Open Journal of Social Sciences
Vol.04 No.03(2016), Article ID:64794,7 pages
10.4236/jss.2016.43019
Research on the Evolution of Supply Chain Finance Mode in the “Internet+” Era
Mengyang Wang
Institute of Industrial Economics, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China

Copyright © 2016 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 23 February 2016; accepted 19 March 2016; published 22 March 2016
ABSTRACT
With the great development of China e-commerce industry, more and more business transaction is moved from offline to online. Generated by a plenty series of transactions online, multi-dimen- sional user data are used to promote the evolution of the Internet finance mode. In the era of “internet+”, all industries are going through changes. The Internet process of supply chain finance also accelerates. Based on the different characteristics on participants, source of different evolution paths, this paper gives an overall classification of supply chain finance under the background of internet, which includes supply chain finance “1 + N” mode dominated by commercial banks, supply chain finance web 2.0, core enterprise and logistic company’s extensive in supply chain finance. Finally, we analyze the characteristic of the different models and summarize the operational mechanism and development trend in the future.
Keywords:
Supply Chain Finance, Internet+, Industrial Upgrade, Online Supply Chain Finance

1. Introduction
In recent five years, China retail sales online keep an average annual growth rate of over 50 percent to more than 4 trillion Yuan at 2015, ranking first in the world. The transaction of China E-commerce reached 20.8 trillion in 2015. The traditional industries and existing business model is shocked by E-commerce platform and some vertical e-commerce website. Chinese Premier Li Keqiang in March 2015 in the government work report proposed the development of “Internet+” Initiative Plan. Promoting mobile Internet, cloud computing, big data, the Internet of Things and so on with modern manufacturing are combined to facilitate electronic commerce, the Internet industry and Internet finance healthily development.
However, most of the Internet enterprises are small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). In traditional financial services system due to lack of effective credit risk control tools, SMEs can hardly get enough financial support from the traditional financial system. In recent years, many banks actively explore the financial services based on relationship in supply chain, and create the supply chain finance mode.
With the development of e-commerce, networking, cloud computing and other information technology, supply chain finance gradually move from offline to online, internet enterprise’ demand, supply chain data and large industrial upgrading combines to promote supply chain finance innovation, supply chain finance is no longer just the bank’s “one-man show”, electronic business platform, information system service providers, core industry companies, logistics companies use their data and industrial advantages of supply chain actively layout, open a new era of supply chain financial development. This paper firstly defines the concept of supply chain finance, and introduces different types of participants in the evolution of supply chain finance mode, risk control and other aspects of the development of the existing supply chain financial model. Combing the various subjects and the development of internet evolution path supply chain finance, their views and suggestions on the future development of supply chain finance on this basis are put forward.
2. Definition of the Supply Chain Finance
With the slow recovery of the world economy and fully upgraded industrial structure, corporate restructuring and industrial chain extension evolution become increasingly frequent, supply chain business model is replacing vertical integration to become industrial organization the mainstream model [1] (see Figure 1). Increasing global sourcing and selling brings substantial challenges on the material flow, information flow, and financial flow along lengthened supply chains. Financial institutions began to base on the information flow, material flow and capital flow in supply chain members, provide various financial products to fund the coordinate and operation of the supply chain.
For the concept of supply chain finance, academia and the business community did not have a uniform definition. From the perspective of supply chain core enterprise, Michael Lamoureux [2] provides a definition of supply chain finance: A core business-led enterprise ecosystem, the availability of funds and the cost of a system optimization process. And Aberdeen [3] from the electronic trading platform provider perspective explained. Timme [4] , Hofmann [5] analyzes the basic process of supply chain finance and components, from the macro and micro level analysis participants of supply chain finance, collaboration features, and tracking cash flow, capital flow as provide insight into the supply chain finance bedding conceptual.
And another major point of view, is discussed from the angle of the bank for supply chain finance, Because the traditional supply chain finance practice dominated by banks, the scholars more elaborates from this point. The supply chain finance can be summarized as follows: Supply chain finance (SCF) is based on its understanding of the supply chain transaction structure and details of the transaction, through the control of a real material flow, business flow, information flow and capital flow with the core of the supply chain, provides liquidity to suppliers by leveraging their buyer’s higher credit rating to achieve value-added process.
SCF boils down to a balanced approach for enhancing working capital for both buyers and sellers in a transaction―using an intermediary tool to link buyers, sellers, and third-party financing entities―thereby reducing supply chain risks/costs and strengthening business relationships. On another way, the SCF solution combines a set of technology solutions and services that link all the parties in the supply chain―the buyers, sellers and providers of financing―in order to enable end-to-end visibility, lower financing costs, increase availability, and expedite the delivery of cash. SCF solutions can help combat the inherent problems created by more traditional
Figure 1. Supply chain model.
supply chain working capital enhancement approaches.
3. The Evolution of the Supply Chain Finance Mode
Financial flow, material flow, and information flow increasingly converge, making the supply chainfinancial more and more important in supply chain management. Commercial banks penetrate through all aspects of the supply chain, to participate in the overall supply chain optimization. Ranking the top 50 global banks have carried out the supply chain finance business, according to a survey done by Aberdeen Group, more than half of international commercial banks recognized the commercial potential of supply chain finance, and the findings Demica even more than 90%. Currently, HSBC Bank is in a leading position worldwide in the payable financing achievement particularly prominent. From a regional market, Citibankholds the dominant position in North America, Royal Bank of Scotland with the acquisition of the Dutch bank in Western Europe in the lead, Standard Chartered Bank (S & C) is an advantage in Asia and Africa, especially pre-shipment financing. In 2006, Shenzhen Development Bank (SDB) proposed in “supply chain finance” concept, by introducing the core enterprises, logistic company and cash flow guidance tools, such as new risk control variables, to provide different nodes of the supply chain credit support and other financial services. Trade finance customers and business volume in 2006 SDB achieved a 50% growth in non-performing rate of only 0.4% [6] .
3.1. Supply Chain Finance the Offline “1 + N” Mode
In the primitiveversion 1.0, supply chain finance mode is generally referred to as “1 + N” (see Figure 2), based on the “1” core enterprise in supply chain higher credit rating, through leveraging their buyer’s higher credit rating to complete a small congregation of micro-enterprises “N” credit financing support. This allows companies to unlock the value in the supply chain in many ways, including: extending buyer’s Accounts Payable terms; accelerating seller’s access to lower cost capital; reducing risks imbedded in the supply chain. It can also enhance bank’s risk control, further deepen “1” reliance on banks, and expand the range of financial services.
Main mode in SCF 1.0 version consists of two categories: accounts receivable financing and prepayment financing. Accounts receivable financing mode are generally applicable to upstream supply chain financing, to solve small and medium sized enterprises at the upstream supplier of financial funding requirements. this mode refers to borrowers with its future anticipated proceeds of receivables as collate ralto obtain bank credit, and access to business financing. Specifically, accounts receivable financing for SMEs applies mostly patterns has the following characteristics:
1) As a supplier, it has long maintained the coredownstream enterprise with credit settlement;
2) Enterprise has a lot receivables, and in need of cash to expand the scale of production, organization of production activities;
3) Enterprises is in the growth phase, lack of fixed assets used for mortgage, but keep stable trade with the downstream core business with long term accounts receivable.
In practice, the power industry, railway industry, supermarkets and other chains are suitable for development of such industry financing pattern. In these supply chains, the number of suppliers in the upstream of the core
Figure 2. Supply chain finance offline “1 + N” mode.
business, more categories, and with the core business remained generally stable trade relations. Currently, accounts receivable financing category include wider application of pattern “Pledge of accounts receivable financing”, “factoring financing” and so on.
Because the buyer is using SCF to mitigate the costs for a seller, it will be well positioned to negotiate better terms and conditions with sellers. As a result of these negotiated terms/conditions, the buyer will realize a significant working capital benefit from an extension in payment terms and will free up cash for use in other critical areas. The seller is obtaining access to capital at a lower cost through leveraging the buyer’s credit rating. Additionally, the seller will see a reduction in Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and an improvement in cash forecasting, two key drivers to effectively navigate through the current credit crunch.
Account prepayments financing mode are generally applicable to the downstream supply chain financing, to solve the problem of capital shortage for downstream distributors. Accounts prepayments financing for SMEs applies mostly patterns has the following characteristics:
1) Supply chain, as the seller of the core business has stronger bargain power, by way of order requested downstream distributors to organize production, leading to a shortage of liquidity dealers.
2) In the supply chain, core corporate commitments to downstream distributors and bulk orders receive a discount, or distributors want to lock in prices, book in advance for goods.
3) Products generally have market price transparency, strong liquidity and other characteristics.
In terms of industry classification, suitable for the development of prepayment financing model class industries include iron and steel, petrochemicals, automobiles, machinery and so on. In practice, prepayments financing include “inventory financing” and “confirmation position” two main modes.
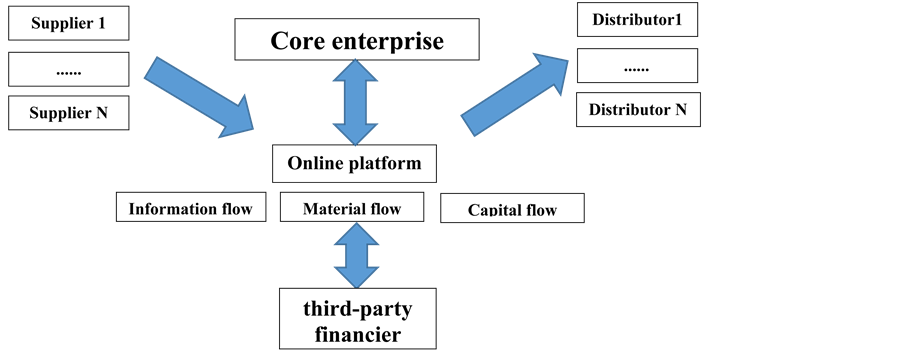
3.2. Supply Chain Finance Web 2.0, SCF Online
Supply Chain Finance web 2.0, move the traditional supply chain finance online (see Figure 3). Through the using a technology platform to automate transactions and provide visibility into the invoice approval status to all parties involved. This allows all participant to unlock the value in the supply chain. Not only the banks, but also third-party includes e-commercial platform and software provider can obtain information of real business at any time.
The SCF web 2.0 solution combines a set of technology solutions and services that link all the parties in the supply chain―the buyers, sellers and providers of financing―in order to enable end-to-end visibility, lower financing costs, increase availability, and expedite the delivery of cash.
3.2.1. Non-Pure Electronic Trading Platform Provider in Supply Chain Financial Model
Non-pure trading platform electricity supplier in the supply chain in addition to providing trading platforms, but also the entire supply chain system of self storage and logistics systems, demand for electricity suppliers to make orders upstream suppliers, supplier deliveries to the electricity supplier, electricity supplier to supply Suppliers out acceptances, and produce accounts receivable. A typical representative of this mode has the Amazon, Jingdong Mall.
Figure 3. Supply chain finance web 2.0 mode.
The financial supply chain mode of no pure trading platform and the traditional supply chain finance “1 + N” mode is essentially the same. Electricity supplier as the core enterprise supply chain system, use its own good reputation and a large number transaction information to provide security for the middle and lower reaches of the SME credit. Electricity supplier cooperation with commercial banks, earning economic benefits by means of financing to suppliers in the supply chain by accounts receivable financing, order financing and Supplier entrusted loan financing. Meanwhile, financing to suppliers enhance the viscosity and node enterprises to their own dependence, and with a stable and mutually beneficial cooperation of the upstream and downstream enterprises, to ensure that their own core supply chain system steady development.
The supply chain finance model of no pure trading platform electricity supplier is the model extended the traditional supply chain financial theory to the electricity supplier supply chain system. The model changes the traditional credit model of a single enterprise’s real estate pledge through the evaluation of the whole supply chain performance and operational risk to provide loans to enterprises in the chain, and not only expands the business scope and service objects, but also helps to reduce transaction risk and transaction costs. The upstream and downstream enterprises in the supply chain in the different industry environment interact with each other. The bank through the core enterprise strengthen the confidence asymmetry of supply chain and each node enterprise business evaluation and supervision, reduce the financing risk and cost causing by nonprofessional factors.
3.2.2. Pure Electronic Trading Platform Provider in Supply Chain Financial Model
In the supply chain system of pure trading business platform, electricity supplier is only to provide trading platform for upstream and downstream suppliers, its own are not engaged in warehousing and logistics system. There aren’t cash transactions between upstream suppliers. The typical representatives of this model are the B2B electricity suppliers Alibaba, C2C Taobao, B2C Tmall.
In the supply chain system of pure trading business platform, electronic commerce platform for logistics and capital flow control is not the degree of non-pure trading platform, but the electricity supplier have the power of control the information flow, all supply chain system transactions are carried out in the electronic business platform, providers can based on a great deal of data analysis of financing risk control.
Pure Trading Platform Supply chain financing is more innovative supply chain financing mode will replace the electricity banks to provide financing services in the traditional supply chain, financial status, and data and the Internet as the core, a rich database of suppliers and credit history using a large customer resources, customer data and transactions cloud computing and other information technology processing means mass for its SME platform to provide credit loans. Electricity supplier through the integration process of the formation of e-com- merce data and credit, to solve the asymmetric information and processes complex problems of the conventional financial sector loans to individuals and small businesses exist to achieve good risk control and return on capital.
Pure Trading Platform supply chain financing innovation model characteristics embodied in the technology and risk control. Technology means: the electricity supplier financing risk control network data model should be introduced credit checks and online video mode, confirm the authenticity of customer information by cross- checking technology combined with third-party verification, customer behavior data in e-commerce network platform maps for businesses and individuals credit rating, these are usually unable to finance through traditional channels to obtain loans of small and medium suppliers bulk loans. Through technological innovation, the use of data analysis rather than guarantee or mortgage financing party credit rating. Risk Control means: electricity supplier by a multi-level micro-loans risk early warning and management system, pre-loan, loans and loan after the three links in close contact, the use of means of data collection and analysis model, based on small and micro suppliers electronic business platform on credit accumulation and behavioral data, repayment ability and willingness to repay the enterprise for a more accurate assessment, at the same time, combined with post-loan monitoring and network shop/account shut down mechanism, improve customer default cost effectively control credit risk.
3.3. Supply Chain Finance Ecosystem “N + N” Mode
Now the commercial bank has gradually shifted ideas, what banks wants to do is to build a cloud services platform, to allow SMEs’ orders, waybills, acquiring, financing, warehousing and other business behavior run in the platform. While introducing logistics, third-party information firm and other enterprises, build a service platform for enterprises to provide supporting services (see Figure 4).
4. Core-Enterprise in the Supply Chain Finance
20th Century 70 - 80 years, large multinational companies are more focused on the core elements of industrial control, and low value-added sectors or to release more competitive and comparative advantages of regional transfer of optimal allocation of resources, these multinational companies naturally become supply core business chain. Core enterprise channel partners including upstream suppliers and downstream distributors, many of which are SMEs, they are separate from the core business, but its proper functioning and loyal cooperation determines the stability of the entire supply chain, which also determines the overall cost of the final product competitiveness. Thus, the core business with banks have an incentive to help channel partners to solve the financing difficulties. Accordingly, the bank will also expand the core business of financial services from the entire supply chain, providing accounts receivable financing for its channel partners, prepayments and payment, inventory financing, financing of raw materials and manufacturing services, these services are called supply chain Finance.
The traditional focus on credit debtor bank credit, and in providing financing for the core enterprise channel partners, banks pay more attention to the status of the debtor in the supply chain, the role and effectiveness of the bank to borrow money usually only give part of the core business of direct deals and usually requires the core business or a large third-party logistics companies to help monitor the debtor and related logistics chain.
For companies that have a strong credit rating relative to their suppliers and are willing to explore alternative working capital strategies, SCF is a powerful tool that brings benefits to multiple parties across the supply chain.
5. Logistics Giant’s Financialization
United Parcel Service (UPS) through its financial platform UPS Capital to provide letters of credit, bill payment, value-added financial services and other financial services loaning. Cash on delivery is the most common international trade settlement (Cash on Delivery, referred COD), customers can check into UPS Capital COD bank account, UPS upon receipt of exporters of goods to the exporter by the UPS Capital provide partial payment in advance, UPS then settled by UPS Capital and importers to collect full payment. Thus, UPS is paid the difference between the sum without interest, while UPS Capital will use these funds to customers rolling loans. UPS spare no effort to promote the concept of supply chain finance, according to its estimated that the global stock of receivables of about $115 billion to support lending market potential assets resulting over $340 billion.
6. Conclusion
In the era of “internet+”, the development of e-commerce and networking technology promotes the evolution of supply chain finance. Supply partner can reap the end-to-end benefits available through effective SCF solutions.
Figure 4. The SCF ecosystem “N + N” mode.
This paper, firstly, on the basis of introducing the basic definition of supply chain finance, gives a sketch map of supply chain model and supply chain finance, and reveals the evolution paths of supply chain finance. Meanwhile, based on the different characteristics on participants, source of funds and target customers of the three evolution paths, this paper gives an overall classification of supply chain finance under the background of internet, which includes supply chain finance “1 + N” mode dominated commercial banks, supply chain finance web 2.0, and analyzes the characteristics of the different models, summarizes the operational mechanism and development trend in the future.
Cite this paper
Mengyang Wang, (2016) Research on the Evolution of Supply Chain Finance Mode in the “Internet+” Era. Open Journal of Social Sciences,04,130-136. doi: 10.4236/jss.2016.43019
References
- 1. Porter, M.E. (1980) Competitive Strategy. The Free Press, New York, 396.
- 2. Lamoureux, M. (2007) A Supply Chain Finance Prime. Supply Chain Finance, 4.
- 3. Aberdeen Group (2008) The 2008 State of the Market in Supply Chain Finance.
- 4. Timme, S. and Williams-Timme, C. (2000) The Financial-SCM Connection. Supply Chain Management Review, 2, 33- 40.
- 5. Hofmann, E. (2005) Supply Chain Finance: Some Conceptual Insights. Logistic Management, 203-214. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-322-82165-2_16
- 6. Shenzhen Development Bank-China Europe International Business School “Supply Chain Finance” Discussion Group (2009) Supply Chain Finance; New Finance under the New Economy. Shanghai Far East Press, Shanghai.