Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.03 No.01(2015), Article ID:53598,6 pages
10.4236/jamp.2015.31012
Characteristics Collocation Method of Compressible Miscible Displacement with Dispersion
Ning Ma, Xiaofei Lu
College of Science, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China
Email: ningma@cup.edu.cn


Received December 2014

ABSTRACT
The compressible miscible displacement in a porous media is considered in this paper. The problem is a nonlinear system with dispersion in non-periodic space. The concentration is treated by a characteristics collocation method, and the pressure is treated by an orthogonal collocation method. Optimal order estimates are derived.
Keywords:
Compressible, Dispersion, Characteristics Collocation, Non-Periodic

1. Introduction
The mathematical controlling model for compressible miscible displacement in porous media with dispersion is given by
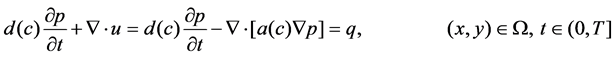 (1)
(1)
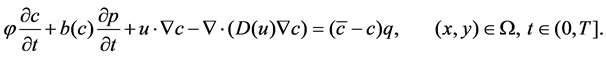 (2)
(2)
where 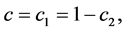
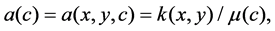
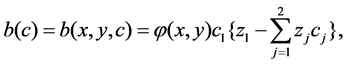
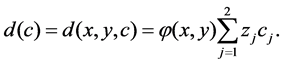
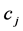 and
and 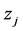 denote the concentration and constant compressibility factor for the i component of the fluid mixture respectively. Let
denote the concentration and constant compressibility factor for the i component of the fluid mixture respectively. Let 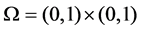 with the boundary
with the boundary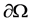 ,
, 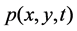 the pressure in the mixture, u is the Darcy velocity of the fluid, and
the pressure in the mixture, u is the Darcy velocity of the fluid, and 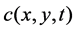 is the relative concentration of the injected fluid.
is the relative concentration of the injected fluid. 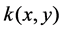 and
and 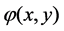 are the permeability and the porosity of porous media,
are the permeability and the porosity of porous media, 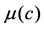 is the viscosity of the fluid.
is the viscosity of the fluid. 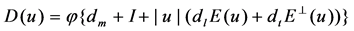 are the molecular dissipation and dispersion terms, where
are the molecular dissipation and dispersion terms, where 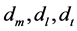 are the molecular dissipation, longitudinal and tangential dispersion coefficients. I is a 2 unit matrix,
are the molecular dissipation, longitudinal and tangential dispersion coefficients. I is a 2 unit matrix, 


We shall assume that no flow occurs across the boundary

where v is the outer normal to

The compressible flow problems are strongly nonlinear coupling system for partial differential equations of two different types, and we consider the system with dispersion in non-periodic space, so these factors lead to many difficulties for convergence analysis of algorithms. The collocation methods are widely used for solving practice problems in engineering due to its easiness of implementation and high-order accuracy. But the most parts of mathematical theory focused on one-dimensional or two-dimensional constant coefficient problems [3] [4]. [5] proposes the collocation method of two-dimensional variable coefficients elliptic problems. The characteristics collocation scheme for the incompressible flow is given in [6]. The characteristics finite element method for the compressible miscible flow is proved in [7]. In the paper we shall use different technique to treat different types of equations, the orthogonal collocation methods solve the pressure equation and the characteristics collocation scheme approximate the concentration equation. We develop some technique to analyze convergence of these algorithms for this strongly nonlinear system with dispersion in non-periodic space. Finally we can obtain the optimal order error estimate. We shall assume the coefficients 


The organization of the rest of the paper is as follows. In Section 2, we will present the formulation of the characteristic collocation scheme for nonlinear system (1) (2). In Section 3, we will analyze convergent rate of the scheme defined in Section 2.
2. Characteristic Collocation Scheme (CCS)
2.1. Preliminaries
In this subsection, we will give some basic notations and definition for the characteristics collocation methods, which will be used in this article. We make the partition of the domain



Define function spaces as follows:

where 




Next, we take four Gauss points as collocation points in



Let 




2.2. CCS
In this subsection we will present the fully discrete characteristic collocation scheme for nonlinear system (1) (2) with dispersion term in non-periodic space. At first time 





The Equation (2) can be put in the form

For (5), we use a backward difference quotient for 

where
So we can obtain the following discrete equation:
Now that use the interpolation operator 




and 
for 


We can understand the following method intuitively from above schematic diagram. When 












3. Convergence Analysis
In this section we consider the existence and uniqueness of the numerical solution, and obtain the optimal error estimate. CCS (8) (9) can be rewritten as the discrete Galerkin method given by [3] [6] [8]


We can get the following convergence conclusion for the above numerical Scheme (11) (12).
Theorem 3.1 Suppose
Proof: Let 

where



Figure 1. Continuation.
We start this induction by seeing that 


for 
Next we will consider the concentration equation, subtracting (12) from the discrete Galerkin scheme of (2),

To obtain optical estimate for 



If

for h sufficiently small and



At last we shall check the induction hypotheses (14) and (17)
for h sufficiently small , and the proof is complete.
Acknowledgements
We thank the fund “Basic Subjects Fund of China University of Petroleum (Beijing) (KYJJ2012-06-04)”.
Cite this paper
Ning Ma,Xiaofei Lu, (2015) Characteristics Collocation Method of Compressible Miscible Displacement with Dispersion. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,03,86-91. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2015.31012
References
- 1. Douglas Jr., J. and Roberts, J.E. (1983) Numerical Methods for a Model for Compressible Miscible Displacement in Porous Media. Math. Comp., 41, 441-459. http://dx.doi.org/10.1090/S0025-5718-1983-0717695-3
- 2. Russell, T.F. (1985) Time Stepping along Characteristics with Incomplete Iteration for a Galerkin Approximation of Miscible Dis-placement in Porous Media. SIAM. J Numer. Anal., 17, 970-1013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/0722059
- 3. Dougals, J. and Dupont, T. (1974) Lecture Notes in Math. Vol. 385, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- 4. Fernandes, R.L. and Fairweather, G. (1993) Analysis of Alternating Direction Collocation Methods for Parabolic and Hyperbolic Problems in Two Space Variables. Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations, 9, 191-211. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/num.1690090207
- 5. Bialecki, B. and Cai, X. (1994) H1-Norm Error Bounds for Piecewise Hermite Bicubic Orthogonal Space Collocation Schemes for Elliptic Boundary Value Problems. SIAM. J Numer.Anal., 31, 1128-1146. http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/0731059
- 6. Ma, N., Lu, T. and Yang, D. (2006) Analysis of Incompressible Miscible Dis-placement in Porous Media by a Characteristics Collation Method. Numer. Methods for Partial Differential Eq., 22, 797-814.
- 7. Yuan, Y. (1992) Time Stepping along Characteristics for the Finite Element Approximation of Com-pressible Miscible Displacement in Porous Media. Mathematica Numerica Sinica, 14, 385-400.
- 8. Ma, N. (1906) Orthogonal Collocation Method for Miscible Displacement with Dispersion. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 46, 78-81.
- 9. Douglas Jr., J. and Roberts, J.E. (1983) Numerical Methods for a Model for Compressible Miscible Displacement in Porous Media. Math. Comp., 41, 441-459. http://dx.doi.org/10.1090/S0025-5718-1983-0717695-3
- 10. Russell, T.F. (1985) Time Stepping along Characteristics with Incomplete Iteration for a Galerkin Approximation of Miscible Dis-placement in Porous Media. SIAM. J Numer. Anal., 17, 970-1013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/0722059
- 11. Dougals, J. and Dupont, T. (1974) Lecture Notes in Math. Vol. 385, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- 12. Fernandes, R.L. and Fairweather, G. (1993) Analysis of Alternating Direction Collocation Methods for Parabolic and Hyperbolic Problems in Two Space Variables. Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations, 9, 191-211. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/num.1690090207
- 13. Bialecki, B. and Cai, X. (1994) H1-Norm Error Bounds for Piecewise Hermite Bicubic Orthogonal Space Collocation Schemes for Elliptic Boundary Value Problems. SIAM. J Numer.Anal., 31, 1128-1146. http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/0731059
- 14. Ma, N., Lu, T. and Yang, D. (2006) Analysis of Incompressible Miscible Dis-placement in Porous Media by a Characteristics Collation Method. Numer. Methods for Partial Differential Eq., 22, 797-814.
- 15. Yuan, Y. (1992) Time Stepping along Characteristics for the Finite Element Approximation of Com-pressible Miscible Displacement in Porous Media. Mathematica Numerica Sinica, 14, 385-400.
- 16. Ma, N. (1906) Orthogonal Collocation Method for Miscible Displacement with Dispersion. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 46, 78-81.











