the end, this study obtains 2688 groups of data (1674 group of sample data in private enterprise and 1014 group of SOE sample data).
Meanwhile, to find the solution to endogenous problems, this study refers to studies initiated by foreign scholars Hermalin (1991) and domestic scholar Fan Haifeng (2009), Liu Yingfei and Ni Yuanyuan (2015), as well as conduct empirical test on data of shareholding of institutional investor during 2011-2013 and financial data of listed companies during 2012-2014.
4.2. Variable Design
This article studies variables and its definition (Table 1).
4.3. Variable Design
To verify the above mentioned 8 hypothesis, this article establishes model (1) and model (2). As regression equation (1) and (2) shows, the influence of shareholding ratio of institutional investors (INST) under property
Table 1. Variables design of model.
differences on enterprise financial value (ROE) and market value (Tobin’Q) is tested by regression Equations (1) and (2). Meanwhile, this article, with existing literature as reference, designs the company size of control variables (SIZE), financial leverage (LEV), growth rate of total assets (GROWTH), OVER charge ratio (MER), turnover of total assets, shareholding ratio of the biggest shareholder (FIRET), and total shareholding proportion of top 10 shareholders (TEN). The regression result of regression (1) could verify the hypothesis 1, 3, 5, 7-the differences brought by correlation coefficient of shareholding proportion of institutional investors and market value (Tobin’Q), and the nature of property (PROPERTY); The regression result of regression (2) could verify the hypothesis 2, 4, 6, 8-the differences brought by correlation coefficient of shareholding proportion of institutional investors and market value (Tobin’Q), and the nature of property (PROPERTY). If INST and ROE have the positive correlation, that means institutional investors provide us with external supervision so as to enhance the governance of our company, and improve the financial value of our enterprise. That proves the authenticity of hypotheses 1. If other situations occur, that proves the non-authenticity of this hypotheses. If INST and ROE have the positive correlation, that means the shareholding proportion of institutional investors could transfer signal, thus improving enterprise market value. That proves the authenticity of hypotheses 2, if other situations occur, that proves the non-authenticity of this hypotheses. Meanwhile nature of property (PROPERTY), as a dummy variable, can be considered as SOE when it is “1”, as private enterprise when it is “2”. If the property is “0”, that means INST and ROE have the positive correlation, which indicates that shareholding proportion of institutional investors is positively correlated with enterprise financial value and market value, thus proving the authenticity of hypotheses 3 and hypotheses 4. If other situations occur, that proves the non-authenticity of these hypothesis. If property is “1”, INST and ROE have the positive correlation, which means shareholding proportion of institutional investors and financial value & market value have the positive correlation, thus proving the authenticity of hypotheses 5 and hypotheses 6. If other situations occur, that proves the non-authenticity of these hypothesis. The condition in which INST is positively correlated with ROE and Tobin’Q, and its coefficient α 1 less than that when property is “0”, proves that governments’ interference aggravates the agency problems in SOE, weakens the role of shareholding of institutional investors in improving enterprise value of SOE. This means the authenticity of hypotheses 7 and hypotheses 8. If other situations occur, that proves the non-authen- ticity of these two hypothesis.
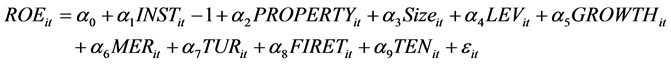 (1)
(1)
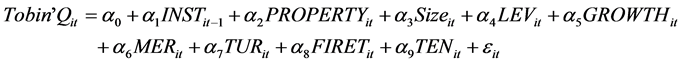 (2)
(2)
5. The Empirical Results and Analysis
5.1. Variable Design
According to Table 2, the average financial value in private enterprise (ROE) and market value (Tobin’Q) in our sample enterprises are both higher than that of SOE. This is because, under the special economic system of China, the government’s involvement in SOE brings these companies so much administrative pressure, causing the principal-agent problem and poor governance of company. Its profit and market recognition are subordinate to private enterprise. After having the contrastive analysis of sample data of SOE and private enterprise, the average shareholding ratio of institutional investor in private enterprise(INST) is lower than that in SOE, which indicates that institutional investors of SOE in sample companies enjoy a comparatively higher shareholding ratio level .SOE has a lower risk compared with private enterprise and gains more popularity from investors because our SOE has a long time-to-market, big scale, protection from government.
5.2. Regression Analysis
(1) Conduct multiple regression analysis for all samples with enterprise value as explained variables.
From Table 3, we can see that, INST past T-test with 1% of confidence level with ROE as explained variable, showing that shareholding of institutional investor can relive agency problem to some degree, therefore improving the governance level of companies, and that the higher the proportion of shareholding of institutional investor is, the better enterprise will become. Proportion of shareholding of institutional investor and enterprise financial value have the positive correlation, thereby verifying hypothesis 1.
With Tobin’Q as explained variables, INST past T test with 1% of confidence level, indicating that shareholding of institutional investor in listed companies can send message about effective internal governance, sound operating condition of enterprise to investors, thereby improving enterprise market value; Meanwhile, the higher the proportion of shareholding of institutional investor is, the more obvious the signals become. Proportion of shareholding of institutional investor and enterprise market value have the positive correlation, thereby verifying hypothesis 2.
(2) With enterprise financial value as the explained variable, this study conducts multiple regression analysis on samples of SOE and samples of private enterprises.
Table 2. The descriptive statistics of major variables.
From the regression analysis in Table 4, we can see that the influence of shareholding proportion of institutional investor(INST) on private enterprise financial value past T test with 1% of confidence level, and its induction coefficient is 0.065, which indicates that shareholding proportion of institutional investor and financial value in private enterprise have positive correlation, thereby verifying H3.
Shareholding proportion of institutional investor (INST), and enterprise financial value(ROE)in SOE past T test with 1% of confidence level, and its induction coefficient is 0.061, which indicates that shareholding proportion of institutional investor and financial value in SOE have positive correlation, thereby verifying H5.
But after contrastive analysis, we can see that, motivation levels of shareholding proportion of institutional investor in enterprises with different natures of property rights are different. An increase of 1% in shareholding proportion of institutional investor will result in an improvement of 0.065% of financial value in private enterprise, which result in an improvement of 0.061% in SOE. Therefore, the essence of “sate-owned” poses a negative impact on institutional investor’ role in enhancing financial value in SOE. Compared with SOE, private enterprise possesses a stronger role in improving financial value of shareholding of institutional investor, thereby verifying H7.
Table 3. All samples of proportion of shareholding of institutional investor and enterprise value.
Table 4. The shareholding proportion of institutional investor and financial value in enterprises with different natures of property rights.
(3) With enterprise market value as the explained variable, this study conducts multiple regression analysis on samples of SOE and samples of private enterprise, the result is shown as Table 5.
From the regression analysis in Table 5, we can see that the influence of shareholding proportion of institutional investor(INST) on private enterprise market value past T test with 1% of confidence level, and its induction coefficient is 0.013, which indicates that shareholding proportion of institutional investor and market value in private enterprise have positive correlation, thereby verifying H4.
Shareholding proportion of institutional investor (INST), and enterprise market value(ROE)in SOE past T-test with 1% of confidence level, and its induction coefficient is 0.004, which indicates that shareholding proportion of institutional investor and market value in SOE have positive correlation, thereby verifying H6.
But after contrastive analysis, we can see that, motivation levels of shareholding proportion of institutional investor in enterprises with different natures of property rights are different. An increase of 1% in proportion of institutional investor will improve 0.013% of market value in private enterprise, yet 0.004% in SOE. Therefore, the essence of “sate-owned” poses negative impact on institutional investor’ role in passing message, as well as a negative impact on institutional investor’s role in enhancing enterprise market value. Therefore, compared with SOE, private enterprise possesses a stronger role in improving market value of shareholding of institutional investor, thereby verifying H8.
6. Conclusions
This article chooses shareholding data of institutional investor during 2011-2013 and financial data of listed companies during 2012-2014 as samples. It analyzes the relation between shareholding of institutional investor and enterprise value and creatively introduces differences of property rights to verify this relation based on the combination of theory and real evidence.
Firstly, this article studies relationship between shareholding of institutional investor and financial value; the result is as follows: proportion of institutional investor and enterprise financial value have positive correlation, indicating that institutional investors can relieve agency problems to some degree and improve the governance level of enterprise, thereby improving enterprise financial performance. Meanwhile, this article further analyzes the relationship between shareholding of institutional investor and enterprise market value. The research results show that shareholding proportion of institutional investor and enterprise market value have positive correlation, which indicates that shareholding of institutional investor in listed companies can send information about effective internal governance and sound operating condition of enterprise to investors, thereby improving enterprise market value.
Table 5. The shareholding proportion of institutional investor and market value in enterprises with different natures of property rights.
Secondly, by dividing total samples into private enterprise samples and SOE samples based on property right factors, this article analyzes the relationship between shareholding of institutional investor and enterprise value with ROE and Tobin’Q as indicators to measure enterprise financial value and enterprise market value. The research results show that the role of shareholding of institutional investor in enhancing financial value and market value in private enterprise is more significant than that in SOE, indicating that government’s involvement exacerbates the agency problems in SOE, and weakens role of shareholding of institutional investor in improving value of SOE.
Since differences still exist in functional mechanisms of governance in different types of institutional investors, the enterprise value will be affected in different levels. This article doesn’t conduct research on the heterogeneity of institutional investors owning to insufficiency of data. In the future, when we conduct on investors and enterprise value, we need to take the heterogeneity of institutional investors into consideration. We also need to study on functional mechanisms of company governance, and analyze different influences of institutional investors under property differences on enterprise financial value and market value.
Meanwhile, external environments also pose great impact on the survival and development of enterprise. For example, investment behaviors of institutional investors are greatly influenced by our national economic situation, and transformation in our industries. This study doesn’t take micro-external factors into consideration. For the study on institutional investors and enterprise value, we need to analyze how different environmental factors (including micro-economy and industry reform) affect the relationship between institutional investors and enterprise value.
Cite this paper
LehuaHuang, (2016) Study on Nature of Property Right, Shareholding of Institutional Investor and Enterprise Value. Journal of Service Science and Management,09,56-65. doi: 10.4236/jssm.2016.91008
References
- 1. Shleifer, A. and Vishny, R.W. (1986) Large Shareholders and Corporate Control. Journal of Political Economy, 94, 461-488.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/261385 - 2. Shleifer, A. and Vishny, R. (1997) A Survey of Corporate Governance. The Journal of Finance, 52, 737-783.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.1997.tb04820.x - 3. Li, W.A. and Li, B. (2008) Empirical Study on Governance of Institutional Investors’ Intervene in Companies-Empirical Research Based on CCGI-(NK). Nankai Business Review, 1, 4-14.
- 4. Ruan, Z.P. and Wang, R. (2008) Research on Ownership Structure of Small-Medium Enterprises and Company Governance Performance-Empirical Research Based on Principal-Agency Theory Explanation. China Management Informationization.
- 5. Bo, X.H. and Wu, L.S. (2009) Governance Effects of State-Owned Holding and Institutional Investor: Surplus Management Angle. Economic Research, 2, 81-91.
- 6. Xiao, Y. and Su, Y.Q. (2014) Shareholding of Institutional Investor, Property Characteristics and Enterprise Value. Friend of Accountant, 25, 37-42.


