Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Conventional and Microwave Calcined Strontium Hexaferrite Powder641
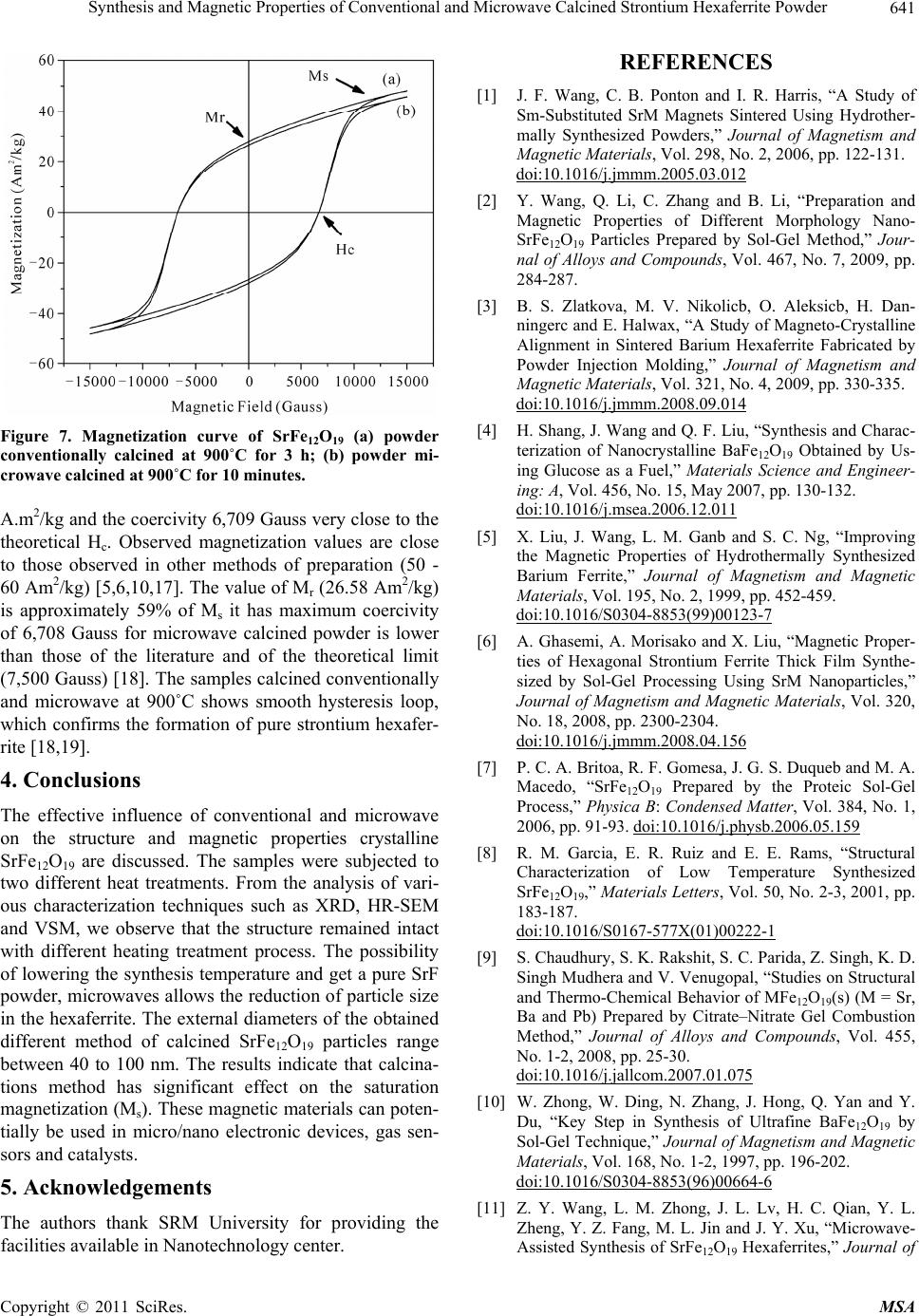
Figure 7. Magnetization curve of SrFe12O19 (a) powder
conventionally calcined at 900˚C for 3 h; (b) powder mi-
crowave calcined at 900˚C for 10 minutes.
A.m2/kg and the coercivity 6,709 Gauss very close to the
theoretical Hc. Observed magnetization values are close
to those observed in other methods of preparation (50 -
60 Am2/kg) [5,6,10,17]. The value of Mr (26.58 Am2/kg)
is approximately 59% of Ms it has maximum coercivity
of 6,708 Gauss for microwave calcined powder is lower
than those of the literature and of the theoretical limit
(7,500 Gauss) [18]. The samples calcined conventionally
and microwave at 900˚C shows smooth hysteresis loop,
which confirms the formation of pure strontium hexafer-
rite [18,19].
4. Conclusions
The effective influence of conventional and microwave
on the structure and magnetic properties crystalline
SrFe12O19 are discussed. The samples were subjected to
two different heat treatments. From the analysis of vari-
ous characterization techniques such as XRD, HR-SEM
and VSM, we observe that the structure remained intact
with different heating treatment process. The possibility
of lowering the synthesis temperature and get a pure SrF
powder, microwaves allows the reduction of particle size
in the hexaferrite. The external diameters of the obtained
different method of calcined SrFe12O19 particles range
between 40 to 100 nm. The results indicate that calcina-
tions method has significant effect on the saturation
magnetization (Ms). These magnetic materials can poten-
tially be used in micro/nano electronic devices, gas sen-
sors and catalysts.
5. Acknowledgements
The authors thank SRM University for providing the
facilities available in Nanotechnology center.
REFERENCES
[1] J. F. Wang, C. B. Ponton and I. R. Harris, “A Study of
Sm-Substituted SrM Magnets Sintered Using Hydrother-
mally Synthesized Powders,” Journal of Magnetism and
Magnetic Materials, Vol. 298, No. 2, 2006, pp. 122-131.
doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.03.012
[2] Y. Wang, Q. Li, C. Zhang and B. Li, “Preparation and
Magnetic Properties of Different Morphology Nano-
SrFe12O19 Particles Prepared by Sol-Gel Method,” Jour-
nal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol. 467, No. 7, 2009, pp.
284-287.
[3] B. S. Zlatkova, M. V. Nikolicb, O. Aleksicb, H. Dan-
ningerc and E. Halwax, “A Study of Magneto-Crystalline
Alignment in Sintered Barium Hexaferrite Fabricated by
Powder Injection Molding,” Journal of Magnetism and
Magnetic Materials, Vol. 321, No. 4, 2009, pp. 330-335.
doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.09.014
[4] H. Shang, J. Wang and Q. F. Liu, “Synthesis and Charac-
terization of Nanocrystalline BaFe12O19 Obtained by Us-
ing Glucose as a Fuel,” Materials Science and Engineer-
ing: A, Vol. 456, No. 15, May 2007, pp. 130-132.
doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.12.011
[5] X. Liu, J. Wang, L. M. Ganb and S. C. Ng, “Improving
the Magnetic Properties of Hydrothermally Synthesized
Barium Ferrite,” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic
Materials, Vol. 195, No. 2, 1999, pp. 452-459.
doi:10.1016/S0304-8853(99)00123-7
[6] A. Ghasemi, A. Morisako and X. Liu, “Magnetic Proper-
ties of Hexagonal Strontium Ferrite Thick Film Synthe-
sized by Sol-Gel Processing Using SrM Nanoparticles,”
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 320,
No. 18, 2008, pp. 2300-2304.
doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.04.156
[7] P. C. A. Britoa, R. F. Gomesa, J. G. S. Duqueb and M. A.
Macedo, “SrFe12O19 Prepared by the Proteic Sol-Gel
Process,” Physica B: Condensed Matter, Vol. 384, No. 1,
2006, pp. 91-93. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2006.05.159
[8] R. M. Garcia, E. R. Ruiz and E. E. Rams, “Structural
Characterization of Low Temperature Synthesized
SrFe12O19,” Materials Letters, Vol. 50, No. 2-3, 2001, pp.
183-187.
doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(01)00222-1
[9] S. Chaudhury, S. K. Rakshit, S. C. Parida, Z. Singh, K. D.
Singh Mudhera and V. Venugopal, “Studies on Structural
and Thermo-Chemical Behavior of MFe12O19(s) (M = Sr,
Ba and Pb) Prepared by Citrate–Nitrate Gel Combustion
Method,” Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol. 455,
No. 1-2, 2008, pp. 25-30.
doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.01.075
[10] W. Zhong, W. Ding, N. Zhang, J. Hong, Q. Yan and Y.
Du, “Key Step in Synthesis of Ultrafine BaFe12O19 by
Sol-Gel Technique,” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic
Materials, Vol. 168, No. 1-2, 1997, pp. 196-202.
doi:10.1016/S0304-8853(96)00664-6
[11] Z. Y. Wang, L. M. Zhong, J. L. Lv, H. C. Qian, Y. L.
Zheng, Y. Z. Fang, M. L. Jin and J. Y. Xu, “Microwave-
Assisted Synthesis of SrFe12O19 Hexaferrites,” Journal of
Copyright © 2011 SciRes. MSA