International Journal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Application
Vol.03 No.05(2014), Article ID:52827,10 pages
10.4236/ijmnta.2014.35028
Nonlinear General Integral Control Design via Equal Ratio Gain Technique
Baishun Liu
Academy of Naval Submarine, Qingdao, China
Email: baishunliu@163.com
Copyright © 2014 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 12 November 2014; revised 13 December 2014; accepted 20 December 2014
ABSTRACT
This paper proposes two kinds of nonlinear general integral controllers, that is, one is generic and another is practical, for a class of uncertain nonlinear system. By extending equal ratio gain technique to a canonical interval system matrix and using Lyapunov method, theorems to ensure regionally as well as semi-globally asymptotic stability are established in terms of some bounded information. Moreover, for the practical nonlinear integral controller, a real time method to evaluate the equal ratio coefficient is proposed such that its value can be chosen moderately. Theoretical analysis and simulation results demonstrated that not only nonlinear general integral control can effectively deal with the uncertain nonlinear system but also equal ratio gain technique is a powerful and practical tool to solve the control design problem of dynamics with the nonlinear and uncertain actions.
Keywords:
General Integral Control, Nonlinear Control, Robust Control, Generic Controller, Equal Ratio Gain Technique, Output Regulation

1. Introduction
Integral control [1] plays an important role in practice because it ensures asymptotic tracking and disturbance rejection when exogenous signals are constants or planting parametric uncertainties appears. However, nonlinear general integral control design is not trivial matter because it depends on not only the uncertain nonlinear actions and disturbances but also the nonlinear control actions. Therefore, it is of important significance to develop the design method for nonlinear general integral control.
For general integral control design, there were various design methods, such as general integral control design based on linear system theory, sliding mode technique, feedback linearization technique and singular perturbation technique and so on, were presented by [2] -[5] , respectively. In addition, general concave integral control [6] , general convex integral control [7] , constructive general bounded integral control [8] and the generalization of the integrator and integral control action [9] were all developed by using Lyapunov method and resorting to a known stable control law. Equal ratio gain technique firstly was proposed by [10] , and was used to address the linear general integral control design for a class of uncertain nonlinear system.
All these general integral controllers above constitute only a minute portion of general integral control, and therefore lack generalization. Moreover, in consideration of the complexity of nonlinear system, it is clear that we can not expect that a particular integral controller has the high control performance for all nonlinear system. Thus, the generalization of general integral controller naturally appears since for all nonlinear system, we can not enumerate all the categories of integral controllers with high control performance. It is not hard to know that this is a very valuable and challenging problem, and equal ratio gain technique can be used to deal with this trouble since it is a powerful and practical tool to solve the nonlinear control design problem.
Motivated by the cognition above, this paper proposes a generic nonlinear integral controller and a practical nonlinear integral controller for a class of uncertain nonlinear system. The main contributions are that: 1) By defining two function sets, the generalization of general integral controller is achieved; 2) A canonical interval system matrix can be designed to be Hurwitz as any row controller gains, or controller and its integrator gains increase with the same ratio; 3) Theorems to ensure regionally as well as semi-globally asymptotic stability is established in terms of some bounded information. Moreover, for the practical nonlinear integral controller, a real time method to evaluate the equal ratio coefficient is proposed such that its value can be chosen moderately. Theoretical analysis and simulation results demonstrated that not only nonlinear general integral control can effectively deal with the uncertain nonlinear system but also equal ratio gain technique is a powerful and practical tool to solve the control design problem of dynamics with the nonlinear and uncertain actions.
Throughout this paper, we use the notation
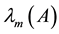 and
and
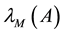 to indicate the smallest and largest eigenva- lues, respectively, of a symmetric positive define bounded matrix
to indicate the smallest and largest eigenva- lues, respectively, of a symmetric positive define bounded matrix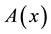 , for any
, for any . The norm of vector x is
. The norm of vector x is
defined as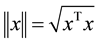 , and that of matrix A is defined as the corresponding induced norm
, and that of matrix A is defined as the corresponding induced norm .
.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the system under consideration, assumption and definition. Sections 3 and 4 present the generic and practical nonlinear integral controllers along with their design method, respectively. Example and simulation are provided in Section 5. Conclusions are presented in Section 6.
2. Problem Formulation
Consider the following controllable nonlinear system,
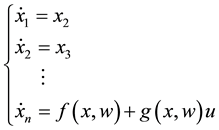 (1)
(1)
where
 is the state;
is the state;
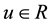 is the control input;
is the control input;
 is a vector of unknown constant parameters and disturbances. The function
is a vector of unknown constant parameters and disturbances. The function
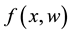 is the uncertain nonlinear action, and the uncertain nonlinear function
is the uncertain nonlinear action, and the uncertain nonlinear function
 is continuous in
is continuous in
 on the control domain
on the control domain . We want to design a control law
. We want to design a control law
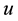 such that
such that
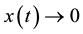 as
as
Assumption 1: There is a unique pair


so that



Assumption 2: Suppose that the functions






for all







Definition 1:





and
hold for all





Definition 2:




and
hold for all


3. Generic Nonlinear Integral Control
The generic nonlinear integral controller is given as,

where







Thus, substituting (7) into (1), obtain the augmented system,

By Assumption 1 and choosing




Therefore, we ensure that there is a unique solution



Now, by Definition 1, 2 and




where


Thus, substituting (9)-(11) into (8), obtain,

where
And


Moreover, it is worthy to note that the function



For analyzing the stability of closed-loop system (12), we must ensure that the matrix





3.1. Hurwitz Stability
Hurwitz stability of the matrix

Step 1: the polynomial of the matrix



By Routh’s stability criterion,






Step 2: based on the gains













Step 3: by










It is well known that Hurwitz stability condition is more and more complex as the order of the matrix



Case 1: for

By Routh’s stability criterion, if





holds, and then the polynomial (14) is Hurwitz for all


Sub-class 1:




By the inequality (16), obtain,
Sub-class 2:






For this sub-class, there are two kinds of cases:
1) if
2) if
Case 2: for

By Routh’s stability criterion, if







holds, and then the polynomial (18) is Hurwitz for all


Sub-class 1:





By the inequality (20), obtain,
Sub-class 2:







For this sub-class, although the situation is complex, a moderate solution can still be obtained, that is,
From the demonstration above, it is obvious that for















Theorem 1: There exist






Discussion 1: From the statements above, it is easy to see that: 1) the system matrix



Proposition 1: A canonical interval system matrix can be designed to be Hurwitz as any row controller gains, or controller and its integrator gains increase with the same ratio.
3.2. Closed-Loop Stability Analysis
The matrix










where


Thus, using


where
Now, using the inequalities (3), (5) and (6), obtain,

where

Substituting (23) into (22), and using

By proposition proposed by [10] , that is, as any row controller gains, or controller and its integrator gains of a canonical system matrix tend to infinity with the same ratio, if it is always Hurwitz, and then the same row solutions of Lyapunov equation all tend to zero, we have,
1)

2)

where
Although there is innumerable







holds for all




Using the fact that Lyapunov function




Theorem 2: Under Assumptions 1 and 2, if the system matrix




and then the equilibrium points




Moreover, if all assumptions hold globally, then it is globally exponentially stable.
Remark 1: From the statements of Subsections 3.1 and 3.2, it is to see that: by extending equal ratio gain technique to a canonical interval system matrix and using Lyapunov method, the asymptotic stability of the uncertain nonlinear system with generic nonlinear integral control can be ensured in terms of some bounded information. This shows that not only nonlinear general integral control can effectively deal with the uncertain nonlinear system but also equal ratio gain technique is a powerful tool to solve the control design problem of dynamics with the nonlinear and uncertain actions.
Discussion 2: From the statements above, it is obvious that: although the generalization of nonlinear general integral control is achieved by defining two function sets, there are two unavoidable drawbacks, that is, one is that the controller (7) is too generic such that it is shortage of pertinence; another is that it is difficulty to obtain the less conservative


4. Practical Nonlinear Integral Control
For making up the shortage indicated by Discussion 2, a practical nonlinear integral controller is given as,

where









the performance of integral control action.

output.



Assumptions 3: By the definition of the controller (26), it is convenient to suppose that the following inequalities,


hold for all




By the same way as Section 3, we have,

where


and the functions




By the design method proposed by Subsection 3.1, the system matrix












where
Now, using the inequalities (4), (5), (6), (27) and (28), obtain,

where

Substituting (31) into (30), obtain,

By proposition proposed by [10] (details see Subsection 3.2), for any moment




holds for all



the inequality (33) holds for all


Using the fact that Lyapunov function


is stable. In fact,



to know that the closed-loop system (29) is uniformly exponentially stable. As a result, we have the following theorem.
Theorem 3: Under Assumptions 1, 2 and 3, if the system matrix





and then the equilibrium point




Moreover, if all assumptions hold globally, and then it is globally uniformly exponentially stable.
Now, the design task is to provide a method to evaluate the instantaneous value



Firstly, by the definitions of




and
Secondly, by the inequality (33), the impermissible minimum of

Finally, by the limitation conditions,


and the iterative method to solve Lyapunov equation,



Discussion 3: From the statements above, it is easy to see that: 1) all the component of the nonlinear integral controller (26) have the clear actions; 2)



uncertain nonlinear action of


or



5. Example and Simulation
Consider the pendulum system [1] described by,
where







and then it can be verified that

By the practical nonlinear integral controller (26), the control law can be given as,
Thus, it is easy to obtain




where
and
The normal parameters are




and 5, respectively, corresponding to double the mass. Thus, we have
Now, with






holds for all




Figure 1 and Figure 2 showed the simulation results under normal (solid line) and perturbed (dashed line) cases. The following observations can be made: 1) The instantaneous value









Figure 1. The values of

Figure 2. System output under normal (solid line) and perturbed case (dashed line).
6. Conclusions
This paper proposes a generic nonlinear integral controller and a practical nonlinear integral controller for a class of uncertain nonlinear system. The main contributions are that: 1) By defining two function sets, the generalization of general integral controller is achieved; 2) A canonical interval system matrix can be designed to be Hurwitz as any row controller gains, or controller and its integrator gains increase with the same ratio; 3) Theorems to ensure regionally as well as semi-globally asymptotic stability are established in terms of some bounded information. Moreover, for the practical nonlinear integral controller, a real time method to evaluate the equal ratio coefficient is proposed such that its value can be chosen moderately.
Theoretical analysis and simulation results demonstrated that not only nonlinear general integral control can effectively deal with the uncertain nonlinear system but also equal ratio gain technique is a powerful and practical tool to solve the control design problem of dynamics with the nonlinear and uncertain actions.
References
- Khalil, H.K. (2007) Nonlinear Systems. 3rd Edition, Electronics Industry Publishing, Beijing, 449-453, 551.
- Liu, B.S. and Tian, B.L. (2012) General Integral Control Design Based on Linear System Theory. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering, 5, 3174-3177.
- Liu, B.S. and Tian, B.L. (2012) General Integral Control Design Based on Sliding Mode Technique. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering, 5, 3178-3181.
- Liu, B.S., Li, J.H. and Luo, X.Q. (2014) General Integral Control Design via Feedback Linearization. Intelligent Control and Automation, 5, 19-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ica.2014.51003
- Liu, B.S., Luo, X.Q. and Li, J.H. (2014) General Integral Control Design via Singular Perturbation Technique. International Journal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Application, 3, 173-181. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijmnta.2014.34019
- Liu, B.S., Luo, X.Q. and Li, J.H. (2013) General Concave Integral Control. Intelligent Control and Automation, 4, 356- 361. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ica.2013.44042
- Liu, B.S., Luo, X.Q. and Li, J.H. (2014) General Convex Integral Control. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 11, 565-570. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11633-014-0813-6
- Liu, B.S. (2014) Constructive General Bounded Integral Control. Intelligent Control and Automation, 5, 146-155. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ica.2014.53017
- Liu, B.S. (2014) On the Generalization of Integrator and Integral Control Action. International Journal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Application, 3, 44-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijmnta.2014.32007
- Liu, B.S. (2014) Equal Ratio Gain Technique and Its Application in Linear General Integral Control. International Journal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Application.
- Gajic, Z. (1995) Lyapunov Matrix Equation in System Stability and Control. Mathematics in Science and Engineering, 195, 30-31.











































