Journal of Service Science and Management
Vol.09 No.05(2016), Article ID:71194,10 pages
10.4236/jssm.2016.95043
Research on the Efficiency of Introducing Strategic Investors in Commercial Banks in China―Based on the Panel Data Model
Tingting Shang, Lixia Yu*
School of Business, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu, China

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: August 25, 2016; Accepted: October 10, 2016; Published: October 13, 2016
ABSTRACT
In order to solve the problem of insufficient capital adequacy, haphazard internal control, the lower international competitiveness and others, the domestic commercial banks have introduced strategic investors. In order to study whether efficiency of introducing the strategic investors is improved, this paper carries out panel data regression analysis, using data of such banks as: the China Construction Bank, Agricultural Bank and other 9 banks which have already introduced strategic investors. Then, the result shows that although the introduction of strategic investors for bank profitability is not significant. It is conducive to improve the bank’s financial innovation ability, cost control ability and risk management capabilities in the overall performance of bank efficiency; and with the increasing investment and shareholding ratios in strategic investors, the beneficial effect to improve the efficiency of China’s commercial banks becomes more obvious. On the basis of empirical research, this article puts forward some suggestions in the management and introduction of strategic investors.
Keywords:
Strategic Investor, The Efficiency of Banks, Panel Data Model

1. Introduction
In order to speed up the reform and development of financial industry, our country has been adjusting the policy and strategy of the foreign bank market access, through the introduction of strategic investors to promote the strategic cooperation of China and foreign investment and equity cooperation.
The course of China’s introduction of strategic investors is divided into three stages: the initial stage, the exploration phase, and constantly deepen the reform phase. Initial stage in China only two regional government investment mechanisms of commercial bank pilot the introduction of strategic investors; in the stage of exploration according to the WTO agreement China’s banking industry in 2006 to implement the full liberalization of foreign financial institutions, the Chinese government began to gradually liberalized the foreign capital to enter the condition; in 2006 after entering the deepened reform stage, Citigroup, Standard Chartered international banks have entered China, in China opened outlets operating RMB retail business.
Facing the direct impact of the international financial tycoon and the opportunities of the introduction of strategic investors in China, more and more commercial banks introduce strategic investors in the process of restructuring and IPO (Initial Public Offerings), to achieve the promotion purposes at the same time draw on the experience of advanced technology and management, and then to solve the problems of those have restricted the development of China’s banking industry so far, such as high rate of non-performing loans, low capital adequacy ratio, and low efficiency of management. However, since 2008, foreign strategic investors rapidly reduce its stakes of state-owned commercial banks. The most significantly example is for Goldman Sachs, in 2013 May, selling the all remaining shares of ICBC, exiting the ranks of ICBC shareholders. Some scholars believe that this is because of the particularity of the banking industry in China, as it is not mature. But we must think about whether foreign capital introduction is conducive to the development of China’s commercial banks. So we hope that we study on the research, using the panel data of those banks, and learn from the introducing experience of strategic investors, to analyze the commercial bank’s efficiency. We also hope it can provide some reference for the subsequent introduction of the banks which have not yet been introduced into the strategic investors.
2. Literature Review
There are mainly two aspects in research on commercial banks to introduce foreign strategic investors: On the one hand is for the subsequent effects on the commercial banks as a whole after the introduction of foreign strategic investors, on the other hand is for the effects on commercial banks themselves.
On the one hand, the subsequent effects on the commercial banks as a whole after the introduction of foreign strategic invest to Many scholars discussed the practical significance in this field, such as Zhengguang Fu (2006) uses Bank of America stakes China Construction Bank as an example, and analyzing the banking industry competition pattern; he thinks commercial banks introducing strategic investors can not only improve China’s banking industry competition pattern but also create awareness of the advanced competition among banks [1] . Huang Ding (2006) also has this view, thr- ough his analysis of Bank M & A and the theory of transnational M & A, combined with the enlightenment of the introduction of strategic investors in the case of the bank restructuring after financial crisis in South Korea. He thinks it can make state-owned commercial banks to realize the diversification of property rights, enhance the comprehensive competitiveness of state-owned commercial banks [2] . However, Cai Weixing, Zeng Cheng (2011) is to the opposite attitude; they carry out empirical research from point of the lending behavior. But the result is that the introduction of strategic investors did not change the overall state-owned commercial bank loan behavior, and there is no actual positive effect on commercial banks [3] .
On the other hand, the effects on commercial bank themselves: Some people think introducing foreign strategic investors has no significant impact on the performance of China’s banks. Jieya Gao (2012) analyses commercial banks’ profit ability and innovation ability from micro and macro aspects. She believes that the effect of the introducing foreign strategic investors is not remarkable on the performance of China’s commercial bank [4] . Coincidentally, Liuqing Yang (2012) uses system generalized matrix method to draw the same conclusion [5] . Yingxin Liao (2012) thinks the reason why the effect of the introducing foreign strategic investors is not remarkable may be that: in a short period of time, foreign strategic investors not only to run with the domestic banks, but also need to be familiar with the domestic market, so as to have a lack of governance. However some people think introducing foreign strategic investors has a promotion effect on the performance level of China’s commercial banks [6] . Ma Zheng (2009) using event method and factor analysis, respectively study the long-term effects and short-term effects of commercial banks through introducing the strategic investors; taken together, he believes that the introduction of foreign strategic investors have a positive role in promoting the financial performance of commercial banks in China. [7] . Zhangyu, Shulu Yin, Tinghua Liu (2014) analysis the impact of the introduction of foreign strategic investors on the total factor productivity of our commercial banks; She thinks that our commercial bank efficiency level rise with the rising rate of foreign strategic investors’ shareholding time [8] . Youzhen Yang, Rui Zhao (2008) also believes that the introduction of foreign strategic investors can, to a certain extent, optimize the equity structure of the domestic commercial banks, increase the bank’s net profit, and improve the efficiency of the bank/s operating, and business costs, etc., the supply and demand of regional market, the historical factors of the region and the promote force of local government and so on [9] .
3. Theoretical Analysis and Hypothesis made on the efficiency of China’s Commercial Banks after introducing strategic Investors
Mostly, there are multiple aspects of in-depth cooperation terms between invested banks and strategic investors in their Strategic agreement; such as retail business, intermediary business, and bank card business. Through this cooperation, China’s commercial banks introduce not only the strong capital but also the related advanced technology and excellent management mode into China’s banking industry. Banks take advantage of those methods and keep reforming, realizing breakthrough time after time, and finally turn up to be the improvement of banks’ efficiency. Specifically, it mainly shows in profitability significantly promoted, the level of cost constantly controlled, financial innovation enhanced and the ability to control risk continuously improved.
3.1. Profitability
Because of the serious homogenization and Single business variety for a long time in our country, most commercial banks rely on deposit-loan difference as the main source of income and their off balance sheet business development was almost at a standstill. After the introduction of strategic investors, commercial banks continuously upgrade the original loan to financial services of deposit business. On this basis, they produce a large number of financial products, agency business and other intermediary business. With the development of risk management of traditional deposit-loan business and the expansion of new intermediate business, the profitability of the commercial banks has gradually increased. The best ratio to reflect the profitability is ROE. According to the annual report of the major banks over the years, commercial banks’ capital gains rate has been significantly improved after introducing strategic investors.
A year before introducing strategic investors, the capital gains rate of Bank of communications is only 6.39%, afterwards, it increased significantly and reached 13.43% in 2015. In order to verify whether the introduction of strategic investors in China’s commercial banks to get its profitability improved, in this paper we put forward the hypothesis 1:
H1: Introducing strategic investors do enhance the profitability of China’s commercial banks.
3.2. Cost Control
As strategic investors bring its advanced technology and excellent management experience into the investment bank, China’s commercial banks’ internal control system is beneficial to this and continuously improved. The most direct effect of the improvement of internal control is that the cost of commercial banks has been reduced, which is mainly due to the good internal control to eliminate the waste of capital and improve the efficiency of the use of capital. In terms of cost control, the best embodiment is the cost to income ratio. According to the annual reports of the construction bank, a year before introducing strategic investors, the cost income ratio is 45.13%. Afterwards, with the help of strategic investors, the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) has been established to improve the efficiency of the use of funds, and the ratio decreased significantly and as low as 26.98% in 2015. In order to verify whether the introduction of strategic investors in China’s commercial banks to get cost control capability improved, in this paper we put forward the hypothesis 2:
H2: Introducing strategic investors do enhance the cost control capability of China’s commercial banks.
3.3. Financial Innovation
As the strategic investors introduced by commercial banks are not only international retail giants as the Bank of America, Citibank, but also professional financial consulting firm as American Express, Goldman Sachs. These strategic investors change the status that China’s commercial banks rely mainly on loans, through providing technical guidance and support to new intermediate business. By studying strategic investors’ advanced technology and combining the actual situation of China’s banking industry, China’s commercial banks creatively launched a series of financial services in line with China’s actual demand. The ability of financial innovation of commercial banks in China rising is mainly reflected in the continuous improvement of non-interest income ratio; in recent years, with the development of economy and technology, our country commercial bank non-interest income hit records. According to the annual reports of the Industrial Bank, the non-interest income account for a straight rise, increased from 3.81% in 2004 to 22.47% in 2015.In order to verify whether the introduction of strategic investors in China’s commercial banks to get financial innovation ability raised, in this paper we put forward the hypothesis 3:
H3: Introducing strategic investors do enhance the financial innovation capability of China’s commercial banks.
3.4. Risk Control
China’s commercial banks keep on learning strategic investors’ excellent risk management and control mechanism. At the same time, they combine with the basic situation in china and then establish their own risk control system. Because of the moving the risk control ability in China’s commercial banks, non-performing loan ratio, capital adequacy ratio and other related indicators which reflect the level of risk is also declining. From the annual report of Bank of China, we can see before the introduction of strategic investors, the non-performing loan ratio was close to 5%, after it declines in 2015 was only 1.43%.
In order to verify whether the introduction of strategic investors in China’s commercial banks to get risk control ability raised, in this paper we put forward the hypothesis 4:
H4: Introducing strategic investors do enhance the risk control capability of China’s commercial banks.
4. The Empirical analysis of China’s Commercial Bank Introducing strategic investors
4.1. The Choice of sample data
Until the end of 2015, there are 16 listed banks in China. In order to analyze whether the bank efficiency of commercial banks of our country is significantly improved by introducing strategic investors, and due to the absence of section data of some commercial banks, this article chooses the 9 banks (CCB, ICBC, BOCM, BOC, CMBC, Huaxia Bank, CEB, Citic Bank, CIB) as the sample of this study. Since the time of the introduction of strategic investors in China’s commercial banks are mostly concentrated in 2004. In order to make the research more practical significant, this paper set time span of the sample from 2004 to 2015.
4.2. Variable Selection
4.2.1. Explained variable
In order to test whether introducing strategic investors can raise the China’ commercial bank’ profit, cost control, financial innovation and risk management capacity and whether it can improve the operating efficiency of China’s commercial banks. This paper selects 4 core indexes to represent these abilities: the capital gains rate (ROE), the cost to income ratio (CIR), non-interest income ratio (NIIR), non-performing loan rate (NPL).
4.2.2. Explaining variable
Since strategic investors have become shareholders, the most obvious change is the structure of the equity of the investment bank. This paper selects the strategic investor ownership ratio (SI) as the independent variable.
4.2.3. Control variables
Taking macro and micro factors which related to the influence of explaining variables into consideration, this paper chooses GDP growth rate (GGDP) as the macro control factors and assets scales(AS), the property rights system (PRS), the equity ratio(ER), these three indicators as the micro control factors.
The definition and calculation methods of each variable are shown in table 1.
Table 1. Definitions and calculation methods of each variable.
4.3. The Establishment of the model
In order to verify the above assumptions, and based on the Kim and Lee (2004) panel data model, this paper establishes the following model:

The subscript in the formula i, t represents i bank’s Cross section data in t year, i = 1, 2 ∙∙∙ N (N = 9, t = 2004-2015. Performanceit represents the Index of efficiency of commercial banks: ROE, CIR, NIIR and NPL. SI says the proportion of strategic investors to invest in shares. Zt means Macro control variable AS; Xit means Microscopic control variables PRS and ER. αt means Constant term. α, β, γ represent Coefficient independent variables. εit is random error term.
Dividing Performanceit into ROE, CIR, NIIR, NPL, then get the following formulas:
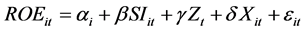

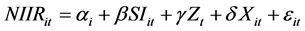
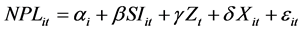
4.4. The Results of Empirical Study
4.4.1. Descriptive Statistics
Before the regression analysis of these panel data, the paper makes a descriptive statistic of the data of the 12 years. The specific descriptive statistical results are as Table 2.
Table 2. Results of descriptive statistics of the variables.
It can be seen from the table, the minimum value of SI in the sample bank is 0; the maximum value reached 24.49%, close to the 25% limit of the China Securities Regulatory commission. We can also see that the ER of sample bank changes considerably: from the minimum value of 11.0184 increased to the maximum value of 44.3703, while ROE, NIIR increase steadily; CIR, NPL decrease gradually.
4.4.2. Regressive Results
In this paper, we use EViews 7.2 software to analyze the factors that affect the efficiency of commercial banks in China after the introduction of strategic investors, and the specific regression results are as Table 3.
Through the analysis of Table 3, we can see that the f value of model (1) does not pass the inspection and the goodness of fit is bad. The other three models pass the inspection, that is to say the better fit. Investors’ shareholding ratio (SI), under the significant levels of 5%, is significantly tested through NIIR model, CIR model, NPL model, except ROE model. In order to further analyze the regression results of each model, the following paper will analyze the corresponding factors of the above models one by one.
1) The impact of profitability. From table 3, SI is not significant to ROE and the regression coefficient of them is low, indicating that the SI cannot be so important to change ROE and therefore override the hypothesis 1, which means the introduction of strategic investors do not improve the profitability of the commercial banks in our country. Furthermore, the AS, PRS, ER, GGDP show no significant influence on ROE. However, when look at PRS, which shows positive correlation to ROE, we can find good news. The phenomenon that commercial banks are currently heavily state-owned is changing with the passage of time. Effects of historical burden of these banks gradually become smaller and release the bank’s overall development.
2) The impact of cost control. We can see SI is significant to CIR at 1% level of significance and the coefficient is −0.282, which means SI for every increase of 1 percentage point CIR lower 0.282 percentage points, to verify the hypothesis 2. At the same time, we can also see GDP, AS, PRS all have significant effect to CIR; AS and CIR show a significant negative correlation, mainly due to continuous expansion of the scale of assets. The cost for daily management of the bank is increased, thus strengthen the cost control.
Table 3. Regression results.
Note: * *, * * *, * * respectively indicates a significant level of 1%, 5% and 10%; in the bracket for the T value.
3) The impact of financial innovation. We can see that SI has a significant positive correlation with NIIR, which means that the higher the SI is, the higher the NIIR is. Obviously, this is in line with the hypothesis of this paper, which means that 3 is established. At the same time, we also see that GGDP, PRS, AS have a significant impact on NIIR. This is mainly due to the continuous development of the economy, science and technology, people management concepts continue to enhance. The bank’s off balance sheet business show a natural growth, mainly due to the continuous innovation of Commercial Bank of our country.
4) The effect of risk control. We can see that the SI has significant positive correlation with the NPL in 1%, and the two has a significant positive correlation, which proves that the model 4 is established. And its coefficient of 0.031 means that the SI per one percentage point increases by the investment bank NPL increased by 0.031. At the same time, we should also see that the NPL has a significant impact on the GDP. The good economic situation will help the bank to reduce the proportion of non-performing loans. Commercial banks can prepare well to control the risk in the economic opportunity.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Empirical Conclusion
Through the empirical analysis of the regression model, we can draw the following conclusions:
1) After the introduction of strategic investors, although the influence of profitability of commercial banks is not significant, the bank’s financial innovation ability, cost control and risk management ability is improved. The overall effect reflects the improvement of bank related capacity indicators, and ultimately exhibits the improvement of operating efficiency of China’s commercial banks. With the continuous improvement of China’s commercial bank efficiency, the overall competitiveness of China’s commercial banks had been continuously enhanced, and ultimately will lead our country’s commercial banks enhance the international status of the original intention.
2) With the increasing of investment and shareholding of strategic investors, the enhancement of the function of bank efficiency in China is becoming more and more obvious. Such enhancement of banks benefits from their own continuous learning. And it gradually solves a series of control problems in the development of China’s banking industry. So we can see that introducing strategic investors is one of the effective ways to improve the bank efficiency in China.
5.2. Relevant Recommendations
When signing a strategic cooperation agreement with strategic investors, we must make a clear entry and exit mechanism for investors to make a clear provision. As the vast majority of China’s commercial banks have not consider their huge development potential in the transfer of ownership, and limited by the evaluation method, the selling price of equity is relatively low. In order to avoid a repeat of the stake sale undervaluing, our country commercial bank must be sure to take the development potential of the banks into account to include it in a comprehensive evaluation of enterprise value system. There may be a lock up period. Banks cannot dump the shares at the moment of the lock period released to pursue short-term capital gains or give up capital dividends over the long term. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a comprehensive incentive mechanism and restraint mechanism. For instance, in order to reduce the impact of strategic investors exit from the bank, we develop a strategic investor gradual withdrawal mechanism.
Paying attention to strengthen communications and combining the strategic investor’s technology and management with China’s actual national conditions. Although the foreign management is advanced, every place has its special historical and cultural. These factors may lead to a long time for China’s commercial banks to get with, so strategic investors and the invested banks should communicate frequently to eliminate the differences. Also invested banks can send staff to learn from strategic investors, which can accelerate the enterprise culture integration, prompting China’s banks to attract strategic investors advanced management mode and to work out a suitable management pattern for its own. Only in this way can shorten the differences.
Cite this paper
Shang, T.T. and Yu, L.X. (2016) Research on the Efficiency of Introducing Strategic Investors in Commercial Banks in China―Based on the Panel Data Model. Journal of Service Science and Management, 9, 388-397. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jssm.2016.95043
References
- 1. Fu, Z.G. (2006) Strategic Investors of Foreign Bank Entry on the Impact of Commercial Bank China Analysis. Shandong University, Jinan.
- 2. Huang, D. (2006) The Introduction of Foreign Strategic Investors of State-Owned Commercial Banks 2006. Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, Chengdu.
- 3. Cai, W.X. and Zeng, C. (2011) Foreign Strategic Investors to Change the Behavior of the State-Owned Commercial Banks Lending—Based on the Empirical Analysis of the Dynamic Panel Data Model. Contemporary Economic Science, No. 1, 13-21
- 4. Gao, Y.J. (2012) The Research of China’s Commercial Banks to Introduce Foreign Strategic Investors. Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou.
- 5. Yang, L.Q. (2012) The Proportion of Foreign Strategic Investors on the Performance of Commercial Bank Chinese. Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, Chengdu.
- 6. Liao, Y.X. (2012) Influence of Foreign Strategic Investors on the Governance Structure and Efficiency of China’s Listed Commercial Banks. Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, Chengdu.
- 7. Ma, Z. (2009) The Introduction of Foreign Strategic Investors in China’s Commercial Banks. Nankai University, Tianjin.
- 8. Zhang, Y., Yin, S.L. and Liu, T.H. (2014) Foreign Strategic Investors, Improve the Operational Efficiency of the Commercial Bank of our Country? Economic Review, 2, 139-149.
- 9. Yang, Y.Z. and Zhao, R. (2008) Domestic Commercial Banks Introduce the Effect of Foreign Strategic Investors: An Empirical Analysis. Finance and Trade Economics, 10, 38-43.


