World Journal of Engineering and Technology
Vol.03 No.03(2015), Article ID:60543,7 pages
10.4236/wjet.2015.33C041
Asymptotic Stability of Gaver’s Parallel System Attended by a Cold Standby Unit and a Repairman with Multiple Vacations
Abdukerim Haji
College of Mathematics and System Sciences, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
Email: abdukerimhaji@sina.com.cn


Received 13 August 2015; accepted 15 October 2015; published 22 October 2015

ABSTRACT
We investigate Gaver’s parallel system attended by a cold standby unit and a repairman with multiple vacations. By analysing the spectral distribution of the system operator and taking into account the irreducibility of the semigroup generated by the system operator we prove that the dynamic solution converges strongly to the steady state solution. Thus we obtain asymptotic stability of the dynamic solution of the system.
Keywords:
Gaver’s Parallel Pystem, C0-Semigroup, Irreducibility, Asymptotic Stability

1. Introduction
Repairable system is not only a kind of important system discussed in reliability theory but also one of the main objects studied in reliability mathematics. ”Repairable” means that if a failure in the system occurs it can be repaired and then the system works normally again. The Gaver’s Parallel system, as one of the classical repairable systems in reliability theory, has been given much attention in previous literatures, see [1]-[3]. In [4], the authors studied Gaver’s parallel system attended by a cold standby unit and a repairman with multiple vacations and obtained some reliability expressions such as the Laplace transform of the reliability, the mean time to the first failure, the availability and the failure frequency of the system by using the supplementary variable method and the generalized Markov progress method as well as the Laplace-transform technique. In [4], the authors used the dynamic solution and its asymptotic stability in calculating the availability and the reliability. But they did not discuss the existence of the dynamic solution and the asymptotic stability of the dynamic solution. In [5], we proved the well-posedness and the existence of a unique positive dynamic solution of the system by using 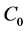 - semigroup theory of linear operators from [6] and [7]. In this paper, we prove that the dynamic solution converging to its static solution in the sense of the norm using the stochastic matrix and irreducibility of the corresponding semigroup, thus we obtain the asymptotic stability of the dynamic solution of this system.
- semigroup theory of linear operators from [6] and [7]. In this paper, we prove that the dynamic solution converging to its static solution in the sense of the norm using the stochastic matrix and irreducibility of the corresponding semigroup, thus we obtain the asymptotic stability of the dynamic solution of this system.
The system can be described by the following partial differential equations (see [4]).
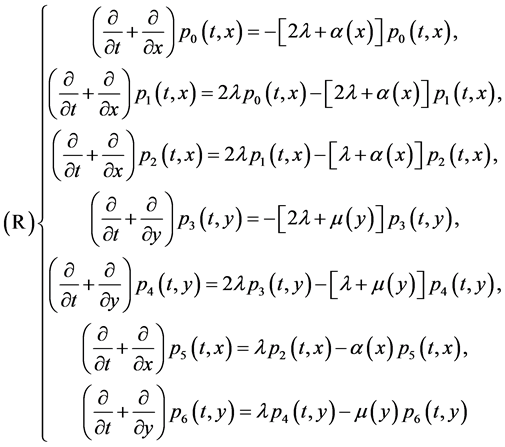
with the boundary condition
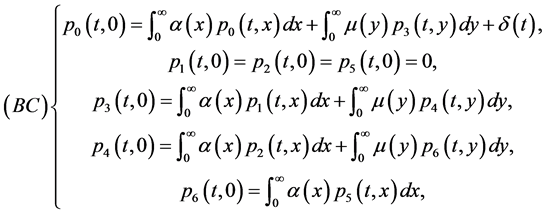
and the initial condition
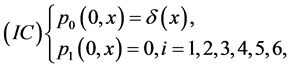 where
where 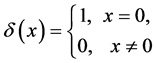
Here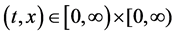 ;
; 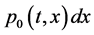 gives the probability that at time t two units are operating, one unit is under standby, the repairman is in vacation, the system is good and the elapsed repair time lies in
gives the probability that at time t two units are operating, one unit is under standby, the repairman is in vacation, the system is good and the elapsed repair time lies in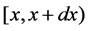 ;
; 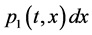 represents the probability that at time
represents the probability that at time 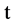 two units are operating, one unit is waiting for repair, the repairman is in vacation, the system is good and the elapsed repair time lies in
two units are operating, one unit is waiting for repair, the repairman is in vacation, the system is good and the elapsed repair time lies in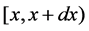 ;
; 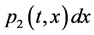 represents the probability that at time
represents the probability that at time 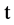 two unit is operating, one unit is waiting for repair, the repairman is in vacation, the system is good and the elapsed repair time lies in
two unit is operating, one unit is waiting for repair, the repairman is in vacation, the system is good and the elapsed repair time lies in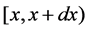 ;
; 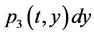 represents the probability that at time
represents the probability that at time 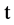 two units are operating, one unit being repaired, the system is good and the hours that the failed unit has been repaired lies in
two units are operating, one unit being repaired, the system is good and the hours that the failed unit has been repaired lies in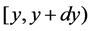 ;
; 











Throughout the paper we require the following assumption for the vacation rate function 

General Assumption 1.1: The functions 

2. The Abstract Cauchy Problem
To apply semigroup theory we use the same method in [5] to rewrite in this section the system



and

To define the system operator 


To model the boundary conditions (BC) we take the “boundary space” 


and

where
If the system operator 


Then the above equations 


By a direct computation we obtain the explicit form of the elements in 
Lemma 2.1: For

We define the operator 
And then using ([8], Lemma 1.2), the domain 


Moreover, since is surjective,
is invertible for each
and call it “Dirichlet operator”.
We can give the form of 
Lemma 2.2: For each


where
For



where
To prove the asymptotic stability of the dynamic solution of the system we apply the following result, which can be found in [9].
Lemma 2.3 (The characteristic equation): Let
(i)
(ii) If 



We obtained the following results in [5].
Theorem 3.4: The operator 


Theorem 3.5: The associated abstract Cauchy problem 
Theorem 3.6: The system 


3. The Asymptotic Stability of the Dynamic Solution
In this section, we will investigate the asymptotic stability of the dynamic solution of the system. We show first the following lemmas:
Lemma 3.1: For the operator 

Proof: By a straightforward calculation we see that the matrix 


Using Lemma 2.3 (ii) we can show that 0 is the only spectral value of A on the imaginary axis.
Lemma 3.2: The spectrum 

Proof: If






We can express the resolvent of 


Lemma 3.3: If

Lemma 3.4: The semigroup 

Proof: We can see as in ([9], Lemma 3.9) that 



With this at hand one can then show the convergence of the semigroup to a one dimensional equilibrium point, see ([9], Th. 3.11).
Theorem 3.5: The space 
where 



Corollary 3.6: For all

where
Applying the above corollary, we now obtain our main result as follows.
Corollary 3.7: The dynamic solution of the system 

where 

Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11361057).
Cite this paper
Abdukerim Haji, (2015) Asymptotic Stability of Gaver’s Parallel System Attended by a Cold Standby Unit and a Repairman with Multiple Vacations. World Journal of Engineering and Technology,03,277-283. doi: 10.4236/wjet.2015.33C041
References
- 1. Gaver, D.P. (1963) Time to Failure and Availability of Paralleled System with Repair. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 12, 30-38. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TR.1963.5218202
- 2. Dhillon, B.S. and Anude, O.C. (1993) Common-Cause Failure Analysis of a Parallel System with Warm Standby. Microelectronics Reliability, 33, 1321-1342. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0026-2714(93)90133-j
- 3. Vanderperre, E.J. and Makhanov, S.S. (2002) On Gaver’s Parallel System Sustained by a Cold Standby Unit and Attended by Two Repairmen. Operations Research Letters, 30, 43-48. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6377(02)00106-2
- 4. Yue, D.Q., Zhu, J.L., Qin, Y.L. and Li, C.Y. (2006) The Gaver Parallel System Attended by a Cold Standby Unit and a Repairman with Multiple Vacations. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 6, 59-68.
- 5. Haji, A. and Yunus, B. (2015) Well-Posedness of Gaver’s Parallel System Attended by a Cold Standby Unit and a Repairman with Multiple Vacations. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 3, 821-827. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.37101
- 6. Engel, K.-J. and Nagel, R. (2000) One-Parameter Semigroups for Linear Evolution Equations. Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 194, Springer-Verlag.
- 7. Nagel, R. (1986) One-Parameter Semigroups of Positive Operators. Springer-Verlag. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BFb0074922
- 8. Greiner, G. (1987) Perturbing the Boundary Conditions of a Generator. Houston J. Math., 13, 213-229.
- 9. Haji, A. and Radl, A. (2007) A Semigroup Approach to Queueing Systems. Semi-group Forum, 75, 609-623. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00233-007-0726-6




































