Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.03 No.11(2015), Article ID:61290,15 pages
10.4236/jamp.2015.311167
New Exact Solutions of the (2 + 1)-Dimensional AKNS Equation
Yepeng Sun
School of Mathematics and Quantitative Economics, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan, China

Copyright © 2015 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 11 October 2015; accepted 17 November 2015; published 20 November 2015
ABSTRACT
N-soliton solutions and the bilinear form of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation are obtained by using the Hirota method. Moreover, the double Wronskian solution and generalized double Wronskian solution are constructed through the Wronskian technique. Furthermore, rational solutions, Matveev solutions and complexitons of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation are given through a matrix method for constructing double Wronskian entries. The three solutions are new.
Keywords:
(2 + 1)-Dimensional AKNS Equation, Rational Solutions, Matveev Solutions, Complexitons

1. Introduction
It is one of the most important topics to search for exact solutions of nonlinear evolution equations in soliton theory. Moreover, various methods have been developed, such as the inverse scattering transformation [1] , the Darboux transformation [2] , the Hirota method [3] , the Wronskian technique [4] [5] , source generation procedure [6] [7] and so on. In 1971, Hirota first proposed the formal perturbation technique to obtain N-soliton solution of the KdV equation. Satsuma gave the Wronskian representation of the N-soliton solution to the KdV equation [8] . Then the Wronskian technique was developed by Freeman and Nimmo [4] [5] . In 1992, Matveev introduced the generalized Wronskian to obtain another kind of exact solutions called Positons for the KdV equation [9] . Recently, Ma first introduced a new kind of exact solution called complexitons [10] . By using these methods, exact solutions of many nonlinear soliton equations are obtained [11] - [16] .
The AKNS (Ablowitz-Kaup-Newell-Segur) equation is one of the most important physical models [17] - [19] . In 1997, Lou and Hu have obtained the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation from the inner parameter dependent symmetry constraints of the KP equation [20] . Moreover, Lou et al. have studied Painlev  integrability of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation [21] . In this paper, we will apply the Hirota method and the Wronskian technique to obtain new exact solutions of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation.
integrability of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation [21] . In this paper, we will apply the Hirota method and the Wronskian technique to obtain new exact solutions of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, the bilinear form of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation and its N-soliton solutions are obtained through the Hirota method. In Section 3, the double Wronskian solution and generalized double Wronskian solution are constructed by using the Wronskian technique. In Sections 4 and 5, rational solutions and Matveev solutions are given. In Section 6, complexitons of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation are provided. Finally, we give some conclusions.
2. N-Soliton Solutions of the (2 + 1)-Dimensional AKNS Equation
We consider the following (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation [21]
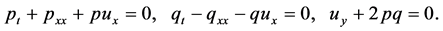 (2.1)
(2.1)
Through the dependent variable transformation
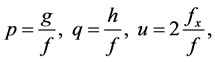 (2.2)
(2.2)
Equation (2.1) is transformed into the following bilinear form
 (2.3a)
(2.3a)
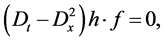 (2.3b)
(2.3b)
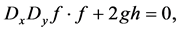 (2.3c)
(2.3c)
where D is the well-known Hirota bilinear operator defined by
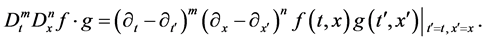
Expanding f, g and h as the series
 (2.4a)
(2.4a)
 (2.4b)
(2.4b)
 (2.4c)
(2.4c)
substituting Equation (2.4) into (2.3) and comparing the coefficients of the same power of 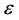 yields
yields
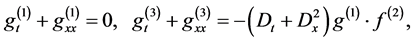

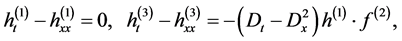
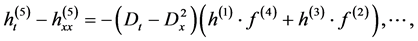
Taking


we can obtain
Letting 




where
In the same way, we can obtain the following N-soliton solutions of Equation (2.3).



where








3. The Double Wronskian Solution and Generalized Double Wronskian Solution
Let us first specify some properties of the Wronskian determinant. As is well known, the double Wronskian determinant is
where 


where D is a 


where 


Employing the Wronskian technique, we have the following result.
Theorem 1. The (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS Equation (2.3) has the double Wronskian solution

where 



Proof. In the following, we use the abbreviated notation of Freeman and Nimmo for the Wronskian and its derivatives [4] [5] , then Equation (3.3) becomes

First, we calculate various derivatives of g and f with respect to x and t.
Then a direct calculation gives

Utilizing Equation (3.2) and Equation (3.4), we get




Noting




Using Equation (3.7) and Equation (3.8), then Equation (3.6) becomes

According to (3.1), it is easy to see that Equation (3.9) is equal to zero. So, the proof of Equation (2.3a) is completed. Similarly Equations (2.3 b) and (2.3 c) can also be proved.
In the following, we give some exact solutions. From Equation (3.4), we deduce that

where 


Taking 
Letting 

then one-soliton solution of Equation (2.1) is
Choosing 

So, we have
Similarly, when 

In the following, we will prove that Equation (2.3) has the generalized double Wronskian solution. First, we give the following lemma [19] .
Lemma 1. Assume that 








where 
Using the Lemma 1 and the Wronskian technique, we construct the following result.
Theorem 2. The (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS Equation (2.3) has the generalized double Wronskian solution

where 





In fact, similar the proof of Theorem 1, we only need to verify that identities (3.7) hold.
(1) If 
from Lemma 1, we can get

Using Equation (3.13), the left-hand side of (3.14) is equal to
Therefore,

From (3.15), we derive further





It is obvious that (3.7) hold.
(2) If 







Using (3.18), Equation (3.12) still satisfies Equation (2.3).
From Equation (3.13), we can get the general solution

where 

lowing result.
Theorem 3. 




4. Rational Solutions
In the section, we will give rational solutions of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS Equation (2.1).
Expanding (3.19) leads to


If

we can obtain solution solutions of Equation (2.3), where

If

it is obvious to know that 


The components of 



In (4.6), taking 


Thus, we can calculate some rational solutions of Equation (2.1).



5. Matveev Solutions
In the following, we will discuss Matveev solutions of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation.
Let A be a Jordan matrix

Without loss of generality, we observe the following Jordan block (dropping the subscript of k)

where 


i.e.,

Substituting (5.2) into (4.1), we get

The components of 



Specially, taking 


Thus, Matveev solutions of Equation (2.1) can be obtained, where


In (5.7), taking

where 


Similarly, choosing

and 



When 



Assume that

letting 



Similarly, taking 



6. Complexitions of the (2 + 1)-Dimensional AKNS Equation
In the following, we would like to consider that A is a real Jordan matrix.

where
and 

In order to prove that, we first observe the simplest case when

Substituting (6.2) into (4.1a) yields

Expanding the above φ and taking advantage of

Similarly,

Further, we consider the matrix A as a Jordan block


where the symbol 


Employing the following formula

then (6.6) can be written as

Substituting (6.8) into (4.1) yields


or


where
According to (6.4), Equation (6.10) can be expressed as the following explicit form:


Thus, the double Wronskian (3.12) is the complextion of Equation (2.3), where
On the other hand, for 

partial derivative with respect to 
For example, taking 






7. Conclusion
In this paper, we have obtained N-solution solutions and the generalized double Wronskian solution of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation through the Hirota method and the Wronskian technique, respectively. Moreover, we have given rational solutions, Matveev solutions and complexitons of the (2 + 1)-dimensional AKNS equation. According to our knowledge, the three solutions are novel.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to express his thanks to the Editor and the referee for their comments. This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (Grant No. ZR2014AM001), and the youth teacher development program of Shandong Province of China.
Cite this paper
Yepeng Sun, (2015) New Exact Solutions of the (2 + 1)-Dimensional AKNS Equation. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,03,1391-1405. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2015.311167
References
- 1. Gardner, C.S., Greene, J.M., Kruskal, M.D. and Miura, R.M. (1967) Method for Solving the Korteweg de Vries Equation. Physical Review Letters, 19, 1095-1097.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.19.1095 - 2. Matveev, V.B. and Salle, M.A. (1991) Darboux Transformations and Solitons. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-00922-2 - 3. Hirota, R. (1971) Exact Solution of the Korteweg-de Vries Equation for Multiple Collisions of Solitons. Physical Review Letters, 27, 1192-1194.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.27.1192 - 4. Freeman, N.C. and Nimmo, J.J.C. (1983) Soliton Solutions of the KdV and KP Equations: The Wronskian Technique. Physics Letters A, 95, 1-3.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(83)90764-8 - 5. Nimmo, J.J.C. and Freeman, N.C. (1983) A Method of Obtaining the N-Soliton Solution of the Boussinesq Equation in Terms of a Wronskian. Physics Letters A, 95, 4-6.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(83)90765-X - 6. Hu, X.B. and Wang, H.Y. (2006) Construction of dKP and BKP Equations with Self-Consistent Sources. Inverse Problems, 22, 1903-1920.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/22/5/022 - 7. Hu, X.B. and Wang, H.Y. (2007) New Type of Kadomtsev-Petviashvili Equation with Self-Consistent Soureces and Its Blinear Bäcklund Transformation. Inverse Problems, 23, 1433-1444.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/23/4/005 - 8. Satsuma, J. (1979) A Wronskian Representation of N-Soliton Solutions of Nonlinear Evolution Equations. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 46, 359-360.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.46.359 - 9. Matveev, V.B. (1992) Generalized Wronskian Formula for Solutions of the KdV Equation: First Applications. Physics Letters A, 166, 205-208.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(92)90362-P - 10. Ma, W.X. (2002) Complexiton Solutions to the Korteweg-de Vries Equation. Physics Letters A, 301, 35-44.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0375-9601(02)00971-4 - 11. Ma, W.X. (2004) Wronskians, Generalized Wronskians and Solutions to the Korteweg-de Vries Equation. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 19, 163-170.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0960-0779(03)00087-0 - 12. Ma, W.X. and Maruno, K. (2004) Complexiton Solutions of the Toda Lattice Equation. Physica A, 343, 219-237.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2004.06.072 - 13. Ma, W.X. and You, Y. (2005) Solving the Korteweg-de Vries Equation by Its Bilinear Form: Wronskian Solutions. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 357, 1753-1778.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1090/S0002-9947-04-03726-2 - 14. Ma, W.X. (2005) Complexiton Solutions to Integrable Equations. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications, 63, 2461-2471.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2005.01.068 - 15. Ma, W.X. (2005) Complexiton Solutions of the Korteweg-de Vries Equation with Self-Consistent Sources. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 26, 1453-1458.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2005.03.030 - 16. Ma, W.X., Li, C.X. and He, J.S. (2009) A Second Wronskian Formulation of the Boussinesq Equation. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications, 70, 4245-4258.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2008.09.010 - 17. Ablowitz, M.J., Kaup, D.J., Newell, A.C. and Segur, H. (1974) The Inverse Scattering Transform-Fourier Analysis for Nonlinear Problems. Studies in Applied Mathematics, 53, 249-315.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sapm1974534249 - 18. Liu, Q.M. (1990) Double Wronskian Solution of the AKNS and Classical Boussinesq Hierarchies. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 59, 3520-3527.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.59.3520 - 19. Chen, D.Y., Zhang, D.J. and Bo, J.B. (2008) New Double Wronskian Solutions of the AKNS Equation. Science in China Series A: Mathematics, 51, 55-69.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11425-007-0165-6 - 20. Lou, S.Y. and Hu, X.B. (1997) Infinitely Many Lax Pair and Symmetry Constraints of the KP Equation. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 38, 6407-6427.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.532219 - 21. Lou, S.Y., Chen, C.L. and Tang, X.Y. (2002) (2 + 1)-Dimensional (M + N)-Component AKNS System: Painlevé Integrability, Infinitely Many Symmetries, Similarity Reductions and Exact Solutions. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 43, 4078-4109.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1490407










































