X. G. Shuai et al. / Natural Science 1 (2009) 37-40 39
Copyright © 2009 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS
3.2 Low-carbon Technology in Building
Materials
The building components can be made from various
building materials, while the “implicit” CO2 emission
differs during the production of different building mate-
rials. The paper adopts the BEES assessment software
developed by National Institute of Standards and Tech-
nology to calculate the “implicit” CO2 impact of differ-
ent building materials. BEES (Building for Environ-
mental and Economic Sustainability, BEES) is a com-
prehensive evaluation software over the construction
environment and sustainability, and has been supported
by the Association of American Environment Protection
and U. S. Government [15]. It uses the Life Cycle As-
sessment (LCA) to quantitatively assess the environ-
mental performance of building materials.
3.2.1. Comparison Between Aluminium Curtain
wall and wall Paintings
There are enormous consumption of fossil fuel and CO2
emission in the production process of aluminium materi-
als, and the energy consumption is 435GJ/t while carbon
emission is 8700kg/t; but the figures in the production of
steel materials are only 35GJ/t and 700kg/t, both of
which are 1/12 of that of aluminium materials [16].
Therefore, the usage of aluminium materials should be
reduced, and other green materials should be adopted.
This article has conducted a calculation over the alu-
minium curtain wall of a university refectory project,
and has analyzed the difference of CO2 emission by
switching to common wall paintings.
The “implicit” CO2 emission of 1m2 aluminium cur-
tain wall and common wall paintings have been calcu-
lated out by BEES software. For the convenience of
calculation, it has been assumed that the transportation
distance for both of them are 200km with a life span of
50 years, then the quantity of CO2 emission are shown as
follows.
As a result, the CO2 emission of aluminium curtain
wall is far larger than that of common wall paintings.
The quantity of aluminium curtain wall in this refectory
project is 2519m2, but if using the common wall paint-
ings it will reduce 34476kg CO2 with an 85% reduction
rate.
Table 3. Comparison between aluminium curtain wall and wall
paintings (gCO2/m2).
life cycle
stage
Raw
materials Manufacturing TransportationTotal
aluminium
curtain wall 14131 1878 40 16050
wall paintings 1755 566 42 2364
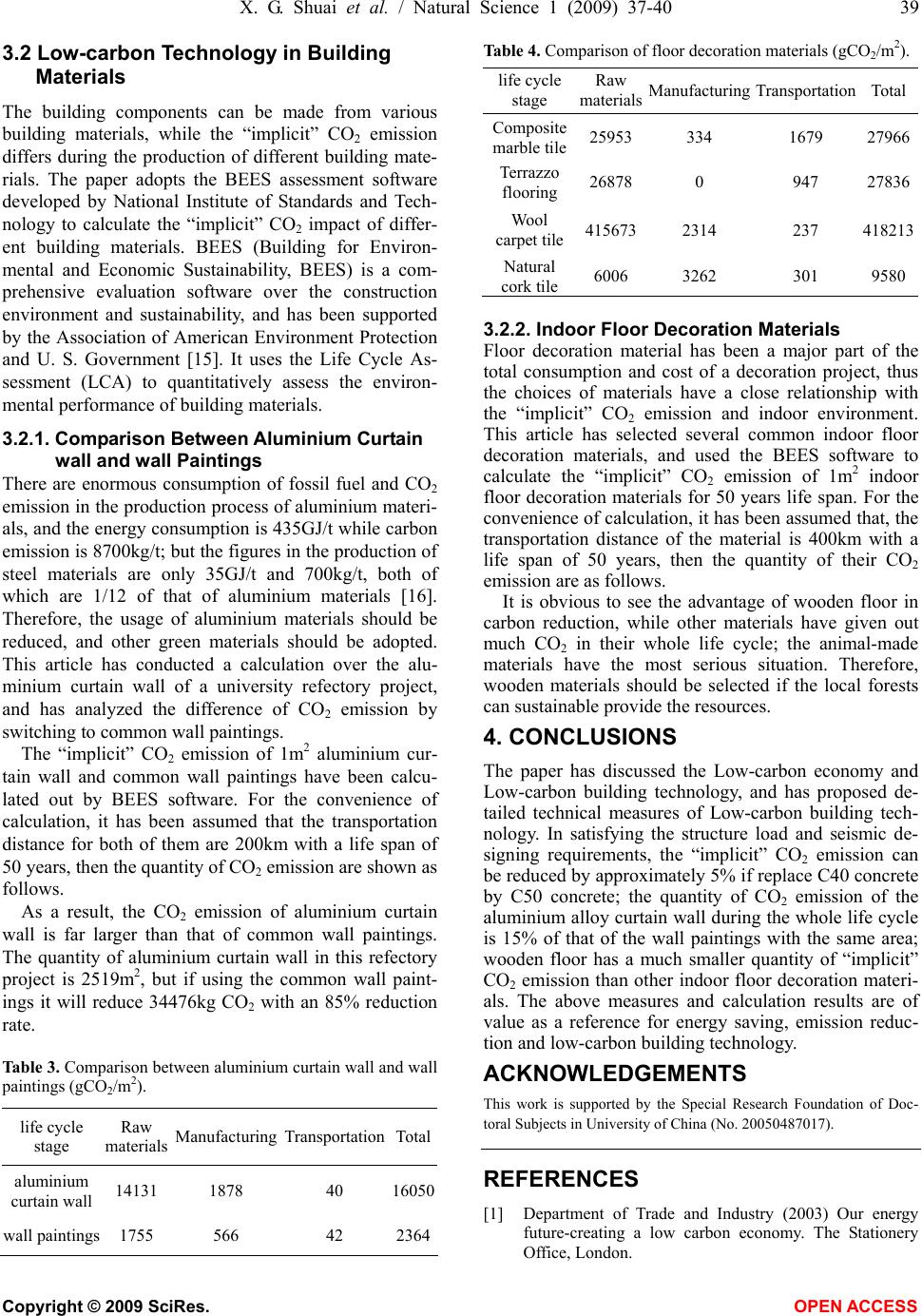
Table 4. Comparison of floor decoration materials (gCO2/m2).
life cycle
stage
Raw
materials Manufacturing TransportationTotal
Composite
marble tile25953 334 1679 27966
Terrazzo
flooring 26878 0 947 27836
Wool
carpet tile415673 2314 237 418213
Natural
cork tile 6006 3262 301 9580
3.2.2. Indoor Floor Decoration Materials
Floor decoration material has been a major part of the
total consumption and cost of a decoration project, thus
the choices of materials have a close relationship with
the “implicit” CO2 emission and indoor environment.
This article has selected several common indoor floor
decoration materials, and used the BEES software to
calculate the “implicit” CO2 emission of 1m2 indoor
floor decoration materials for 50 years life span. For the
convenience of calculation, it has been assumed that, the
transportation distance of the material is 400km with a
life span of 50 years, then the quantity of their CO2
emission are as follows.
It is obvious to see the advantage of wooden floor in
carbon reduction, while other materials have given out
much CO2 in their whole life cycle; the animal-made
materials have the most serious situation. Therefore,
wooden materials should be selected if the local forests
can sustainable provide the resources.
4. CONCLUSIONS
The paper has discussed the Low-carbon economy and
Low-carbon building technology, and has proposed de-
tailed technical measures of Low-carbon building tech-
nology. In satisfying the structure load and seismic de-
signing requirements, the “implicit” CO2 emission can
be reduced by approximately 5% if replace C40 concrete
by C50 concrete; the quantity of CO2 emission of the
aluminium alloy curtain wall during the whole life cycle
is 15% of that of the wall paintings with the same area;
wooden floor has a much smaller quantity of “implicit”
CO2 emission than other indoor floor decoration materi-
als. The above measures and calculation results are of
value as a reference for energy saving, emission reduc-
tion and low-carbon building technology.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the Special Research Foundation of Doc-
toral Subjects in University of China (No. 20050487017).
REFERENCES
[1] Department of Trade and Industry (2003) Our energy
future-creating a low carbon economy. The Stationery
Office, London.