Applied Mathematics
Vol.07 No.01(2016), Article ID:63029,7 pages
10.4236/am.2016.71008
Iterative Technology in a Singular Fractional Boundary Value Problem with q-Difference
Xiuli Lin, Zengqin Zhao*, Yongliang Guan
School of Mathematical Sciences, Qufu Normal University, Qufu, China

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 19 December 2015; accepted 23 January 2016; published 26 January 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper, we apply the iterative technology to establish the existence of solutions for a fractional boundary value problem with q-difference. Explicit iterative sequences are given to approxinate the solutions and the error estimations are also given.
Keywords:
Fractional Boundary Value Problem with q-Difference, Iterative Sequence, Green’s Function, Error Estimation

1. Introduction
This paper deals with the existence of solutions for the following fractional boundary value problem with q-difference
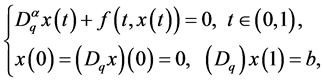 (1.1)
(1.1)
where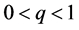 ,
, 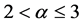 and
and 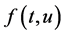 may be singular at
may be singular at 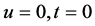 (and/or
(and/or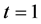 ).
).
Fractional differential equations have been of great interest recently because of their intensive applications in economics, financial mathematics and other applied science (see [1] -[13] and the references therein). The q-difference calculus or quantum calculus is an old subject and is rich in history and in applications. In recent years, there have been papers investigating the existence and uniqueness of the positive solution for the frac- tional boundary value problem with q-difference (see [1] - [4] and the references therein).
For problem (1.1), there have been paid attention to the existences of solutions. Rui [1] investigated the exi- stence of positive solutions by applying a fixed point theorem in cones. By fixed point theorem again, Li and Han [2] considered a similar fractional q-difference equations given as
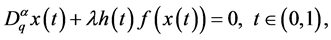
subject to the boundary conditions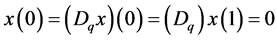 . In this work, we will apply the iterative technology ( [9] [11] [14] ), and as far as we know, there are few papers to establish the existence of solutions by the iterative technology for the boundary value problem with q-difference.
. In this work, we will apply the iterative technology ( [9] [11] [14] ), and as far as we know, there are few papers to establish the existence of solutions by the iterative technology for the boundary value problem with q-difference.
Motivated by the work mentioned above, with the iterative technology and properties of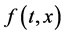 , explicit iterative sequences are given to approximate the solutions and the error estimations are also given.
, explicit iterative sequences are given to approximate the solutions and the error estimations are also given.
2. Preliminaries and Some Lemmas
In this section, we introduce some definitions and lemmas.
Definition 2.1 [1] . Let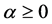 ,
, 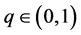 and f be a function defined on
and f be a function defined on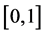 . The fractional q-integral of the Riemann-Liouville type is defined by
. The fractional q-integral of the Riemann-Liouville type is defined by 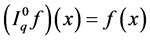 and
and
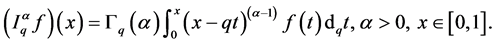
The q-integral of a function f defined in the interval  is given by
is given by
and q-integral of higher order 
Remark 1:






Definition 2.2 [1] . Let



where m is the smallest integer greater than or equal to
and q-derivatives of higher order by
Lemma 2.1 [1] . Suppose 


has the unique solution
where


Lemma 2.2 [1] . Function G defined as (2.2). Then G satisfies the following properties:
(1)


(2) 

Lemma 2.3. Function G defined as (2.2). Then
Proof. Note that (2.2) and


3. Main Result
First, for the existence results of problem (1.1), we need the following assumptions.
(A1) 
(A2) For



Then, we let the Banach space

Clearly P is a normal cone and Q is a subset of P in the Banach space E.
In what follows, we define the operator

where 
Now, we are in the position to give the main results of this work.
Theorem 3.1. Suppose (A1), (A2) hold. Then problem (1.1) has at least one positive solution 

Proof. We shall prove the existence of solution in three steps.
Step 1. The operator T defined in (3.2) is
For any

Then from (A2): 

where
is implied by the equivalent form to (3.1): if
From (3.4) and Lemma 2.3, we can have
and
where
This implies T is
Step 2. There exist iterative sequences

Since 



For 


Let


Then it follows that
In fact, from (3.6)-(3.8) , we have



Then, by (3.9)-(3.11), (A2) and induction, the iterative sequences

Step 3. There exists 
Note that
Thus, for 

This yields that there exists 
Moreover, from (3.12) and
we have
Letting 


Theorem 3.2. Suppose the conditions hold in Theorem 3.1. Then for any initial







where k is a constant with 

Proof. Let 


For 

Then define 




For the error estimation (3.13), it can be obtained by letting 
Example 3.3. Consider the function




By Theorem 3.1, the following problem
has at least one positive solution.
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to the referees for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Support
Project supported by Program for Scientific research innovation team in Colleges and universities of Shandong Province, the Doctoral Program Foundation of Education Ministry of China (20133705110003), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (ZR2014AM007), the Natural Science Foundation of China (11571197).
Cite this paper
XiuliLin,ZengqinZhao,YongliangGuan, (2016) Iterative Technology in a Singular Fractional Boundary Value Problem with q -Difference. Applied Mathematics,07,91-97. doi: 10.4236/am.2016.71008
References
- 1. Ferreira, R.A.C. (2011) Positive Solutions for a Class of Boundary Value Problems with Fractional q-Differences. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 61, 367-373.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2010.11.012 - 2. Li, X., Han, Z. and Li, X. (2015) Boundary Value Problems of Fractional q-Difference Schröinger Equations. Applied Mathematics Letters, 46, 100-105.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2015.02.013 - 3. Ferreira, R. (2011) Positive Solutions for a Class of Boundary Value Problems with Fractional q-Differences. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 61, 367-373.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2010.11.012 - 4. Li, X., Han, Z. and Sun, S. (2013) Existence of Positive Solutions of Nonlinear Fractional q-Difference Equation with Parameter. Advances in Difference Equations, 2013, 260.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2013-260 - 5. Al-Salam, W.A. (1966-1967) Some Fractional q-Integrals and q-Derivatives. Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society, 15, 135-140.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0013091500011469 - 6. Agarwal, R.P. (1969) Certain Fractional q-Integrals and q-Derivatives. Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 66, 365-370.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0305004100045060 - 7. Rajkovic, P.M., Marinkovic, S.D. and Stankovic, M.S. (2007) Fractional Integrals and Derivatives in q-Calculus. Applicable Analysis and Discrete Mathematics, 1, 311-323.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2298/AADM0701311R - 8. Jankowski, T. (2014) Boundary Problems for Fractional Differential Equations. Applied Mathematics Letters, 28, 14-19.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2013.09.004 - 9. Mao, J., Zhao, Z. and Xu, N. (2010) On Existence and Uniqueness of Positive Solutions for Integral Boundary Boundary Value Problems. Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations, 16, 1-8.
http://dx.doi.org/10.14232/ejqtde.2010.1.16 - 10. Guo, D.J. and Lakshmikantham, V. (1988) Nonlinear Problems in Abstract Cones. Academic Press, Boston.
- 11. Zhang, X., Liu, L. and Wu, Y. (2012) The Eigenvalue Problem for a Singular Higher Order Fractional Differential Equation Involving Fractional Derivatives. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 218, 8526-8536.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2012.02.014 - 12. Liu, Y., Zhang, W. and Liu, X. (2012) A Sufficient Condition for the Existence of a Positive Solution for a Nonlinear Fractional Differential Equation with the Riemann-Liouville Derivative. Applied Mathematics Letters, 25, 1986-1992.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2012.03.018 - 13. Vong, S. (2013) Positive Solutions of Singular Fractional Equations with Integral Boundary Conditions. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 57, 1053-1059.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2012.06.024 - 14. Lin, X. and Zhao, Z. (2013) Existence and Uniqueness of Symmetric Positive Solutions of 2n-Order Nonlinear Singular Boundary Value Problems. Applied Mathematics Letters, 26, 692-698.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2013.01.007
NOTES
*Corresponding author.
































