 Creative Education 2011. Vol.2, No.3, 174-180 Copyright © 2011 SciRes. DOI:10.4236/ce.2011.23024 Educating through Movies: How Hollywood Fosters Reflection Pablo G. Blasco1, Mariluz González Blas co2, Marcelo R. Levites3,Graziela Moreto3, James W. Tysinger4 1Brazilian Society of Family Medicine Rua Silvia, São Paulo, Brazil; 2Philosophy Department Mirasierra Institute, Madrid, Spain; 3Brazilian Society of Family Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil; 4Faculty Development University of Texas, Health Science Center, San Antonio, USA. Email: pablogb@sobramfa.com.br, mlgonzalezblasco@educa.madrid.org, marcelolevites@sobramfa.com.br, graziela@sobramfa.com.br, tysinger@uthscsa.edu Received April 14th, 2011; revised May 7th, 2011; accepted May 20th, 2011. Learning through aestheti c s —i n w h i ch c in ema is included—stimulates learner reflecti on . Because emotions play key roles in learning attitudes and changing behavior, teachers must impact learners’ affective domain. Since feelings exist before concepts, the affective path is a critical path to the rational process of learning. Likewise, faculty use their own emotions in teaching, so learning proper methods to address their affective side is a com- plementary way to improve their communication with students. This paper presents experiences of how to use cinema for educating emotions, among students and teachers, to foster reflection and improve teaching skills. Keywords: Cinema and Education, Affective Education, Innovative Teaching Methodology, Learning through Emotions, Reflection among Peer s Background: Why Teach with Movies? Using movies to educate and facilitate reflection among phy- sicians is an important instructional method for medical educa- tors. As children, our parents taught us much through movies, but many medical teachers don’t use this method either because they are unfamiliar with it, or are reluctant to use engage in the discussion that is so integral to this approach. Consider how Frank Capra’s “It’s a Wonderful Life” teaches us about valuing relationships; or Gary Cooper’s “Sergeant York” models stead- fastly holding onto one’s values. This method of using movies to teach was re-discovered by one of the authors at a meeting of Family Medicine educators. At this meeting he and two co- presenters, both medical students, showed a movie clip to the session’s attendees. After the clip was shown, this author com- mented on the scene, but was surprised to see his co-presenters crying. Afterwards, he asked: “What was wrong? You already knew what was in this clip, but you had this emotional response when viewing it. Why?” The students responded by identifying a key attribute of this method: “Preparing and previewing the clip is one thing, but watching it here made us think how the content of the clip applies to our lives”. After this experience, the authors started integrating movies into medical talks. Thus, lectures like “Patient-Centered Medi- cine” and “Leadership Strategies for Medical Students” went from traditional presentations to interactive discussions among faculty, residents, and medical students with movie clips always included. Even lectures specifically developed for faculty also included movie clips. At that point, this same author’s aca- demic research which resulted in his PhD dissertation was supported by movies: “Medical education, family medicine and humanism: analyzing medical students’ expectative, dilemmas and motivation through a cinema teaching context”. Thus, since 2002 the authors’ presentations have always contained movie clips. During the last eight years the Brazilian Society of Family Medicine (SOBRAMFA, www.sobramfa.com.br ) and its close colleagues have spread this cinema-based teaching method in two main venues. One, our presentations at medical meetings like the Society of Teachers of Family Medicine’s Annual Spring Conference and the World Family Doctors Organiza- tion’s (Wonca) meetings have used movies to teach faculty, medical students, and family medicine residents (Blasco, Levites et al., 2008; Blasco, Garcia et al., 2010; B lasco, Môna co et al., 2010). Two, the authors have used movies while teaching high school students and faculty. This article describes the authors’ movie-based teaching ex- periences from 2003 to present in workshops with high school students and teachers and faculty development workshops to physicians in Spain, Brazil, Latin America, and Europe. We encourage other medical school and residency faculty to adapt our approach to their particular learners. From Emotions to Reflection: Movies’ Contributions to Education Technical knowledge and skills can be acquired through training with little reflection; but refining attitudes, acquiring virtues and incorporating values requires reflection. In life, people learn important attitudes, values, and beliefs by observ- ing role models, a process that impacts lear ners ’ e moti ons (Ruiz, 1999). Since feelings exist before concepts, the affecttive path is a critical way to the rational process of learning. Learning through aesthetics—in which movies are included—stimulates learner reflection. Teaching through humanities includes several modalities in which art is involved. Literature and theatre (Shapiro, 2000),  P. G. BLASCO ET AL. 175 poetry (Whitman, 2000), opera (Blasco, Moreto, & Levites, 2005) are all useful tools when the goal is to promote learner reflec- tion and construct what has been called the professional phi- losophic exercise. Using movies in teaching is an effective way to reach peo- ple’s affective domain, promote reflective attitudes (Blasco, Mônaco et al., 2010; Blasco, Moreto et al., 2006), and link learning to experiences. Teaching using movies triggers dis- closing emotions, and this allows questions, expectations and dilemmas to arise for both learners and faculty. Movies provide a narrative model grounded in the learners’ familiar world that are framed in emotions and images. Life stories are a powerful resource in teaching. In ancient cultures, such as classical Greece, the art of story-telling was often used to teach ethics and human values (MacIntyre, 1984). Stories are one reasonable solution to the problem that most people, especially young people, can only be exposed to a lim- ited range of life experiences. Story-telling, theatre, literature, opera, and movies all have the capacity to supplement learners’ understanding of the broad universe of human experience. Ex- posure to life experience—either the real lived one or the one lived through story—provides what Aristotle called catharsis. Catharsis has a double meaning, both of which deal with a hu- man’s feelings. One, catharsis means literally to “wash out” the feelings retained in the soul. Two, catharsis implies an organiz- ing process in which the person sorts through, orders, and makes sense of emotions. In short, in the normal course of events people keep their feelings inside, storing them in an untidy fashion, but don’t think about them. Catharsis helps empty one’s emotional drawers and reorganized them in ways that provide a pleasant sense of order and relief. Beside this classic concept regarding aesthetic learning, the educator needs to recognize that learners are immersed in a popular culture framed in emotions and images (Ferres, 2000). Emotions and images are privileged in popular culture so they should be the front door in learners’ learning process. Life sto- ries and narratives enhance emotions, and therefore lay the foundation for conveying concepts. When strategically incur- porated into the educational process and allowed to flow easily in the learning context, emotions facilitate a constructive ap- proach to understanding that uses the learners’ own empathetic language. Furthermore, in dealing with the learners’ affective domain the struggle in learning comes close to the felt pleasure, and it is possible to take advantage of emotions to identify atti- tudes and foster reflection over them. Thus, when the subject is emotions, attitudes, and promoting reflection, life histories de- rived from movies fit well with the learners’ context and ex- pectations. Because they are familiar, evocative, and non-threatening, movies are useful in teaching the human dimension required for a developing personality and for building identity in young learners and confirm teaching roles in their faculty. The movie learning scenario allows teaching points quickly and directly with specific scenes, putting emotions together, and helping the learners immediately understand and recognize issues. Foster- ing reflection stimulates discussion about the breadth of human experience and this discussion often elicits profound conflicts and concerns learners have about their future professional roles and personal lives. In addition, learners have the opportunity to “translate” life stories from movies into their own lives. In this way movies create a new learning process, and through it learners integrate learning into their lives. The movie experience acts like emo- tional memory for learners’ developing attitudes and allows them to proceed through daily activities. Real learning has more to do with the affection and love teachers invest in educating people that with theoretical rea- soning (Palmer, 1998). To educate through emotions doesn’t mean to limit learning about values and attitudes exclusively in the affective domain. The point is to provoke students to reflect on those values and attitudes (Blasco & Alexander, 2005) To impact emotions is the short-cut for reaching learners, a type of track for taking-off and moving deeper afterwards. Besides the specific knowledge students must master, learners must refine attitudes, construct identities, and develop personalities. Fos- tering reflection is required to do this. Teaching reflection is a goal for excellent educators who want to move beyond transmitting subject matter content. These faculty view teaching as fostering learning, and they believe that they will better understand their students and the nature and processes of learning if they can create more sup- portive learning environments. The best teaching is often both an intellectual creation and a performing art, and teaching is conceived by excellent educators as the opportunity to create good learning environments (Bain, 2004). Therefore, excellent teachers develop their teaching skills through constant self- evaluation, reflection, the willingness to change, and the drive to learn something themselves (Palmer, 1998). Teaching with movies is an innovative method for promoting learning that education requires today. Preparing for the Presentation Although this movie-based educational methodology was positively received by Brazilian medical students and faculty, we wondered if the approach would also work with people from different cultures and educational and social backgrounds. Lan- guage barriers also concerned us: We use American movies with subtitles in Portuguese that almost no one in these settings could read. Thus, before every presentation we asked: “Will this approach work with this audience?” We consider two variables when planning a presentation: The number of people in the audience and the amount of teach- ing time available. Experience has taught us that a small audi- ence (e.g., 30 people) and a larger time period (e.g., 2 hours) is the best scenario for a workshop that uses movie clips. How- ever, the method can also work with a larger audience (e.g., 100 people) and a shorter time period (e.g., 1 hour), but we adapt by giving a shorter lecture using fewer movie clips to stimulate discussion. Next, we consider our presentation attendees. Who are they, and why will they attend our session? If the audience is small (e.g., less than 30 people) and have enough time, we ask atten- dees individually what they want to gain from the session. Some people attend because they have heard about our teaching methodology and want to learn more; others just love watching movies, and those who already use movies in their teaching want to compare their approach with ours. If the audience is large and the presentation time brief, we write potential re- sponses on a flipchart and ask people to raise their hands when the response that matches their reason for attending is read  P. G. BLASCO ET AL. 176 aloud. In each situation, the audience feels comfortable in shar- ing what they want to hear and learn. The Strategy for Planning the Session, Selecting Movie Clips, and Making Comments We start each session by briefly introducing the facilitators and stating the session objectives. For the next 20 - 30 minutes multiple movie clips are shown in rapid sequence with a facili- tator following each with focused comments. A discussion follows with the audience asking questions and sharing their reflections, feelings, and thoughts. If the audience is large and we have enough time, we break the audience into small groups to encourage discussion. At the end of the session the small groups reform into the large group, and a spokesperson from each small group will share the topics discussed in his/her group. Selecting the movies and specific scenes on a specific topic to stimulate discussion and adapting the movies to the audience or to the topics being presented takes experience. Our basic guidance: Insure the clips relate to your presentation’s object- tives. For a broad selection of movie clips, we refer readers to several papers we have published (Blasco, Moreto et al., 2006; Blasco, Garcia et al., 2010; Blasco, Pinheiro et al., 2009). However, presenters must adapt their comments to the specific audience. Adapting to the audience requires facilitators to un- derstand the people to whom they are speaking and to reflect on the clips before framing their comments. The point is to pro- mote participant reflection on attitudes, human values from a broad perspective. The comments that really stimulate reflec- tion are those based on the audience’s response to the clip being shown. What Happens in the Session? Is It All about Tears or Is There Reflection? Emotions can be seen on the participants’ faces as they view the movie clips and hear the facilitators’ comments. Sighs are heard, handkerchiefs appear, and some people are seen crying with no shame as room lights are turned on. People from both genders, including facilitators, cry . Sometimes everyone is m ove d and in tears. Fostering reflection is next. “Fostering reflection” is the main concept noted in all eva- luations from the audience. The whole process—brief movie clips along with the facilitator’s comments—stimulates reflec- tion. While the clips’ quickly changing scenes evoke concerns and reflection in individual audience members, the facilitators’ comments amplify the whole process. Because each member of the audience is involved in her personal reflective process, she/he may agree or disagree with the facilitator’s comments and draw their own conclusions. This is a desirable outcome once participants note that divergent comments are desired to facilitate reflection. Understanding Audience Feedback and Making Connections The value in teaching with movies is reinforced through the audience’s feedback. Analyzing data from participants (i.e., comments through field notes and session evaluations, inter- views and written assignments) have helped us see the value of teaching with movie clips. Since it is well suited for such an analysis, we use a qual itative app r oa ch t o an alyze this data . Qualitative analysis is useful for researchers who understand their discipline as more empirical and craft-based than theo- retical (Crabtree & Miller, 1999). This is especially true when the session objectives deal with emotions, attitudes and profes- sional values. Qualitative designs are flexible, iterative, and continuous. Good qualitative research is always more of a cir- cular process than a linear one. The ultimate canon of evidence in any qualitative research is that the report carries “sufficient conviction” to enable others to obtain the same results and ap- preciate the account’s truth as the original observer. Discussion and focus group are one of the features of qualitative research. The goal of a discussion group is to gather information based on the participant’s interaction, not to build consensus or aid decision-making. Through an interactive exchange among the participants, multiple stories are produced, diverse experience related, similarities and differences emerge, and contrary opin- ions can be explored to generate new areas of inquiry. Thus, a qualitative approach is well suited for analyzing the data and identifying the results from the movie clips and educational experiences. It must be said that the results include the re- searchers’ interpretation of notes and records of what was ob- served. As the literature states, “the researcher is the primary research tool, so it is essential to include his/her feelings and reflections over the analysis. The experience had in the field is not merely observed and recorded, but is also felt. Reflection on feelings is essential (Crabtree & Miller, 1999)”. Audience feedback consists of ratings (e.g., “The presenters allowed me to interact with others”: 5-point scale ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”) and comments made in response to specific questions. When analyzing audience com- ments, we divide the data into two specific groups: Learners and faculty. If necessary, each group can be further divided into other units (e.g., medical students, first year residents, second year residents). Here comments from high school students and faculty are included to illustrate key themes. Comments from High School Students Young people today live in a dynamic and sensitive envi- ronment characterized by rapid information acquisition and high emotional impact. Movies provide a quick and direct teaching scenario that accesses their emotions. “If I were a teacher, I would try to improve communication with my students and reach their emotions, touching them since in this way they will grow up like human beings. There is a barrier between teachers and students, and we need to go further than (subject matter) content to overcome this barrier. We need to reach peoples’ heart for providing good education”. (Student’s quote) (Sq). Students want more practical education: Not just theoretical content, but concepts connected with reality. They want room for more creativity. Education must foster their creativity and imagination. “When Aristotle and Plato talk about education they focus it on the person. It is a kind of education for life, education for relationships, for citizenship in society. Teachers need  P. G. BLASCO ET AL. 177 to help us grow up and develop as people instead of just focusing on learning issues, content…” (Sq). “There is a problem with (subject matter) content. And that is students are unable to find out how such content will help them. There is a gap between theoretical issues and real life. Students must understand why the content we are taught is really useful for us.” (Sq). We strive to help students reflect, rather than to show them how to incorporate a particular attitude. High school students exposed to this method often change their attitudes. “You need to get students motivated the right way, get them involved somehow.” (Sq). “What really matters in education is to foster people’s de- velopment as human beings. We need to value the person more than content. In this way we can get from them the best they have in their minds.” (Sq). The movie clip method is used to direct student attention to professional attitudes and to produce leaders. Showing movie clips fits well with the dynamic and emotional nature of stu- dents’ lived experience. In this context using movie clips to teach is logical because they are brief, many can be shown quickly, and they impact the emotions. From factors related to career choice, idealism, unspoken vocational doubts; students move to a more reflective attitude in choosing their professional careers, become more committed to their career choices, and recognize that the movie discussions make them aware of struggles they could not articulate before. “Maybe one of the best outcomes in education is to accom- plish what happens in the ‘Lion King’ movie clip we saw a few minutes ago. Teachers should get students to look in- side, like the Lion King, and to find their own motivations to take their place in the circle of life. When you find your own motivations, they are more powerful and stronger than motivations coming from the outside.” (Sq). Comments from Faculty Faculty groups often come anticipating this methodology, and their expectation are supported. That is, faculty realize they can improve their teaching strategies to reach students more efficiently. “I was told about the informal curriculum, and they said it works fine among the students. How can I be more credible to my students and help them more? Must their teachers have special skill s?” (Faculty quote) (Fq). “What can we do when we are short of time, have a lot of work to do, too many students, and can’t give them good feedback? Is there any short-cut I can use? Am I missing something in this? Maybe we don’t reach the students be- cause we don’t understand them. How can we ask them the right questions?” (Fq). Faculty face challenges when they teach alone. Even when they discuss educational issues with their colleagues, they often spend most of this time talking about problematic students. Faculty seldom think about themselves and usually lack the time to disclose their feelings before encountering new chal- lenges. When searching for excellence in teaching, one’s fellow teachers are useful resources. After all, our colleagues can teach us a great deal about ourselves and our craft. “We need to meet and get in touch with each other, before we start teaching. And the teaching session we just finished showed us how to do this in a fun way. We get to grow in our relationships. (…) We have limited time to reflect on our teaching endeavors” (Fq). “I want to be comfortable in teaching, teach well, know my colleagues, and feel supported by them. (…) We can set an informal group to continue these reflections on teaching. Nothing official, but a good informal get-together for mu- tual support. (…) This workshop at the very beginning of the year, in advance, is a good start.” (Fq). “Get common ground among us. Be positive, and we will try to reach consensus in each meeting. (…) We need to share the outcomes: the good ones, what is working, and the bad ones, what is not working (...) We also need to learn to value an individual’s success. If we get a few faculty in- volved, we could achieve much more because the news about having a reflective environment spreads quickly. (…) Cooperation and service: We must get the faculty to adopt these attitudes as a team.” (Fq). Movie clips offer faculty a special environment for fostering open discussions that help them better know themselves, im- prove their self awareness, and develop closer relationships with colleagues and students through the affective domain. Thus, the process helps faculty become more reflective: They begin by sharing their weaknesses and frustrations as teachers and asking why they lose energy and ideals. “We are ashamed of sharing our feelings, frustrations, and expectations. We don’t talk about what really matters, those major issues that really concern.” (Fq) “We can’t cope with our frustrations and bad results with the students. And we don’t talk about out bad outcomes be- cause we have no room for it. All we talk about is problem- atic students, not about our failures.” (Fq) “What gets me down is to lose my ideals, I mean, my en- thusiasm for teaching.” (Fq). ”My doubts are not just mine: They are others’ doubts, too. We need to share knowledge and methods.” (Fq). The clips help faculty state new paradigms, gain skills that help them better communicate with learners, and recognize the need to better know themselves so they can facilitate learning. “We are teaching in the same way we were taught. And that might change in the se sessions.” (Fq). “For sure, what really matters in education is what we do, more than what we say. We teach what we are. (…) Raise your flag, don’t say anything. Attitude is the best resource for a leader.” (Fq). “That’s the main faculty role: Foster reflection, help stu- dents find their gifts and use them properly. (…) Don’t ask students for what you are not ready to give them. Get the best from them. This is what we must do all the time as teachers.” (Fq). “Students are the principal characters in education. So the Oscar for best actor and actress always should go to them, not to the teacher. A good teacher deserves the Oscar for the best supportive actor or actress. Not more than that.” (Fq). “Throw out the schedules (like in that movie, with the chessboard without pieces)… Maybe schedules and syllabi impede good teaching.” (Fq). The movie clip method can improve faculty teaching and  P. G. BLASCO ET AL. 178 stimulate their professional growth. The clips point out solu- tions and challenges they want to face to refine their teaching role. “We need much more simplicity. Be realistic, and just start improving what we already have. (…) And, for sure, work with patience and learn how to wait. I like that expression: ‘watchful waiting’.” (Fq). “What really matters is not my subject matter, but the con- cepts that interest students. (…) The best outcome for me: There are many ways to reach my students. And there will always be students we can’t reach.” (Fq). “What first matters is the human side of students (…) We need to love and have fun while communicating something: That’s teaching. Improving the way I communicate is like that.” (Fq). “I wish I had words for this. I have just emotions (...) I need to look inside me to be a better teacher. And for now, there is a challenge: To be divided no more, so I am the same person in life and as when I teach.” (Fq). “The teacher’s role? To foster reflection, that’s the corner- stone. And to share our expectations and dilemmas with the students. They are grown people.” (Fq). Finally, there are always major questions that call for an- swers. The movie clip education method is an opportunity to pose these inquiries so faculty can reflect on them. That is the method’s good outcome: Ongoing reflection. “How can I be effective with all my students? How do I get to know them? How do I get them involved and committed to solving educational problems? How can I always have the student on my side?” (Fq). “Could I reach my students through emotions? How do I motivate them? How do I better communicate with them? How do I measure the outcomes in all this?” (Fq). “Am I losing my ideals? Are we afraid of innovation? Could we, as faculty, share experiences and disclose our- selves? How can this workshop be a starting point and that gets us to engage in reflective practice?” (Fq). Summary Movie clips are useful resources for teaching medical stu- dents, residents, and faculty because they help people better understand human emotions. The learners’ emotions easily emerge through movies, and faculty can impact learning by broadening their perspectives of learner de velopmen t. Like wise, faculty use their own emotions in teaching, so learning proper methods to address their affective side is a complementary way to improve their communication with students. References Bain, K. (2004). What the best college teachers do. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. Blasco, P. G., & Alexander, M. (2005). Ethics and human values. In M. Alexander, P. Lenahan, & A. Pavlov (Eds.), Cinemeducation: A comprehensive guide to using film in medical education. Oxford: Radcliffe Publishi ng . Blasco, P. G., Garcia, D. S. O., Benedetto de, M. A. C., Moreto, G., Roncoletta, A. F. T., & Troll, T. (2010). Cinema for educating global doctors: From emotions to reflection, approaching the complexity of the human being. Primary Care, 10, 45-47. Blasco, P. G., Lev ites, M. R., Janaudis, M. A., Moreto , G., Roncoletta, A. F., Benedetto de, M. A., & Pinheiro, T. R. (2008). Family medi- cine education in Brazil: Challenges, opportunities and innovation. Academic Medicine, 83 , 684-690. doi:1097/ACM.0b013e3181782a67 Blasco, P. G., Mônaco, C. F., Benedetto De, M. A. C., Moreto, G., & Levites, M. R. (2010). Teaching through movies in a multicultural scenario: Overcoming cultural barriers through emotions and reflec- tion. Family Medicin e , 42, 22-24. Blasco, P. G., Moreto, G., & Levites, M. R. (2005). Teaching humani- ties through opera: Leading medical students to reflective attitudes. Family Medicine, 37, 18-20. Blasco, P. G., Moreto, G., Roncoletta, A. F., Levites, M. R., & Janaudis, M. A. (2006). Using movie clips to foster learners’ reflection: Im- proving education in the affective domain. Family Medicine, 38, 94-96. Blasco, P. G., Pinheiro, T. R. P., Ulloa-Rodriguez, M., & Angulo-Calderón, N. (2009). El cine en la formación ética del médico: Un recurso pedagógico que facilita el aprendizaje. Persona y Bioética, 13, 114- 127. Crabtree, B. J., & Miller, W. L. (Eds.) (1999). Doing qualitative re- search in primary care: Multiple strategies (2nd ed.). Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications. Ferres, J. (2000). Educar en una cultura del espectáculo. Barcelona: Paidós. MacIntyre, A. C. (1984). After virtue. A study in moral theory. Notre Dame, IN: University of Notre Dame Press. Palmer, P. J. (1998). The courage to teach. San Francisco, CA: Jossey- Bass. Ruiz, R. A. (1999). Pulchrum. Madrid: Rialp. Shapiro, J. (2000). Literature and the arts in medical education. Family Medicine, 32, 157-158. Whitman, N. (2000). A poet confronts his own mortality: What a poet can teach medical students and teachers. Family Medicine, 32, 673- 674. 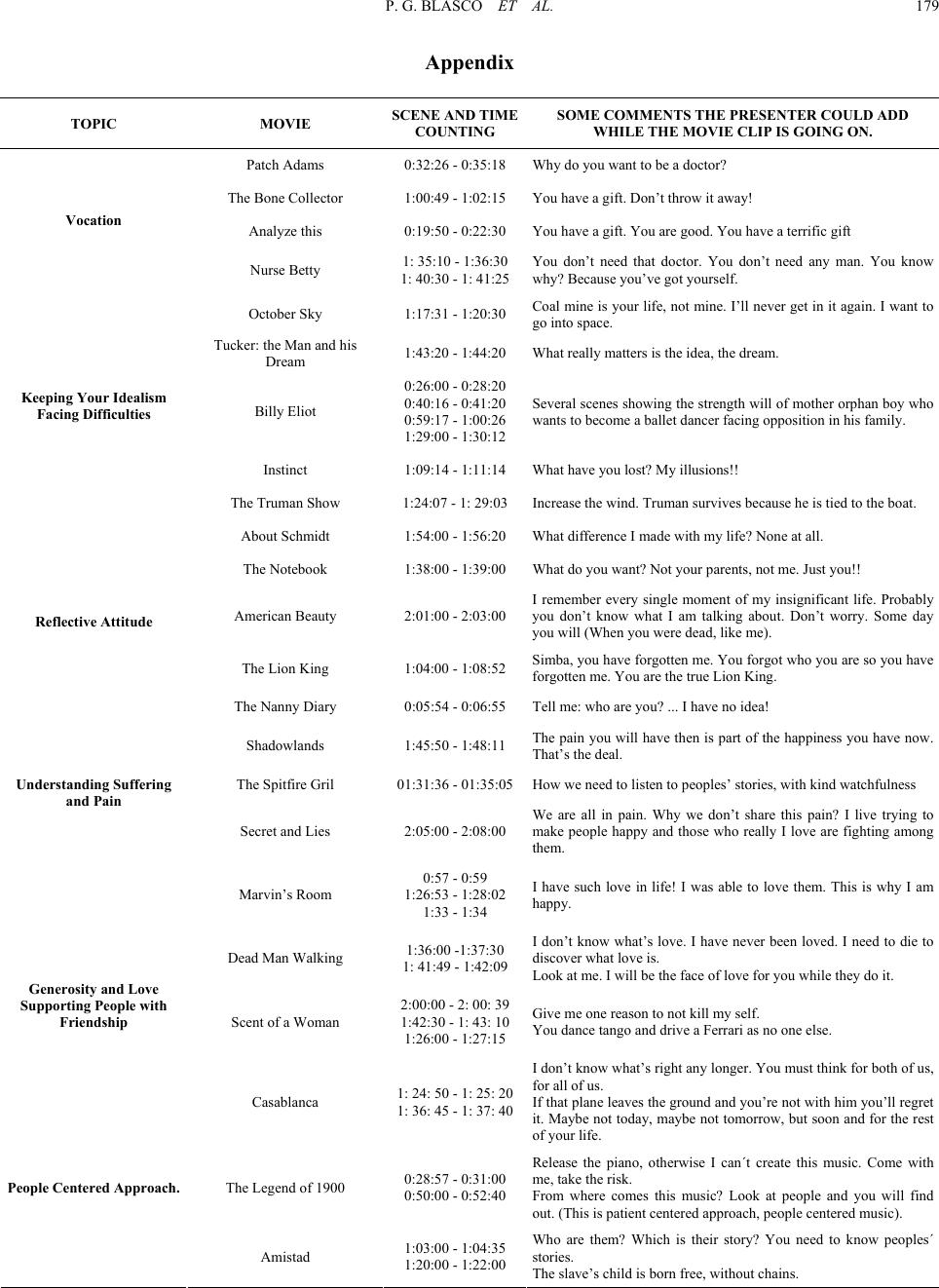 P. G. BLASCO ET AL. 179 Appendix TOPIC MOVIE SCENE AND TIME COUNTING SOME COMMENTS THE PRESENTER COULD ADD WHILE THE MOVIE CLIP IS GOING ON. Patch Adams 0:32:26 - 0:35:18 Why do you want to be a doctor? The Bone Collector 1:00:49 - 1:02:15 You have a gift. Don’t throw it away! Analyze t his 0:19:50 - 0:22:30 You have a gift. You are good. You have a terrific gift Vocation Nurse Betty 1: 35:10 - 1:36:30 1: 40:30 - 1: 41:25 You don’t need that doctor. You don’t need any man. You know why? Because you’ve got yourself. October Sky 1:17:31 - 1:20:30 Coal mine is your life, not mine. I’ll never get in it again. I want to go into space. Tucker: the Man and his Dream 1:43:20 - 1:4 4:20 What really matters is the idea , the dream. Billy Eliot 0:26:00 - 0:28:20 0:40:16 - 0:41:20 0:59:17 - 1:00:26 1:29:00 - 1:30:12 Several scenes showing the strength will of mother orphan boy who wants to become a ballet da ncer facing opposition in his fa mily. Instinct 1:09:14 - 1:11:14 What have you lost? My illusions!! Keeping Your Idealism Facing Diffic ulties The Truman Show 1:24:07 - 1: 29:03 Increase the wind. Truman survives because he is tied to the boat. About Schmidt 1:54:00 - 1:56:20 What difference I made with my life ? None at all. The Notebook 1:38:00 - 1:39:00 What do you want? Not your parents, not me. Just you!! American Beauty 2:01:00 - 2:03:00 I remember every single moment of my insignificant life. Probably you don’t know what I am talking about. Don’t worry. Some day you will (When you were dead, like me). The Lion King 1:04:00 - 1:08:52 Simba, you have forgotten me. You forgot who you are so you have forgotten me. You are the true Lion K i ng. Reflective Attitude The Nanny Diary 0:05:54 - 0:06:55 Tell me: who are you? ... I have no idea! Shadowlands 1:45:50 - 1:48:11 The pain you will have then is part of the happiness you have now. That’s the deal. The Spitfire Gril 01:31:36 - 01:3 5 : 05How we nee d t o l is ten to peoples’ stories, with kind watchfulness Understanding Suffering and Pain Secret and Lies 2:05:00 - 2:08:00 We are all in pain. Why we don’t share this pain? I live trying to make people happy and those who really I love are fighting among them. Marvin’s Room 0:57 - 0:59 1:26:53 - 1:28:02 1:33 - 1:34 I have such love in life! I was able to love them. This is why I am happy. Dead Man Walkin g 1:36:00 -1:37:30 1: 41:49 - 1:42:09 I don’t know what’s love. I have never been loved. I need to die to discover what love is. Look at m e. I will be the face of love for you while th ey do it. Scent of a Woman 2:00:00 - 2: 00: 39 1:42:30 - 1: 43: 10 1:26:00 - 1:27:15 Give me one reason to not kill my self. You dance tango and drive a Ferrari as no one else. Generosity and Love Supporting People with Friendship Casablanca 1: 24: 50 - 1: 25: 20 1: 36: 45 - 1: 37: 40 I don’t know what’s right any longer. You must think for both of us, for all of us. If that plane leaves the ground and you’re not with him you’ll regret it. Maybe not today, maybe not tomorrow, but soon and for the rest of your life. The Legend of 1900 0:28:57 - 0:31:00 0:50:00 - 0:52:40 Release the piano, otherwise I can´t create this music. Come with me, take the risk. From where comes this music? Look at people and you will find out. (This is patient centered approach, people centered music). People Centered Appr oach. Amistad 1:03:00 - 1:04:35 1:20:00 - 1:22:00 Who are them? Which is their story? You need to know peoples´ stories. The slave’s child is born free, without chains.  P. G. BLASCO ET AL. 180 Cast Away 0:48:36 - 0:50:00 Although no one ask him to do it, even he doesn’t know if he will survive, buries his colleague and find out who is the dead person and his family and write the name beside the grave. Searching f or Bobby Fisher 0:35:00 - 0:37:00 I will make easier for you ( the teachers throws the chess pieces down). Dead Poet Society 0:21:12 - 0:23:35 0:25:30 - 0:25:59 0:43:00 - 0:43:43 Revolutionary new paradigms in education, leading people to think by them selves. Good Will Hunting 0:46:54 - 0:50:33 You know just what you can read in books. But you have never smelt the f ragrance of th e Sixtin Chap el neither yo u have hold you r best friend’s head while he was dying. You don’t know anything about lost because you are selfish and don’t love anyone more than yourself. Music from the Heart 0:28:00 - 0:29:00 1:48:00 - 1:49:00 What really matters is to get strength insid e. Don’t look at the audience, look at me. And play from the heart. New Paradigms in Education Pretty Woma n 1:26:19 - 1:28:49 How can someone change in a two hour opera performance, even without understanding Italian language and lacking knowledge about Opera. Saving Private Ryan 1:48:30 - 1:51:27 2:36:21 - 2:36:50 2:38:40 - 2:39:10 2:39:25 - 2:41:30 They are th e only brothers I have now. James earn this. Every day I think about what you said to me. I tried to live my life the best I could, and I hope before your eyes I earned what you all did for me. Man of Honor 1:57:21 - 1:59:37 Mentoring is essential to bring the best from people. I want my twelve steps, repot to this line. Responsibility and Commitment Gattaca 1:30:00 - 1:34:0 0 I never saved forces for the swimming back!! This is how I could do it. Any given S unday 1:57:20 -1:59:30 Gentleman, we’re a team, and or we heal like a team or we’ll perish as individuals. Gladiator 1:10:30 - 1:11:00 1:23:50 - 1:24:20 Win the crowd and you’ll b e free. I don’t know what’s coming out from that gate, but if we stay to- gether we’ll s urvive. Spartacus 0:49:30 - 0:5 0: 50 IIpart Who is Spartacus? I am Spartacus, I am Spartacus. Everyone is Spartacus. More than a person it is an idea. Working in a Team Ladder 49 0:49:53 - 0:50:36 I have just come to tell a mother that her son is dead and you are fighting like this, in my house!! We honor the dead colleague when we turn back to work every single day. The Patriot 2:13:55 - 2:15:40 2:26:17 - 2:28:00 Two great flag scenes. As anyone can carry a gun in the battle, just the leader is able to put up the flag and push people to victory. Glory 0:50:36 - 0:51:55 1:27:40 - 1:30:00 If you man w o u l d t ake no pay, then none of us will. The 540 of Massachusetts asks for the honor to lead the attack. There is more than rest in fight; there is character, strength of heart. The Last Castle 0:10:00 - 0:1 2:00 1:23:00 - 1:25:00 Any man with a collection like this never set foot on a battle, These points out the difference between natural leadership and official command Leaders must be understood, and for that they need to explain their attitudes, making them rational. Schindler’s List 0:44:55 - 0:46:55 IIpart. I could save more people. The leader knows how further he can go. We were soldiers (0:16:50 - 0:17:35) (0:34:00 - 0:35: 00 ) Take care of your men. When all this begin all we have is each other. I will be the fir s t to set foot on the battle and the last to step off. Enemy at the gates 0:24:28 - 0:26:21 Give them her oes, examples to follow. Give them hope. K 19. The Widomaker 1:45:30 - 1:47:45 Don’t give orders to the men. Just ask them. Leadership The Last Samurai 2:10:35 - 2:16:10 Impressive Scene with the enemies kneeling down before the dead Samurai.
|