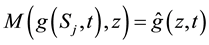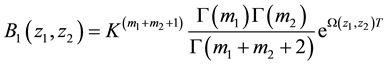Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.05(2015), Article ID:56259,9 pages
10.4236/am.2015.65074
Integral Representations for the Price of Vanilla Put Options on a Basket of Two-Dividend Paying Stocks
Sunday Emmanuel Fadugba1, Chuma Raphael Nwozo2*
1Department of Mathematical Sciences, Ekiti State University, Ado Ekiti, Nigeria
2Department of Mathematics, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria
Email: emmasfad2006@yahoo.com, *crnwozo@yahoo.com
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 8 April 2015; accepted 7 May 2015; published 12 May 2015
ABSTRACT
This paper presents integral representations for the price of vanilla put options, namely, European and American put options on a basket of two-dividend paying stocks using integral method based on the double Mellin transform. We show that by the decomposition of the integral equation for the price of American basket put option, the integral equation for the price of European basket put option can be obtained directly.
Keywords:
Black-Scholes Partial differential Equation, Double Mellin Transform, Early Exercise Premium, Vanilla Basket Put Option

1. Introduction
An option is a contingent claim that presents its holder with the right, but not obligation, to purchase a given amount of underlying asset at some future date. In practice, the underlying asset is often the price of stock, commodity, foreign exchange rate, debit instrument, stock indices or future contract. Although the history of options extended back to several decades, it was not until 1973 that the trading of option was formalized by the establishment of the Chicago Board of Options of Exchange (CBOE). This same year was also a trading point for research in the valuation of financial derivatives.
Black and Scholes [1] published their seminar work on options valuation, in which they described a mathematical frame work for finding the fair price of a European option by means of a non-arbitrage argument to describe a second order partial differential equation which governed the evolution of the option price with respect to the time to expiry and the price of the underlying asset. Since then, there has been an explosive growth, both in the trading and the study of options of various kinds. Despite the success of the Black-Scholes model on hedging and pricing contingent claims, Merton [2] noted early that options quoted on the markets differed systematically from their predicted values, which led up to questioning the distributional assumptions based on geometric wiener process. European options are options that can be exercised only at the maturity date whereas American options can be exercised on or before the expiration date. The valuation of American options has received a lot of attention because most of options traded are of the American type. The early exercise premium of American options leads to a free boundary value problem under the framework of the Black and Scholes.
Basket option is defined as an option on a collection or basket of stocks. In other words, basket options are options whose payoff depends on the value of a basket, i.e., a portfolio of assets. Equity index options and currency basket options are classical examples of basket options. However, basket options are becoming increasingly widespread in commodity and particularly energy markets. The volatility of the basket is lower than the individual volatilities of the stocks and therefore these options are popular as hedging tools. The valuation of basket options is a challenging task because the underlying value is a weighted sum of individual asset prices. The common assumption of log-normality (and hence, the famous Black-Scholes formula) cannot be applied directly, because the sum of log-normal random variables is not log-normal. The valuation problem for American option on a basket of two-dividend paying stocks leads to the solution of a multi-dimensional free boundary problem.
Panini and Srivastav [3] considered option pricing with Mellin transforms. They derived the integral equation representations for the price of European and American basket put options with non-dividend yield using the Mellin transform techniques. Basket option pricing using Mellin transforms was considered by Manuge and Kim [4] . They used the Mellin transform to derive the analytical pricing formulas and Greeks for European and American basket put options.
For mathematical background, applications of the Mellin transforms and various numerical methods for the valuation of basket options (see [5] - [11] ) just mention a few.
In this paper, we apply double Mellin transform to derive integral representations for the prices of vanilla basket put options, namely, European and American basket put options with dividend yields. The rest of the paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents the overview of the Black-Scholes partial differential equation for vanilla basket options of multi-dividend paying stocks. In Section 3, we apply the double Mellin transform method to derive the integral equations for the representations of the price of both European and American put options on a basket of two-dividend paying stocks. Section 4 concludes the paper.
2. Black-Scholes Partial Differential Equation for Vanilla Basket Options of Multi-Stocks with Dividend Yields
Consider the price of the underlying asset for the multi-stocks given by
 (1)
(1)
Equation (1) is defined on the probability space 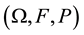 and follows the geometric wiener process given by
and follows the geometric wiener process given by
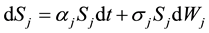 (2)
(2)
where  is a sample space,
is a sample space,  is a set of events,
is a set of events, 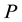 is the probability measure,
is the probability measure, 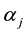 is the drift parameter,
is the drift parameter, 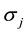 is the volatility and
is the volatility and 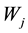 is the Brownian motion.
is the Brownian motion.
The non-homogeneous Black-Scholes partial differential equation for vanilla options on a basket of multi- stocks with dividend yield is given by
 (3)
(3)
Equation (3) can also be written as
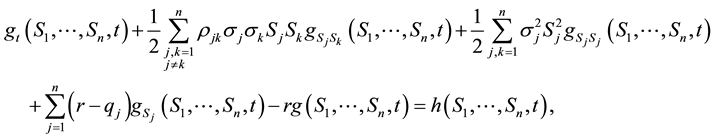 (3a)
(3a)
Suppose 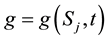 is a multi-asset options with Lipschitz payoff function
is a multi-asset options with Lipschitz payoff function . The boundary conditions imposed on (3) are reliant on the type of option (call or put). In general we let
. The boundary conditions imposed on (3) are reliant on the type of option (call or put). In general we let 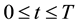 and
and 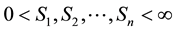 .
.
Consider a vanilla put option; recall that when the option is granted exercise rights for any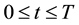 , the problem divides the price space into two regions. This early exercise boundary will depends on the payoff function of the option under consideration. The payoff function for a vanilla put option on a basket of multi-stocks is given by
, the problem divides the price space into two regions. This early exercise boundary will depends on the payoff function of the option under consideration. The payoff function for a vanilla put option on a basket of multi-stocks is given by
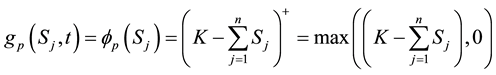
Equation (4) is called the terminal condition for vanilla put option. For the put option, the continuation region
C exists for 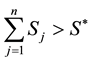
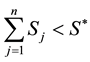
be stated as
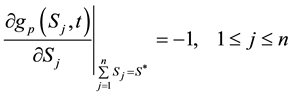
When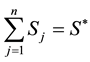
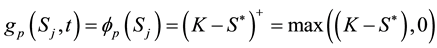
Similar to the single asset option, the payoff function is equivalent to (4). As usual the option must satisfy the condition 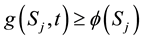
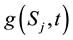
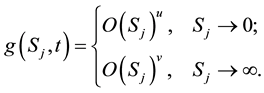
for any 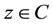
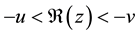
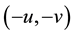
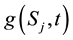
The Mellin transform of 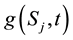
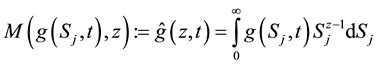
By definition, the inversion formula for the Mellin transform of (8) is given by
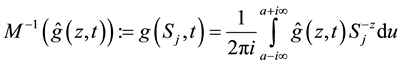
where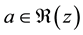
3. Integral Representations for the Price of Vanilla Put Options on a Basket of Two-Dividend Paying Stocks
This section presents the Mellin transform method for the valuation of European and American put options on a basket of two stocks with dividend yields.
3.1. Integral Representation for the Price of European Put Options on a Basket of Two-Dividend Paying Stocks
Setting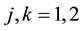
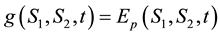
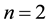
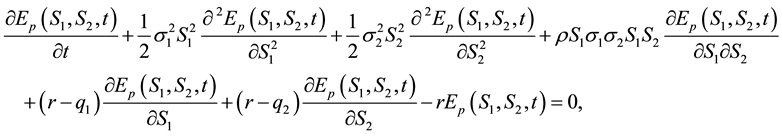
where 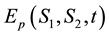
The boundary conditions for (10) are given by
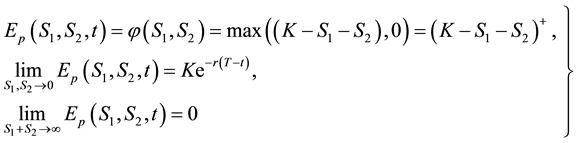
Now, we find an integral representation for the price of European put option 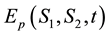
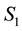
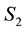
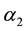
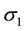
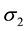
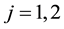
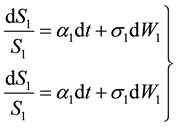
where the wiener processes 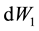
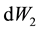
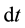
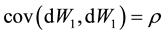
Let 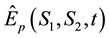
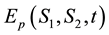
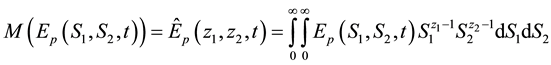
Conversely, the inversion formula of (13) is given by
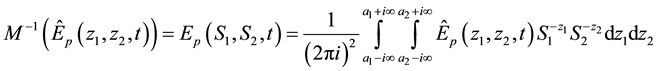
Taking the Mellin transform of (10), yields
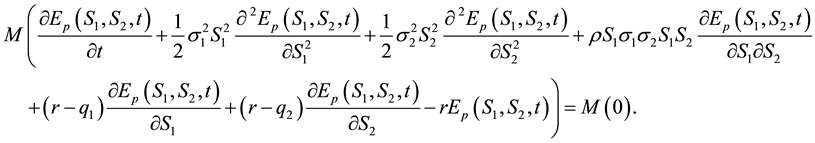
where

Substituting (16) into (15), we have
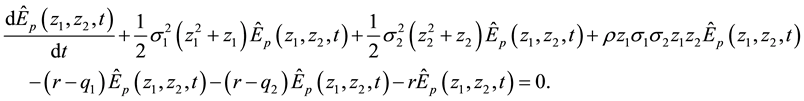
Simplifying further, (17) becomes
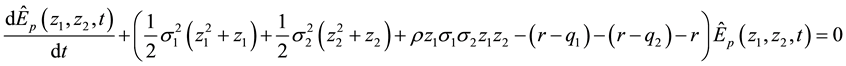
Setting
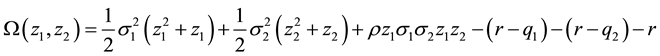
Thus, (18) becomes
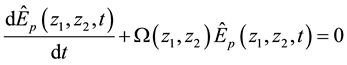
The general solution of (20) is called the complementary solution since it is homogeneous first order differential equation. The general solution is given by
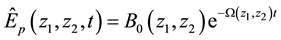
where 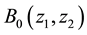
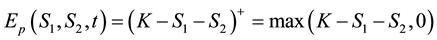
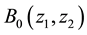
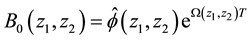
where 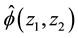
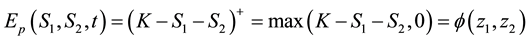
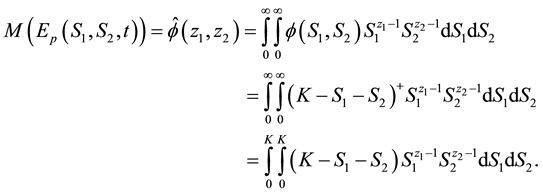
We introduce dimensionless variables
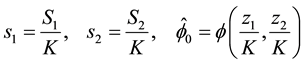
and using the localizing assumption that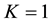
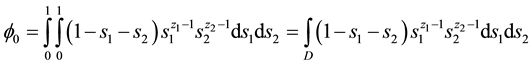
where
Let

Solving for the new domain gives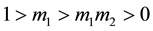
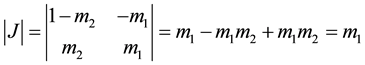
Thus,
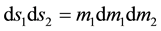
Substituting (25a) and (25c) into (25), we have that
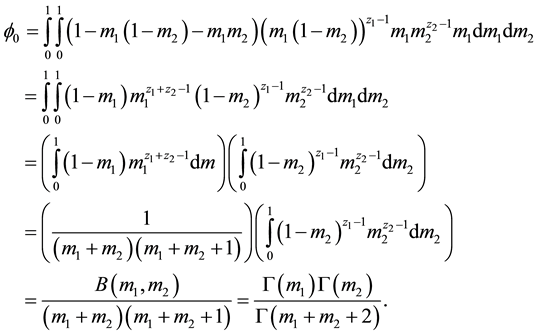
From (24), for
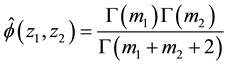
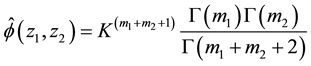
Using (22) and (26), then (21) yields
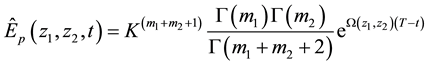
Substituting (27) into (14), we have that
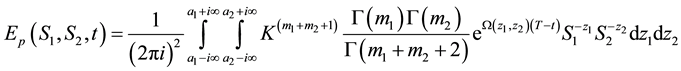
Equation (28) is the integral representation of the price of European put option on a basket of two stocks with dividend yield via the double Mellin transform method.
3.2. Integral Representation for the Price of American Put Option on a Basket of Two-Dividend Paying Stocks
Now we consider the double Mellin transforms in order to derive the expression for the price of American put option on a basket of two stocks. American put option on a basket of two stocks gives the option’s holder the right to sell the basket stocks at any time from 0 to 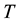
The non-homogeneous Black-Scholes partial differential equation for American put option on a basket of two stocks with dividend yield is given by
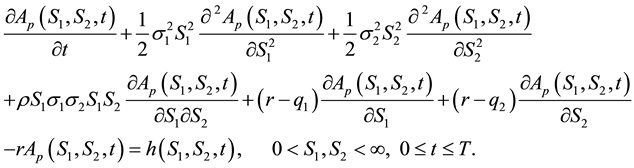
where
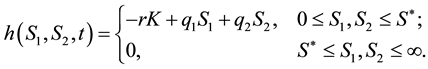
The final time condition or terminal condition is given by
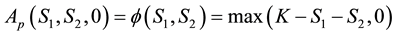
The other boundary conditions are given by
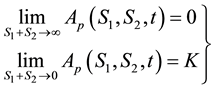
Let us assume that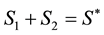
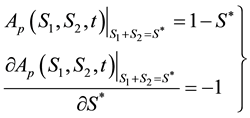
Using the same procedures of the double Mellin transform as for the case of European put option on a basket of two stocks with dividend yield. Let us denote the double Mellin transform for the price of American basket put option 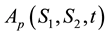
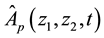
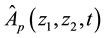
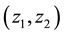
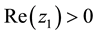
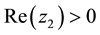
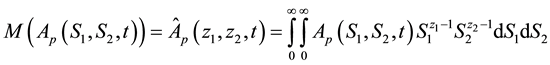
Conversely the inversion formula of the double Mellin transform is given by
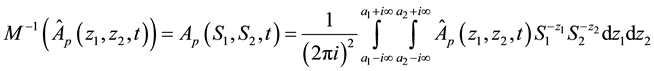
Taking the Mellin transform of (29), we have that
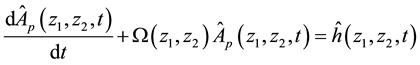
where 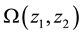
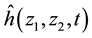
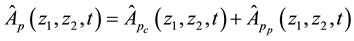
where 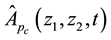
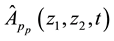
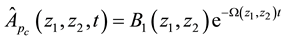
where 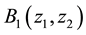
Therefore,
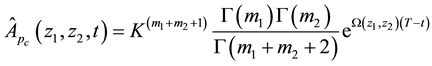
Taking the double Mellin transform of (39) yields
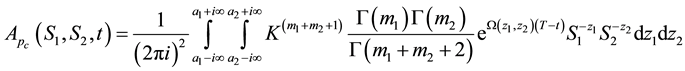
Let us consider the nonhomogeneous part of (36) whose solution is given by
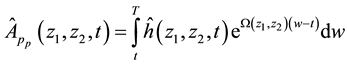
But
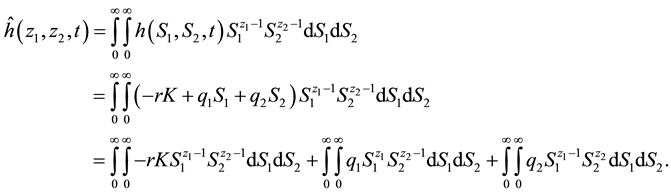
Setting
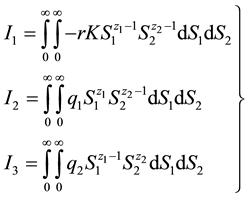
So,
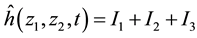
Solving (42a), we have respectively
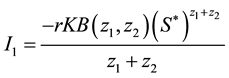
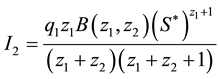
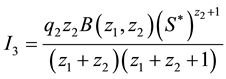
Substituting (44), (45) and (46) into (43)
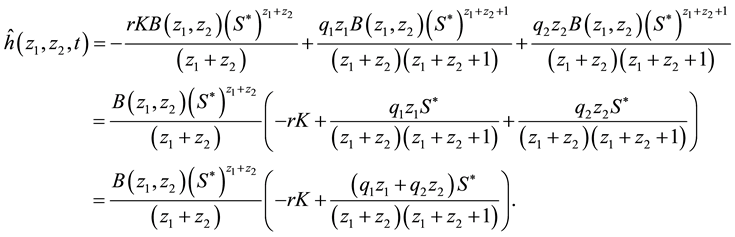
Substituting (47) into (41) yields
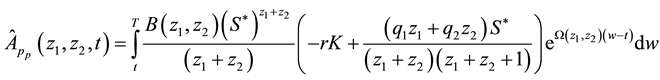
Taking the double Mellin transform of (48), we have that
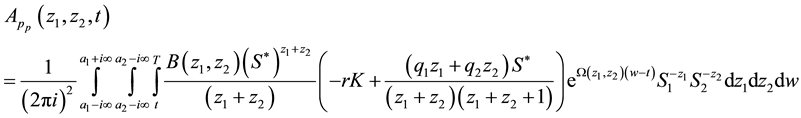
The inverse double Mellin transform of (37) is given by
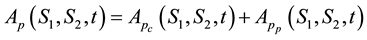
Substituting (40) and (49) into (50)
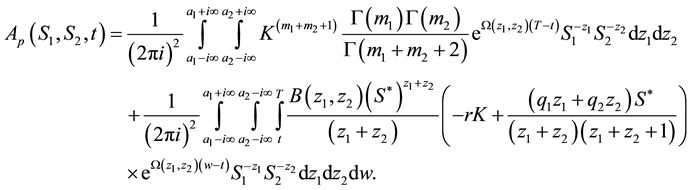
where 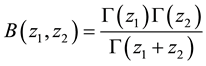
Remarks
・ The integral equation for the price of European put option on a basket of two stocks with dividend yield can be obtained directly from the price of its counterpart, the American put option on a basket of two stocks. Hence, (51) can be written as
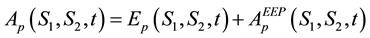
・ The second term in (51) is called early exercise premium.
・ For the case of non-dividend yield, (51) becomes
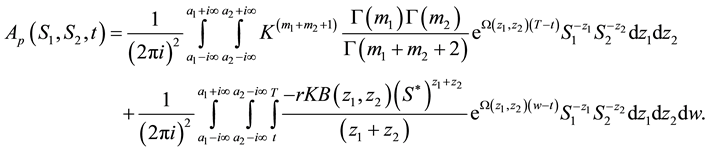
4. Conclusion
In this paper, we have considered vanilla basket put options, namely, European and American put options on a basket of two stocks with dividend yield. We used the integral method based on the double Mellin transform to derive the integral representations for the price of European and American put options on a basket of two-divi- dend paying stocks. We deduce from our results that by the decomposition of the price of American put option on a basket of two stocks, its counterpart “European put option” can be obtained directly as shown in (52).
References
- Black, F. and Scholes, M. (1973) The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities. Journal of Political Economy, 81, 637-654. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/260062
- Merton, R.C. (1973) Theory of Rational Option Pricing. Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science, 4, 141- 183. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3003143
- Panini, R. and Srivastav, R.P. (2004) Option Pricing with Mellin Transforms. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 40, 43-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2004.07.008
- Manuge, D.J. and Kim, P.T. (2015) Basket Option Pricing Using Mellin Transforms. Mathematical Finance Letter, 1, 1-9.
- AlAzemi, F., AlAzemi, A. and Boyadjiev, I. (2014) Mellin Transform Method for Solving the Black-Scholes Equation. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 97, 287-301. http://dx.doi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v97i3.3
- Boyle, P.P., Evnine, J. and Gibbs, S. (1989) Numerical Evaluation of Multivariate Contingent Claims. Review of Financial Studies, 2, 241-250. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/rfs/2.2.241
- Fadugba, S.E. (2014) The Mellin Transforms Method as an Alternative Analytic Solution for the Valuation of Geometric Asian Option. Applied and Computational Mathematics, Special Issue: Computational Finance, 3, 1-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.11648/j.acm.s.20140301.11
- Frontczak, R. and Sch bel, R. (2009) On Modified Mellin Transforms, Gauss-Laguerre Quadrature and the Valuation of American Call Options. Working Paper, Tubinger Diskussionsbeitrag, No. 320.
- Huynh, C.B. (1994) Back to Baskets. Risk, 5, 59-61.
- Sneddon, I.N. (1972) The Use of Integral Transforms. McGraw-Hill, New York.
- Turnbull, S.M. and Wakeman, L.M. (1991) A Quick Algorithm for Pricing European Average Options. The Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 26, 377-389. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2331213
- Nwozo, C.R. and Fadugba, S.E. (2014) Mellin Transform Method for the Valuation of Some Vanilla Power Options with Non-Dividend Yield. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 96, 79-104. http://dx.doi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v96i1.7
NOTES
*Corresponding author.