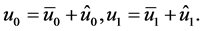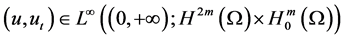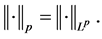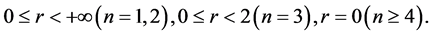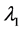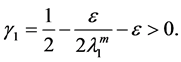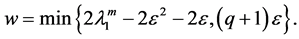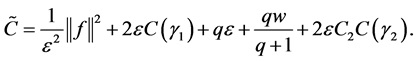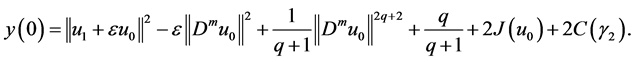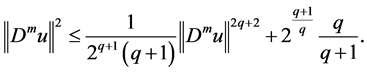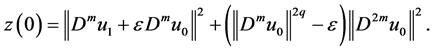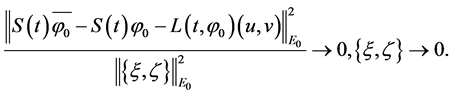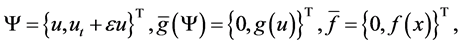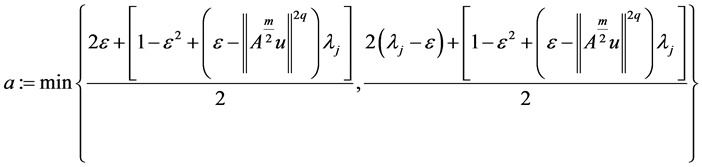International Journal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Application
Vol.05 No.04(2016), Article ID:72185,18 pages
10.4236/ijmnta.2016.54018
The Global Attractors and Their Hausdorff and Fractal Dimensions Estimation for the Higher-Order Nonlinear Kirchhoff-Type Equation with Strong Linear Damping
Yunlong Gao, Yuting Sun, Guoguang Lin
Department of Mathematics, Yunnan University, Kunming, China

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: October 10, 2016; Accepted: November 20, 2016; Published: November 23, 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper, we study the longtime behavior of solution to the initial boundary value problem for a class of strongly damped Higher-order Kirchhoff type equations: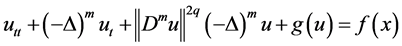 . At first, we prove the existence and uniqueness of the solution by priori estimation and the Galerkin method. Then, we obtain to the existence of the global attractor. At last, we consider that the estimation of the upper bounds of Hausdorff and fractal dimensions for the global attractors are obtained.
. At first, we prove the existence and uniqueness of the solution by priori estimation and the Galerkin method. Then, we obtain to the existence of the global attractor. At last, we consider that the estimation of the upper bounds of Hausdorff and fractal dimensions for the global attractors are obtained.
Keywords:
Nonlinear Higher-Order Kirchhoff Type Equation, The Existence and Uniqueness, The Global Attractors, Hausdorff Dimensions, Fractal Dimensions

1. Introduction
In this paper, we are concerned with the existence of global attractor and Hausdorff and Fractal dimensions estimation for the following nonlinear Higher-order Kirchhoff-type equations:
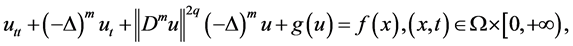 (1.1)
(1.1)
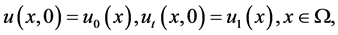 (1.2)
(1.2)
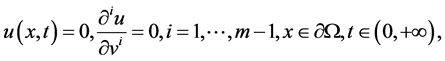 (1.3)
(1.3)
where 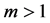 is an integer constant, and
is an integer constant, and 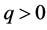 is a positive constant. Moreover,
is a positive constant. Moreover, 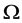 is a bounded domain in
is a bounded domain in 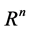 with the smooth boundary
with the smooth boundary 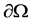 and v is the unit outward normal on
and v is the unit outward normal on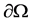 .
. 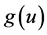 is a nonlinear function specified later.
is a nonlinear function specified later.
Recently, Marina Ghisi and Massimo Gobbino [1] studied spectral gap global solutions for degenerate Kirchhoff equations. Given a continuous function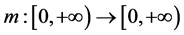 , they consider the Cauchy problem:
, they consider the Cauchy problem:
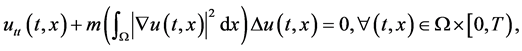 (1.4)
(1.4)
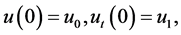 (1.5)
(1.5)
where 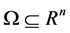 is an open set and
is an open set and 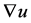 and
and 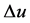 denote the gradient and the Laplacian of u with respect to the space variables. They prove that for such initial data
denote the gradient and the Laplacian of u with respect to the space variables. They prove that for such initial data 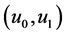 there exist two pairs of initial data
there exist two pairs of initial data 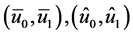
Yang Zhijian, Ding Pengyan and Lei Li [2] studied Longtime dynamics of the Kirchhoff equations with fractional damping and supercritical nonlinearity:
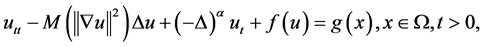
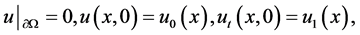
where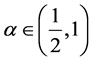
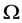
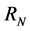
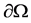
and the nonlinearity 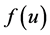
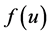
that is, 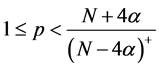
lutions of the equation are of the characters of the parabolic equation; (ii) when
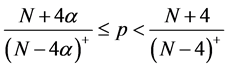
and possesses a weak global attractor.
Yang Zhijian, Ding Pengyan and Liu Zhiming [3] studied the Global attractor for the Kirchhoff type equations with strong nonlinear damping and supercritical nonlinearity:
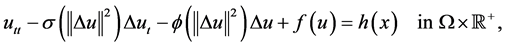
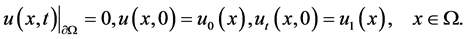
where 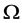
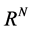
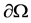
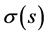
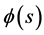
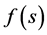
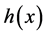
Li Fucai [4] studied the global existence and blow-up of solutions for a higher-order nonlinear Kirchhoff-type hyperbolic equation:
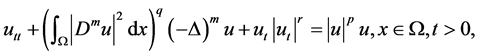
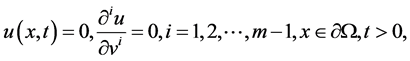
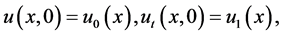
where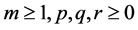
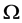
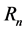
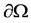
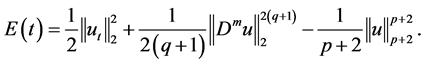
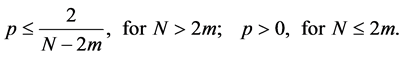
Their main results are the two theorems:
Theorem 1. Suppose that 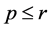
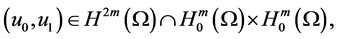
Theorem 2. Suppose that 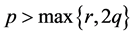
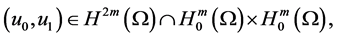
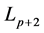
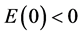
Li Yan [5] studied The Asymptotic Behavior of Solutions for a Nonlinear Higher Order Kirchhoff Type Equation:
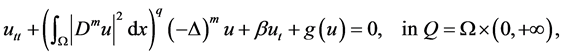
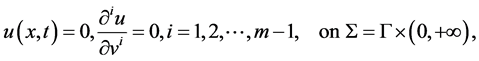
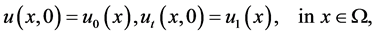
where 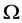
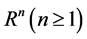
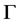

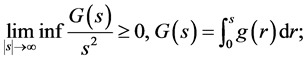
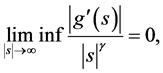
where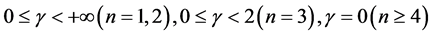
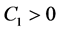
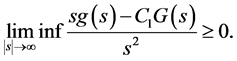
At last, Li Yan studied the asymptotic behavior of solutions for problem (1.14) - (1.16).
For the most of the scholars represented by Yang Zhijian have studied all kinds of low order Kirchhoff equations and only a small number of scholars have studied the blow-up and asymptotic behavior of solutions for higher-order Kirchhoff equation. So, in this context, we study the high-order Kirchhoff equation is very meaningful. In order to study the high-order nonlinear Kirchhoff equation with the damping term, we borrow some of Li Yan’s [5] partial assumptions (2.1) - (2.3) for the nonlinear term g in the equation. In order to prove that the lemma 1, we have improved the results from assumptions (2.1) - (2.3) such that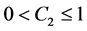
that the equation has a unique smooth solution
and obtain the solution semigroup 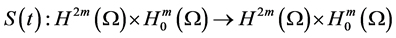
For more related results we refer the reader to [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] . In order to make these equations more normal, in section 2 and in section 3, some assumptions, notations and the main results are stated. Under these assumptions, we prove the existence and uniqueness of solution, then we obtain the global attractors for the problems (1.1) - (1.3). According to [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] , in section 4, we consider that the global attractor of the above mentioned problems (1.1) - (1.3) has finite Hausdorff dimensions and fractal dimensions.
2. Preliminaries
For convenience, we denote the norm and scalar product in 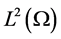

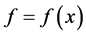
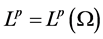
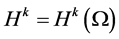
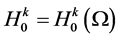

According to [5] , we present some assumptions and notations needed in the proof of our results. For this reason, we assume nonlinear term 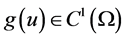
(H1) Setting 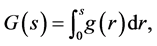
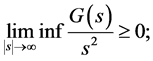
(H2) If
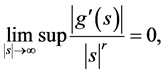
where
(H3) There exist constant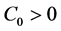
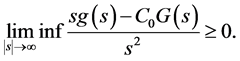
(H4) There exist constant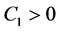
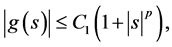
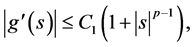
where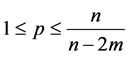
For every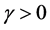
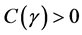
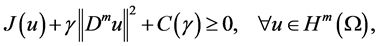
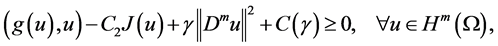
where 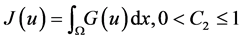
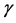
Lemma 1. Assume (H1)-(H3) hold, and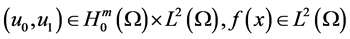
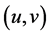
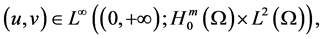

where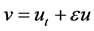
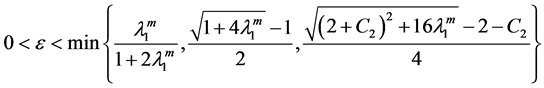
is the first eigenvalue of 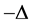
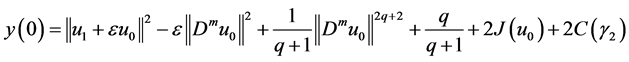
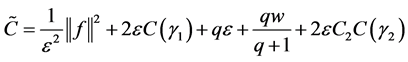
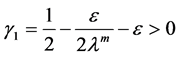
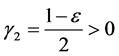
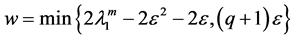
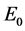
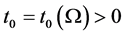
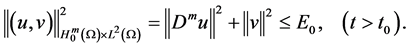
Proof. We take the scalar product in 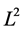
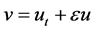
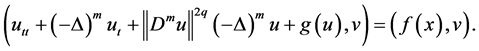
After a computation in (2.10), we have
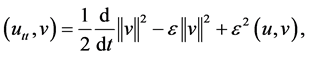
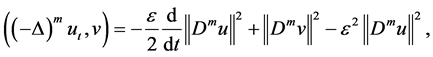
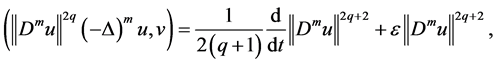
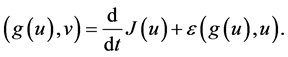
Collecting with (2.11) - (2.14), we obtain from (2.10) that
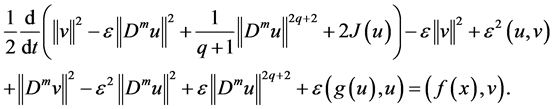
Since 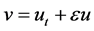
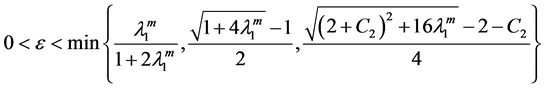
equality Young’s inequality and Poincaré inequality, we deal with the terms in (2.15) one by one as follow:
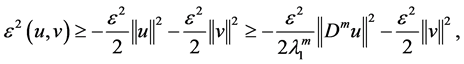
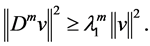
By (2.7), we can obtain
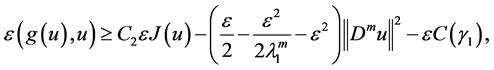
where
Because of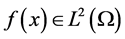
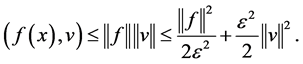
By (2.16) - (2.19), it follows from that
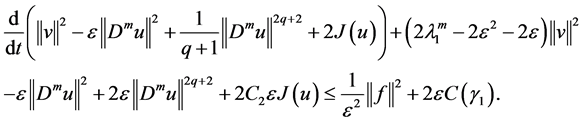
By Young’s inequality and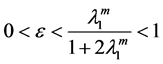
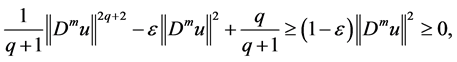
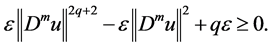
By (2.22), we get
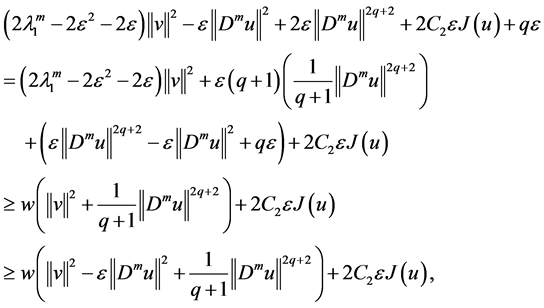
where
By (2.21) and substituting (2.23) into (2.20), we receive
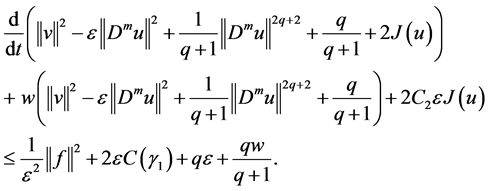
Since 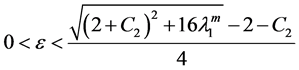
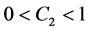
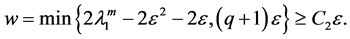
By (2.6) and (2.21), we have
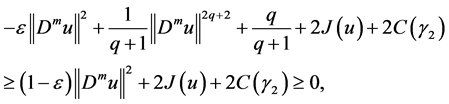
where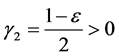
Combining with (2.25) and (2.26), formula (2.24) into
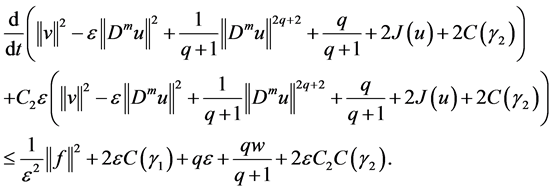
We set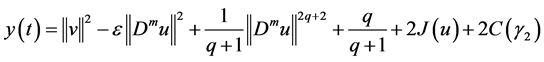
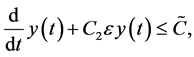
where
From conclusion (2.26), we know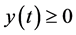
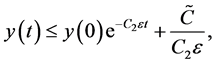
where
By generalized Young’s inequality, we have
Then, we get
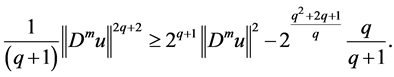
By (2.26) and (2.30), we have
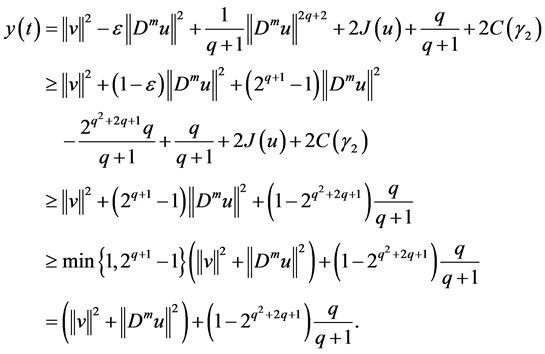
Combining with (2.29) and (2.31),we obtain
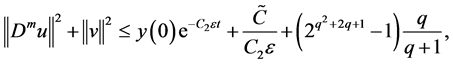
Then,
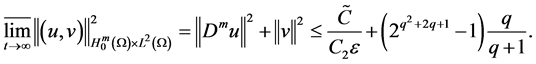
So, there exist 
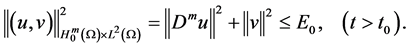
Lemma 2. In addition to the assumptions of Lemma 1, (H1) - (H4) hold. If (H5): 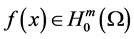
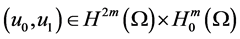
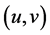
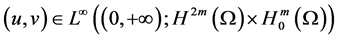
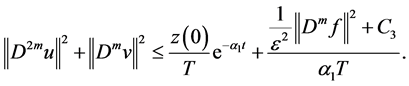
where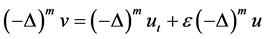
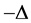
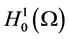
and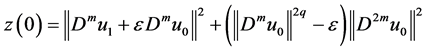
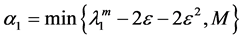
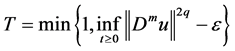
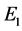
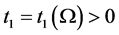
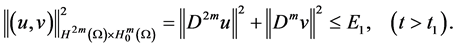
Proof. Taking L2-inner product by 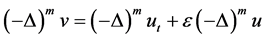
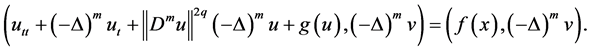
After a computation in (2.37) one by one, as follow
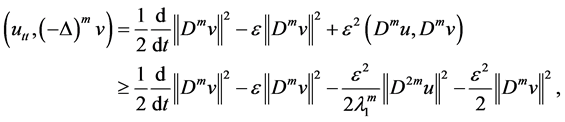
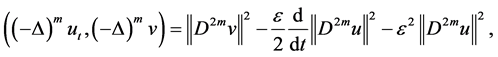
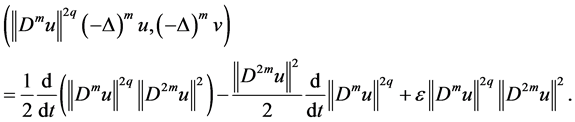
By Young’s inequality, we get
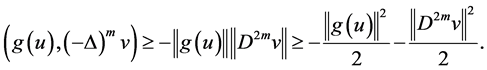
Next to estimate 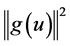
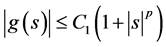
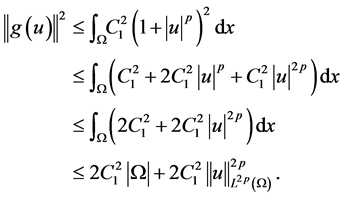
By 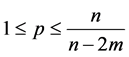
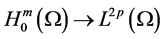
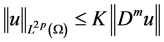
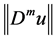
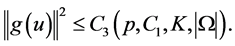
Collecting with (2.43), from (2.41) we have
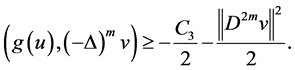
By 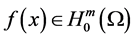
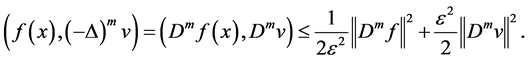
Integrating (2.38) - (2.40), (2.44) - (2.45), from (2.37) entails
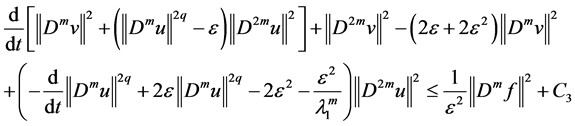
By Poincaré inequality, such that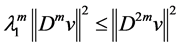
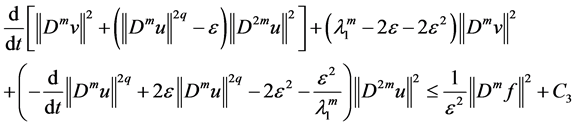
First, we take proper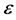
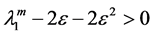
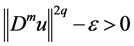
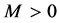
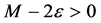
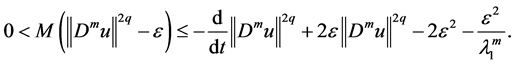
to
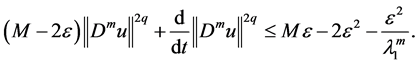
By Gronwall’s inequality, we get
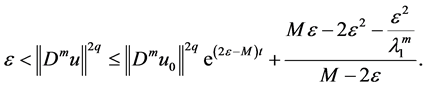
On account of Lemma 1, we know 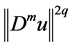
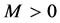
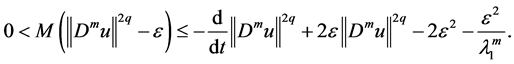
Substituting (2.50) into (2.47), we receive
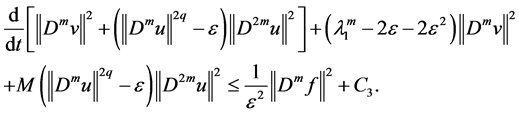
Taking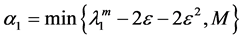
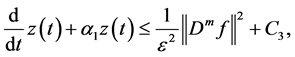
where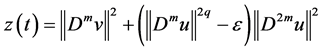
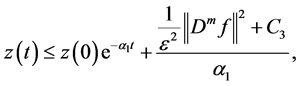
where
Let 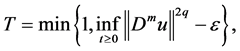
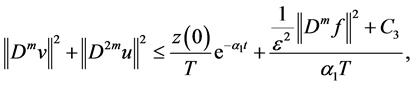
Then
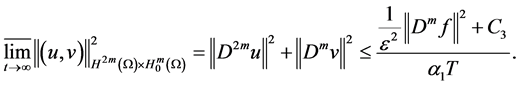
So, there exists 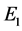
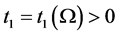
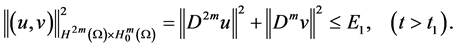
3. Global Attractor
3.1. The Existence and Uniqueness of Solution
Theorem 3.1. Assume (H1) - (H4) hold, and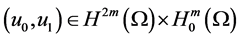
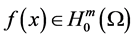
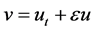
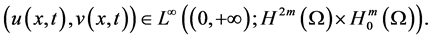
Proof. By the Galerkin method, Lemma 1 and Lemma 2, we can easily obtain the existence of Solutions. Next, we prove the uniqueness of Solutions in detail.
Assume 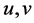
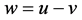
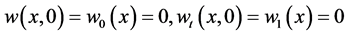
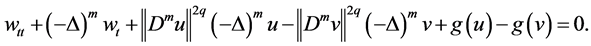
By multiplying (3.2) by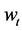
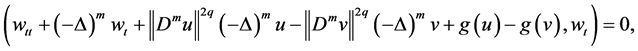
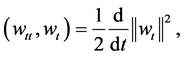
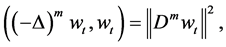
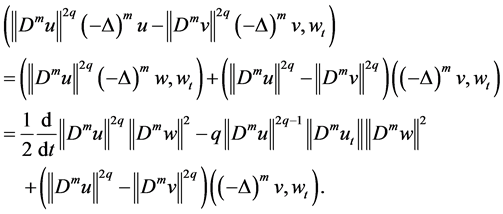
Exploiting (3.4) - (3.6), we receive
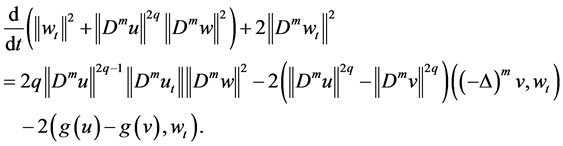
In (3.7), according to Lemma 1 and Lemma 2, such that
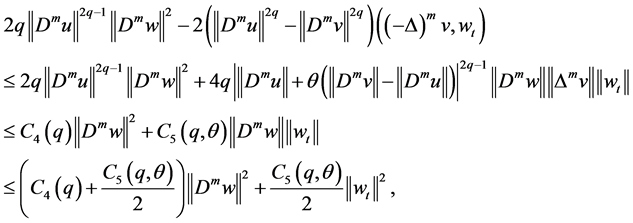
where 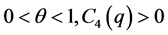
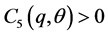
By (H4), we obtain
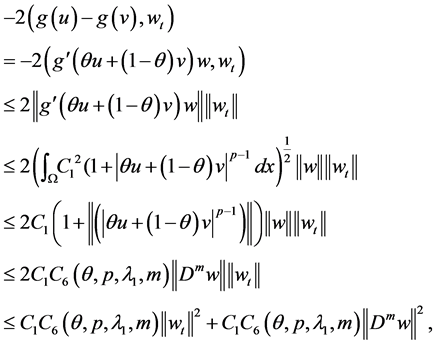
where 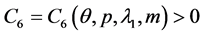
From the above, we have
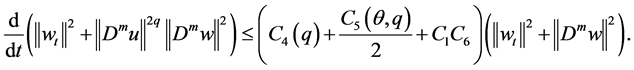
For (3.10), because 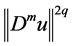
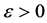
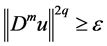
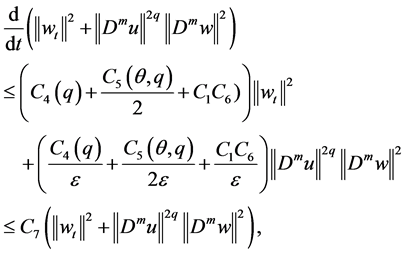
where 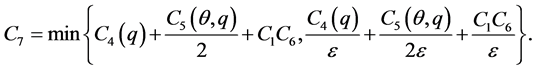
wall’s inequality for (3.11), we obtain
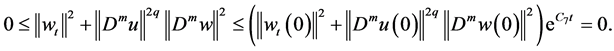
Hence , we can get 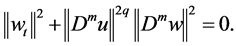
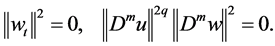
That is
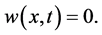
Therefore
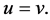
So we get the uniqueness of the solution.
3.2. Global Attractor
Theorem 3.2. [10] Let E be a Banach space, and 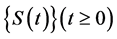
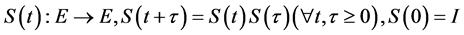
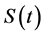
1) 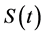
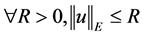
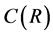
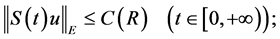
2) It exists a bounded absorbing set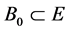
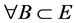
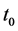
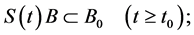
where 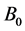
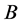
3) When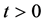
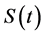
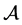
Theorem 3.3. Under the assume of Lemma 1, Lemma 2 and Theorem 3.1, equations have global attractor
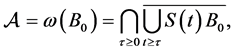
where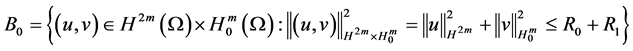
is the bounded absorbing set of 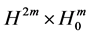
1)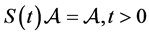
2)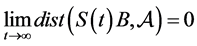
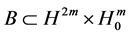
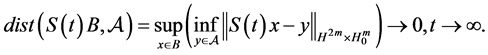
Proof. Under the conditions of Theorem 3.1, it exists the solution semigroup S(t), 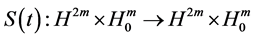
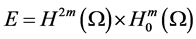
(1) From Lemma 1 to Lemma 2, we can get that 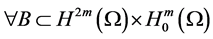
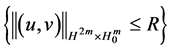
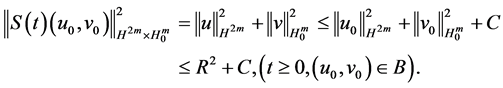
This shows that 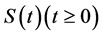
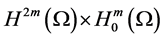
(2) Furthermore, for any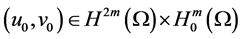
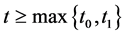
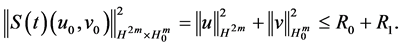
So we get 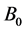
(3) Since 
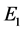
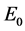
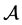
4. The Estimates of the Upper Bounds of Hausdorff and Fractal Dimensions for the Global Attractor
We rewrite the problems (1.1) - (1.3):
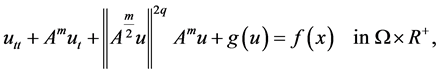
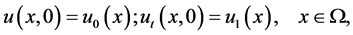
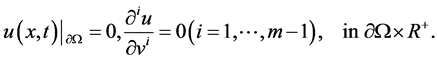
Let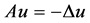
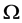
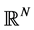
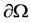
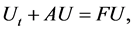
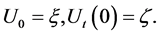
Let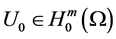
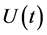
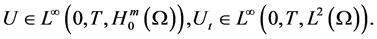
mapping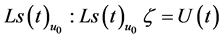
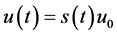
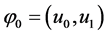
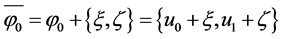
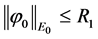
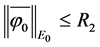
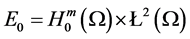
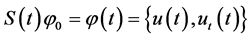
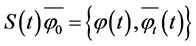
Lemma 4.1 [6] Assume H is a Hilbert space, 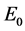
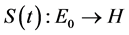
1)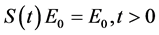
2) If 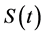
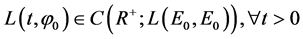
The proof of lemma 4.1 see ref. [6] is omitted here. According to Lemma 4.1, we can get the following theorem :
Theorem 4.1. [6] [7] Let 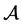
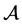
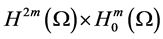
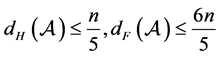
Proof. Firstly, we rewrite the equations (4.1), (4.2) into the first order abstract evolution equations in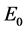
Let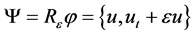
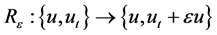
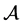
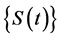
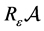
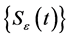
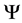
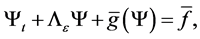
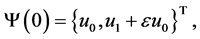
where
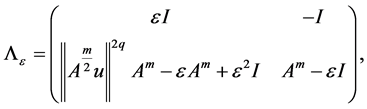
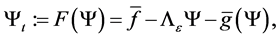
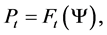
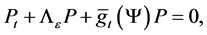
where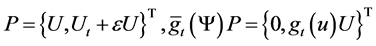
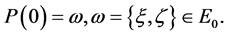
We take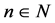
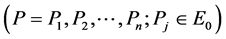
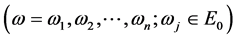
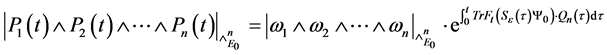
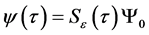
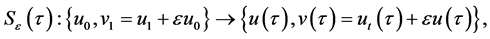
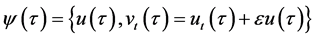
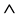
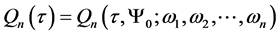
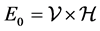
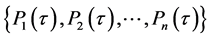
For a given time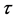
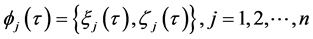
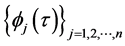
standard orthogonal basis of the space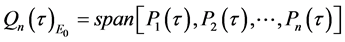
From the above, we have
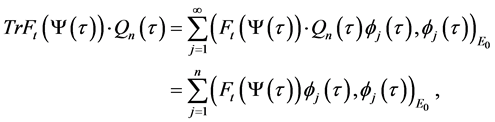
where 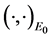
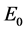
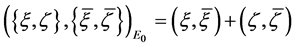
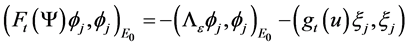
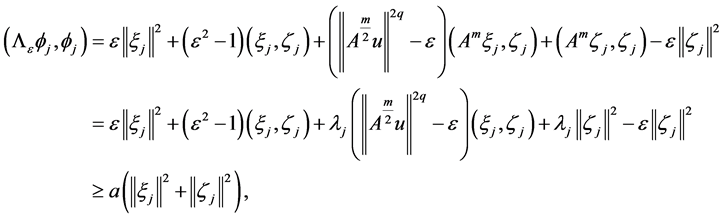
where
Now, suppose that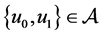
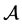
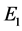
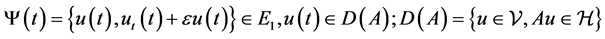
Then there is a 
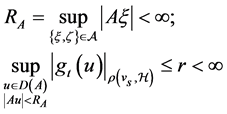
where 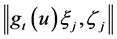
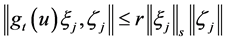
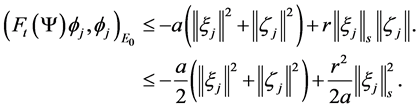
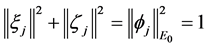
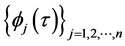
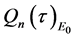
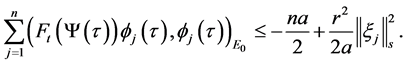
Almost to all t, making
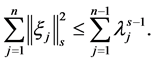
So
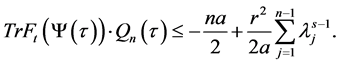
Let us assume that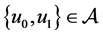
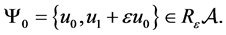
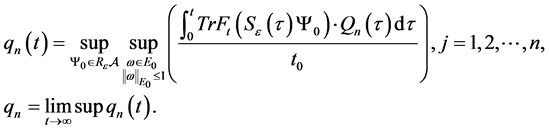
According to (4.19), (4.20), so
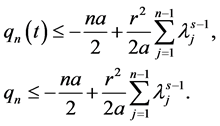
Therefore, the Lyapunov exponent of 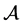
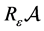
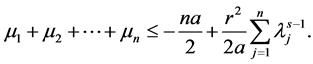
From what has been discussed above, it exists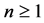
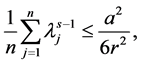
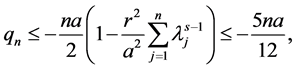
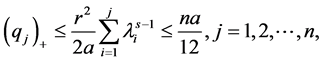
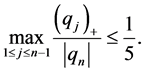
According to the reference [6] [7] , we immediately to the Hausdorff dimension and fractal dimension are respectively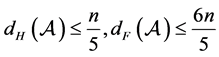
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we prove that the higher-order nonlinear Kirchhoff equation with linear damping in 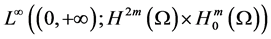
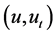
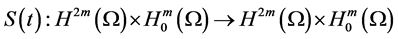
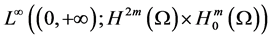
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to the aonymous reviewer for his/her careful reading of the paper, giving valuable comments and suggestions. These contributions greatly improved the paper.
Fund
This work is supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of People’s Republic of China under Grant 11561076.
Cite this paper
Gao, Y.L., Sun, Y.T. and Lin, G.G. (2016) The Global Attractors and Their Hausdorff and Fractal Di- mensions Estimation for the Higher-Order Nonlinear Kirchhoff-Type Equation with Strong Linear Damping. International Jour- nal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Appli- cation, 5, 185-202. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijmnta.2016.54018
References
- 1. Ghisi, M. and Gobbino, M. (2009) Spectral Gap Global Solutions for Degenerate Kirchhoff Equations. Nonlinear Analysis, 71, 4115-4124.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2009.02.090 - 2. Yang, Z.J., Ding, P.Y. and Li, L. (2016) Longtime Dynamics of the Kirchhoff Equations with Fractional Damping and Supercritical Nonlinearity. Journal of Mathematical Analysis Application, 442, 485-510.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2016.04.079 - 3. Yang, Z.J., Ding, P.Y. and Liu, Z.M. (2014) Global Attractor for the Kirchhoff Type Equations with Strong Nonlinear Damping and Supercritical Nonlinearity. Applied Mathematics Letters, 33, 12-17.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2014.02.014 - 4. Li, F.C. (2004) Global Existence and Blow-Up of Solutions for a Higher-Order Kirchhoff-Type Equation with Nonlinear Dissipation. Applied Mathematics Letters, 17, 1409-1414.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.am1.2003.07.014 - 5. Li, Y. (2011) The Asymptotic Behavior of Solutions for a Nonlinear Higher Order Kirchhoff Type Equation. Journal of Southwest China Normal University, 36, 24-27.
- 6. Teman, R. (1998) Infinite Dimensional Dynamics Systems in Mechanics and Physics. Springer, New York.
- 7. Wu, J.Z. and Lin, G.G. (2009) The Global Attractor of the Bossinesq Equation with Damping Term and Its Dimension Estimation. Journal of Yunnan University, 31, 335-340.
- 8. Yang, Z.J. (2007) Longtime Behavior of the Kirchhoff Type Equation with Strong Damping on RN. Journal of Differential Equations, 242, 269-286.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jde.2007.08.004 - 9. Yang, Z.J. and Liu, Z.M. (2015) Exponential Attractor for the Kirchhoff Equations with Strong Nonlinear Damping and Supercritical Nonlinearity. Applied Mathematics Letters, 46, 127-132.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2015.02.019 - 10. Lin, G.G. (2011) Nonlinear Evolution Equation. Yunnan University Press, Kunming.