Journal of Human Resource and Sustainability Studies
Vol.03 No.01(2015), Article ID:54798,4 pages
10.4236/jhrss.2015.31007
The Study on Incentive Mode Design of Pay-Through Phantom Equity
Liangtie Dai, Qiongyu Zhou
Management School, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China
Email: zhouqy1990@163.com
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 23 February 2015; accepted 18 March 2015; published 18 March 2015
ABSTRACT
Phantom equity incentive in enterprises can be mainly divided into two modes: pay-through phantom equity and pure phantom equity. The main difference is whether the incentive object needs actual investment and whether they have phantom stock option. This research makes a comparative study on pay-through phantom equity and pure phantom equity, and designs a practical incentive mode of pay-through phantom equity.
Keywords:
Pay-Through Phantom Equity, Phantom Equity, Equity Incentive, Incentive Mode

1. Introduction
Equity incentive, as a long-term compensation incentive, originated in the United States in the 1950s. In 1952, the US Company Pfizer first carried out stock options to the staff for tax avoidance, which opened up a precedent for equity incentive system [1] .
In China, equity incentive was implemented late in listed companies. Before 2006, though there were many practical cases of equity incentive in listed companies, the development was very slow as the original Company Law banned companies to repurchase stocks and prohibited the transfer of stocks their senior executive held [2] . Until 31 December 2005, China Securities Regulatory Commission issued the “Equity Incentive Management of Listed Companies (Trial)”, which allowed equity incentive to develop more flexible in practice. Phantom equity (hereinafter referred to as PE) is a new equity incentive way on the basis of stock appreciation rights and gradually optimized on the basis of developed equity incentive [3] .
PE is an incentive mode that enterprises change their cash reward to phantom stock reward based on the enterprise interests, employees’ work performance, working year in the enterprise and job opposition, etc. PE incentive is a mode between actual equity and cash incentive [4] .
In human resource management theory and practice, PE is an important employee incentive way. PE refers to a long-term incentive mode that enterprises grant a certain number phantom stocks to motivate employees. Compared with traditional incentives, PE incentive makes employees and employers form a closer relationship of shared interests, as an employee can be both the worker and owner of the enterprise [5] . Being the owner means that the employee has the rights to allocate corporate profits, which finally enhance the effectiveness of the incentive.
The main purpose to implement PE is to make an interest link between the enterprise and the staff, especially the senior managers, which will ensure that the decision-making can fit the long-term development of and encourage them to create long-term value and sustainable development for the enterprise [6] . What’s more, PE can also optimize the structure of property rights, and attract and retain key employees.
In the practice of enterprise, PE incentive mainly contains two modes, pure PE and pay-through PE. In this study, we will focus on pay-through PE in the following text.
2. The Concept of Pay-Through PE
In the practice of enterprise, PE incentive mainly contains two modes, pure PE and pay-through PE. By making a comparison of pure PE and pay-through PE, researchers conclude a concept of pay-through PE. Here come the three aspects of concept of pay-through PE [7] :
1) Investment way. The similarity of pure PE mode and pay-through PE mode is that number of stocks for incentive object mainly depends on work-related performance. However, the pure PE don’t need actual payment as the phantom stocks are given free while the pay-through PE incentive need to pay for the stocks.
2) Rights of PE. In pure PE mode, the owners only have stock dividends as they haven’t pay for the stocks. In pay-through PE, the owners have both stock dividends and stock appreciation right.
3) Concentration on enterprise. Pure PE mode makes incentive object concentrate on the long-term development of the enterprise while the pay-through PE mode makes incentive object care more about short-term business conditions and the value of enterprise assets.
3. The Characteristics of Pay-Through PE Incentive
The characteristics of pay-through PE incentive are mainly summarized to 3 points as follows:
Firstly, pay-through PE incentive, as phantom stocks, is the PE awarded to the incentive object beyond actual total equity, which means that it doesn’t change the equity structure of the enterprise, cannot change the proportion of original shareholders and their rights of control. Meanwhile, pay-through PE is for internal management use, without business registration and external disclosure.
Secondly, the shareholders’ equity of pay-through PE is incomplete, since shareholders only have stock dividends and stock appreciation right without the right to vote for actual decisions and make transactions with a third-party on the markets as actual shareholders.
Finally, the shareholders of pay-through PE will have a strong responsibility of the enterprise as the phantom stocks they hold will vary with the development of enterprise and even change to actual stocks. In practice, the disposal ways of phantom stocks are mainly as follows: 1) phantom stock is converted to actual equity if the enterprise lists; 2) phantom stock is paid in cash if the enterprise cannot list in a few years; 3) phantom stock can be converted to the parent enterprise’s equity if the enterprise is the subsidiary.
4. Implementation Plan of Pay-Through PE Incentive System
In the establishment of pay-through PE incentive system, enterprises typically have the following steps, shown as Figure 1.
4.1. Establishing Pay-Through PE Incentive Management Committee
Shareholders meeting of enterprises establish the pay-through PE incentive management committee (hereinafter referred to as The Committee) according to the relevant laws and regulations to take charge of matters related to PE incentive. The Committee is responsible to and directly reports to the shareholders. The main duties of the Committee are: 1) to develop specific terms of incentive plan including incentive object, extraction method of incentive funds, implementation detail, personal allocation, etc.; 2) to modify and improve incentive plan regu-
Figure 1. The steps to establish a pay-through PE incentive system. Source: literature study.
larly; 3) to change or terminate the incentive plan if needed.
The Committee members should mainly be enterprise owners, operators, important business (department) heads, chief financial officer, human resources officer, etc. Information about finance, human resource or others is supposed to be reported to The Committee to make the right decisions.
4.2. Determining the Qualification of Incentive Object
The Committee needs to set the qualification in accordance with its real condition. In general, incentive object should simultaneously meet the need of position rank, performance, working years in the current company, etc. In addition to the above conditions, to obtain the Committee’s assessment and the final approval of results the shareholders meeting is also needed.
4.3. Setting the Phantom Equity
The methods of determining the price of phantom stocks are mainly net asset pricing method, EVA growth method and price-earnings ratio method. This study is based on price-earnings ratio method [8] .
1) To ensure total equity. Total equity is the amounts of phantom stocks that the enterprise issued. For convenient management, it’s generally calculated in 100 million, billion and other integer.
2) To ensure market value. Market value is the premise condition of stock price. Non-listed enterprises don’t really have the concept of market value. In order to determine the phantom stock price, it should be the first to evaluate enterprise’s value roughly. According to the conventional stock market practice:
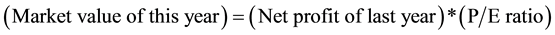
3) To ensure P/E ratio. Firstly, we should find out the average P/E ratio value of industry group where the enterprise is listed (refer to the Shanghai stock exchange, Shenzhen stock exchange data). According to the experienced practice of NASDAQ, if you want to predict other enterprises of this industry group, it should be hit 7 fold on this basis, while for non-listed companies it should resort to 5 - 7 discounts on this basis. In the end you can get P/E ratio of this enterprise.
4) To ensure stock price.
(Phantom stock price of this year) = (Enterprise market value of this year)/(Total Phantom stock price)
4.4. The Way to “Purchase a Stock”
Incentive object will reach a total quota when he purchases the phantom stock. Incentive object of different positions can’t continue to buy when he reach the quota. Total quota is based on the results of the job evaluation. Enterprise should make a job evaluation to the incentive object when setting the quota.
To extend the incentive aging, total quota can’t be purchased one time. Enterprise should set a deadline for several years for incentive object to buy the virtual stock and the incentive object can hold a certain amount of quota every year. The quota is related to post grades, performance, serve year and so on. Details are shown in Table 1.
If incentive object retires during the implementation of the program, enterprise will cancels the purchase of the PE when he retires. Enterprise should set purchase time at beginning of the year and account the figures such as the stock market capitalization of that year. Incentive object need to sign “Virtual Equity Incentive Agreement” when purchasing. Here is:
(Purchase cost every year) = (Stock price of the year) * (The actual phantom stock amount purchased that year)
4.5. The Mechanism of Bonus
(The bonus amount one incentive object can get) = (Enterprise profits this year) * (Phantom stock amount the object holds)/(Total Phantom stock price). If the enterprise suffers a deficit, its Profit will be 0.
Table 1. The setting of PE quota.
4.6. The Mechanism of Quit and Redemption
Quit includes two cases, normal quit and mandatory quit.
For the case of normal quit:
1) Renew when contract expires. If contract normally expires and the employee signs labor contract with the company, he has two choices as follows. Firstly, confirm the expiration date of the contract. if the contract days of this year is more than half a year, the employee can share half of the bonus last year; if the contract days of this years is less than half a year, the employee do not share the bonus and his PE will be redeemed by his enterprise at the redemption cost of last year. Secondly, continue to hold the dividend shares and do not need the redemption.
2) Do not renew when contract expires. Employee doesn’t renew the contract when Contract expires and he does not violate the restrictions. Confirm the expiration date of the contract, if the contract days of this years is more than half a year, the employee can share half of the bonus last year; if the contract days of this years is less than half a year, the employee don’t share the bonus and the PE will be redeemed by enterprise at the redemption cost of last year.
3) Notice the quit with a written letter 30 days in advance. According to Labor Law, in this case he doesn’t violate the restrictions. Confirm the expiration date of the contract, if the contract days of this years is more than half a year, the employee can share half of the bonus last year; if the contract days of this years is less than half a year, the employee doesn’t share the bonus and the PE will be redeemed by enterprise at the redemption cost of last year.
4) Retire. The dealing way is the same as the situation “Do not renew when contract expires”.
5) Incapacity or death. Confirm the date of incapacity or death. If the contract days of this year is more than half a year, the employee can share half of the bonus last year; if the contract days of this year is less than half a year, the employees doesn’t share the bonus and the PE will be redeemed by enterprise at the redemption cost of last year.
For the case of mandatory quit:
1) Other quit. If the employee doesn’t meet quit conditions, the PE will be redeemed by the enterprise and can’t share the bonus after the confirmed date.
2) Dismissal. The PE will be redeemed by the enterprise and can’t share the bonus after the dismissal date.
3) Violate the restrictions. The PE will be redeemed by the enterprise and can’t share the bonus after the confirmed date.
For the redemption calculation, there’s two ways:
1) (Redemption cost) = (Redemption share price of last year) * (Amount of PE purchased last year).
2) (Redemption cost) = ∑ (Single purchase price) * (1 + (The bank’s one-year deposit rate))n.
“n” means the time between payment of purchase and redemption. In the redemption, when meeting normal quit conditions, the employee redeems the PE in the way that the redemption cost is higher; when meeting the mandatory quit conditions, the employee redeems the PE in way (2).
4.7. Restrictions
Enterprises should set some restrictions for the virtual equity of payment type to regulate the behavior of incentive object. If the enterprises violate the restrictions, the << Virtual Equity Incentive Agreement >> between the enterprises and the employees will be invalid, meeting the mandatory quit conditions and No longer be awarded bonus equity purchase quota.
Restrictions usually include: incentive objects will be subjected to criminal penalties; incentive object seriously damage the interests of the company (as to the relevant laws and regulations and the company’s rules and regulations); violations of the company relevant confidential or non-compete clauses; other circumstances that company shareholders’ meeting or board think shall make the decision.
5. Conclusions
This study shows how an enterprise establishes a set of feasible pay-through PE incentive mode. It has set operational method from equity set to redemption. Enterprises can refer to the method of this study and combine with their own circumstance to make personalized PE incentive mode.
What should be stressed is that a pay-through PE incentive mode is not suitable for all enterprises. Before an enterprise chooses a pay-through PE incentive plan, it should consider the affordability of the proposed incentive objects. If the majority of the proposed incentive objects have a strong willingness to invest and have certain ability to pay, it’s more suitable to carry out this plan, otherwise it’s good to consider other incentive modes.
References
- Aggarwal, R.K. and Samwick, A.A. (2006) Emprie Builders and Shirkers: Investment, Firm Performance and Managerial Incentives. Journal of Corporate Finance, 12, 489-515. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2006.01.001
- Lv, C.J., Zheng, H.L., et al. (2009) Equity Incentive System Design in Listed Company: Incentive or Welfare? Management World, 9, 133-147.
- Zhou, Q.H. (2014) The Study on the Phantom Equity Mode of Enterprise. Money China, 5, 120.
- Miao, X.Y. (2005) The Virtual Equity Incentive of Listed Companies. Human Resources, 11, 60-62.
- Yang, F.R., Dou, H.S. and Zheng, Q.Q. (2011) Phantom Equity Incentive Design on the Basis of Human Resource Value. Commercial Age, 18, 87-88.
- Su, D.W. and Lin, D.P. (2010) Equity Incentive, Earnings Management, Enterprise Governance. Economic Research, 11, 88-100.
- Wang, H. (2012) Virtual Equity Incentive Plan. Enterprise Management, 7, 46-47.
- Xie, Z.Y. (2014) The Research on EVA Phantom Equity Incentive Mode Based on Enterprise Growth Cycle. Decision-Making Participation, 1, 55-59.



