Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.03 No.07(2015), Article ID:57911,5 pages
10.4236/jamp.2015.37103
Blow-Up of Solution to Cauchy Problem for the Singularly Perturbed Sixth-Order Boussinesq-Type Equation
Changming Song, Li Chen
College of Science, Zhongyuan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China
Email: cmsongh@163.com


Received 6 May 2015; accepted 7 July 2015; published 14 July 2015

ABSTRACT
We consider the singularly perturbed sixth-order Boussinesq-type equation, which describes the bidirectional propagation of small amplitude and long capillary gravity waves on the surface of shallow water for bond number (surface tension parameter) less than but very close to 1/3. The sufficient conditions of blow-up of solution to the Cauchy problem for this equation are given.
Keywords:
Singularly Perturbed Sixth-Order Boussinesq Equation, Cauchy Problem, Blow-Up of Solution

1. Introduction
In this paper, we consider the following Cauchy problem
 (1.1)
(1.1)
 (1.2)
(1.2)
where  is the unknown function,
is the unknown function, 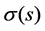 is the given function,
is the given function, 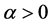 and
and 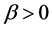 are real numbers,
are real numbers,  and
and 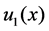 are given initial value functions.
are given initial value functions.
In [1], the author has proved the existence and uniqueness of the global generalized solution and the global classical solution for the initial boundary value problem of Equation (1.1).
In [2], the author has discussed the nonexistence of global solution to the initial boundary value problem of Equation (1.1) in some condition.
In order to prove that blow-up of Cauchy problem (1.1), (1.2), we shall consider the following auxiliary problem
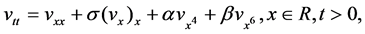 (1.3)
(1.3)
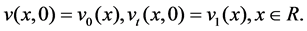 (1.4)
(1.4)
Then, we can obtain blow-up of the Cauchy problem (1.1), (1.2) from (1.3), (1.4) by setting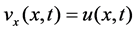 ,
,
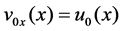 and
and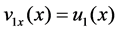 .
.
2. Main Theorems
Throughout this paper, we use the following notation: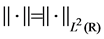 . Now, we give the following main lemmas and theorems.
. Now, we give the following main lemmas and theorems.
Lemma 2.1 (convex lemma [3]) Suppose that a positive twice-differential function 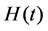 satisfies on
satisfies on  the inequality
the inequality
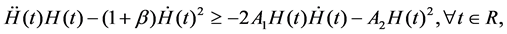 (2.1)
(2.1)
where 


(1) If 




(2) If 



and
Lemma 2.2 [4] Suppose that



where 
Lemma 2.3 Suppose that 



Proof Multiplying both sides of (1.3) by

integrating the product over
Theorem 2.1 Suppose that
constant 


Then, the solution 
(1)
(2)
(3)
Proof Suppose that the maximal time of the solution for (1.3), (1.4) is infinite. Let

where 



By using the Hölder inequality, it follows from (2.5) that

Differentiating (2.5) with respect to

By virtue of interpolating inequality,
Observing the identity (2.7), we get

Combing (2.2), (2.3), (2.4), (2.6) with (2.8), we infer

(1) If

When 





(2) If

By virtue of assumption (2), we see 




(3) If

Defining
then

By virtue of assumption (3), we have
Thanks to the continuity of



Integrating (2.11) with respect to 

By virtue of assumption (3), we see that
Since 


It follows from the definition of 


Hence there is some

So 

Thus, 

Theorem 2.2 Suppose that


Then, the solution 
(1)
(2)
(3)
where
Proof Let
where 

By virtue of assumption Theorem 2.1, 

Then
Substituting the above change (2.13) to the Cauchy problem (1.1), (1.2), we have


Integrating (2.14) and (2.15) over


Let
where 






Fund
This project is supported by NSF Grant 11271336, NSF of Henan Province Grant 122300410166.
Cite this paper
Changming Song,Li Chen, (2015) Blow-Up of Solution to Cauchy Problem for the Singularly Perturbed Sixth-Order Boussinesq-Type Equation. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,03,834-838. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2015.37103
References
- 1. Song, C., Li, H. and Li, J. (2013) Initial Boundary Value Problem for the Singularly Perturbed Boussinesq-Type Equation. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 709-717.
- 2. Song, C., Li, J. and Gao, R. (2014) Nonexistence of Global Solutions to the Initial Boundary Value Problem for the Singularly Perturbed Sixth-Order Boussinesq Equation. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Applied Mathematics.
- 3. Becken, E.F. and Bellman, R. (1983) Inequalities (Fourth Printing). Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- 4. Y D. (1989) L2 Theory of Partial Differential Equations. Peking University Press, Beijing. (In Chinese)



























