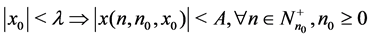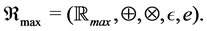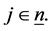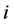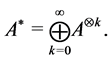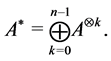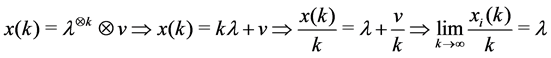Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.03 No.07(2015), Article ID:57916,7 pages
10.4236/jamp.2015.37104
The Relation between the Stabilization Problem for Discrete Event Systems Modeled with Timed Petri Nets via Lyapunov Methods and Max-Plus Algebra
Zvi Retchkiman Konigsberg
Instituto Politécnico Nacional, CIC Mineria 17-2, Col. Escandon, Mexico D.F 11800, Mexico
Email: mzvi@cic.ipn.mx


Received 19 April 2015; accepted 7 July 2015; published 14 July 2015

ABSTRACT
A discrete event system is a dynamical system whose state evolves in time by the occurrence of events at possibly irregular time intervals. Timed Petri nets are a graphical and mathematical modeling tool applicable to discrete event systems in order to represent its states evolution where the timing at which the state changes is taken into consideration. One of the most important performance issues to be considered in a discrete event system is its stability. Lyapunov theory provides the required tools needed to aboard the stability and stabilization problems for discrete event systems modeled with timed Petri nets whose mathematical model is given in terms of difference equations. By proving stability one guarantees a bound on the discrete event systems state dynamics. When the system is unstable, a sufficient condition to stabilize the system is given. It is shown that it is possible to restrict the discrete event systems state space in such a way that boundedness is achieved. However, the restriction is not numerically precisely known. This inconvenience is overcome by considering a specific recurrence equation, in the max-plus algebra, which is assigned to the timed Petri net graphical model.
Keywords:
Discrete Event Systems, Lyapunov Methods, Max-Plus Algebra, Timed Petri Nets

1. Introduction
A discrete event system, is a dynamical system whose state evolves in time by the occurrence of events at possibly irregular time intervals. Timed Petri nets are a graphical and mathematical modeling tool applicable to discrete event systems in order to represent its states evolution where the timing at which the state changes is taken into consideration Timed Petri nets are known to be useful for analyzing the systems properties in addition of being a paradigm for describing and studying information processing systems, where the timing at which the state changes is taken into consideration. For a detailed discussion of Petri net theory see [1] and the references quoted therein. One of the most important performance issues to be considered in a discrete event system is its stability. Lyapunov theory provides the required tools needed to aboard the stability and stabilization problems for discrete event systems modeled with timed Petri nets whose mathematical model is given in terms of difference equations [2]. By proving stability one guarantees a bound on the discrete event systems state dynamics. When the system is unstable, a sufficient condition to stabilize the system is given. It is shown that it is possible to restrict the discrete event systems state space in such a way that boundedness is achieved. However, the restriction is not numerically precisely known. This inconvenience is overcome by considering a specific recurrence equation, in the max-plus algebra, which is assigned to the timed Petri net graphical model. This paper proposes a methodology consisting in combining Lyapunov theory with max-plus algebra to give a precise solution to the stabilization problem for discrete event systems modeled with timed Petri nets. The presented methodology results to be innovative and it is not, in general, known. The main objective of the paper is to spread its results along large audiences. The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, Lyapunov theory for discrete event systems modeled with Petri nets is given. Section 3 presents max-plus algebra and max-plus recurrence equations for timed event Petri nets. Section 4 considers the solution to the stabilization problem for discrete event systems modeled with timed Petri nets. Finally, the paper ends with some conclusions.
2. Lyapunov Stability and Stabilization of Discrete Event Systems Modeled with Petri Nets [2]-[4]
NOTATION: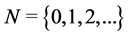 ,
, 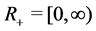 ,
,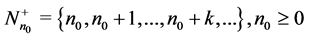 . Given
. Given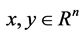 ,
, 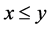 is equivalent to
is equivalent to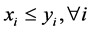 . A function
. A function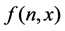 ,
, 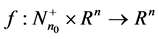 is called nondecreasing in
is called nondecreasing in 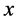 if given
if given 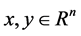 such that
such that 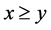 and
and 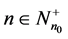 then,
then,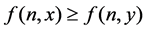 . Consider systems of first ordinary difference equations given by
. Consider systems of first ordinary difference equations given by
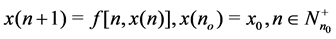 (1)
(1)
where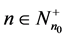 ,
, 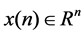 and
and 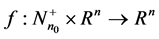 is continuous in
is continuous in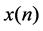
Definition 1 The 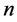
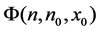
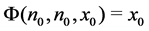
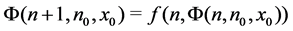
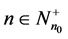
Definition 2 The system (1) is said to be practically stable, if given 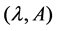
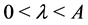
Definition 3 A continuous function 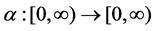
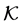
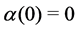
Consider a vector Lyapunov function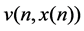
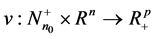
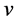
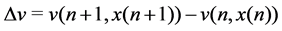
Theorem 4 Let 
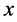
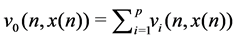
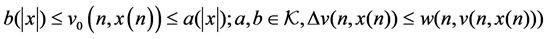
for
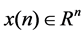
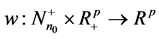
that: 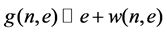
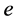
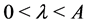
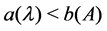
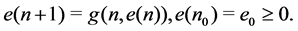
imply the practical stability properties of system (1).
Corollary 5 In Theorem (4): If 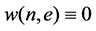
Definition 6 A Petri net is a 5-tuple, 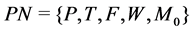
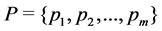
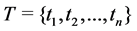
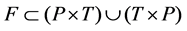
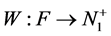
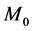
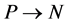
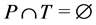
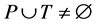
Definition 7 The clock structure associated with a place 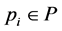
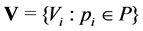
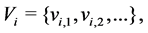
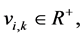
The positive number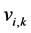
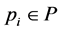
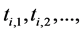
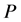
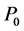
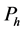
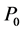
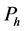
Definition 8 A timed Petri net is a 6-tuple 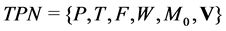
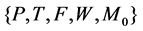
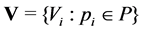
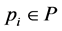

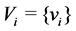
Notice that if 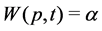
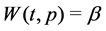
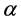
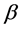
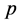
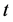
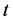
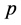
Let 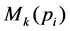
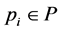
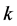
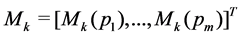
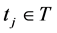
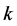
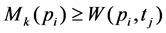
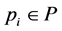
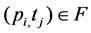
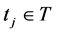
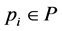
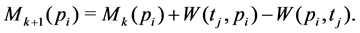
Let 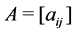
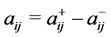
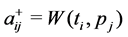
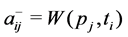
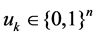
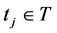
corresponding firing vector is 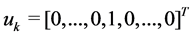
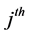
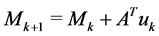
where if at step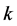
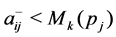
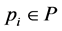
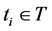
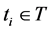
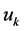
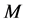
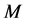
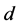
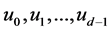
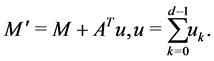
Let 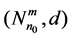
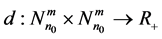
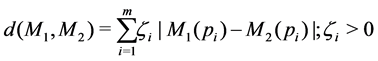
Proposition 9 Let 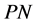
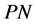
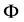
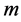
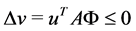
Moreover, 
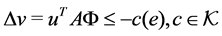
Lemma 10 Let suppose that Proposition (9) holds then,
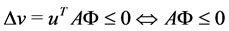
Remark 11 Notice that since the state space of a TPN is contained in the state space of the same now not timed PN, stability of PN implies stability of the TPN.
Lyapunov Stabilization
Definition 12 Let 

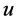
Proposition 13 Let 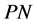
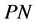
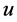
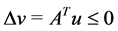
Remark 14 By fixing a particular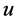
3. Max-Plus Algebra [5] [6]
3.1. Basic Definitions
NOTATION:
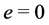
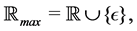
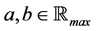
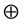
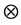
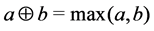

Definition 15 The set 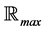
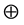
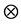
Definition 16 A semiring is a nonempty set 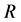
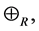
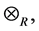
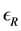
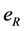
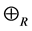
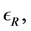
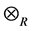
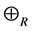
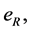
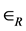
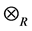
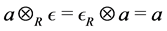
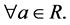

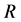
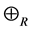
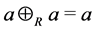
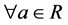
Theorem 17 The max-plus algebra 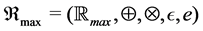
3.2. Matrices and Graphs
Let 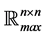
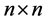
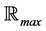
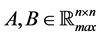
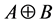
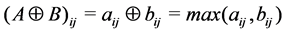
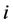
The product of matrices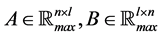
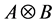
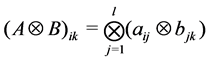
and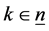
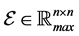
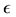
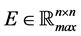
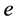
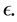
Theorem 18 The 5-tuple 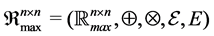
Definition 19 Let 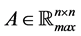

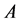
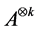
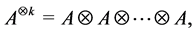
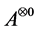
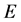
Definition 20 A matrix 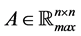
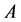
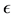
Definition 21 Let 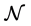
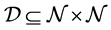
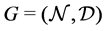
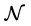
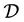
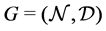
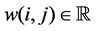
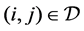
Let 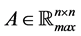
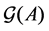
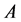
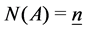
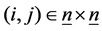
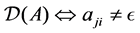
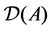
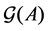
Definition 22 A path from node 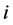
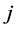
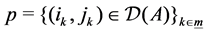
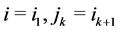
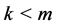
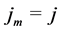
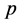
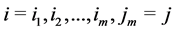
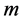
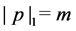
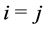
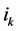
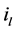
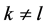
Let us denote by 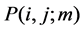
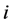
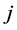
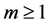
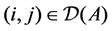
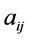
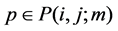
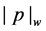
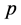
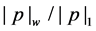
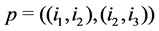
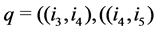
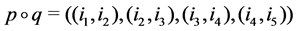
Theorem 23 Let
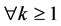
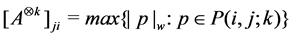
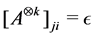
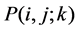
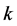
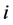
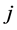
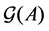
Definition 24 Let 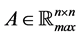
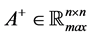
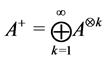
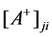
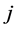
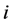
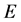
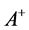
Lemma 25 Let 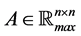
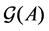
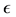
Definition 26 Let 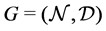
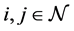
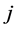
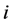
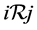
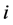
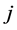
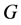
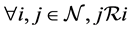
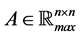
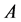
Remark 27 In this paper irreducible matrices are just considered. It is possible to treat the reducible case by transforming it into its normal form and computing its generalized eigenmode see [5].
Spectral Theory and Linear Equations
Definition 28 Let 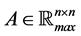
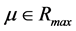
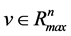
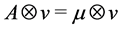
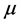
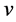
Let 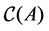
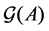
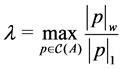
average circuit weight. Notice that since 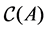
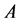
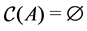
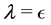
Definition 29 A circuit 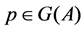
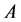
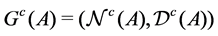
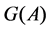
Theorem 30 If 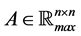
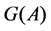
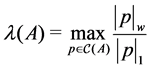
Theorem 31 Let 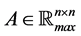
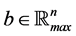
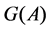
weight less than or equal to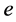

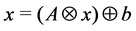
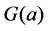
3.3. Max-Plus Recurrence Equations for Timed Event Petri Nets
Definition 32 Let 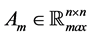
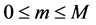
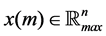
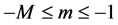
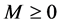
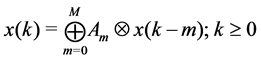
Theorem 33 The Mth order recurrence equation, given by equation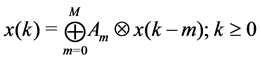
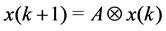
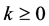
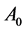
With any timed event Petri net, matrices 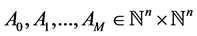
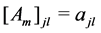
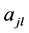
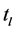
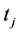
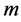
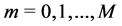
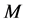
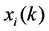
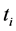
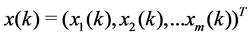
state of the system, satisfies the Mth order recurrence equation:
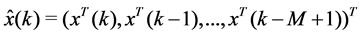

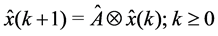
4. The Solution to the Stability Problem for Discrete Event Dynamical Systems Modeled with Timed Petri Nets
Definition 34 A TPN is said to be stable if all the transitions fire with the same proportion i.e., if there exists 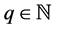
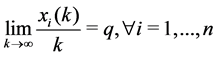
This means that in order to obtain a stable 
Lemma 35 Consider the recurrence relation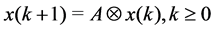
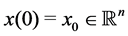
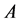
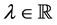
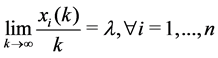
Proof. Let 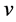
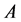
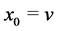
Now starting with an unstable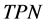
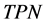
5. Conclusion
The main objective of the proposal is to make it knowledgeable to large audiences. This paper gives a complete and precise solution to the stabilization problem for discrete event systems modeled with timed Petri nets combining Lyapunov theory with max-plus algebra. The presented methodology results to be innovative.
Cite this paper
Zvi Retchkiman Konigsberg, (2015) The Relation between the Stabilization Problem for Discrete Event Systems Modeled with Timed Petri Nets via Lyapunov Methods and Max-Plus Algebra. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,03,839-845. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2015.37104
References
- 1. Murata, T. (1989) Petri Nets: Properties, Analysis, and Applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 77, 541-580. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/5.24143
- 2. Retchkiman, Z. (2005) Stability Theory for a Class of Dynamical Systems Modeled with Petri Nets. International Journal of Hybrid Systems, Vol. 4, No. 1.
- 3. Lakshmikantham, V., Matrosov, V.M. and Sivasundaram, S. (1991) Vector Lyapunov Functions and Stability Analysis of Nonlinear Systems. Kluwer Academic Publ., Dordrecht.
- 4. Retchkiman, Z. (1999) From Stability to the Stabilization problem of Discrete event Systems modeled by Petri Nets. American Control Conference ’99, San Diego, Cal, June 1999.
- 5. Heidergott, B., Olsder, G.J. and van der Woude, J. (2006) Max Plus at Work. Princeton University Press.
- 6. Baccelli, F., Cohen, G., Olsder, G.J. and Quadrat, J.P. (2001) Synchronization and Linearity. Web-Edition.