Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.03 No.07(2015), Article ID:57638,10 pages
10.4236/jamp.2015.37094
Hopf Bifurcation Analysis for a Modified Time-Delay Predator-Prey System with Harvesting
Yang Ni, Yan Meng, Yiming Ding
School of Mathematics and physics, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
Email: ny123ling@126.com


Received 28 April 2015; accepted 23 June 2015; published 30 June 2015

ABSTRACT
In this paper, we consider the direction and stability of time-delay induced Hopf bifurcation in a delayed predator-prey system with harvesting. We show that the positive equilibrium point is asymptotically stable in the absence of time delay, but loses its stability via the Hopf bifurcation when the time delay increases beyond a threshold. Furthermore, using the norm form and the center manifold theory, we investigate the stability and direction of the Hopf bifurcation.
Keywords:
Hopf Bifurcation, Time-Delay, Predator-Prey Model

1. Introduction
Due to its universal existence and importance, the study on the dynamics of predator-prey systems is one of the dominant subjects in ecology and mathematical ecology since Lotka [1] and Volterra [2] proposed the well- known predator-prey model [3]-[6]. Recently, a new method of central manifold has been developed to study the stability of delay induced bifurcation. In this paper, we study the following system:
 (1)
(1)
with
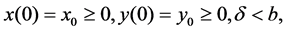 (2)
(2)
where dot means differentiation with respect to time ,
, 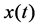 and
and 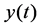 are the prey and predator population densities, respectively. Parameter
are the prey and predator population densities, respectively. Parameter 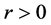 is the specific growth rate of prey in the absence of predation and without environment limitation.
is the specific growth rate of prey in the absence of predation and without environment limitation. 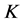 is environmental carrying capacity. The functional response of the predator is of Holling’s type with
is environmental carrying capacity. The functional response of the predator is of Holling’s type with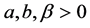 . And all parameters involved with the model are positive.
. And all parameters involved with the model are positive.
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the effect of time-delay on a modified predator-prey model with harvesting. We discussed the existence of Hopf bifurcation of system (1) and the direction of Hopf bifurcation and the stability of bifurcated periodic solutions are given.
2. Positive Equilibrium and Locally Asymptotically Stabiliy
After some calculations, we note system (1) has no boundary equilibria. However, it is more interesting to study the dynamical behaviors of the interior equilibrium points 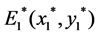 and
and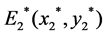 , where
, where
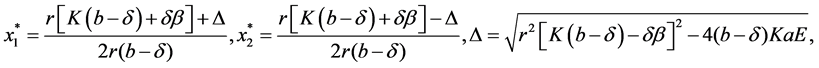
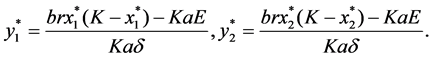
The two distinct interior equilibrium points 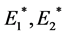 exist whenever
exist whenever
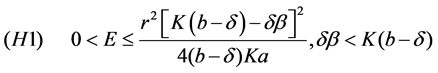
holds.
We transform the interior equilibrium 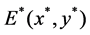 to the origin by the transformation
to the origin by the transformation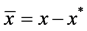 ,
,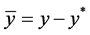 . Respectively, we still denote
. Respectively, we still denote 




First, we give the condition such that 

The characteristic polynomial of 

where
Now we consider the locally asymptotically stabiliy of the system without time-delay. Then we have

If
holds, then it follows from the Routh-Hurwitz criterion that two roots of (6) have negative real parts.
Theorem 1. If 


3. Hopf Bifurcaion
In the section, we study whether there exists periodic solutions of system (1) about the interior equilibrium point
Theorem 2. If the system (1) satisfies the hypothesis 







By the use of the instability result for the delayed differential Equations, in order to prove the instability of the equilibrium point, it is sufficient to show that there exists a purely imaginary 


where 
If 

which leads to

Let

Since 



Set 


where

Then 


Then by the Butler’s Lemma, 





Theorem 3. If the system (1) satisfies the hypothesis 




Proof. The Hopf bifurcation will be proved if we can show that

From Equation (7), we have

Substituting Equation (8) into Equation (16), we have

Substituting Equation (14) into the above equation, we have
Therefore, the transversality condition is satisfied. Therefore Hopf bifurcation occurs at
4. The Direction and Stability of the Hopf Bifurcation
In this section, we analyze the direction and stability of the Hopf bifurcation of (3) obtained in Theorem 3 by taking 
Let



We define 

Rewrite system (18) to

where

We use the method which is based on the center manifold and normal form theory, and define

where 


and

where



In fact, we can choose

where 


and

Thus system (21) is equivalent to

where 

For

and a bilinear inner product

where





Suppose 




Then we have

Similarly, let 




Therefore

In order to ensure, we need to determine the value of

Then we can choose 

where 

Next we will compute the coordinate to describe the center manifold 




On the center manifold












We rewrite above equation as

where

From Equation (35) and Equation (36), we obtain that

Substituting Equation (23) and Equation (40) into Equation (39), we have

where 
Comparing Equation (39) and Equation (41), we get

Since 





where

From Equation (36), we have

It follows from Equation (39) that

Comparing the coefficients of 


Then for

Comparing the coefficients of 


From the definition of 

Since

where 

where 




and

where


Then we have

Comparing both sides of Equation (56), we obtain

where 





where
Since 




Therefore, substituting Equation (53) and Equation (59) into Equation (60), we have

that is

where

Thus









where

Thus










Then the Hopf bifurcating periodic solutions of system (1) at 

Here 






Theorem 4. The Hopf bifurcation of the system (1) occurring at 



5. Conclusion
This paper introduces modified time-delay predator- prey model. Then we study the Hopf bifurcation and the stability of the system. Our results reveal the conditions on the parameters so that the periodic solutions exist surrounding the interior equilibrium point. It shows that 

Acknowledgements
This project is jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Grant No. 61074192). We also would like to thank the anonymous referees which have improved the quality of our study.
Cite this paper
Yang Ni,Yan Meng,Yiming Ding, (2015) Hopf Bifurcation Analysis for a Modified Time-Delay Predator-Prey System with Harvesting. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,03,771-780. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2015.37094
References
- 1. Lotka, A.J. (1925) Elements of Physical Biology. Nature, 116, 461. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/116461b0
- 2. Volterra, V. (1926) Fluctuations in The Abundance of A Species Considered Mathematically. Nature, 118, 558-560. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/118558a0
- 3. Yan, X. and Li, W. (2007) Bifurcation and Global Periodic Solutions in A Delayed Facultative Mutualism System. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 227, 51-69. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2006.12.007
- 4. Tian, C. and Zhang, L. (2013) Hopf Bifurcation Analysis in a Diffusive Food-Chain Model with Time Delay. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 66, 2139-2153. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2013.09.002
- 5. Kar, T.K. and Jana, S. (2012) Stability and Bifurcation Analysis of a Stage Structured Predator Prey Model with Time Delay. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 219, 3779-3792. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2012.10.007
- 6. Zhang, J., Li, W. and Yan, X. (2011) Hopf Bifurcation and Turing Instability in Spatial Homogeneous and Inhomogeneous Predator-Prey Models. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 218, 1883-1893. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2011.06.071











