Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 Advances in Chemical Engineering and Science, 2011, 1, 147-153 doi:10.4236/aces.2011.13022 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.SciRP.org/journal/aces) Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ACES Study of Rice Husk Ash as Potential Source of Acid Resistance Calcium Silicate Muhammad Mansha, Syed Hassan Javed, Mohsin Kazmi, Nadeem Feroze Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Engineering & Technology, Lahore, Pakistan E-mail: muhammad_mansha@uet.edu.pk Received May 6, 2011; revised June 9, 2011; accepted July 4, 2011 Abstract In present work acid resistant calcium silicate has been synthesized from silica of rice husk and calcium ox- ide of analytical grade. The silica from rice husk was extracted at 550˚C in amorphous form and then al- lowed to react with calcium oxide in the presence of excess water by Sol-Gel technique to obtain calcium silicate hydrate gels. The molar ratios of Si/Ca were adjusted each time to obtain silica rich calcium silicate hydrates. The gels were dried in oven and calcined in muffle furnace at various temperatures to obtain acid resistant calcium silicate. The products were tested by analytical technique and by FTIR and XRD machines. Studies show that at higher molar ratio of Si/Ca, the heat treatment improves the acid resistivity of calcium silicate whereas at lower molar ratios the heat treatment does not make it acid resistant. Keywords: Calcium Silicate, Rice Husk, Amorphous Silica, Acid Resistance, XRD, FTIR 1. Introduction Silica finds numerous applications as an important raw material for assorted types of industries including ce- ramics, electronics and polymers. It has different sources such as quartz, flint, natural silicates and siliceous agri- culture wastes. Rice husk (RH) is an abundantly avail- able agricultural by product in rice producing areas. On weight basis rice husk weighs ~20% of the paddy pro- duced. Rice husk finds multiple applications in a wide range of industries. It is employed as a fertilizer for crops and supplementary material for cement and concrete manufacturing units. It has high percentage of silicon which makes it a valuable starting material for a variety of compounds like silica and its carbides and nitrides [1-4]. Another major application of rice husk is in the power sector on account of its high calorific value (13,000 - 16,000 kj/kg) [4]. The combustion of RH results in pro- duction of rice husk ash (RHA). RHA is light in weight and its color varies from grey to white [5]. Its safe dis- posal is a big liability as it signifies terrific generation of waste, loss of energy and environmental pollution. Thus, an optimum use of RHA has become a great challenge. Silica and carbon are the major components of RHA. Silica claims 80% - 85% in RHA produced by heat gen- erating systems and thus it can suitably be used for many applications [6]. One such application can be the produc- tion of acid resistant calcium silicate (ARCS). Acid resistant calcium silicate is a white powder, usu- ally used as filter aid in acidic media. It is also used as an ion exchanger and for immobilization or removal of fatty acids and heavy metal ions from the wastewater. It has a high melting point of 1540˚C and a very low material density of 2.9 g/cm3. Because of low density it is being used in refractory materials and fireproof cladding. The existing method for preparing ARCS is high pressure hydrothermal reaction between calcium oxide and sili- ceous material having high silica contents [5]. Amor- phous silica shows high reactivity with calcium hydrox- ide in the presence of water and form calcium silicate hydrates whereas crystal silica acts as an inert ingredient under similar conditions. Amorphous silica can be ob- tained from rice husk under controlled burning condi- tions such as residence time, temperature and air flow system in the furnace [7]. In present study Sol-Gel technique was used to syn- thesize calcium silicate hydrates which were converted into ARCS by heat treatment with higher molar ratios of Si/Ca. The specific objectives of this investigation were: 1) to study the effect of calcination temperature and sil- ica to calcium oxide ratio on acid resistance of calcium silicate, 2) To characterize the acid resistant calcium silicate through FTIR and XRD.  M. MANSHA ET AL. Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ACES 148 2. Materials and Methods Rice husk was thoroughly washed with distilled water to remove soluble impurities followed by drying in electric oven at 110˚C for 10 hours followed by grinding and finally screening through 20 mesh sieve. Rice husk at this stage was termed as powdered rice husk. It was burned in muffle furnace for 90 minutes at 550˚C in china dish by gradual rise in temperature. The ash ob- tained was cooled down at room temperature and con- verted into fine powder. The grounded rice husk ash (GRHA) was screened through 200 mesh sieve and stored in plastic container to protect it from moisture. 2.1. Theoretical Background of Sol-Gel Technique Calcium carbonate (Merk, Germany) was heated in a furnace at 1000˚C for 4 hours to decompose into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide: 3(S)(s) 2(g) CaCOCaO CO A calculated amount of calcium oxide was slowly added to boiling water to prepare calcium hydroxide: (s)2 (l)2(Aq) CaOH OCaOH Known amount of GRHA was made to react with cal- cium hydroxide in the presence of excess water such that each time the amount of water was 7 times of solids used to form calcium silicate hydrate gels by the following reaction: 2(s)3(s)2 (l) 2(Aq) CaOHSiOCaSiOH O The mixture was boiled for one hour and then placed into the oven for 10 hours to form calcium silicate hy- drate gel. Fully developed gel was then dried in oven for 10 hours at 110˚C to make sure absence of physically absorbed water. Several samples were prepared by chang- ing molar ratios of Si/Ca from 1.4 to 2.4. The gels ob- tained from each molar ratio were dried and stored in plastic containers to protect them from atmospheric car- bon dioxide and moisture. 2.2. Heat Treatment Calcium silicate hydrate gels made with different Si/Ca molar ratios were heated in muffle furnace from 500˚C to 1100˚C for four hours. The product so obtained after heat treatment was termed as acid resistant calcium silicate (ARCS). 2.3. Acid Resistance Test (ART) ART was performed by immersing 15 g of each ARCS in 200 ml of hydrochloric acid (30%) and also with sul- phuric acid (1M) solution for four hour [8]. It was then filtered and repeatedly washed with distilled water to make acid free solids. The wet solids were dried in an electric oven at 110˚C for 10 hours. This procedure was performed for every sample obtained with different Si/Ca ratios. 2.4. Characterization X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a technique for the study of crystal materials and atomic spacing. XRD analyses were performed using Philips Model PANlytical x-pert ma- chine having X-ray tube (Philips PW 3373/00) operated at 40 kV and current Intensity 40 mA. Spectra were ob- served from 0 to 90 degree at a step size of 0.052 degree for 400 second scanning time. Fourier Transform Infra Red (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed using KBr pel- let technique on JASCO model 4100. Approximately 1 mg of sample was mixed with 100 mg of KBr and then grounded and pressed to prepare the pellets. FT-IR spec- tra were obtained in the range of 400 to 4000 cm–1. 3. Results and Discussion 3.1. Characterization of Ground Rice Husk Ash Calcium hydroxide usually reacts with amorphous silica in the presence of water and forms calcium silicate hy- drates. The reaction of calcium hydroxide with crystal silica is almost negligible whereas with amorphous silica it is quite rapid [6]. At elevated temperature the amorphous silica of RHA converts itself into crystal silica. Therefore, rice husk was carefully burned in the muffle furnace at 550˚C. The formation of amorphous silica was confirmed by XRD machine and the pattern obtained is shown in Figure 1. It shows the characteristic peak at around 22 degrees con- firming the formation of amorphous silica. In order to perform ART samples of ARCS made at various molar ratios of Si/Ca were soaked in 200 ml of HCl and H2SO4 each for a retention period of 4 hours. It was found that weight losses of ARCS in case of HCl were similar to H2SO4. Table 1 shows the ART results for HCl. It is interesting to note that all samples calcined at less than 800˚C were dissolved in HCl solution nonetheless those samples were calcined above 800˚C showed resis- tivity against HCl at room temperature. It is also inter- esting to note that by increasing the calcination tem- perature the resistivity against acid increases. It can also be seen from Table 1 that by increasing the molar ratio of Si/Ca, the weight loss of ARCS becomes zero at and 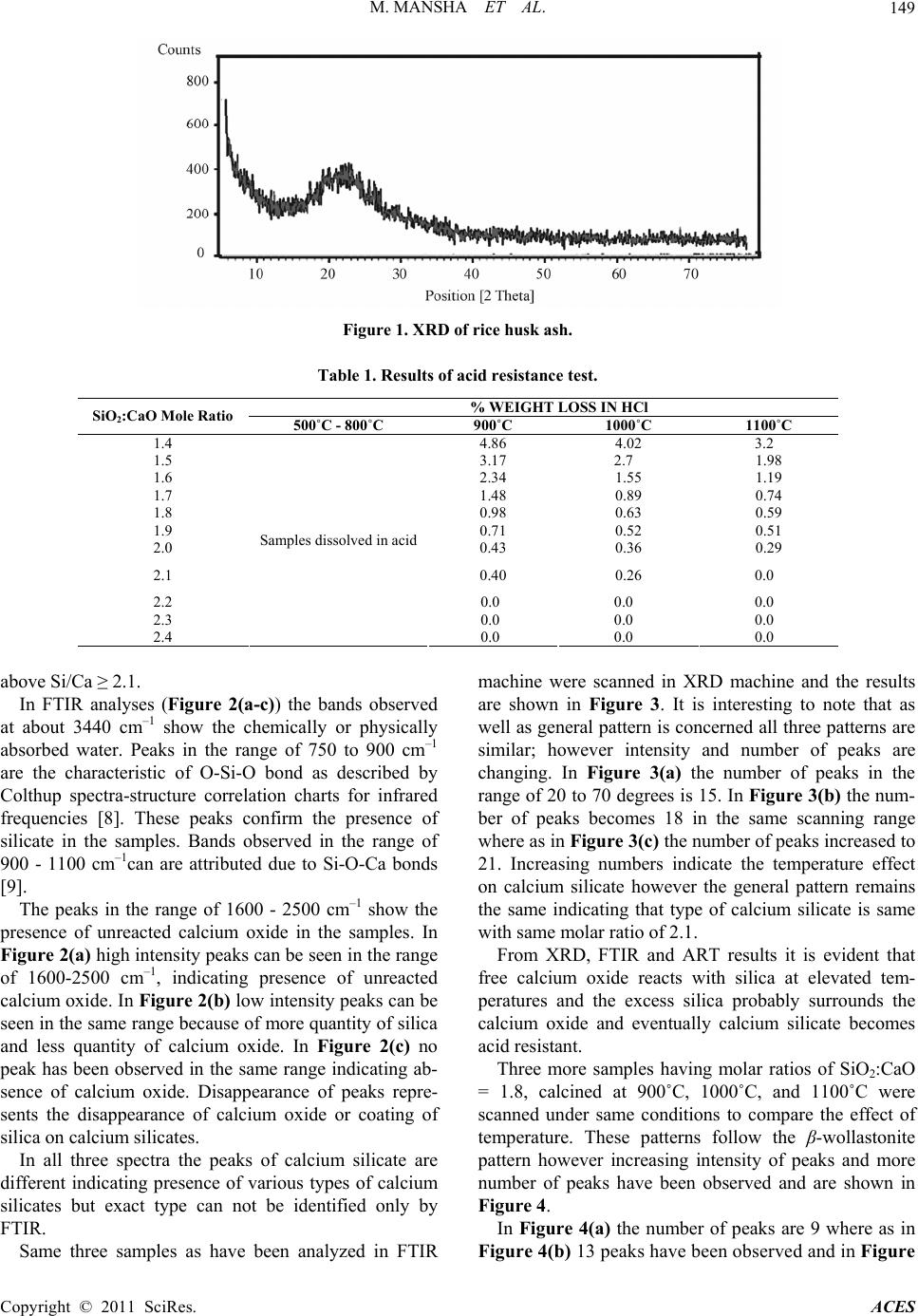 M. MANSHA ET AL. Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ACES 149 Figure 1. XRD of rice husk ash. Table 1. Results of acid resistance test. % WEIGHT LOSS IN HCl SiO2:CaO Mole Ratio 500˚C - 800˚C 900˚C 1000˚C 1100˚C 1.4 4.86 4.02 3.2 1.5 3.17 2.7 1.98 1.6 2.34 1.55 1.19 1.7 1.48 0.89 0.74 1.8 0.98 0.63 0.59 1.9 0.71 0.52 0.51 2.0 0.43 0.36 0.29 2.1 0.40 0.26 0.0 2.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 2.3 0.0 0.0 0.0 2.4 Samples dissolved in acid 0.0 0.0 0.0 above Si/Ca ≥ 2.1. In FTIR analyses (Figure 2(a-c)) the bands observed at about 3440 cm–1 show the chemically or physically absorbed water. Peaks in the range of 750 to 900 cm–1 are the characteristic of O-Si-O bond as described by Colthup spectra-structure correlation charts for infrared frequencies [8]. These peaks confirm the presence of silicate in the samples. Bands observed in the range of 900 - 1100 cm–1can are attributed due to Si-O-Ca bonds [9]. The peaks in the range of 1600 - 2500 cm–1 show the presence of unreacted calcium oxide in the samples. In Figure 2(a) high intensity peaks can be seen in the range of 1600-2500 cm–1, indicating presence of unreacted calcium oxide. In Figure 2(b) low intensity peaks can be seen in the same range because of more quantity of silica and less quantity of calcium oxide. In Figure 2(c) no peak has been observed in the same range indicating ab- sence of calcium oxide. Disappearance of peaks repre- sents the disappearance of calcium oxide or coating of silica on calcium silicates. In all three spectra the peaks of calcium silicate are different indicating presence of various types of calcium silicates but exact type can not be identified only by FTIR. Same three samples as have been analyzed in FTIR machine were scanned in XRD machine and the results are shown in Figure 3. It is interesting to note that as well as general pattern is concerned all three patterns are similar; however intensity and number of peaks are changing. In Figure 3(a) the number of peaks in the range of 20 to 70 degrees is 15. In Figure 3(b) the num- ber of peaks becomes 18 in the same scanning range where as in Figure 3(c) the number of peaks increased to 21. Increasing numbers indicate the temperature effect on calcium silicate however the general pattern remains the same indicating that type of calcium silicate is same with same molar ratio of 2.1. From XRD, FTIR and ART results it is evident that free calcium oxide reacts with silica at elevated tem- peratures and the excess silica probably surrounds the calcium oxide and eventually calcium silicate becomes acid resistant. Three more samples having molar ratios of SiO2:CaO = 1.8, calcined at 900˚C, 1000˚C, and 1100˚C were scanned under same conditions to compare the effect of temperature. These patterns follow the β-wollastonite pattern however increasing intensity of peaks and more number of peaks have been observed and are shown in Figure 4. In Figure 4(a) the number of peaks are 9 where as in Figure 4(b) 13 peaks have been observed and in Figure 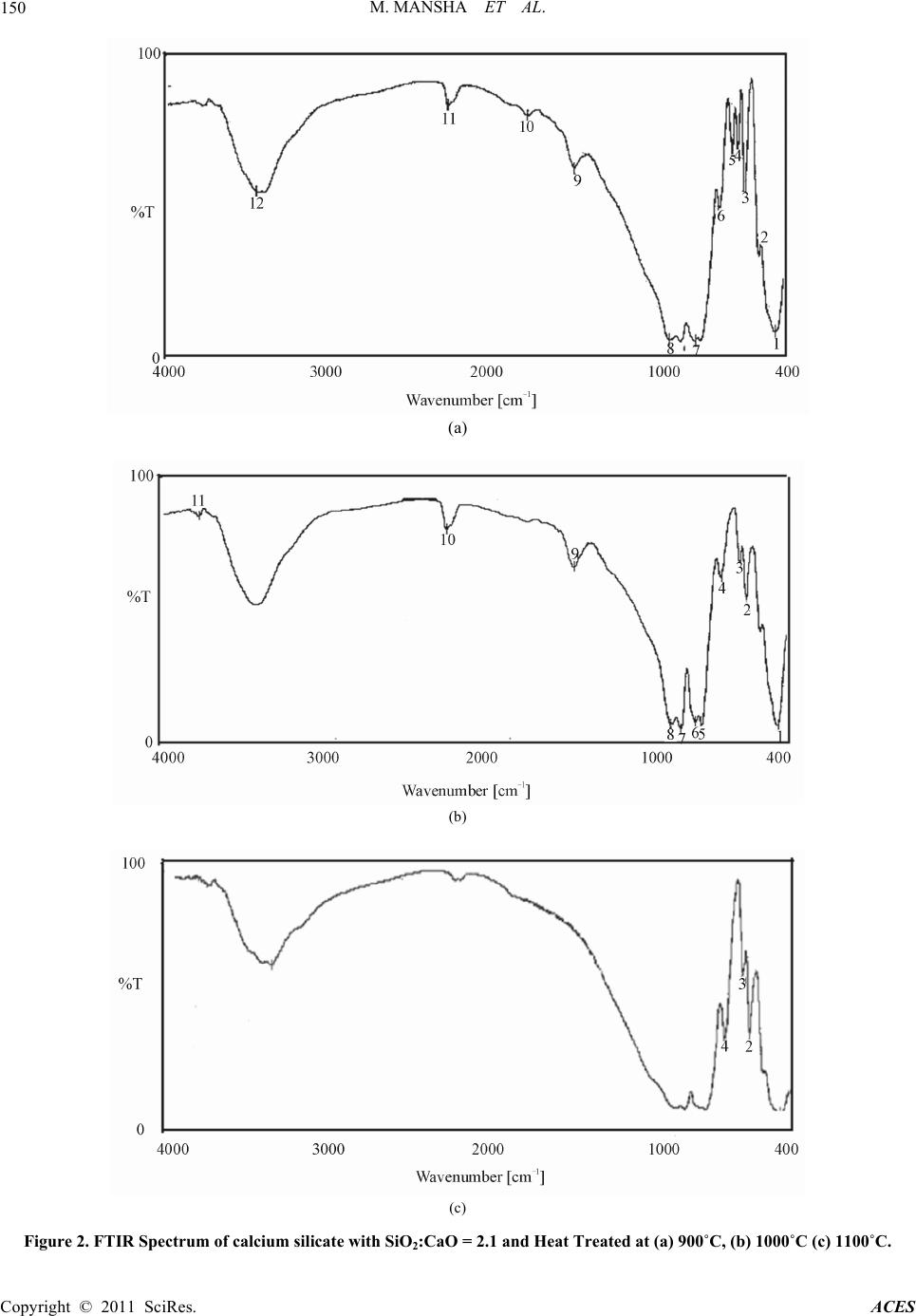 M. MANSHA ET AL. Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ACES 150 (a) (b) (c) Figure 2. FTIR Spectrum of calcium silicate with SiO2:CaO = 2.1 and Heat Treated at (a) 900˚C, (b) 1000˚C (c) 1100˚C.  M. MANSHA ET AL. Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ACES 151 Figure 3. XRD pattern of calcium silicate with SiO2:CaO = 2.1, calcined at (a) 900˚C (b) 1000˚C and (c) 1100˚C. (a) (a) (b) (c) 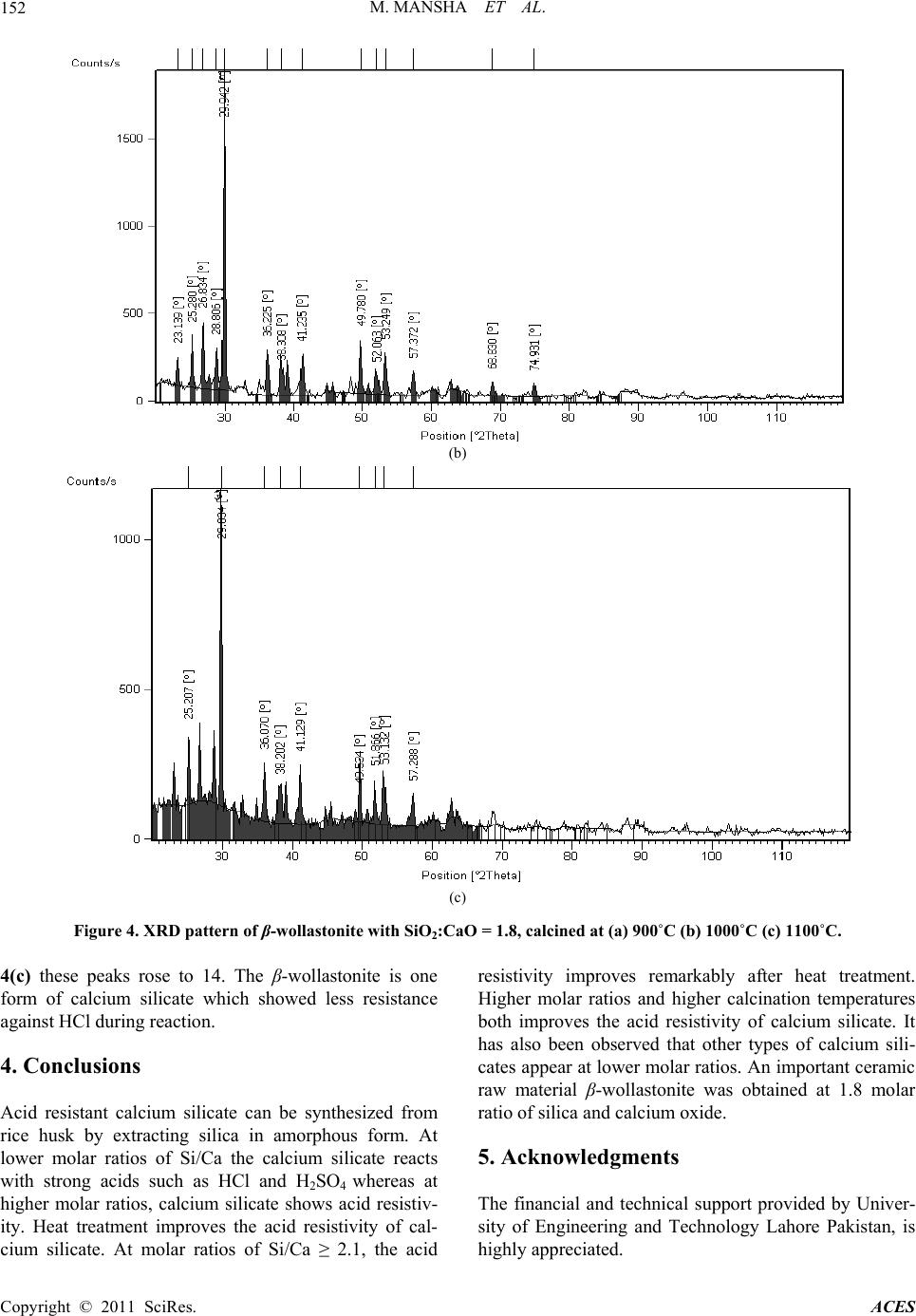 M. MANSHA ET AL. Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ACES 152 (b) (c) Figure 4. XRD pattern of β-wollastonite with S iO 2:CaO = 1.8, calcined at (a) 900˚C (b) 1000˚C (c) 1100˚C. 4(c) these peaks rose to 14. The β-wollastonite is one form of calcium silicate which showed less resistance against HCl during reaction. 4. Conclusions Acid resistant calcium silicate can be synthesized from rice husk by extracting silica in amorphous form. At lower molar ratios of Si/Ca the calcium silicate reacts with strong acids such as HCl and H2SO4 whereas at higher molar ratios, calcium silicate shows acid resistiv- ity. Heat treatment improves the acid resistivity of cal- cium silicate. At molar ratios of Si/Ca ≥ 2.1, the acid resistivity improves remarkably after heat treatment. Higher molar ratios and higher calcination temperatures both improves the acid resistivity of calcium silicate. It has also been observed that other types of calcium sili- cates appear at lower molar ratios. An important ceramic raw material β-wollastonite was obtained at 1.8 molar ratio of silica and calcium oxide. 5. Acknowledgments The financial and technical support provided by Univer- sity of Engineering and Technology Lahore Pakistan, is highly appreciated.  M. MANSHA ET AL. Copyright © 2011 SciRes. ACES 153 6. References [1] V. P. Della, I. Kuhn and D. Hotza, “Rice Husk Ash as an Alternate Source for Active Silica Production,” Materials Letters, Vol. 57, No. 4, 2002, pp. 818-821. doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(02)00879-0 [2] Q. Yu, K. Sawayama, S. Sugita, M. Shoya and Y. Isojima, “The Reaction between Rice Husk Ash and Ca(OH)2 So- lution and the Nature of Its Product,” Cement and Con- crete Research, Vol. 29, No. 1, 1999, pp. 37-43. doi:10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00172-0 [3] D. G. Nair, A. Fraaij, A. A. K. Klaassen and A. P. M. Kentgens, “A Structural Investigation Relating to the Pozzolanic Activity of Rice Husk Ashes,” Cement and Concrete Research, Vol. 38, No. 6, 2008, pp. 861-869. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.10.004 [4] D. An, Y. Guo, Y. Zhu and Z. Wang, “A Green Route to Preparation of Silica Powders with Rice Husk Ash and Waste Gas,” Chemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 162, No. 2, 2010, pp. 509-514. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2010.05.052 [5] S. Tsunematsu, H. Yamada, E. Abe and K. Inoue, “Method for Preparation of Acid Resistant Calcium Silicate,” US Patent No. 5750038, 1998. [6] P. Chindarprasirt and P. Kanchanda, “Sulfate Resistance of Blended Cements Containing Fly Ash and Rice Husk Ash,” Construction and Building Materials, Vol. 21, No. 6, 2007, pp. 1356-1361. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.10.005 [7] S. Tsunematsu, H. Yamada, K. Kimura and K. Inoue, “Improvement of Acid Resistance of Calcium Silicate by Thermal Treatment,” Cement and Concrete Research, Vol. 34, No. 4, 2004, pp. 717-720. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.09.010 [8] D. L. Palva, G. M. Lampman, G. S. Krlz and J. R. Vy- vyan, “Introduction to Spectroscopy,” Brooks/Cole, Cen- gage Learning, Belmont, 2009. [9] A. Meiszterics and K. Sinko, “Sol-Gel Derived Calcium Silicate Ceramics,” Colloids and Surfaces A, Vol. 319, No. 1-3, 2008, pp. 143-148. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.08.021 |

