Journal of Service Science and Management
Vol.08 No.04(2015), Article ID:58499,5 pages
10.4236/jssm.2015.84050
Study on the Cultivating Mode of Undergraduate Talents in Tourism Management: Literature Review, Analysis and Discussion
Dongbei Xu1,2
1School of Government, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
2School of Business Administration, Tonghua Normal University, Tonghua, China
Email: xdb8056@126.com
Copyright © 2015 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 15 July 2015; accepted 27 July 2015; published 31 July 2015
ABSTRACT
Based on the related research articles about undergraduate talents cultivation in tourism management on http://www.cnki.net/, this paper reviews the cultivating mode of undergraduate tourism talents, analyzes the achievements and shortcomings of the existing research literature and discusses the problems of constructing the cultivating mode of undergraduate tourism talents from theoretical basis, practice demand, policy orientation, regional characteristics, developing trend and educational resources.
Keywords:
Talents Cultivating Mode, Undergraduate Tourism Talents, Tourism Management

1. Introduction
Tourism talents in mainland China were increasing at a considerably high rapid in the past over 30 years. There were no specialized tourism colleges or schools before 1978, but in 2014 there were 565 regular universities or colleges that have undergraduate tourism management major with 201,161 undergraduate students in Mainland China. However, the specialized talents still cannot meet the needs of tourism industry especially the tourism enterprises because on the one hand, more and more university students from tourism major prefer working in the industries of advertising, transportation and so forth, other than tourism industry like hotels or travel agencies; on the other hand, tourism enterprises complain that the students of tourism major have no necessary working skills that the tourism industry demands and some students cannot adapt to the working environment and have no chances to develop their careers. Most tourist enterprises and education institutes believe that graduates of the major of tourism should meet the need of the tourism industry, and stress on the practical ability. So it is required for the graduates to start with a grass-roots job in the industry. This traditional training philosophy causes the conflicts between education and practice. As a result, lower employment rate and higher job- shifting rate emerge. Therefore, enterprises, education institutes and graduates are not satisfied with the situation.
Currently, the crucial problem regarding talent-cultivation in China’s tourism institutions is that education cannot fit the needs of the industries and the supply and demand of the talents between colleges and enterprises are in disorder. Therefore, it is imperative to establish a talent-cultivation mode that adapts to the rapid development of tourism industry. With the fast development of tourism and further fierce competition of international tourism, industry tourism employees are facing more challenging requirements than before. More and more countries and enterprises have realized that the competition in the 21st century is actually the competition of tourism talents. Starting with the literature review of talent-cultivation in China’s tourism institutions, this paper reviews the cultivating mode of undergraduate tourism talents, analyzes the achievements and shortcomings of the existing research literature and discusses the problems of constructing the cultivating mode of undergraduate tourism talents from theoretical basis, practice demand, policy orientation, regional characteristics, developing trend and educational resources.
2. Literature Review
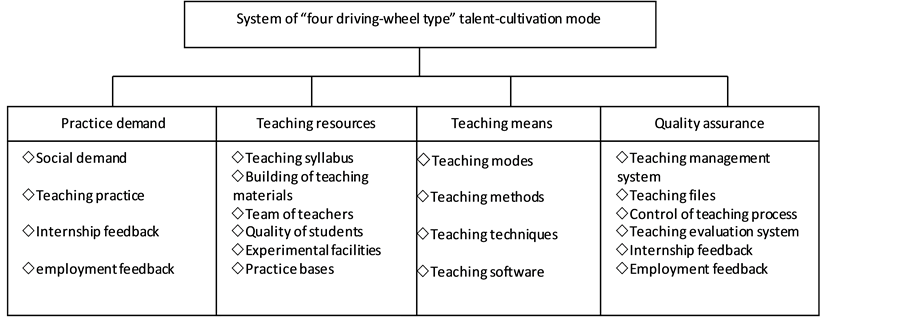
In order to cultivate students’ “tourism complex”, “tourism thinking” and professional competence, Zhang, P.Y., Zhao, Y., Shi, C.B. (2004) [1] tried to systematically summarize the training mode and educating methods in higher tourism education in an attempt to form a complete set of education and teaching programs that combine theory with practice. To cope with the current rapid development of China’s tourism industry and its demand for upgrading the quality of tourism professionals, MA, Y., WEI, W., DENG, N.M. (2005) [2] put forward the “four driving-wheel type” talent-cultivation mode in the major of tourism management (see Figure 1).
Through the analysis of the changes of school-running condition brought by local regional enrollment and cross-provincial enrollment, Zhao, J.J. (2005) [3] put forward new thoughts on constructing the cultivating model of specialized tourism management talents in the major of tourism management in local colleges and universities. He pointed out that constructing the cultivating model of specialized tourism management talents in local colleges should take into account the following 8 aspects: 1) be responsible for the students’ sustainable competitiveness in job-hunting; 2) consider the particularity of tourism management discipline in the allocation of educational resources; 3) respect the freedom of students’ choice on courses and profession but give necessary guidance; 4) cultivate the students’ travel service skills, service awareness and professional dedication; 5) attach great importance to the formation of students’ scientific research consciousness; 6) adapt to the develop-
Figure 1. “Four driving-wheel type” talent-cultivation mode.
ment of tourism and have certain forward-looking consciousness; 7) cultivate students’ general management skills; 8) constantly update knowledge, theories and ideas. Zhang, P.Y., Sun, Q., Shi, C.B. (2006) [4] pointed out that cultivating tourism talents with innovative quality has been an urgent mission for tourism higher education. The innovative teaching system should include knowledge training system characterized by “wide knowledge, strong comprehensive nature, large selection and course module”, “double channel” training system of practical competence and innovative educational quality administrative system. The teaching model of organic combination of “industry, learning and research” is a kind of practice with innovative significance in tourism higher education.
The divorce of theory from practice in the professional teaching of tourism management major results in students’ low ability of transforming knowledge, lack of professional moral and disequilibrium between supply and demand. Wang, Q.R. (2006) [5] pointed out that innovating the talent-cultivating pattern through experience- type teaching can not only solve the above-mentioned problems, but also develop a basic pattern of cultivating “compound, applied and open-type” talents. Based on the theories of emotional teaching method and learning of constructivism and in combination of the characteristics of tourism management major, he made a systematic discussion of the aspects including principle of putting into practice, construction of teaching environment, teaching content, teaching methods as well as teaching organization.
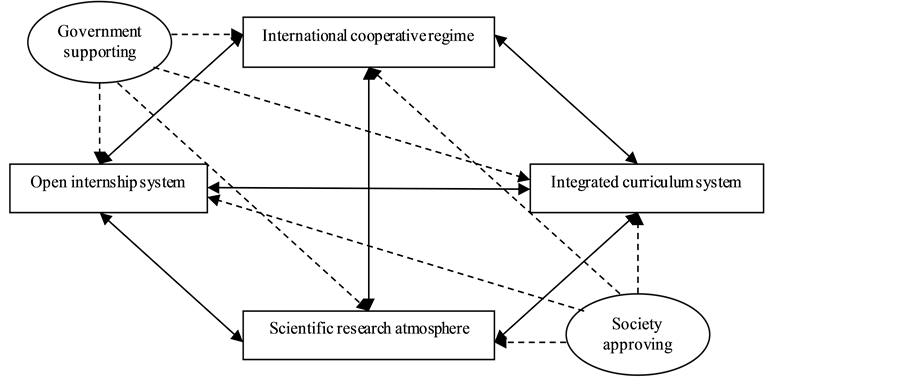
Based on random questionnaire and interviews with experts, employers, alumni and graduates, Li, Y., Wang, Y.L., Liang, L., Hong, Y. (2009) [6] offered a new reformative way about the cultivation of talents in tourism institutions, providing scientific basis for establishing talent-cultivation mode. The laggard development of tourism education has become the bottleneck of sustainable development of the tourism industry in our country, so systematic and comprehensive study of tourism professionals training model in colleges and universities has highly practical guiding significance. Zou, T.Q., Liu, J., Wang, X.F. (2009) [7] proposed the “diamond-type” model of tourism personnel training (see Figure 2).
It is urgent for the development of tourism to cultivate applied tourism management professionals with a strong spirit of innovation and a sense of service. Guo, Y.H. (2010) [8] explained the necessity of cultivating applied talents of tourism management and put forward effective forms of training applied talents of tourism management with good quality by analyzing the contradiction between present training modes of tourism management professionals and their corresponding social demands.
To explore a new training philosophy and operating pattern of senior talents in the major of tourism in tertiary education of China, Zheng, X.M., Fan, X.L. (2010) [9] , firstly, analyzed the supply and demand of tourism talents and existing patterns of tourism education, and then proposed a new pattern which would solve the current problems. The pattern operation needs the creation of curriculum and teaching and theory and the combination between theory and practice, it also needs the cooperation of education institutes, tourism enterprises and talents. The education institutes should establish and put forward the cultivation model and try to smooth the relation-
Figure 2. “Diamond-type” pattern of cultivating professionals.
ship among students, enterprises and schools; meanwhile the enterprises should cooperate with the education in- stitutes to cultivate qualified talents for the tourism industry.
The work-integrated learning is a kind of training model which manifests the characteristic of tourism management education. The “work-integrated learning” training model has become an effective way of the international tourism education. Chen, G.S., Lu, L.J. (2011) [10] discussed the background of the implementation of work-integrated learning model, summarized the practice of “work-integrated learning” training model in Yangtze River normal university, analyzed the localization of tourism management specialized talented person under the work-integrated learning pattern, pointed out that the work-integrated learning model is an effective way of tourism education, and proposed that the reform and the curriculum construction based on the professional ability is the core of this model.
To cultivate applied talents for tourism, benefiting from experiential learning model, Men, L. (2013) [11] put forward an experiential careers guidance mode, which must emphasize employment experience and professional practice, integrate professional roles, workplace environment, work experience into educational guidance and make the students improve and perfect themselves in employability through constant summaries of practical experience.
3. Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Analysis
3.1.1. Achievements
Based on different conditions and situations, the researchers studied the cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management from different perspectives. For example, Zhang, P.Y., Zhao, Y., Shi, C.B. (2004) focused on students’ “tourism complex”, “tourism thinking” and professional competence; MA, Y., WEI, W., DENG, N.M. (2005) attached importance on practice demand, teaching resources, teaching means and quality assurance; Zhao, J.J. (2005) took students’ sustainable competitiveness in job-hunting, the allocation of educational resources, students’ choice on courses and profession, students’ travel service skills, service awareness and professional dedication, students’ scientific research consciousness, the development of tourism and forward-looking consciousness, students’ general management skills, new knowledge, theories and ideas into account; Zhang, P.Y., Sun, Q., Shi, C.B. placed emphasis on knowledge training system characterized by “wide knowledge, strong comprehensive nature, large selection and course module”, “double channel” training system of practical competence and innovative educational quality administrative system; Wang, Q.R. (2006) put for- ward experience-type teaching; Li, Y., Wang, Y.L., Liang, L., Hong, Y. (2009) offered a new reformative way about the cultivation of talents in tourism institutions, providing scientific basis for establishing talent-cultiva- tion mode; Zou, T.Q., Liu, J., Wang, X.F. (2009) concentrated on international cooperative regime, open intern- ship system, integrated curriculum system, scientific research atmosphere, government supporting, and society approving; Guo, Y.H. (2010) paid attention to the contradiction between present training modes of tourism management professionals and their corresponding social demands; Zheng, X.M., Fan, X.L.(2010) emphasized the creation of curriculum and teaching and theory and the combination between theory and practice, the cooperation of education institutes, tourism enterprises and talents, the relationship among students, enterprises and schools; Chen, G.S., Lu, L.J. (2011) discussed work-integrated learning model; Men, L. (2013) put forward an experiential careers guidance mode. These research results enriched the theory of tourism education and talent cultivation and laid the foundation for follow-up study.
3.1.2. Shortcomings
From the existing research results, the studies on the cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management were lack of the systematic, scientific, integrated framework.
3.2. Discussion
According to the analysis of the existing research literature, I try to discuss cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management from theoretical basis, practice demand, policy orientation, regional characteristics, developing trend and educational resources.
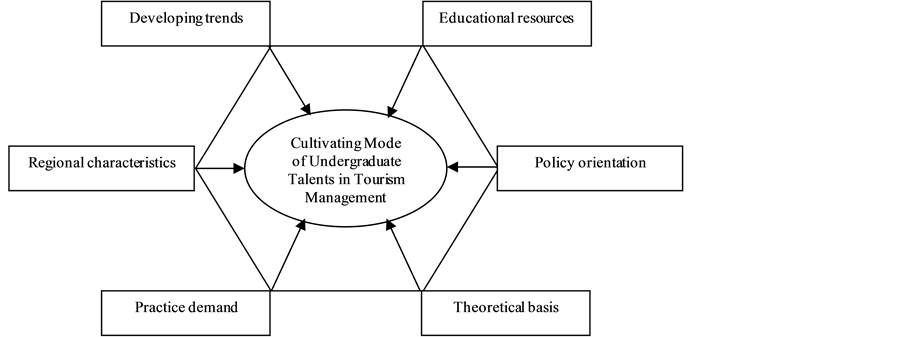
3.2.1. Theoretical Basis
“Talents cultivating mode” refers to the combination of the process of implementing talent education, under the guidance of the modern education theory and thought, according to specific training goals and talents specifications, with relatively stable teaching contents, curriculum system, management system and evaluation methods. In order to construct the cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management, we must grasp the theories about the existing research literature.
3.2.2. Practice Demand
Practice demand means the demand that is suitable to the social and economic development practices. With the vigorous development of tourism industry, great achievements have been made in talent tank building. However, its further construction has been impeded by deep structural obstacles in personnel system: the unchanged pattern of tourism education (unintegrated, small, weak and unqualified), unimproved applied talents training system and career paths for tourism talents, and obscure future development channels of tourism talents. It is necessary to establish an education system stressing on applied talents, and a system of professional titles and vocational qualifications so as to break through the bottleneck.
3.2.3. Policy Orientation
National industrial policy is the combination of various policies by which government can intervene in the formation and development of industry in order to achieve certain economic and social goals. Tourism industrial policies and relevant policies can plan, guide, promote, adjust, protect, support or restrict the development of tourism economy. So analyzing the national tourism industrial policies carefully is the important factor of constructing the cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management.
3.2.4. Regional Characteristics
Different regions have their own developing characteristics. There are 34 provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities and special administrative regions in China. Each has its unique tourist resources and developing characteristics. Constructing the cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management should adapt to the regional characteristics.
3.2.5. Developing Trends
Developing trends in society, politics, economy, and culture can give directions to make decisions in cultivating talents. Forecasting the developing trend and orientation of tourism industry can contribute to the construction of the cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management. We must take developing trends in different fields into account in the course of constructing the talents cultivating mode.
3.2.6. Educational Resources
Educational resources include education knowledge, education experience, education skills, education assets, education expense, education system, education brand, education personality, education idea, education facilities and the sum of the internal and external relationships in the education field, which were created in the practice of the education during the education activities and education history in the long-term evolution of civilization and education. Each university has its own unique educational resources, which refers to material resources, human resources, information resources. So it is necessary to consider the existing educational resources in the course of constructing the cultivating mode of undergraduate talents in tourism management.
Acknowledgements
This study was a part of “Research on Building Tourism Talents Training Model of Higher Tourism Education in Jilin Province”, Jilin Province Education Science Planning Project in 2012 (No. GH12424).
Cite this paper
DongbeiXu,11, (2015) Study on the Cultivating Mode of Undergraduate Talents in Tourism Management: Literature Review, Analysis and Discussion. Journal of Service Science and Management,08,496-501. doi: 10.4236/jssm.2015.84050
References
- 1. Zhang, P.Y., Zhao, Y. and Shi, C.B. (2004) Thoughts and Practice on Cultivating Mode of Tourism Talents and Training Methods. Tourism Tribune, S1, 113-116.
- 2. Ma, Y., Wei, W. and Deng, N.M. (2005) On the Construction of Talent-Cultivation Mode in the Major of Tourism Management and Evaluation of the Implementation Effect. Tourism Tribune, S1, 62-66.
- 3. Zhao, J.J. (2005) New Thoughts about Cultivating Models of Specialized Tourism Management Talents in Local University. Tourism Tribune, S1, 67-70.
- 4. Zhang, P.Y., Sun, Q. and Shi, C.B. (2006) On Establishing and Practicing Innovative Teaching System in Tourism Higher Education. Tourism Tribune, S1, 51-54.
- 5. Wang, Q.R. (2006) A Tentative Study on Talent-Cultivating Pattern through Experience-Type Teaching in the Major of Tourism Management. Tourism Tribune, S1, 89-92.
- 6. Li, Y., Wang, Y.L., Liang, L. and Hong, Y. (2009) Investigation and Study of Talent-Cultivation Mode in Tourism Institutions. Tourism Tribune, 7, 84-89.
- 7. Zou, T.Q., Liu, J. and Wang, X.F. (2009) A Study on the Diamond Pattern of Cultivating Higher Tourism Professionals. Journal of Beijing International Studies University, 11, 63, 79-82.
- 8. Guo, Y.H. (2010) Effective Forms of Training Modes of Tourism Management Professionals. Journal of Social Sci ence of Hunan Normal University, 4, 103-105.
- 9. Zheng, X.M. and Fan, X.L. (2010) Training Philosophy and Operating Pattern of Senior Talents in the Major of Tourism in Tertiary Education of China. Human Geography, 6, 146-149.
- 10. Chen, G.S. and Lu, L.J. (2011) Fundamental Researches on Training Model of Tourism Management Specialty in Practical University Based on the Concept of “Work-Integrated Learning”. Tourism Research, 1, 82-86.
- 11. Men, L. (2013) Exploratory New Models on Careers Guidance for Applied Tourism Talents-Experiential Employment. Tourism Forum, 2, 99-103.