Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.04 No.07(2016), Article ID:68925,6 pages
10.4236/jamp.2016.47136
The Existence and Stability of Synchronizing Solution of Non-Autonomous Equations with Multiple Delays
Jinying Wei1, Yongjun Li1, Xiaohua Zhuo2
1School of Mathematics, Lanzhou City University, Lanzhou, China
2Gansu Province Health School, Lanzhou, China



Received 24 May 2016; accepted 12 July 2016; published 15 July 2016

ABSTRACT
In this paper, we consider an abstract non-autonomous evolution equation with multiple delays in a Hilbert space H: 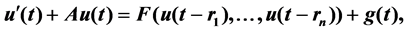 where
where 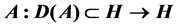 is a positive definite selfadjoint operator,
is a positive definite selfadjoint operator,  is a nonlinear mapping,
is a nonlinear mapping, 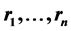 are nonnegative constants, and
are nonnegative constants, and 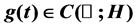 is bounded. Motivated by [1] [2], we obtain the existence and stability of synchronizing solution under some convergence condition. By this result, we provide a general approach for guaranteeing the existence and stability of periodic, quasiperiodic or almost periodic solution of the equation.
is bounded. Motivated by [1] [2], we obtain the existence and stability of synchronizing solution under some convergence condition. By this result, we provide a general approach for guaranteeing the existence and stability of periodic, quasiperiodic or almost periodic solution of the equation.
Keywords:
Pullback Attractor, Cocycle System, Stability, Synchronizing Solution

1. Introduction
In this paper, we consider the following non-autonomous evolution equation with multiple delays in a Hilbert space H:
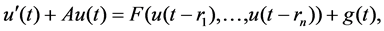 (1.1)
(1.1)
where  is a positive definite selfadjoint operator with compact resolvent,
is a positive definite selfadjoint operator with compact resolvent,  is a nonlinear mapping,
is a nonlinear mapping, 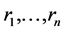 are nonnegative constants, and
are nonnegative constants, and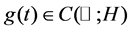 is bounded.
is bounded.
This partial differential equations with delays (1.1) has extensive physical background and realistic mathematical model, hence it has been considerably developed and the numerous properties of their solutions have been studied, see [3]-[5] and references therein. Ref. [4] and [5] mainly discussed the existence and stability of periodic solutions of (1.1). Ref. [3] is concerned with the existence of locally almost periodic solutions of (1.1) by pullback attractor theory.
In this paper, our aim is to study the existence and stability of synchronizing solution of Equation (1.1). Motivated by [1] [2], we obtain the existence and stability of synchronizing solution under some convergence condition. The result be of most interest when we choose 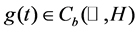 be translation compact (resp. recurrent or almost periodic or quasiperiodic or periosdic), then we can obtain the synchronizing solution of Equation (1.1) is also translation compact (resp. recurrent or almost periodic or quasiperiodic or periosdic). This result provides a general approach for guaranteeing the existence and stability of periodic, quasiperiodic, almost periodic or recurrent solution of the equation.
be translation compact (resp. recurrent or almost periodic or quasiperiodic or periosdic), then we can obtain the synchronizing solution of Equation (1.1) is also translation compact (resp. recurrent or almost periodic or quasiperiodic or periosdic). This result provides a general approach for guaranteeing the existence and stability of periodic, quasiperiodic, almost periodic or recurrent solution of the equation.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we provide some preliminaries. In Section 3, we establish the existence and stability of synchronizing solutions under some convergence condition.
2. Preliminaries
This section consists of some preliminary work.
2.1. Analytic Semigroups
Let H be a Hilbert space with the inner product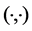 . We will use
. We will use  to denote the norm of H and use
to denote the norm of H and use  to denote the norm of bounded linear operators on H. Let
to denote the norm of bounded linear operators on H. Let

be a positive definite selfadjoint operator with compact resolvent, and let

Be the eigenvalues of A (counting with multiplicity) with the corresponding eigenvectors 
For

Let
Then, 


respectively. We also know that for any


2.2. Pullback Attractors
We recall some basic definitions and facts in the theory of non-autonomous dynamical systems for skew-product flows on complete metric spaces.
Let 




1)
2)
Definition 2.1 A mapping 

1)
2) 

3) 
The mapping 
forms a semigroup on 
Definition 2.2 A family 


and pullback attracting, that is, for any bounded subset B of X,
and is the minimal family of compact sets that is both invariant and pullback attracting.
2.3. Global Pullback Attractor of (1.1)
We present essential conditions on the nonlinearity F to guarantee the dissipation and the existence of pullback attractor of (1.1).
We first discuss the well-posedness of the initial value problem of the equation.
Let


For 


Consider the initial value problem of the evolution equation with delays

where 


(H1) For all 
(H2)
(H3) For any 

for all 



and 

Theorem 2.3 Assume that 


Proof. The proof can be obtained by Theorem 5 in [3].
Remark 2.4 

Let the space 
It is well known that this topology is metrizable and 
Give 

So the shift operator 


forms a continuous dynamical system on the base space
Define 
where 





Since Theorem 12 in [3], we have the following existence result concerning the pullback attractors.
Theorem 2.5 Let


3. Synchronizing Solutions
In this section, we establish some results on synchronizing solutions for (1.1), by developing some techniques inspired by works [2] and [1]. It is known that if g has some special structure, i.e., periodic, quasiperiodic, almost periodic etc., then we can obtain a compact base space with same structure. Combined with the theory of uniform pullback attractors for dynamical systems in [6], we will prove that under some convergence condition, Equation (1.1) have some entire solution 

Now, we consider that 

If furthermore, the Lipschitz coefficients 


then we have the following results about synchronizing solutions for (1.1).
Theorem 3.1 Assume


1) There exists a 



2) For any



Proof. By Theorem 2.5, we have proved that the cocycle mapping 



As Definition 2.2, it is 
One can also write the non-autonomous invariance property as

In what follows we show that for each

for some
Let


We know that
where 

where 

Let
Taking inner product with 


which yields that

where

where
Let

Since 


Then, we can obtain that

which implies 


Now define 
We infer from Corollary 2.8 in [6] that 






By invariance property of 




where 

Thus we can deduce that
The proof is complete.
Corollary 3.2 Let 

Proof. Let 





Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NNSF (11261027), NNSF (11161026) and the Research Funds of Lanzhou City University (LZCU-BS2015-01).
Cite this paper
Jinying Wei,Yongjun Li,Xiaohua Zhuo, (2016) The Existence and Stability of Synchronizing Solution of Non-Autonomous Equations with Multiple Delays. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,04,1294-1299. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2016.47136
References
- 1. Bongolan-Walsh, V.P., Cheban, D. and Duan, J. (2003) Recurrent Motions in the Nonautonomous Navier-Stokes System. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems-Series B, 3, 255-262. http://dx.doi.org/10.3934/dcdsb.2003.3.255
- 2. Li, D. and Duan, J. (2009) Structure of the Set of Bounded Solutions for a Class of Nonautonomous Second-Order Differential Equations. Journal of Differential Equations, 246, 1754-1773. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jde.2008.10.031
- 3. Li, D., Wei, J. and Wang, J. (2013) On the Dynamics of Abstract Retarded Evolution Equations. Abstract and Applied Analysis, 2013, 9 p.
- 4. Li, Y. (2011) Existence and Asymptotic Stability of Periodic Solution for Evolution Equations with Delays. Journal of Functional Analysis, 261, 1309-1324. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jfa.2011.05.001
- 5. Zhu, J., Liu, Y. and Li, Z. (2008) The Existence and Attractivity of Time Periodic Solutions for Evolution Equations with Delays. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 9, 842-851. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2007.01.004
- 6. Cheban, D., Kloeden, P.E. and Schmalfuss, B. (2002) The Relationship between Pullback, Forwards and Global Attractors of Nonautonomous Dynamical Systems. Nonlinear Dynamics and Systems Theory, 2, 9-28.
































