Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.04 No.05(2016), Article ID:66666,11 pages
10.4236/jamp.2016.45099
Properties of Solutions of Kolmogorov-Fisher Type Biological Population Task with Variable Density
Muhamediyeva Dildora
CDSPHSC under TUIT, Tashkent, Uzbekistan

Copyright © 2016 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 5 April 2016; accepted 20 May 2016; published 23 May 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper, we discussed population model of two competing populations with non-linear double diffusion and variable density which described by nonlinear system of competing individuals. We identify new properties, such as finite speed of propagation, and localization of the outbreaks in a specific area.
Keywords:
Model of Biological Population, Reaction-Diffusion, Double Nonlinearity, Self-Similar Solution, Variable Density, Fast Diffusion, Low Diffusion

1. Introduction
Population models are studied for a long time. The first such work was done by Gause G.F. and Fisher R.D., and mathematical studies were performed by Kolmogorov, Petrovskii (KPP) and Piskunov (1937) in the famous paper [1] - [4] . They were interested in the behavior of the speed of the wave solutions and the resulting estimate of the speed of wave propagation.
Then there were other models of the population [5] - [8] . In recent years, intensive study of nonlinear models was based on diffusion and revealed new properties of finite speed of propagation of diffusion waves (see [3] and the literature given there). We have proposed a population model of two competing populations with non-linear double diffusion and variable density that are described by nonlinear system of competing individuals. We identify new properties, such as finite speed of propagaton, and localization of the outbreaks in a specific area. In particular, in the critical case, the rate type CPT generalizes their result.
Statement of the Task
In this paper, we investigate the properties of solutions of biological population task of Fisher-Kolmogorov type in the case of variable density. The main research method is a self-similar approach. Considering in the field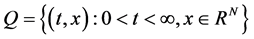 , there is a parabolic system of two quasilinear equations of reaction-diffusion
, there is a parabolic system of two quasilinear equations of reaction-diffusion
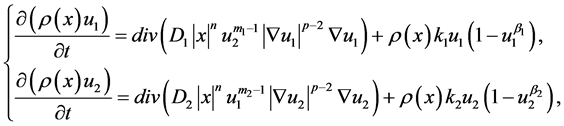 (1)
(1)
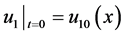 ,
, 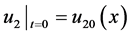 , (2)
, (2)
which describes the process of biological population of Kolmogorov-Fisher in a nonlinear two-component environment, and mutual diffusion coefficients which are respectively equal to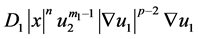 ,
, 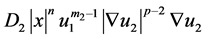 . Numeric parameters
. Numeric parameters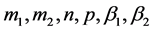 ,
, 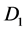 ,
, 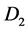 are positive real numbers, and
are positive real numbers, and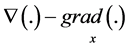 ,
, 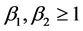 ,
, 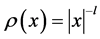 ,
,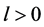
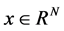 ;
;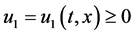 ,
, 
We study properties of solutions to problem (1), (2) based on the self-similar analysis of solutions of a system of equations constructed by the method of nonlinear splitting and a reference equations and bringing the system (1) for radially symmetric mind. Note that replacing in (1)

leads to the form



If



we get the following system of equations:

where

If



A significant role in the study of the Cauchy problem and boundary problems for Equations (1) has self- similar solutions. Under self-similar solution we will understand as particular solutions of Equation (1), depending on the combination of t and x. Knowledge of them plays a sometimes crucial role in the study of various properties of solutions of the original equations.
Below we describe one way of obtaining self-similar system for the system of Equations (5). It consists in the following. We find first the solution of a system of ordinary differential equations
in the form


for the case of





in the form


then the solution of system (5) is sought in the form

and 
if
Then for 

where

If

Then substituting (10) into (8) with respect to 

where 

System (11) has an approximate solution of the form


where А and В are constants and


In this paper, on the basis of the aforesaid methods, we studied qualitative properties of solutions of the system (1), solved the problem of choosing the initial approximation for iterative, leading to fast convergence to the solution of the Cauchy problem (1), (2), depending on the values of numerical parameters and initial data. For this purpose, as the initial approximation was used, we found the asymptotic representation of the solution. This has allowed to perform numerical experiments and visualization of the process described by system (1), depending on the values included in the system of numeric parameters.
2. Construction of Upper Solutions
Let us build an upper solution for system (11).
Note that the functions 
and
We choose A and B from the system of nonlinear algebraic equations
Then functions 

in the classical sense.
Due to the fact that
function 

We choose A and B such that the inequality of inequality

Since then
It is due to the fact that
from (12) we have
Then in the field Q according to the comparison principle of solutions have
Theorem 1. Let 
where
Note that the solution of system (1) when 
where B(a, b)-Euler Beta function.
It is proved that this view is the self-similar asymptotics of solutions of systems (1).
Here
3. Slow Diffusion
Case 
where



and

Let’s take the function
Theorem 2. The finite solution of system (11) when 

Proof. We seek a solution of Equation (8) in the following form

where





where 
Note that the study of the solution of the last equation is equivalent to examining the solution of Equation (11), each of which in a certain period 


Let us show first of all that decision 



Then for the Equation (14) has the form

To analyze the last expression we introduce a new helper function

where






And so for the function 


Hence, given that



get the following algebraic equation
The latter system gives 

Theorem 2 is proved.
4. Fast Diffusion
Case 
where
Theorem 3. At 

Proof. In the proof of theorem used the transform

where
Substituting (15) into (11) for 

where 
Note that the study of the solution of the last equation is equivalent to examining the solution of Equation (11), each of which in a certain period 


Let us show first of all that solution 


troduce the notation

To analyze the last expression we introduce a new helper function

where 






Therefore for the function 



Hence, when

The calculation of the last equation gives 

Theorem 3 is proved.
5. Computational Experiment
Investigation of qualitative properties of system (1) has allowed to perform numerical experiment depending on the values included in the system of numeric parameters. For this purpose, the initial approximation was used to construct asymptotic solutions. The numerical solution of the problem for the linearization of system (2) was used linearization methods of Newton and Picard. To build self-similar system of equations of biological population used the method of nonlinear splitting [1] [6] .
For the numerical solution of the problem (1) we will construct a uniform grid
and temporal grid

Replace the problem (1) implicit difference scheme and receive differential task with the error
It is known that the main problem for the numerical solution of nonlinear problems is the appropriate choice of the initial approximation and the method of linearization of system (1).
Consider the function:
where 

Record 




Created on input language Matlab the program allows you to visually trace the evolution process for different values of the parameters and data.
Numerical calculations show that in the case of arbitrary values 
Figure 1. Results of numerical simulations at


Figure 2. The results of numerical simulations at


Figure 3. The results of numerical simulations at


Figure 4. The results of numerical simulations at


6. Conclusions
Thus, the proposed nonlinear mathematical model of biological populations with double nonlinearity and variable density properly describes the studied process. Numerical study of nonlinear processes described by equations with a double nonlinearity and analysis results on the basis of evaluation solutions provides a comprehensive picture of the process in two-component systems competing biological population with the preservation of localization properties in the target area and the size of the flash.
Results in future will provide an opportunity to evaluate the speed of propagation of diffusive waves.
Cite this paper
Muhamediyeva Dildora, (2016) Properties of Solutions of Kolmogorov-Fisher Type Biological Population Task with Variable Density. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,04,903-913. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2016.45099
References
- 1. Aripov, M. (1988) The Method of Standard Equations for the Solution of Nonlinear Boundary Value Problems. Tashkent: Fan Publishing, Uzbekstan, 137.
- 2. Belotelov, N.V. and Lobanov, A.I. (1997) The Population Model with Nonlinear Diffusion. Mathematical Modeling, No. 12, 43-56.
- 3. Volterra, V. (1976) Mathematical Theory of Struggle for Existence. Nauka, Moscow, 288 p.
- 4. Gause, G.F. (1934) Processes of Destruction of One Species by another in Populations of Ciliates. Zoology Journal, 13, No. 1.
- 5. Aripov, M. and Muhammadiev, J. (1999) Asymptotic Behaviour of Automodel Solutions for One System of Quasilinear Equations of Parabolic Type. Buletin Stiintific-Universitatea din Pitesti, Seria Matematica si Informatica, No. 3, 19-40.
- 6. Aripov, M.M. and Muhamediyeva, D.K. (2013) To the Numerical Modeling of Self-Similar Solutions of Reaction-Diffusion System of the One Task of Biological Population of Kolmogorov-Fisher Type. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2, No. 11.
- 7. Aripov, M.M. and Muhamedieva, D.K. (2013) Approaches to the Solution of One Task of Biological Popu-lation. Issues of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 129, 22-31.
- 8. Murray James, D. (1983) Diffusion of Nonlinear Equations in Biology. Clarendon Press, Oxford, 397 p.






































