T. ABOUELDAHAB ET AL.
Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ICA
181
[4] K. S. Narendra and K. Parthasarathy, “Identification and
Control of Dynamical Systems Using Neural Networks,”
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Vol. 1, No. 1,
1990, pp. 4-27. doi:10.1109/72.80202
[5] L. Chen and K. S. Narendra, “Nonlinear Adaptive Con-
trol Using Neural Networks and Multiple Models,” Pro-
ceedings of the 2000 American Control Conference, Chi-
cago, 2002, pp. 4199-4203.
[6] R. Zhan and J. Wan “Neural Network-Aided Adaptive
Unscented Kalman Filter for Nonlinear State Estimation,”
IEEE Signal Processing Letters, Vol. 13, No. 7, 2006, pp.
445-448. doi:10.1109/LSP.2006.871854
[7] A. S. Poznyak, W. Yu, E. N. Sanchez and J. P. Perez,
“Nonlinear Adaptive Trajectory Tracking Using Dynamic
Neural Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Net-
works, Vol. 10, No. 6, 1999, pp. 1402-1411.
doi:10.1109/72.809085
[8] P. A. Mastorocostas, “A Constrained Optimization Algo-
rithm for Training Locally Recurrent Globally Feedfor-
ward Neural Networks,” Proceedings of International
Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Montreal, 31 July
4 August 2005, pp.717-722.
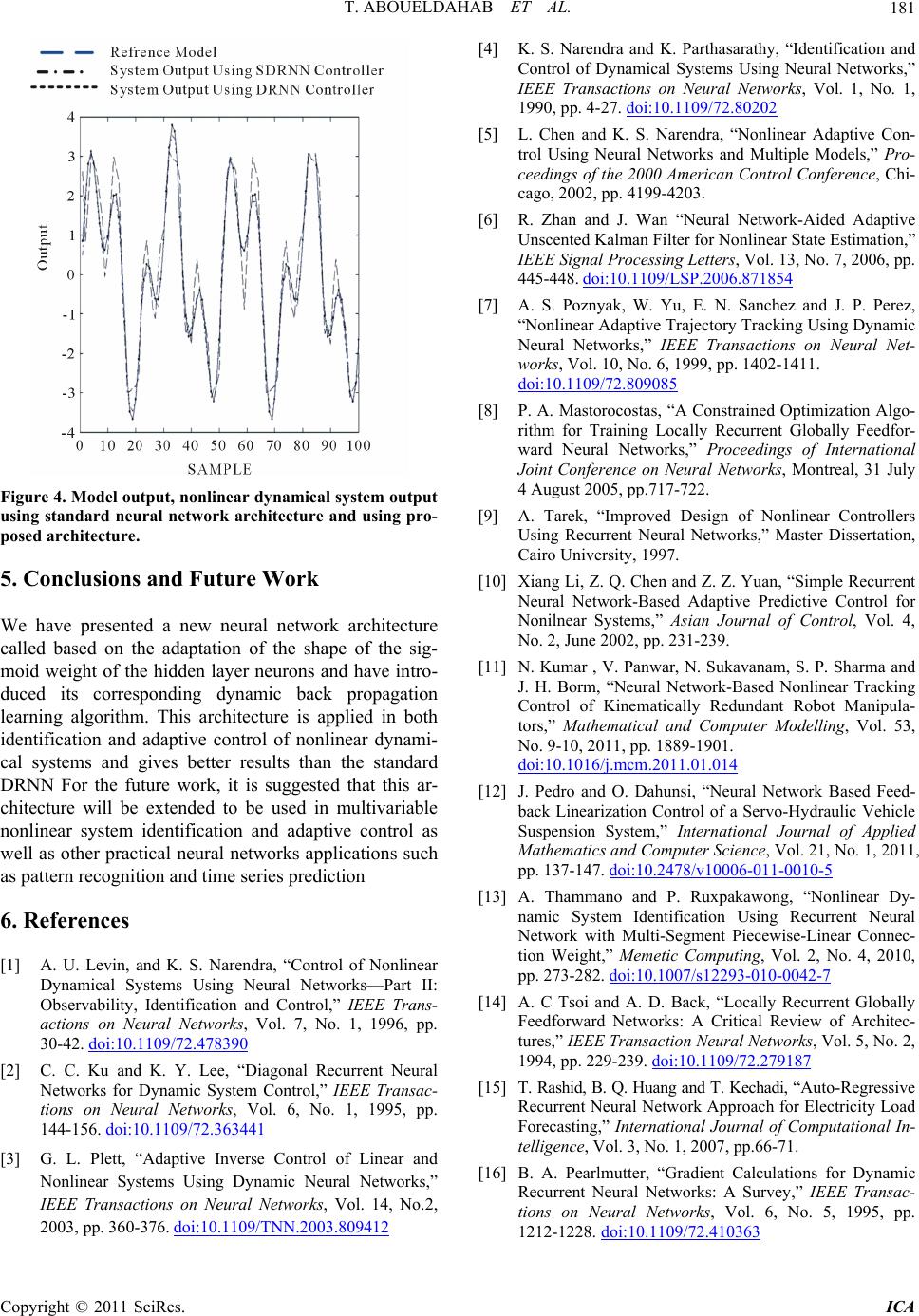
Figure 4. Model output, nonlinear dynamical sy stem output
using standard neural network architecture and using pro-
posed architecture. [9] A. Tarek, “Improved Design of Nonlinear Controllers
Using Recurrent Neural Networks,” Master Dissertation,
Cairo University, 1997.
5. Conclusions and Future Work [10] Xiang Li, Z. Q. Chen and Z. Z. Yuan, “Simple Recurrent
Neural Network-Based Adaptive Predictive Control for
Nonilnear Systems,” Asian Journal of Control, Vol. 4,
No. 2, June 2002, pp. 231-239.
We have presented a new neural network architecture
called based on the adaptation of the shape of the sig-
moid weight of the hidden layer neurons and have intro-
duced its corresponding dynamic back propagation
learning algorithm. This architecture is applied in both
identification and adaptive control of nonlinear dynami-
cal systems and gives better results than the standard
DRNN For the future work, it is suggested that this ar-
chitecture will be extended to be used in multivariable
nonlinear system identification and adaptive control as
well as other practical neural networks applications such
as pattern recognition and time series prediction
[11] N. Kumar , V. Panwar, N. Sukavanam, S. P. Sharma and
J. H. Borm, “Neural Network-Based Nonlinear Tracking
Control of Kinematically Redundant Robot Manipula-
tors,” Mathematical and Computer Modelling, Vol. 53,
No. 9-10, 2011, pp. 1889-1901.
doi:10.1016/j.mcm.2011.01.014
[12] J. Pedro and O. Dahunsi, “Neural Network Based Feed-
back Linearization Control of a Servo-Hydraulic Vehicle
Suspension System,” International Journal of Applied
Mathematics and Computer Science, Vol. 21, No. 1, 2011,
pp. 137-147. doi:10.2478/v10006-011-0010-5
[13] A. Thammano and P. Ruxpakawong, “Nonlinear Dy-
namic System Identification Using Recurrent Neural
Network with Multi-Segment Piecewise-Linear Connec-
tion Weight,” Memetic Computing, Vol. 2, No. 4, 2010,
pp. 273-282. doi:10.1007/s12293-010-0042-7
6. References
[1] A. U. Levin, and K. S. Narendra, “Control of Nonlinear
Dynamical Systems Using Neural Networks—Part II:
Observability, Identification and Control,” IEEE Trans-
actions on Neural Networks, Vol. 7, No. 1, 1996, pp.
30-42. doi:10.1109/72.478390
[14] A. C Tsoi and A. D. Back, “Locally Recurrent Globally
Feedforward Networks: A Critical Review of Architec-
tures,” IEEE Transaction Neural Networks, Vol. 5, No. 2,
1994, pp. 229-239. doi:10.1109/72.279187
[2] C. C. Ku and K. Y. Lee, “Diagonal Recurrent Neural
Networks for Dynamic System Control,” IEEE Transac-
tions on Neural Networks, Vol. 6, No. 1, 1995, pp.
144-156. doi:10.1109/72.363441
[15] T. Rashid, B. Q. Huang and T. Kechadi, “Auto-Regressive
Recurrent Neural Network Approach for Electricity Load
Forecasting,” International Journal of Computational In-
telligence, Vol. 3, No. 1, 2007, pp.66-71.
[3] G. L. Plett, “Adaptive Inverse Control of Linear and
Nonlinear Systems Using Dynamic Neural Networks,”
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Vol. 14, No.2,
2003, pp. 360-376. doi:10.1109/TNN.2003.809412
[16] B. A. Pearlmutter, “Gradient Calculations for Dynamic
Recurrent Neural Networks: A Survey,” IEEE Transac-
tions on Neural Networks, Vol. 6, No. 5, 1995, pp.
1212-1228. doi:10.1109/72.410363