Creative Education
Vol.10 No.06(2019), Article ID:93068,9 pages
10.4236/ce.2019.106084
The Applying of Chemistry Laboratory Based on Maritime Culture
Dwi Laksmiwati, Eka Junaidi, Suhaili, Aliefman Hakim*
Chemistry Education Program, FKIP, University of Mataram, Mataram, Indonesia
Copyright © 2019 by author(s) and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: October 20, 2018; Accepted: June 15, 2019; Published: June 18, 2019
ABSTRACT
This research was aimed to find out the effect of maritime culture based on basic chemistry laboratory towards university students’ critical thinking ability in titration and chemistry material substance in second semester students, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, University of Mataram in academic year 2017/2018. This research was a quasi-experiment with pretest-posttest nonequivalent control group design. The population of this research includes all of the students in chemistry education major who take basic chemistry which is divided into A class and B class. The method used in determining the sample was surfeited sampling method. Samples in this research were A class students as experiment class and B class students as control class. In experiment class, some methods and activities were given related to the application of maritime culture based on basic chemistry laboratory; meanwhile in control class the method used was a kind of conventional method. Hypothesis examination in this research used T-Test. The result of T-Test statistic in the level of significance of 5% showed that Ha was accepted and Ho was abandoned. Based on the result, it can be concluded that the application of maritime culture based on basic chemistry laboratory in titration and substance chemistry material had a positive effect.
Keywords:
Maritime Culture, Basic Chemistry Laboratorium and Students’ Critical Thinking Ability

1. Introduction
Indonesia is the biggest archipelagic country (state of archipelagic) in the world, consisting of 5 big islands and 30 small archipelagos. Totally it is noted that there are about 17.504 islands: 8.651 islands already have names, 8.853 unnamed islands, and 9.842 verified islands. Strategic geographical condition outstretched as long as 5.150 km among Australia and Asia continents and also split great Indies and Pacific oceans under equator line. The Region of Indonesia covers its continent region and water territorial region covering territorial water of hinterland, territorial water of archipelago, and includes its air territorial above, undersea territory, along with ground under it, including entire properties which consist in it (UU RI No. 43 year 2008 about State regional, LNRI No. 177 year 2008). Based on that condition, besides becoming an archipelagic country, Indonesia is also conceived as a maritime state. Pursuant to section 46 of Convention of United Nations about Maritime Law (UNCLOS 1982), archipelagic country is a state which entirely consists of one or more archipelagos and can include or cover other islands. Hereinafter it is affirmed in Section 2 sentence (1) of Law Republic of Indonesia of No. 6 Year 1996 about Water Territorial of Indonesia, and State Republic of Indonesia is an archipelagic country. The entire of Indonesian sea width (Total of Indonesian Waters) is 5.8 million km2 which composes of territorial water of archipelago or Nusantara ocean (Total of Archipelagic Waters)—2.3 million km2, width of territorial water (Total of Territorial Waters)—0.8 million km2, width of ZEE Indonesia territorial water (Total of ZEE Indonesian Waters)—2.7 km2, and coastline length (Coast Line of Indonesian)—95.181 km (Working Group of Marine and Fisheries for Data and Statistics, 2009).
Seeing Indonesia as a maritime country, hence most of the society living around the coastal areas work as fisherman. Activities related to maritime life are referred as maritime culture. A culture represents the overall human being ideas which are capable to yield various masterpiece results and actions. Hence, maritime culture is the overall human being ideas which are capable to yield behavior and actions and become a property of a collective society who remains and lives near the coastal areas. Activities that relate to maritime culture are interconnected with chemical knowledge, for example fishermen do not use materials from iron while making a boat but choose wood instead. This fisherman’s habit or culture can be explained in chemistry which includes corrosion. Therefore, it is important to explore maritime culture with the content and substance from basic chemistry.
Chemistry as one of the science branch has characteristic of experiment based knowledge (Hakim, et al., 2016; Hakim & Jufri, 2017; Hakim, et al., 2018; Hakim & Jufri, 2018). In order to comprehend theory and concept in chemistry, experimental activity through practical work or laboratory work is required as direct experience. By applying this practical work or laboratory work, students can get direct experience and develop erudite attitude so that the result of students’ learning will be retrieved longer in their memory (Rahmawati, Haryani, & dan Kasmui, 2014). In the learning process which apply practical work or laboratory work method requires a lab work guidance. This laboratory work guidance is aimed to lead students in doing practical work or laboratory work and assist teacher in reaching the target of study. Through activity of experiment or practical work or lab work, students are expected to explain the relation between maritime culture with chemistry.
The result of the early observation which has been conducted at the third week of October 2017 through interview towards the first semester students of Chemistry Education Program Faculty of Teacher Training and Education University of Mataram in academic year 2017/2018. The interview comprises of questions which directs at the early understanding of student about their tendency to think critically. The questions given relate to the relation between maritime culture with chemistry. From the result of interview, many students saying that maritime culture do not have relation with chemistry. There are also students saying that maritime culture has a close relation with chemistry, however those students cannot explain more nor elaborate about the relation of maritime culture with chemistry.
The difficulties that students face in learning chemistry may come from the difficulty in comprehending special term in chemistry, difficulty in comprehending chemical concept, and difficulty of number (Anwar, 2012). Difficulty of this study can be solved by applying management of study of good chemistry especially in planning phase while studying and execution of study process so that student can improve their understanding in chemistry besides improve the ability to think critically and also can improve their learning result in general. For students, the ability to think critical is really needed especially to comprehend concepts in each of the subjects. Through the ability to think critically, student will be able to analyze problem, identifying related or relevant concepts, considering credibility of information source, choosing relevant information, analyzing argument, criticizing opinion, and evaluating solution which possible to yield the best solution. The ability to think critically must be built among students so that it will become a character in students’ life to solve all of their problems. Ability to think critically plays a vital role to student because this ability makes students able to behave rationally and choose best alternative choice for themselves (Widiyowati, 2015). Students owning ability to think critically will always ask themselves every time they face problems to determine the best for them.
Considering the importance of ability to think critically specially to chemical teacher candidate student, critical thinking ability shall be developed earlier since the first year of college life either through lecturing of theory and or practical work. Basic chemistry subject is one of the subject given to the first year college students which is being integrated to theory and practice. Chemical Practical work or lab work in basic chemistry subject is foundation to conduct further chemical practical work or lab work, so that it requires a serious handle especially to develop concept understanding, skill of science process, and students’ ability to think critically. Considering to the importance of maritime culture integration in Chemical practical work or laboratory work in basic chemistry subject, hence writer conducted a research entitled “The Influence of Applying Maritime culture based Chemical Practical work or lab work toward students’ Ability to Think Critically”.
2. Method
This Research was conducted in the Faculty of Teacher Training and Education University of Mataram in April 2018. This research used quasi experiment method. The research design used in this research is pretest-posttest nonequivalent control group design. In this research, experiment class and control class were given treatments and final test. Experiment class was given treatment by applying maritime culture based Chemical practical work or lab work, while class control was given Conventional Base Chemical practical work or lab work.
Free Variable in this research is the application of maritime culture base Chemical practical work or lab work for the experiment class and Conventional Base Chemical practical work or lab work for the class of control. Tied Variable in this research is the ability to think critically in cognative domain. Population of this research is the entire second semester students who were taking Basic Chemistry 2 Subject, in Faculty of Teacher Training and Education University of Mataram in academic year 2017/2018 consisting of 81 students and divided into become A class and B class. The sample of this research was that A class as experiment class and B class as control class. Both of these samples were taken through saturated sampling technique that is a technique to determine the sample if all of the population become the member of the sample (Sugiyono. 2012).
This research used a Test to test students’ ability to think critically as its instrument. The Test used was in the form of essay test. The Instruments which have been compiled were tested beforehand to test its validity level, in which the content of the test was tested by using Aiken’s V statistic validity test and the question items were tested using Correlation of Product Moment validity test. To test the instrument’s reliability, researcher used formula of Alpha Cronbach. Hypothesis test in this research was tested using Gain T-test. Gain T-test was conducted after data were being analyzed with test of normality and its homogeneity, while in order to know the improvement of ability to think critically was tested by using normalized Gain test.
3. Findings and Discussion
Focus of this research is the influence of applying of maritime culture based Chemical practical work or lab work towards students’ ability to think critically at the titration and chemistry element materials. The Influence of applying this kind of model of practical work or lab work can be seen from the improvement of students’ test score between the early pre-test and final post-test in cognitive domain. The execution of practical work or lab work was conducted in each class for two meetings with the first meeting about titration practical work or lab work and the second was about chemical element practical work or lab work. Besides doing practical work or lab work, presentation activity also should be done by students in the classroom. The presentation should be done by each class as many as six of times of meetings including the activity of pretest and posttest.
Result of the early data analysis pointed out to the students’ score in pretest, hence homogeneity test was conducted. From the result of calculation, it was obtained that A class and B class were homogeneous. Result of the data homogeneity test showed that A class and B class, with Fcount < Ftable (1.24 < 1.71), so that it can be assumed that class control and experiment class were homogeneous.
On the other hand, Normality test in this research used formula of chi square. Pursuant to the result of calculation, it was obtained that the value of (χ2count) pretest at experiment class was 6.01 and class control was to 9.39. Value of (χ2count) was later consulted at the value of (χ2table) within significant level of 5% that is equal to 11.07 with dk = 5, so that χ2count < χ2table meaning that the data result from pretest in both classes are normally distributed. At the posttest score, value of (χ2count) in experiment class equal to 2.85 and class control equal to 11.86. Value of (χ2count) was later consulted at the price of (χ2table) in significant level of 5% that is equal to 12.59 with dk = 6, so that χ2count < χ2table meaning that data result of pretest in both of the classes are normally distributed (Sugiyono, 2014).
Homogeneity test variation in this research used formula of F-test. Based on the calculation by using posttest score data it was obtained that value of Fcount equal to 1.29. Value of Fcount was consulted with Ftable at the counter of dk = 38 and denominator dk = 41, and it was obtained that the value of Ftable at the significant level of 5% equal to 1.69 so that value of Fcount < Ftable (1.29 < 1.69) hence variation in both of the data can be stated as homogeneous (Sugiyono, 2016).
In order to prove the hypothesis of this research, hence data result of ability think critically of students were processed by using formula of Gain T-test because in this research there are group control and experiment group which were given pretest and posttest, the examination was conducted not to examine the average score but to the difference of average score (Arikunto, 2010). Pursuant to the result of calculation, it was obtained that the value of t-count (3.10) > t-table (1.67) at the significant level of 5%. This matter indicated that statistically by applying maritime culture based Chemical practical work or lab work had positive effect to the students’ ability to think critically.
The model of maritime culture based Practical work or lab work in basic chemistry class is one of the application of practical work or lab work using materials of practical work or lab work coming from region of maritime like from the ocean. Besides, the application of this practical work or lab work also will hook therelations between cultural phenomenon of the maritime society with Science specially chemistry. Students shall no longer accept totally practical work or lab work to be executed, however students have to look for the real example from practical work or lab work which can be lifted from titration and element chemistry materials which relate to the maritime culture. Therefore, the process of practical work or lab work does not point out mostly at the researcher or lecturer, but at the student itself. This matter will create a more meaningful learning atmosphere and students’ understanding about learning materials also will be more relate either to the society’s culture or habit.
Data differences of the average score between experiment class and control class can be seen in Graph 1.
The data indicates that the average score of pretest control class was bigger than experiment class, but the average score of posttest in experiment class was bigger than control class. The result of pretest in both classes showed low average value. This low score was due to the students’ condition who were not yet master the entire titration and element chemistry subject materials though before pretest have been given by the opportunity of autodidact use of students’ text book and from internet for 10 minutes. Meanwhile at the result of posttest, the average score in both of the classes were improved. The improvement of this average score was caused by the condition in which both of the classes were given treatments of model application of practical work or lab work and students had also studied the materials besides doing practical work or lab work in laboratory at the titration and element chemistry subject materials. Pursuant to the calculation of gain test normalization, the improvement of average score at experiment class pertained significant enough (medium) however in control class pertained a low improvement.
The acquirement of mean result of posttest which high enough by applying the maritime culture based Chemical practical work or lab work model raced students to comprehend more and master the lesson together with their group and also lifted practical work or lab work which relate to society’s culture who
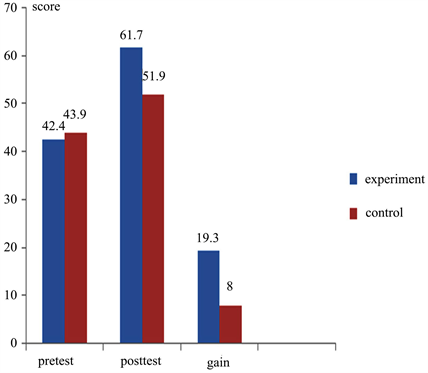
Graph 1. Difference of average score between experiment class and control class.
live in coastal area, for example society’s opinion saying that consumed salt only contain NaCl however the fact is that salt contains many mineral besides NaCl. To answer that society’s ascription, hence chemical practical work or lab work with titration concept can be applied to calculate the rate of NaCl in salt sample and seawater. Besides that, society who exists in Kalimantan also exploits cockle shell to become “kapur sirih”. When it is burned, the flame color which is yielded from combustion of the cockle shell is rose colored orange, so that the compound in the shell can be used to make “kapur sirih”. To answer the question, hence it can be lifted a chemical practical work or lab work that use flame test. With that cultural discourse of maritime culture, hence students will look for relation between chemistry with culture of maritime.
Step of maritime culture based practical work or lab work model may give positive influence to students’ ability to think critically at the third phase of this practical work or lab work model, that is at the first phase student will look for example of practical work or lab work related to element chemistry and titration as according to cultural discourse of maritime culture given by the researcher and they will present their result in front of the class, second phase, the student execute activity of practical work or lab work, and third phase that is presenting the result in front of the class. When students discuss in presentation activity, they may exchange over each other opinion and information concerning their result as according to discourse and items given by researcher and also can solve given problems. It means that, all of the students involve actively in group activity. At the presentation activity, researcher also made an assessment through observation sheet assisted by some observer, in which this observation sheet comprise ability indicator to think critically by assessing the attitude in doing presentation. This observation sheet was aimed at supporting the research data to see the ability to think critically of the students. Besides, they would get more knowledge and understanding about the items of the material because all students told their opinion and also created a more meaningful learning atmosphere.
The application of maritime culture based Chemical practical work or lab work presented an experience to learn in a pleasant group and more meaningful. Every student can converse and have a notion and also conscript their entire ability in comprehending given items and lift theme of practical work or lab work by correlating it with culture of maritime, so that the result of learning they mount would have a positive effect to their ability to think critically. The role of the researcher was only as motivator or facilitator who controlled students during the process of practical work or lab work and presentation.
According to Gasong in Aryati (2010), a learning process which takes a base on practical work or lab work make study more focus at learning experimental and pursuant to the real experience, discussion with friend later on will be obtained by new concept and idea. A learning process, base on practical work or lab work become study alternative which both for educative participant (students) to develop skill, ability to think because students are claimed to be active in solving problem, thinking creative and critical in analyzing the concept application and principles in order to have more meaningful learning. Ability to think critically and think creatively represents the essence of the target of education and become requirement to student to face the real world.
A learning process which based on practical work or lab work also give opportunity to student to design and find the knowledge, find new concepts and the new knowledge construction in mind (constructivism). Concept and new knowledge which are obtained can be integrated into theory which henceforth earns the real application in life. This matter is in line with the result of research which have been conducted by Aryati (2010) saying that by applying practical work or lab work can improve ability to think critically of the students.
The Existence of the improvement of ability to think critically indicates that the study of Chemical practical work or lab work taking a basis on maritime culture could entangle student in learning activity which needs higher level of cognitive skill so that could train student to develop a better ability to think critically. The similar opinion also stated by Nickerson in Aryati (2010) that skill to think always expand and can be learned. In the matter of learning, the development of the ability to think critically in entangling educative participant is important.
The improvement of ability to think naturally and critically of the students after applying Chemical practical work or lab work in a basis of maritime culture conducted by students have been instructed actively to develop critical thinking ability through the activity which involved perception and direct practical work or lab work.
4. Conclusion
Based on the data result of solution and research, it can be concluded that applying chemical practical work or lab work in the basis of maritime culture gave positive influence to the ability to think critically of the students at titration items and element chemistry towards second semester students of Chemistry Education Program, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, University of Mataram in academic year 2017/2018.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Cite this paper
Laksmiwati, D., Junaidi, E., Suhaili, & Hakim, A. (2019). The Applying of Chemistry Laboratory Based on Maritime Culture. Creative Education, 10, 1116-1124. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2019.106084
References
- 1. Anwar, M. (2012). Pembelajaran Aktif Kooperatif dalam Perkuliahan Kinetika Kimia untuk meningkatkan Keterampilan Generik Sains Calon Guru. Tesis. Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia. [Paper reference 1]
- 2. Arikunto, S. (2010). Prosedur Penelitian (Suatu Pendekatan Praktik). Jakarta: Rineka Cipta. [Paper reference 1]
- 3. Aryati, E. (2010). Pembelajaran Berbasis Praktikum untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis Mahasiswa. Jurnal Matematika dan IPA, 1, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.26418/jpmipa.v1i2.194 [Paper reference 3]
- 4. Hakim, A., & Jufri, A. W. (2017) Applications of Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Secondary Metabolites in Natural Product Chemistry Laboratory. In Advances in Chemistry Research. New York: NOVA Publisher. [Paper reference 1]
- 5. Hakim, A., & Jufri, A. W. (2018). Natural Products Laboratory Project: Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Piperin from Piper nigrum and Andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata. Journal of Turkish Science Education, 15, 15-28. [Paper reference 1]
- 6. Hakim, A., Andayani, Y., & Rahayuan, B. D. (2018). Isolation of Ethyl P-Methoxy Cinnamate from Kaemferia galanga L. Journal of Physics Conference Series, 2018, Article ID: 012039. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1095/1/012039 [Paper reference 1]
- 7. Hakim, A., Liliasari, Kadarohman, A., & Syah, Y. M. (2016). Improvement of Student Critical Thinking Skills with the Natural Product Mini Project Laboratory Learning. Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, 16, 315-321. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.21149 [Paper reference 1]
- 8. Rahmawati, R., Haryani, S., & dan Kasmui (2014). Penerapan Praktikum Berbasis Inkuiri Untuk Meningkatkan Keterampilan Proses Sains Siswa. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Kimia, 8, 1390-1397. https://doi.org/10.33654/jpl.v11i2.414 [Paper reference 1]
- 9. Sugiyono, A. (2012). Statistika Untuk Penelitian. Bandung: Alfabeta. [Paper reference 1]
- 10. Sugiyono, A. (2014). Penelitian Pendidikan Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R & D. Bandung: Alfabeta. [Paper reference 1]
- 11. Sugiyono, A. (2016). Metode Penelitian Kombinasi (Mixed Methods). Bandung: Alfabeta. [Paper reference 1]
- 12. Widiyowati, I. I. (2015). Hubungan Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis dengan Respon Mahasiswa Terhadap Penggunaan Model Pembelajaran Advance Organizer Pada Materi Larutan Penyangga. Pancaran Pendidikan, 4, 89-104. https://doi.org/10.24114/jpb.v6i2.6548 [Paper reference 1]
- 13. Working Group of Marine and Fisheries for Data and Statistics (2009). Marine and Fisheries in Figures 2009. Ministry of Marine and Fisheries Indonesia. [Paper reference 1]

