Open Journal of Social Sciences
Vol.04 No.07(2016), Article ID:69432,7 pages
10.4236/jss.2016.47002
Study on the Quality Control of Reputation-Based on Incentive Service-Oriented Manufacturing Network
Liangqing Feng*, Kunkun Zeng, Fangling Shu
School of Economics and Management, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang, China



Received 29 March 2016; accepted 18 July 2016; published 25 July 2016

ABSTRACT
Manufacturing enterprises, manufacturing services and customer constitute the service-oriented manufacturing dynamic network (SMN). The quality of SMN mainly depends on the service module provider. Under the condition of information asymmetry in the market, service module provider pursuits for self-interest maximization, may take quality speculation. Based on the reputation incentive theory, this paper establishes an optimal SMN node quality behavior dynamic model of the contract which combines with dominant incentive mechanism and reputation incentive mechanism, discusses the factors which influence the service module provider’s effort level, the conditions of realizing effective reputation incentive and the ways to improve reputation incentive effect.
Keywords:
Service-Oriented Manufacturing Network, Service Module, The Quality of Speculation, Reputation Incentive

1. Introduction
Under the condition of information asymmetry in the market, the reputation, as a signal which reflects the information of enterprises, is delivered among different traders, and traders make choices depend on corporate reputation before making a deal. Establishing a good corporate reputation can not only make the enterprise get more development opportunities also can bring long-term economic value. W. Liu [1] studied the r & d outsourcing dynamic incentive mechanism based on the theory of the reputation, and established a dynamic incentive mechanism model of corporate r & d outsourcing; Y.Q. Tan [2] studied the effect of reputation in the outsourcing service provider reputation incentive mechanism, raised that reputation incentive can improve service provider’s effort in the early stage and constraint moral hazard from service provider; H.M. Guo [3] studied the dynamic incentive contract of supply chain which considered the cost of reputation, found out the relationship between reputation compensation and the type of manufacturers, cost, achieved the effect of weakening “ratchet effect”; B.H. Peng [4] built the trust game model between the module integrator and suppliers, pointed out that the reputation had became an effective incentive of cooperative members.
The service-oriented manufacturing network which is formed in the process of manufacturing and services integration development, is a kind of ability and demand cooperation network. The value module node of manufacturing enterprises base on service demand and service ability, service enterprises of relevant departments or personnel and customer is the composition of the SMN, and mainly contains service integration module node, service production and productive service module module node. Each node through the exchange of each others products or services to gain economic interests to promote the development of itself. The quality problem of the trade in tangible goods, and intangible items, such as service products, service attitude, goods delivery time. The above issues are collectively referred to as network node quality problems. H. P. Liang [5] presented the arrangement way of quality control in manufacturing network; J. X. You [6] studied the quality control of supply chain strategy problem under the condition of moral hazard; L. Q. Feng [7] marched the modular classification for SMN, established the model, respectively to measure the adaptability quality coordination and cooperation, the quality contract modular coordination level of quality.
This paper analyzes the role of the relationship between individual nodes from the perspective of the reputation contract, try to research the influence of reputation on the service module provider engaged in its own node quality behavior.
2. Basic Assumptions and Symbols Introductions
This paper considers only a simple SMN structure. For the convenience of modeling and analysis, the service production and the productive service module node are collectively referred to as service module provider, and the service integration module node is called service module integrator.
Hypothesis 1: Service module provider as the agent, service module integrator as the principal. Service module integrator cannot directly observe the management ability and the effort level what service module provider engaged in its node quality behaviors, can only observe some other variables.
Hypothesis 2: Principal-agent contract only has two phases, service module provider each phase of the output function:
 (1)
(1)
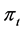 is the output of service module provider in the first phase ;
is the output of service module provider in the first phase ; 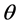 is service module providers management ability and its size is not related to the time;
is service module providers management ability and its size is not related to the time;  is the effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behaviors in the
is the effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behaviors in the  phase,
phase, 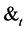 represents exogenous random factors, such as the uncertainty of technology or market.
represents exogenous random factors, such as the uncertainty of technology or market.
Hypothesis 3: Effort level  is the service module providers private information, output is the known information,
is the service module providers private information, output is the known information, 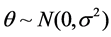 ,
, ; Assuming that the random variables
; Assuming that the random variables 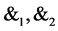 are independent of each other, so
are independent of each other, so ,
, 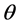 and
and  is not relevant.
is not relevant.
Hypothesis 4: Service module integrator is risk neutral, Service module provider is risk averse,  is absolute risk aversion,
is absolute risk aversion, 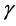 is reputation discount rate,
is reputation discount rate, 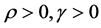 (risk averse
(risk averse 


Hypothesis 5: Service module provider’s effort cost function is




Hypothesis 6: The principal-agent linear contract is




Hypothesis 7: The market is rational expectations. In the first phase equilibrium, 










Make




According to the above hypotheses, it is concluded that the following formulas:






In the Formula (2), 






3. The Establishment of the Model and Analysis
3.1. The Static Contract Model of SMN’s Node Quality Behavior without Considering Reputation Incentive Mechanism
The static optimal contract model is set up as follows:
Get the models first-order conditions:


The results suggest that the optimal effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behaviors depends on the effort cost coefficient 

3.2. The Dynamic Contract Model of SMN’s Node Quality Behavior Considering Reputation Incentive Mechanism
Considering the influence of reputation in phase 1, the theoretical dynamic contract model is set up as follows:
The Equation (13b) refers that at the beginning of phase 1, service module providers certainty equivalent income by contract can’t less than the external opportunity cost expectations





Make






By Equation (16), it can be seen that the maximization of the service module integrator in the target equals the principal-agent both sides the certainty equivalent income sum of the two phases. The determination of the optimal contract also needs to satisfy the service module provider’s incentive compatibility constraint in two stages:
(IC1)
(IC2)
Because we assume the linear contract only two phases, the output of the phase 2 will not affect service module provider’s reward of the late, so under the condition of having been given contracts of the phase 2, service module provider will choose 

At the beginning of the second phase, service module integrator bases on the information of phase 1 to set the current contract which must satisfy the participation constraint of service module provider to maximize his certainty equivalent income in phase 2. Similar to the type (16), Service module integrator also refers to the maximization about the principal-agent both the certainty equivalent income sum of the two phases:
(TC)
Summarize the above discussion, the optimal model of the dynamic contract design is established as follows:
By Equations (1), (2), (5), get:


Further:
Put Equations (19 c), (20) (21) into type (19d):
Equation (22) shows that the optimal effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behaviors only depends on the effort cost coefficient 

Put Equations (14), (15) into type (19b), get:


Among them,
By (25) and (17),

Put Equations (22), (25), (20) into (19a), we could get the optimal first-order conditions

4. The Analysis and Conclusion of Two Models
By contrasting Equations (22) and (10), 
sidering reputation mechanism, the effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behavior in Phase 2 is better than the level without considering reputation mechanism. The quality of SMN is mainly depends on the effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behavior, so we get proposition 1.
Proposition 1: After the introduction of reputation mechanism, the quality level of SMN in the phase 2 is improved.
By (28)



Proposition 2: when
By


Proposition 3: Before the event, the more uncertain that service module integrator to service module providers management ability (
Comparing Formula (28) and (10), if

Proposition 4: the effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behavior in Phase 1 is better than the level without considering reputation mechanism, in other words, the quality level of SMN in the phase 1 is improved.
Analyzing formulas (25), we can see that reputation influences 



Proposition 5: when
Synthesize the above discussions, If reputation mechanism can well control the quality of SMN, it is thus clear that 
5. Conclusion
In order to control the quality of SMN, improve the effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behavior, this paper establishes an optimal dynamic linear contract model which combined explicit incentive mechanism and reputation incentive mechanism. The model under certain conditions can achieve the effective reputation incentive and enhance the reputation incentive effect. When meet the conditions, considering the reputation mechanism of the SMN node quality behavior model of the dynamic contract design compares to without considering quality reputation incentive mechanism of the SMN node behavior static model of the contract, effectively improves the effort level that service module provider engaged in his own node quality behavior, improves contract incentive strength, the quality of SMN and realizes the Pareto improvement.
Acknowledgements
This paper is one of periodic achievements of the following three projects: funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71362019), the Jiangxi Provincial Education Department of Science and Technology Project (GJJ13513), and China Scholarship Foundation (Grant No. 201408360080).
Cite this paper
Liangqing Feng,Kunkun Zeng,Fangling Shu, (2016) Study on the Quality Control of Reputation-Based on Incentive Service-Oriented Manufacturing Network. Open Journal of Social Sciences,04,10-16. doi: 10.4236/jss.2016.47002
References
- 1. Liu, W., Guo, J. and Yang, S.B. (2009) R&D Outsourcing Dynamic Incentive Mechanism Based on Reputation Theory Study. Journal of Technology Economy, 11, 17-21. http://www.jishujingji.cn/ch/index.asp
- 2. Tan, Y.Q. and Li, Y.X. (2010) Outsourcing Services in the Incentive Mechanism with Considering the Effect of Reputation. Journal of Shang-hai Management Science, 1, 81-83. http://www.sjtu.edu.cn/info/1626/57064.htm
- 3. Guo, H.M., Wang, X.Y. and Wang, X.H. (2011) The Dynamic Incentive Contract of Supply Chain with Considering the Cost of Reputation. Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing System, 11, 2483-2492. http://www.cims-journal.cn/CN/volumn/home.shtml
- 4. Peng, B.H. and Feng, L.Q. (2011) The Trust Games of the Modular Production Network and Reputation Incentive Study. Science and Technology and Management, 1, 29-33. http://kjygl.hrbust.edu.cn/
- 5. Liang, H.P. (2010) Manufacturing Network Collaborative Quality Control Strategy Re-search. Tianjin University.
- 6. You, J.X. and Zhu, L.L. (2010) The Research of Quality Control Strategy of Supply Chain under the Condition of Moral Hazard. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 7, 1092-1098. http://tjxb.cnjournals.cn/ch/index.aspx
- 7. Feng, L.Q. (2012) The Quality of Service-Oriented Manufacturing Network Node Behavior Research. Nanchang University.
- 8. Zhang, W.Y. (2004) Game Theory and Information Economics. Shanghai People’s Publishing House, Shanghai, 260-269.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.








