Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.04 No.10(2016), Article ID:71549,14 pages
10.4236/jamp.2016.410194
Solving of Klein-Gordon by Two Methods of Numerical Analysis
Joseph Bonazebi Yindoula1*, Alphonse Massamba2, Gabriel Bissanga1
1Laboratory of Numerical Analysis, Kibernetics and Applications, University Marien NGOUABI, Brazzaville, Congo
2Division of Physics, Brazzaville Institute of Technology, Brazzaville, Congo

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: August 15, 2016; Accepted: October 23, 2016; Published: October 27, 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper, the Decomposion Laplace-Adomian method and He-Laplace method are used to construct the solution of Klein-Gordon equation.
Keywords:
Laplace-Adomian Method, He-Laplace Method, Klein-Gordon Equation

1. Introduction
In field theory, the description of the free partide for the wave function in quantum physics obeys to Klein-Gordon equation [1] . In addition, it also appears in nonlinear optics and plasma physics.
In sum, the Klein-Gordon equation rises in physics in linear and non linear forms. In this paper we examine the Klein-Gordon equation, using the Laplace-Adomian de- composition method and He-Laplace method to get the exact solution. The Klein- Gordon equation is described as:
 (1)
(1)
where 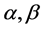 are constants (spin zero) charged field,
are constants (spin zero) charged field,  is a source term and
is a source term and
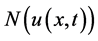 is a nonlinear function of
is a nonlinear function of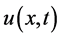 .
.
2. Describing of Both Method
2.1. The Laplace Transform [2]
Let’s note the laplace transform by
 (2)
(2)
From (1), we have:
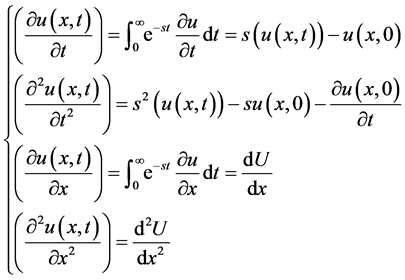 (3)
(3)
2.2. Laplace-Adomian Decomposition Method (LADM) [3] - [6]
Suppose that we need to solve the following equation:
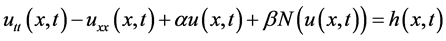 (4)
(4)
subject to initial conditions:
 (5)
(5)
E is a Banach space, where  is a linear or a nonlinear operator,
is a linear or a nonlinear operator,  and u is the unknown function.
and u is the unknown function.
Let’s suppose that operator F can be decomposed under the following form:
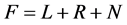 (6)
(6)
where 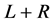 is linear, N nonlinear. Let’s suppose that L is inversible to the sense of Adomian with
is linear, N nonlinear. Let’s suppose that L is inversible to the sense of Adomian with 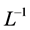 as inverse.
as inverse.
From above, by applying the Laplace transform to both sides of Equation (4), we have:
 (7)
(7)
From the Equation (7), it follows:
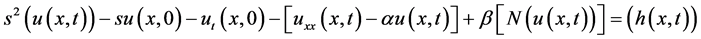 (8)
(8)
and this equation gives
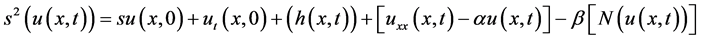 (9)
(9)
So, from the above Equation (9), we can write:
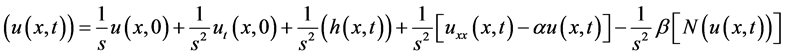 (10)
(10)
We have now

We research solution of (4) in the following series expansion form

and we consider

where 


Using Equation (12) and Equation (13) in Equation (11) we have:

From (15), we have the following Adomian algorithm:

and we obtain the Adomian algorithm:

Remark
In order overcome the short coming, we assume that 



Instead of the iteration procedure Equation (17) we suggest the following modifi- cation

The solution through the modified Laplace decomposition method highly depends upon the choice of 

2.3. He-Laplace Method [7]
We consider a general nonlinear non homogeneous partial differential equation with initial conditions of the form

N represents the general nonlinear differential operateur and 
Taking the Laplace transform on both sides of (20), we obtain:

Û

Applying the initial conditions given in (22), we have:

Operating the inverse Laplace transform on both sides of (23), we have

Now, we apply the homotopy perturbation method

and the non linear term can be decomposed as

for some He’s polynomials 

Sustituding Equation (25) and Equation (26) in Equation (24), we get

Comparing the coefficients of like powers of p, we have the following approxima- tions:

3. Illustrative Examples
To demonstrate the applicability of the above-presented method, we have applied it to two linear and two non linear partial differential equations. These examples have been chosen because they have been widely discussed in literature.
3.1. Example 1
Consider the following linear Klein-Gordon equation

3.1.1. Application of the LADM
Applying the Laplace transform on both side of Equation (30) with the initial con- ditions, we have:

The inverse Laplace transform give us:

Û

We suppose that solution of (30) has the following form:

From (34) and (33). we have:

This result garantee that the following Adomian algorithm is:

Consequently,we obtain:

So that the solution of (30) is given by

which is the exact solution of problem.
3.1.2. Application of the He-Laplace Method
Applying the Laplace transform on both side of Equation (30) with the initial con- ditions, we obtain:

By applying inverse Laplace transform, we have:


Now applying the homotopy perturbation method, we have:

Comparing the coefficient of like powers of p, we have

which gives us

So that, the solution 

3.2. Exemple 2
Consider the following nonlinear Klein-Gordon equation

where
3.2.1. Laplace-Adomian Method
Using the Laplace transform, we have

Û

by applying inverse Laplace transformation to Equation (48), we hace

Supposing that the solution of (46) has the following form:

and

Taking (50) and (51) in to (49), we obtain:

According to the standard Adomian algorithm (52), we need to chose


have the following Adomian algorithm

then garantee that:

So the exact solution of (46) is

3.2.2. He-Laplace Method
Using the Laplace transform, we have:

Now, we apply the inverse Laplace transformation to Equation (46), we have:

Applying the homotopy perturbation method, we have:

where 

Comparing the coefficients of the like powers of p, we have:



So that, the exact solution 

4. Applications
4.1. Problem 1
Consider the following linear Klein-Gordon equation

Application of the LADM
Using the Laplace transform, we have

Û

By appling the inverse Laplace transform, we have:

Û
Û

From above equation, we have the following modified Adomian allgorithm:

Equation (69) give us:

Thus

and the exact solution of Equation (64) is

4.2. Problem 2
Consider the following nonlinear Klein-Gordon equation

Application of the LADM
Using the Laplace transform from (73), we have:

Now, we apply the inverse Laplace transform, we have:

Thus

Denoting that the solution of (73) has the following form:


Taking (77) and (78) into (76), we have:

and we obtain the following Adomian algorithm:

Calculation

Thus

So that, the solution 

which is the exact solution of the problem.
4.3. Problem 3
Consider the following nonlinear Klein-Gordon equation

Application of the LADM
Using the Laplace transform, we have:

The inverse Laplace transformation is applied to Equation (85) we get

As before, we defines the solution 

and 

The nonlinear term 

Substituting (87), (88) and (89) into both sides of Equation (86) we obtain

The recursive relation is defined by

(91) give us

Thus

and the exact solution of Equation (84) is

5. Conclusion
Through these examplles, we showed again the usefulness of Laplace-Adomian Decomposition method and the He-Laplace method, in the search of an approximate solution of Klein-Gordon equation holds for the accepted forms of strong interaction of antiparticles in modern physics.
Cite this paper
Yindoula, J.B., Massamba, A. and Bissanga, G. (2016) Solving of Klein-Gordon by Two Methods of Numerical Analysis. Journal of Applied Ma- thematics and Physics, 4, 1916-1929. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2016.410194
References
- 1. Behe, H.A. (2002) Modern Quantum Theory. 4th Edition, Freeman and Co., San Francisco.
- 2. Fadaei, J. (2011) Application of Laplace-Adomian Decomposition Method on Linear and Nonlinear System of PDEs. Applied Mathematical Sciences, 5, 1307-1315.
- 3. Abbaoui, K. (1995) Les fondements de la méthode décompositionnelle d'Adomian et application à la résolution de problèmes issus de la biologie et de la médécine. Thèse de doctorat de l’Université Paris VI.
- 4. Abbaoui, K. and Cherruault, Y. (1994) Convergence of Adomian Method Applied to Differential Equations. Mathematical and Computer Modellings, 28, 103-109.
- 5. Abbaoui, K. and Cherruault, Y. (1994) Convergence of Adomian’s Method Applied to Non Linear Equations. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 20, 60-73.
- 6. Abbaoui, K. and Cherruault, Y. (1999) The Decomposition Method Applied to the Cauchy Problem. Kybernetes, 28, 68-74.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/03684929910253261 - 7. He, J.H. (2005) Application of Homotopy Perturbation Method to Nonlinear Wave Equation. Chaos, Solitons, Fractals, 26, 295-300. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2005.03.006



