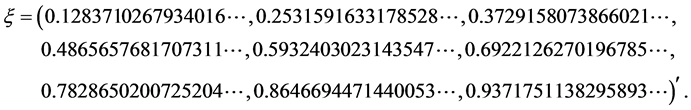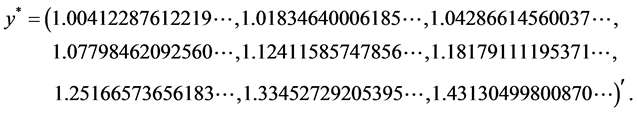Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.04 No.11(2016), Article ID:72119,9 pages
10.4236/jamp.2016.411203
Gauss-Legendre Iterative Methods and Their Applications on Nonlinear Systems and BVP-ODEs
Zhongli Liu1*, Guoqing Sun2
1College of Biochemical Engineering, Beijing Union University, Beijing, China
2College of Renai, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: October 24, 2016; Accepted: November 15, 2016; Published: November 18, 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper, a group of Gauss-Legendre iterative methods with cubic convergence for solving nonlinear systems are proposed. We construct the iterative schemes based on Gauss-Legendre quadrature formula. The cubic convergence and error equation are proved theoretically, and demonstrated numerically. Several numerical examples for solving the system of nonlinear equations and boundary-value problems of nonlinear ordinary differential equations (ODEs) are provided to illustrate the efficiency and performance of the suggested iterative methods.
Keywords:
Iterative Method, Gauss-Legendre Quadrature Formula, Nonlinear Systems, Third-Order Convergence, Nonlinear ODEs

1. Introduction
We consider the general form of a system of nonlinear equations as follows:
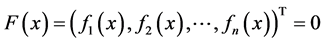 , (1)
, (1)
where  is a given nonlinear vector function, and each function
is a given nonlinear vector function, and each function 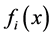 can be thought of as mapping of a vector
can be thought of as mapping of a vector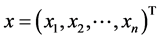 , which is the n- dimensional space
, which is the n- dimensional space 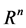 into the real number R.
into the real number R.
Numerical solutions for systems of nonlinear equations have always appealed greatly to people in scientific computation and engineering fields. Some boundary-value problems of nonlinear ordinary differential equations (ODEs) can be transformed to nonlinear systems like (1) by the finite difference method. Constructing an efficiently iterative method to approximate the root 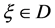 (such that
(such that ) of Equation (1) is a typical and important issue in nonlinear numerical computation. The Newton’s method (see [1] [2] ) is one of the widely used methods for solving nonlinear equations by iteration as follows:
) of Equation (1) is a typical and important issue in nonlinear numerical computation. The Newton’s method (see [1] [2] ) is one of the widely used methods for solving nonlinear equations by iteration as follows:
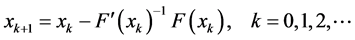 , (2)
, (2)
where 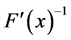 is the inverse of first Fréchet derivative
is the inverse of first Fréchet derivative 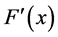 which is a Jacobian matrix of the nonlinear vector function
which is a Jacobian matrix of the nonlinear vector function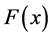 . It converges quadratically when an initial guess value
. It converges quadratically when an initial guess value 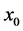 is close to the root
is close to the root  of Equation (1). In recent years, several iterative methods have been used to solve nonlinear equations and systems of nonlinear equations. In order to improve the order of convergence, a few two-step variants of Newton’s methods with cubic convergence have been proposed in some literature [3] - [11] and references therein for solving systems of nonlinear equations. S. We era-
of Equation (1). In recent years, several iterative methods have been used to solve nonlinear equations and systems of nonlinear equations. In order to improve the order of convergence, a few two-step variants of Newton’s methods with cubic convergence have been proposed in some literature [3] - [11] and references therein for solving systems of nonlinear equations. S. We era-
koon and T. Fernando [5] using the Newton theorem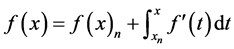 ,
,
proposed the Newton-type method with third-order convergence for nonlinear equation and systems. M. Darvishi and A. Barati [6] received a third-order convergence iterative method based on Adomian decomposition method to the systems of nonlinear equations. M. Frontini and E. Sormani [7] presented third-order midpoint-methods using numerical quadrature formula. A. Cordero and J. R. Torregrsa [8] developed third-order convergence Newton-Simpson’s method and Open Newton’s method using the simple Simpson’s rule and an open quadrature formula of high order respectively. These are all classic two-step Newton-type methods to approximate the root of a system of nonlinear equations.
In Section 2 of this paper, we propose a group of two-step iterative methods with third-order convergence by Gauss-Legendre quadrature formula [12] :
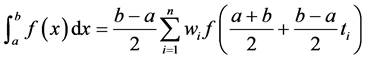 , (3)
, (3)
where the necessary symmetrical conditions is
 ,
, 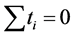 ,
,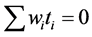 . (4)
. (4)
Several numerical examples are provided in Section 3 using Gauss-Legendre iterative method for solving systems of nonlinear equations and boundary-value problems of nonlinear ODEs, and we finally make conclusions in Section 4.
2. The Iterative Methods and Cubic Convergence
Assume 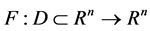
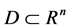
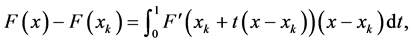
Using the left rectangular integral rule:
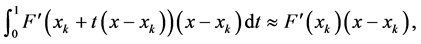
And by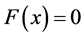
Now, we apply the Gauss-Legendre quadrature formula (3) to approximate the integral on the right side of Equation (5), that is,
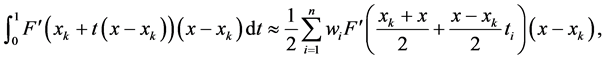
and using 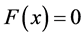
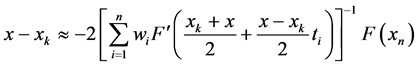
Herein, taking x as the next iterative step of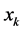
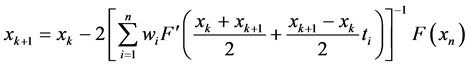
We use the k-th iteration 
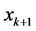
We state and prove the convergence theorem for the schemes (10) as follows:
Theorem Let 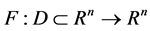
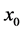
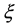
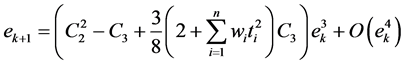
Proof. As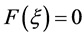
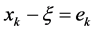
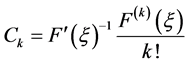
By Taylor’s expansion, we have
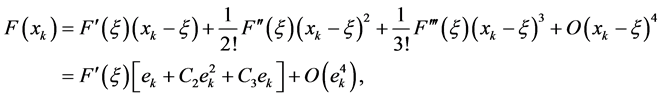
and
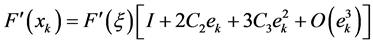
Then, suppose that
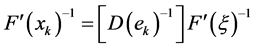
where
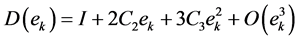
The inverse of 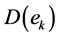
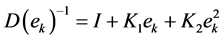
where 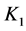
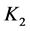
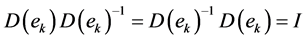
That is
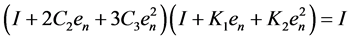
From (17), we have
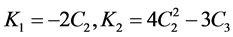
Therefore,
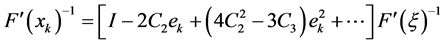
And
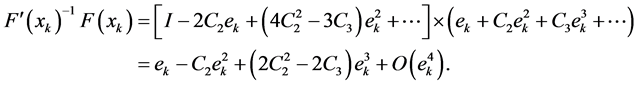
By the first step of (10), we have
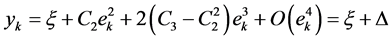
Here, suppose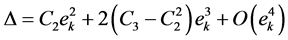
So,
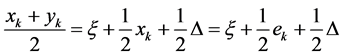
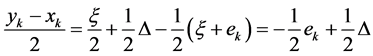
Furthermore,
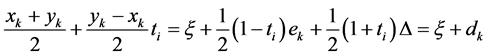
where,
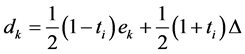
Then,
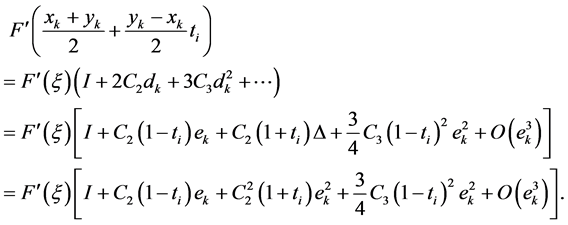
Let
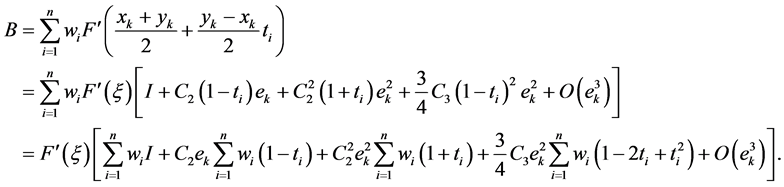
By the conditions (4), we have
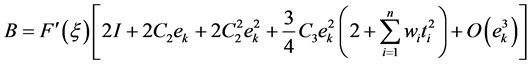
So the iterative schemes (10) can be written as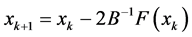
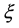
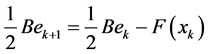
that is
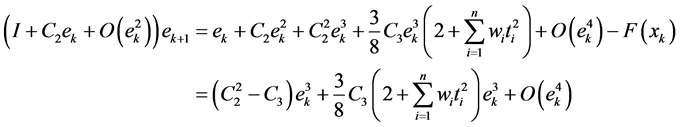
Therefore, the error equation is
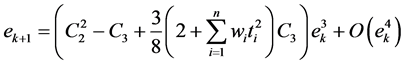
This shows that the group of iterative methods (10) is third-order convergent.
As for the iterative methods (10), when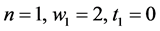
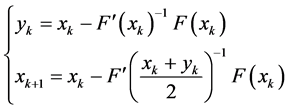
When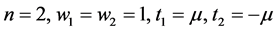
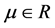
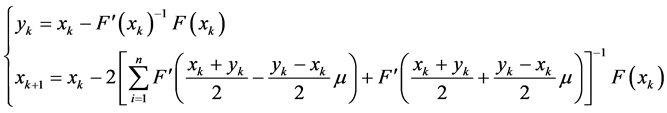
Especially, we take the parameter 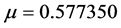
3. Numerical Examples
The iterative method (33) with 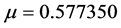
Example 1. Consider a system of nonlinear equations with variables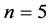
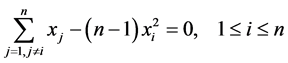
where 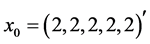

Example 2. Consider solving the following two-point boundary-value problem of nonlinear ODE:
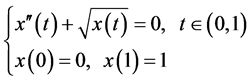
We discretize the nonlinear ODE (35) with the finite difference method. Taking nodes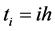
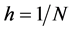
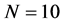
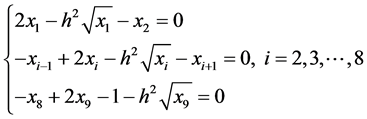
where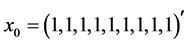
The numerical results for the system of nonlinear Equations (36) derived from ODE (35) are shown in Table 2.
According to results of the above two numerical experiments, the iterative method (33) can achieve third-order convergence for systems of nonlinear equations, and their numerical solutions show also the method is feasible.
Table 1. The numerical solutions and errors of the system of Equation (34) using the method (33).
Table 2. The numerical solutions and errors of the system of nonlinear Equation (36).
Example 3. Solving the following two-point nonlinear boundary-value problem of ODE with exact solution:
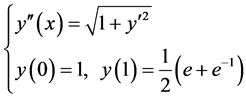
The exact solution for this problem of ODE (37) is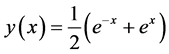
find the numerical solutions using the present method and compare them with the exact solution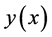
By the finite difference method, partitioning the interval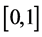
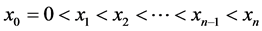
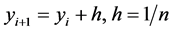
Let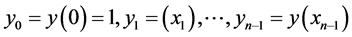
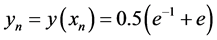
using the numerical differential formula for the second derivative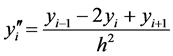
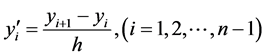
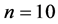
hence obtain the following system of nonlinear equations with nine variables:
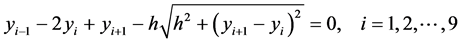
where 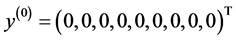
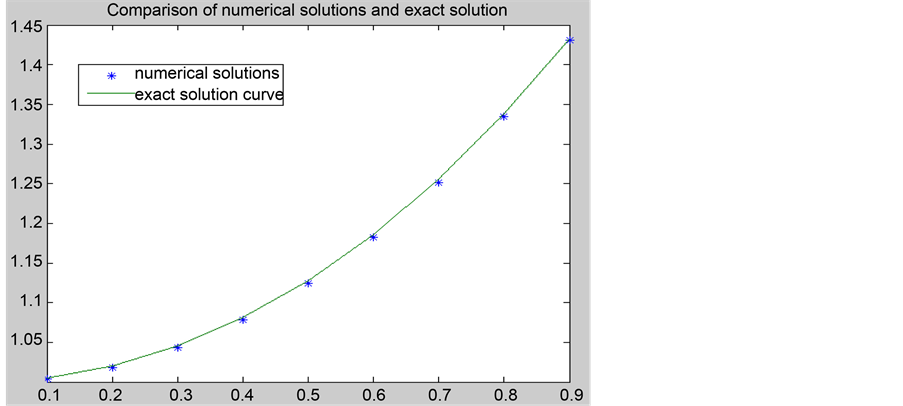
Comparison of the numerical results of the boundary-value problem of ODE (37) and the exact solutions 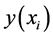
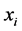
The error comparisons of the numerical solutions and exact solutions at different nodes 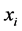
Table 3.Numerical comparison results for the problem of ODE (37).
Figure 1. Error comparisons for solving the problem of ODE (37).
4. Conclusion
In this paper, we construct a group of iterative methods with cubic convergence for the systems of nonlinear equations by using the Gauss-Legendre quadrature formula. Numerical results we gave are in consistence with the theoretical analysis, and meanwhile they also demonstrate that the presented scheme is efficient and feasible to solve systems of nonlinear equations and to solve two-point boundary-value problems of nonlinear ordinary differential equations.
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the Science and Technology Program of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (No. KM201511417012).
Cite this paper
Liu, Z.L. and Sun, G.Q. (2016) Gauss-Legendre Iterative Methods and Their Applications on Nonlinear Systems and BVP-ODEs. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 4, 2038-2046. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2016.411203
References
- 1. Ortega, J.M. and Rheinboldt, W.G. (1970) Iterative Solution of Nonlinear Equations in Several Variables. Academic Press, New York.
- 2. Traub, J.F. (1964) Iterative Methods for the Solution of Equations. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs.
- 3. Noor, M.A. and Noor, K.I. (2006) Improved Iterative Methods for Solving Nonlinear Equations. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 183, 774-779.
https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.05.084 - 4. Chun, C. (2006) A New Ityerative Method for Solving Nonlinear Equations. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 178, 415-422.
https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.11.055 - 5. Weerakoon, S. and Fernando, T.G.I. (2000) A Variant of Newton’s Method with Accelerated Third-Order Convergence. Applied Mathematics Letters, 13, 87-93.
https:/doi.org/10.1016/S0893-9659(00)00100-2 - 6. Darvishi, M.T. and Barati, A. (2007) A Third-Order Newton-type Method to Solve Systems of Nonlinear Equations. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 187, 630-635.
https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.08.080 - 7. Frontini, M. and Sormani, E. (2004) Third-Order Methods from Quadrature Formulae for Solving Systems of Nonlinear Equations. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 149, 771-782.
https:/doi.org/10.1016/S0096-3003(03)00178-4 - 8. Cordero, A. and Torregrosa, J.R. (2007) Variants of Newtons Method Using Fifth-Order Quadrature Formulas. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 190, 686-698.
https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2007.01.062 - 9. Noor, M.A. and Wasteem, M. (2009) Some Iterative Methods for Solving a System of Nonlinear Equations. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 57, 101-106.
https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2008.10.067 - 10. Hafiz, M.A. and Bahgat, M.S.M. (2012) An Efficient Two-Step Iterative Method for Solving System of Nonlinear Equations. Journal of Mathematics Research, 4, 28-34.
- 11. Khirallah, M.Q. and Hafiz, M.A. (2012) Novel Three Order Methods for Solving a System of Nonlinear Equations. Bulletin of Mathematical Sciences & Ap-plications, 1, 1-14.
https:/doi.org/10.18052/www.scipress.com/BMSA.2.1 - 12. Guan, Z. and Lu, J.F. (1998) Numerical Analysis. High Education Press, Beijing.