Health
Vol. 4 No. 1 (2012) , Article ID: 16988 , 6 pages DOI:10.4236/health.2012.41006
Characteristics of anxiety among primary and middle school teachers: A content-based approach to state anxiety
![]()
Center for Psychological Health Research & School of Psychology, Southwest University, Chongqing, China; *Corresponding Author: wlj0407@swu.edu.cn
Received 25 October 2011; revised 27 November 2011; accepted 6 December 2011
Keywords: Primary and Secondary Teachers; State Anxiety; Characteristics
ABSTRACT
Anxiety has become one of the major psychological problems which harass people in modern times; this problem is particularly obvious with primary and middle school teachers. Based on the contents of anxiety, the self-compiled Teachers’ State Anxiety Questionnaire (TSAQ) was used to investigate the effective of 1930 subjects in seven regions of China through stratified random sampling methodology. The results show that that the sense of anxiety for satisfaction and control is higher in male teachers; and the sense of teachers’ anxiety for satisfaction and conflict is severe in the key middle school; and the sense of conflict anxiety in the married teachers is the highest; the anxiety in all are high in teachers with poor physical health and main teacher as well as the teachers with poor economic situation in their family. The feasibility of measures to improve the teachers’ state anxiety in primary and middle school should be considered to enhance the level of teachers’ mental health, work efficiency and quality of life.
1. INTRODUCTION
With increasing competition in modern society, people experience the increasing pressure and confusion, anxiety and other psychological problems has become a serious issue. In real life, about 30% to 40% of people experience the disturbance of anxiety and distress (BellDolan & Wessler, 1994) [1]. The incidence of anxiety is the highest in all the psychological problems, (Kasri, Agoub, Gnaoui, Berrada, Moussaoui, 2007) [2]. An investigation from Social Research Center “China Youth Daily,” has shown that anxiety has become a normalstate of life for modern people: 34% of respondents often caught by anxiety, 62.9% of respondents are occasional anxiety; only 0.8% of respondents said they have never experienced anxiety (Xie, 2006) [3]. Apparently, the anxiety has become a major psychological problem which troubled the normal life of modern people.
Teacher is one of the highest pressure profession (Håseth K., 2005 [4]; Fang & Liang, 2009 [5]), but the mental health of teachers has not yet attracted enough attention all the time, many teachers because of the pressure from work, life or personal development have bring them the sense of loneliness, anxiety and disappointment. Especially in the primary and middle schools, the various contradictions from life and work take teachers in a dilemma; education faces many difficulties. A survey shows that 83.01% of middle school teachers work for more than 9 hours in their school, of which 30.82% of the teachers working 12 hours or more each day in their school; the teacher of graduating class work over 80 hours per week, not only they are not rest on Saturdays and Sundays, they hardly have a rest even on statutory holidays (Peng, 2007) [6]. Teachers of primary and middle school not only have to meet the challenges of education reform and social development, but they also have to face the multiple pressures coming from educational institutions, students, parents, community. Excessive pressure inevitable make them in confusion, and even cause anxiety, this anxiety in turn affect their quality of life, productivity and mental health. Therefore, focusing on teachers’ anxiety in primary and middle school, improving teacher ability of anti-anxiety should be given sufficient attention to the current reform of basic education in China.
State anxiety is an anxiety state which happens occasionally, manifested in specific situations, short duration, and intensity varied with obvious physical reaction. It is the individual’s response to the changing environmental conditions or environmental stress. According to Spielberger’s study, state anxiety is the emotional flow of individuals living in a temporary cross-section, it is caused by the subjective stress, anxiety, nervousness, fear and other psychological feelings and formed by the activation and wake-up of the autonomic nervous system (Gaudry, Vagg & Spielberger, 1975) [7], that is a phenomenon which on the basis of knowledge or experience, the individuals apprecive the current threat or danger. The definition has been generally recognized and accepted by Scholars both at home and abroad. Based on this definition, we may define the teachers’ state anxiety as: it is the anxiety that caused by specific situation on teachers’ work, short duration, intensity but rapidly changes. It is because the teachers lack the sense of control for outside or inside the teaching environment, teaching events and so on; It is because they lack the sense of satisfaction for life events, material and spiritual conditions and so on, or it exists the sense of conflict in the aspect of teachers’ role, self-profession which caused by the fear, tension, anxiety in their psychology, a series of physical discomfort and behavioral coping responses. Teachers who are often in a state of anxiety will decrease their physical and psychological function and maladjust their behavioral function.
There are few researches aim at teachers’ state anxiety, there are some studies that discuss the behaviour of teachers’ anxiety in different subjects and the phrase of age, such as Alasheev & Bvkov (2002) [8], Bayani & Kocheki (2007) [9], they discuss about the teachers’ irritable mood, happiness and the occurrence of professional crisis and so on. However, the research of teachers’ anxiety at home mainly gather on teachers in urban and suburb areas, sports teachers, and compare the differences of teachers’ anxiety in different qualifications, and their use of tools is the “State-Trait Anxiety Inventory,” or “selfrating anxiety scale.” The research of the sources of stress on teacher’s professional anxiety owe the main cause of the teacher’s anxiety to their overburdened work, their students’ poor behavior, role conflict and so on (KovessMasfe’ty, Rios-Seidel, & Sevilla-Dedieu, 2007 [10]; Skaalvik & Skaalvik, 2010 [11]). The current study did not clearly define the state anxiety of teachers, nor use the specific scale for the state anxiety of teachers, there are two shortcomings because of them, one is that the investigation only aims at the anxiety symptoms, making it impossible to distinguish the susceptibility of anxiety from the experience of emotional anxiety, besides, it is difficult to reflect the group differences of resulting the anxiety.
Therefore, using Teachers’ State Anxiety Questionnaire (TSAQ) whose theme is anxiety, a large-scale of investigations on primary and middle school teachers’ state anxiety are made in seven regions of our country, we desire to make a further discussion on the character of state anxiety in China’s primary and middle school teachers, and provide strategies and methods to resolve this problem.
2. METHOD
2.1. Participants
We use the stratified random sampling method, take China’s seven region of 26 key middle school, ordinary middle schools and primary schools about 2360 people to be tested, collect 2093 pieces of the filled questionnaires, and the collected rates is 88.69%; eliminate 163 pieces of invalid questionnaires, remain 1930 pieces of valid questionnaires, and the effective rate is 81.78%.
2.2. Measures
The self-compiled TSAQ composed by the 30 problem items, it adopts the four-point scoring system, the form of one in four choice investigation. TSAQ is divided into five first-order factors; there are Low agreement between the work and the reward, Low agreement between the self-desired goals and the results, Conflict of professional self, Conflict between teacher role and family role, and Sense of control. The self-compiled TSAQ which the α coefficient is 0.946, possesses high reliability and validity; the confirmatory factor analysis shows that the questionnaire has good construct validity; it is associated Zung prepared Self-Rating Anxiety Scale and the Spielberger prepared State Anxiety Scale with the Pearson correlation of 0.425 and 0.433, Spearman correlation of 0.440 and 0.447, has good criterion validity.
There are two differences between TSAQ and other state anxiety scale: in its structure, it rewards the structure of the primary and middle school teachers’ state anxiety as a multidimensional structure; while prepare the content base on reasons that cause the teachers’ state anxiety.
3. RESULTS
3.1. The General Situation
In order to review the basic situation of primary and middle school teachers’ states anxiety, we collect the average and standard deviation of statistics on participating the survey of 1930 teachers in primary and middle school teachers’ state anxiety and the various factors. The highest score is 4 points; the lowest is 1 point, moderate critical value is 2.5 points. Due to various factors including the different number of items, it is impossible to directly compare the average and standard deviation of the whole score, so it shows only the factor score of average and standard deviation after dealing with the average terms. See Table 1.
From the collectivity of primary and middle school teachers in state anxiety and the distribution of various
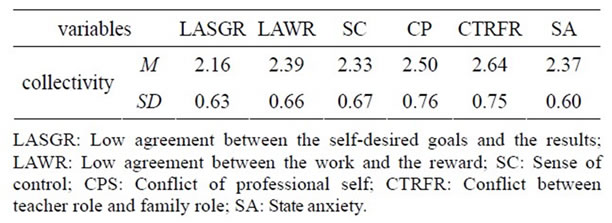
Table 1. Primary and middle school teachers’ state anxiety and factors of average and standard deviation.
mean factors, Conflict between teacher role and family role get the highest score (M = 2.638), Low agreement between the work and the reward is the lowest (M = 2.162).
3.2. Differences in Gender
In gender, the results of independent sample t-test shows that male teachers get higher scores than female teachers in state anxiety and various factors.
3.3. Differences in School Type
The school type, the one factor results of ANOVA shows that except the factors of Sense of control, teachers in different types of primary and middle school, there are significant differences either in overall state anxiety or other levels of factors. The further multiple comparisons find that: for the overall state anxiety, the key middle school teachers are obvious higher than ordinary middle school teachers and primary school teachers (both Sig. = 0.000), it is not obvious between ordinary middle school teachers and primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.507); for Low agreement between the work and the reward , the key middle school teachers is obvious higher than the ordinary middle school teachers (Sig. = 0.027) and primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.000), the ordinary middle school teachers are obvious higher than primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.001); for Low agreement between the self-desired goals and the results, key middle school teachers and the ordinary middle school teachers are significantly higher than primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.000), the differences between key middle school teachers and ordinary middle school teachers (Sig. = 0.286) are not obvious; for Conflict of professional self, key middle school teachers are significantly higher than ordinary middle school teachers (Sig. = 0.000) and primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.015), the ordinary middle school teachers is obvious lower than primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.507 ); for Conflict between teacher role and family role , key middle school teachers are significantly higher than ordinary middle school teachers (Sig. = 0.000) and primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.000), and it is not obvious between ordinary middle school teachers and primary school teachers (Sig. = 0.839).
3.4. Differences of Becoming the Main Teacher
The word Whether become the main teacher, the results of independent samples t-test shows that either on the overall level of state anxiety or the level of various factors, the anxiety scores of main teachers are significantly higher than other teachers.
3.5. Differences of Subjects
We classify all the subjects in primary and middle schools, classify some of major subjects as one kind, such as Chinese, mathematics; and some others to be another kind, such as music, sports, art, etc., which is divided into eight kinds. It is found by analysis of variance test, either in the overall level of state anxiety or the level of various factors, the difference is not obvious between these groups.
3.6. Differences in Other Aspects
The differences comparison of the state anxiety and other factors in whether a teacher gets married or not, having different situation of family economy and health shows that:
1) On the groups of marriage, the married teachers are obvious higher than unmarried teachers in general state anxiety, sense of control anxiety, Conflict of professional self, Conflict between teacher role and family role; but there is no significant differences in the two groups of Low agreement between the work and the reward and the Low agreement between the self-desired goals and the results.
2) On the economic status of families, the teacher family with well economic status is significantly lower than the teacher family with medium economic status (their Sig. are respective for 0.007; 0.048; 0.004; 0.001; 0.027; 0.002) and the family with poor economic status (both Sig. are 0.000) in the overall state anxiety, Low agreement between the work and the reward, Conflict of professional self, Conflict between teacher role and family role , and the teacher family with medium economic status is significantly lower than the teacher family with poor economic status(both Sig. are 000); on the factor of Low agreement between the self-desired goals and the results and Sense of control, the teacher family with well economic status is significantly lower than the teacher family with poor economic status(both Sig. are 0.000) but it is not obvious between the teacher family with well economic status and the teacher family with medium economic status(Sig. = 0.199, Sig.= 0.182), and the teacher family with medium economic status is significantly lower than the teacher family with poor economic status (both Sig. are 0.000).
3) On the status of physical health, there exists an obvious difference on state anxiety and other factors in primary and middle school teachers. Moreover, this differrence present some consistency, that is the teacher with better physical health is significantly lower than the teachers with good health in the level of anxiety, and the teachers with good physical health is significantly lower than the teachers with poor physical health.
4. DISCUSSIONS
4.1. The General Situation
The template is designed so that author affiliations are not repeated each time for multiple authors of the same affiliation. Please keep your affiliations as succinct as possible (for example, do NOT post your job titles, positions, academic degrees, zip codes, names of building/street/district/-province/state, etc.). This template was designed for two affiliations.
We found that 52.1% of teachers in state anxiety levels are higher than the overall average score (M = 2.366), only 6.1% of teachers think that their almost complete absence of state anxiety, which average score below 1.5 points. The results is consistent with the findings of Meng Siqing, that is 59.9% of primary and middle school teachers in Tianjin represents positive on the factor of state anxiety (Meng Siqing, 2006) [12]. Therefore, the current level of state anxiety in the primary and middle school teachers is a matter of great concern. There are many reasons cause to this, and the main cause are that teachers are hard to reflect their value, overloaded work, serious conflict of teacher’s role and family role, the varying levels of students and parents of students, the school education is unable to go on in the family, the negative impact of social diversity and so on. However, the distribution of teachers’ state anxiety and other factors level is not inconsistent, the basic sequence is: Conflict between teacher role and family role (M = 2.638) > professional self conflict (M = 2.498) > Low agreement between the self-desired goals and the results (M = 2.385) > sense of control anxiety (M = 2.326) > Low agreement between the work and the reward (M = 2.162), and the differences of each groups reached a significant level. This shows that primary and middle school teachers feel the most obvious conflict and stress from different aspects in their teaching. focus on regardless of pursuit the rate of further education is the current situation, a large number of teachers spend their time with his family and their rest time in teaching, but the influence of smoothly realizing the goals of education is complex, diverse, teachers’ efforts may not be able to well translate into the improving of the students’ performance. When they have not reached to the target in a variety of efforts, teachers will come into being anxiety, irritability, guilt (to their family) and other negative emotions (Wei Qing, Gui Shiquan, 2006) [13]. Teachers’ repetitive work, the uncertainty of the results, the specificity of outcome evaluations, determining the teacher’s labor can not be able to harvest the immediate effect; the achievement of their labor can not be completely attributed to an individual teacher. In this way, teachers can hardly be matched the labor with intensity of individual value, thus a strong sense of conflict anxiety come into being.
The order of each factor also shows that the factors of low self-desirability of pay and reward is relegated to the last which shows that the imbalance sense of teachers in low self-desirability of pay and reward is not serious. The reason is that the reward is flexible in the factor of low self-desirability of pay and reward, for the reward can be material as well as mental, such as they are adored by students and their parents alike. So the conflict is not same as the sense of conflict anxiety is irreconcilable. As teachers, they can be effective to relieve anxiety by considering the relative reward in multi-angle (Zhang Dajun, 1997) [14], understanding more about mental health approach, giving up some of the irrational ideas, avoiding the psychology of pursuit the absolute fairness, it can also receive psychological counseling if condition available.
4.2. School Type, the Subjects and to Be the Head Teacher
The key middle school teachers’ state anxiety either in collectivity or the level of other factors are significantly higher than the teachers in ordinary middle school and primary school. Key middle school teachers because of their high expectations for the effect of work, they have to endure the heavy workloads, long working hours, heavy work pressure, and the furious competition.
The state anxiety level in different subjects of primary and middle school teachers do not exist significantly differences, it does not match our estimates and hypothesis. The reason is that different subjects are attached different importance by different schools and students, this make the teachers in different situation and receive different recognition and rewards. In other words, each has their own anxiety. For a simple example, music lessons are not generally taken it seriously. But the problem is that there are thousands of students in some schools but only one or two music teachers available, and these music teachers have to undertake all the music class in these school, their workload is great. In addition to music lessons is not taken seriously, the music teacher is worthless both in the eyes of students, parents or other teachers, so that they do not experience the value of their own. Having large amount of work but experience a sense of less value, which brings to a very strong state anxiety. Some teachers in major subjects such as Chinese and mathematics, the schools and students attach high importance on them, they can get the sense of satisfaction on its “high importance”, but it is because of its importance, either the schools, students or the parents of students give the high requirements in these subjects, this pressure also bring teachers a strong sense of state anxiety.
To be the main teacher has a strong positive predictive role for the state anxiety level of primary and middle school teachers. The reason is that to be the main teacher will not be reduced his other work because he is the main teacher, but add the work of a class teacher to the normal workload. This extra work not only means that he has to work more hours a day, but also be fully responsible to the students’ learning and living. It is not only need to spend a lot of time and physical strength, it also requires teachers to pay a lot of emotion, the fine arts of education and good skill to balance the mood. It is because the teachers spend too much, that their levels of state anxiety are much higher than the average teachers. Therefore, the teachers themselves should continue to explore economic and efficient working methods and ways to enhance their education art, and seek to achieve a multiplier effect in their education; it may be capable to deal with this overload, high-pressure work.
4.3. Gender, Family Economic Status, Health Condition and Marriage
The difference of gender is significantly different on the level of state anxiety and other factors in primary and middle school teachers. This is similar to the research results of Yang et al. (2009) [15] on the quality life of China’s primary and middle school teachers and their professional pressure. They find that male teachers in a number of pressure targets are obvious higher than female teachers. First, from the individual perspective of achievement motivation, Chinese men have higher expectations of success, higher sense of achievement competition, higher self-evaluation of achievements and accomplishments of autonomy (Jing, 1995) [16], which determines the male possessing a higher level of evocation in a competition process, and thus cause higher levels of state anxiety. Secondly, from the perspective of seeking social support, women seek more support from society; they usually seek support from other women especially under stressful conditions. men are tend more to individualism, while women are tend more to collectivism, these tendencies also determines them to choose deal with them by themselves or seek help from others when they caught by the situations of pressure, this differences exist the consistency of cross-culture (Jordan & Revenson, 1999) [17]. It is because many teaching events are a pressure situation for primary and middle school teachers, facing these pressures events, female teachers are more willingly to seek help, while male teachers are more willingly to choose to bear themselves, so female teachers on the level of state anxiety are significant lower than male teachers.
Family economic status is a person’s backbone. If primary and middle school teachers dedicate all their time and energy to work, and can not spend more time and energy to improve the economic status, they must worry about their families, and thus increasing the level of state anxiety. In our investigation we find that the teacher family with poor economic status on the lever of state anxiety is significantly higher than the teacher family with well economic status and the teacher family with medium economic status, the teacher family with medium economic status is significantly higher than the teacher family with well economic status. This result is associated with the study results of Alasheev & Bvkov (2002) [8]. Further analysis shows that the economy situation of primary and middle school teachers is being worried, the being tested 1930 subjects, the evaluation of their family economic status as “good” are only 90 people, which take up 4.66%, the evaluation of their family economic status as “poor” are 513 people, which take up as much as 26.58%.
Different health situation is obvious different on the levels of state anxiety and other factors in primary and middle school teachers. Teachers with poor physical health condition on the levels of state anxiety are significantly higher than the teachers with better or well physical health condition, teachers with well physical health condition on the level of state anxiety is significantly higher than the teachers with better health condition. Studies have shown that teachers work itself leads many teachers suffer from various diseases, such as Xu et al. (1996) [18] found that, it has 55.98% of the teachers are suffer from ill or chronic diseases in the objects of the investigation, teachers’ poor health condition cause by the heavy workload, long working hours, lack of timely treatment in time of getting ill. The more severe report about the health condition of teachers is that the Beijing Ciji Health Center in recent years make a medical examination for 7,000 teachers from 17 schools find that only 42 of them are health, take up to the total number of 0.6% (Fang, 2009) [5]. In our investigation of 1930 primary and middle school teachers, evaluate their own physical health as poor are of 440 people, take up to 22.80%, evaluate their physical health as well are only 260 people, take up to 13.47%. Teachers’ serious overworked leads to a serious health problem, which in turn increase the level of teachers’ state anxiety, make a vicious cycle.
Married teachers are significantly higher than unmarried teachers in Sense of control and the sense of conflict anxiety, it is because the married teacher need to take care of his family, the requirement of teacher either in economy or obligation are very high, it brings the married teachers greater economic pressures and fulfill their family roles and the teacher’s role in conflict, this make the level of state anxiety absolutely high.
5. CONCLUSION
From what we have mentioned above, we can draw the following conclusions: the levels of state anxiety in primary and middle school teachers are generally high; there exists significant differences in gender school types, to be the main teacher, marriage, the family’s economic status and physical health, etc. There exists no significant difference only in subjects. This shows that to solve the problem of state anxiety in primary and middle school teachers, it needs to undertake from the evaluation mechanisms, workload, social support, economy, health and so on, we need to pay more attention to male teachers and married teachers. Besides, it is an effective way for the society or students to give teachers their mental encouragement, appreciation and recognition.
6. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The present research is sponsored by Eleventh Five-year Project in Educational Sciences in Chongqing 2010 (no. 2010-GJ-0202), Research Program for Doctorates (no. SWU0909324), the Research Program on Strategies for Fostering Juveniles’ Cognition by Chongqing Key Research Center for Arts and Humanities), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU1009089).
![]()
![]()
REFERENCES
- Bell-Dolan, D. and Wessler, A.E. (1994) Attributional style of anxious children: Extensions from cognitive theory and research on adult anxiety. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 8, 79-96. doi:10.1016/0887-6185(94)90025-6
- Kasri, N., Agoub, M., Gnaoui, S. EI, Berrada, S. and Moussaoui, D. (2007) Prevalence of anxiety disorders: A population-based epidemiological study in metropolitan area of Casablanca, Morocco. Annals of General Psychiatry, 6, 6. doi:10.1186/1744-859X-6-6
- Xie, X.L. (2006) 47.8% More are feeling “more anxious” comparing with five years ago. China Youth Daily, December 4, 2006.
- Håseth, K. (2005) Norwegian adaptation of the job stress survey. In: Spielberger, C.D. and Sarason, I.G. Eds., Stress and Emotion: Anxiety, Anger, and Curiosity. Routledge Taylor & Francis Group, New York, 293-312.
- Fang, D.L. and Luo, Y.L. (2009) A brief analysis on the harmful mental states. Journal of Chengdu University (Educational Sciences Edition), 23, 48-50.
- Peng, J.L. (2008) The universal complaint of primary and middle school teachers: “We are exausted!” http://blog.luohuedu.net/blog/30115.aspx
- Gaudry, E., Vagg, P. and Spiefberger, C.D. (1975) Validation of the state-trait distinction in anxiety research. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 10, 331-341.
- Alasheev, S.I., and Bvkov, S.Y. (2002) Teachers’ state of anxiety. Russian Education and Society, 45, 62-72. doi:10.2753/RES1060-9393441262
- Bayani, A.A. and Kocheki, A.M. (2007) Relationship between anxiety and hostility among teachers. Abstract for Poster Sessions/European Psychiatry, 22, 268. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.01.901
- Kovess-Masfe’ty, V., Rios-Seidel, C. and Sevilla-Dedieu, C. (2007) Teachers’ mental health and teaching levels. Teaching and Teacher Education, 23, 1177-1192. doi:10.1016/j.tate.2006.07.015
- Skaalvik, E.M. and Skaalvik, S. (2010) Teacher selfefficacy and teacher burnout: A study of relations. Teaching and Teacher Education, 26, 1059-1069. doi:10.1016/j.tate.2009.11.001
- Meng, S.Q. (2006) A Research on the mental health problems of Tianjin’s primary and middle school teachers and its countermeasures. Science of Social Psychology, 21, 83-90.
- Wei, Q. and Gui, S.Q. (2006) The self-maintenance of the mental health of primary and middle school teachers. Journal of the Chinese Society of Education, 9, 17-20.
- Zhang, D.J. (1997) Some theoretical issues of the social bearing capacity. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Philosophical and Social Science Edition), 4, 7- 13.
- Yang, X., Ge, C., Hu, B., Chi, T. and Wang, L. (2009) Relationship between quality of life and occupational stress among teachers. Public Health, 123,750-755. doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2009.09.018
- Jing, H.B. (1995) A research paper on the sexual differences of Chinese achievement motivation. Psychological Science, 18, 180-182.
- Jordan, C. and Revenson, T.A. (1999) Gender differences in coping with infertility: A meta-analysis. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 22, 341-358. doi:10.1023/A:1018774019232
- Xu, J.G. and Xu, Y.G. (1996) A research on the mental status of primary school teachers. Educational Science Research, 5, 23-25.

