Applied Mathematics
Vol.07 No.10(2016), Article ID:67353,8 pages
10.4236/am.2016.710092
Reduced Differential Transform Method for Solving Linear and Nonlinear Goursat Problem
Sharaf Mohmoud1, Mohamed Gubara2
1Department of Mathematics, College of Science, Omdurman Islamic University, Khartoum, Sudan
2Department of Mathematics, College of Science, AL-Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 12 April 2016; accepted 12 June 2016; published 15 June 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper a new method for solving Goursat problem is introduced using Reduced Differential Transform Method (RDTM). The approximate analytical solution of the problem is calculated in the form of series with easily computable components. The comparison of the methodology presented in this paper with some other well known techniques demonstrates the effectiveness and power of the newly proposed methodology.
Keywords:
Reduced Differential Transform Method, Goursat Problem, Adomian Decomposition Method (ADM), Variational Iteration Method (VIM)

1. Introduction
In this paper, we consider the standard form of the Goursat problem [1] [2] as provided below
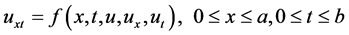 (1)
(1)
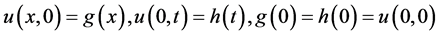 (2)
(2)
This equation has been examined by several numerical methods such as Runge-Kutta method, finite difference method, finite elements method and Adomian Decomposition Method (ADM).
We will prove the applicability and effectiveness of RDTM on solving linear and non-linear Goursat problems. The main advantage of RDTM is that it can be applied directly to the problems without requiring linearization, discretization or perturbation.
2. One Dimensional Differential Transform Method
The differential transform of the function 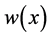 is defined as follows
is defined as follows
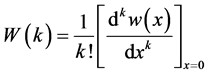 (3)
(3)
where 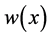 is the original function and
is the original function and 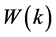 is the transformed function. Here
is the transformed function. Here 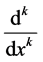 means the kth deriv-
means the kth deriv-
ative with respect to x.
The differential inverse transform of 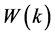 is defined as
is defined as
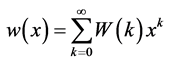 (4)
(4)
Combining (3) and (4) yields
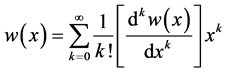 (5)
(5)
From (3) and (4) it is easy to see that the concept of the differential transform is derived from Taylor series expansion [see Table 1].
3. Analysis of the Reduced Differential Transform Method
The basic definitions of reduced differential transform method are introduced below.
Definition
Assume that the function 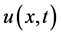 is analytic and continuously differentiable with respect to time t and space x in the domain of interest, then let
is analytic and continuously differentiable with respect to time t and space x in the domain of interest, then let
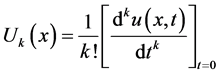 (6)
(6)
Where the t-dimensional spectrum function 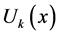 is the transformed function. The differential inverse of
is the transformed function. The differential inverse of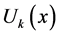 is defined as follows
is defined as follows
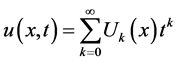 (7)
(7)
Then combining Equation (6) and (7) we can write

Table 1. One-dimensional differential transformation [3] .
Now, we express the Goursat problem in the standard operator form.

With the initial conditions

where
We applying RDTM of Equations (1) and (2) giving




where 



By iterative calculations we obtain the following values of 

From (7) we have.

One can get the exact solution of (1) by substituting (14) and (15) in (16).
With reference to the articles [4] [5] . We easy prove the transformation in the following Table 2.
Table 2. Reduced differential transformation.
4. Application and Results
In this section, we apply the method to some linear and non linear Goursat problem in order to demonstrate its efficiency.
A. The linear homogeneous Goursat problem
We first consider the linear homogeneous Goursat problem defined below


Where 
Example 1: Consider the homogeneous Goursat problem


Taking RDTM of (19) and (20), we obtain


Substituting (22) into (21) and using the recurrence relation, we will reach to the results listed below.
And so on. In general, we have 



Example 2: Now consider the homogeneous Goursat problem


Applying RDT to (23) and (24) we obtain


Substituting (26) into (25) and using the recurrence relation we have
And so on. By substituting all 

B. The linear inhomogeneous Goursat problem:
We now consider inhomogeneous Goursat problem
where 
Example 3: We first consider the linear in homogeneous Goursat problem.


Taking RDM of (27) and (28) will lead to


Substituting (30) into (29) and using the recurrence relation we have
And so on. In general, we have 



Example 4: Consider the linear in homogeneous Goursat problem


Taking RDM of (31) and (32) gives rise to


Substituting (34) into (33) and using the recurrence relation we have
And so on. In general, we have 


tion
C. The non-linear Goursat problem:


where

Here, we apply RDTM to non-linear Goursat problem.
Example 5: We first consider the non-linear Goursat problem .


Taking RDM of (37), (38) yields

And


Substituting (41) into (40) and (39) and using the recurrence relation we have


Example 6: We finally consider the non-linear Goursat problem


Taking RDM of (42) and (43) we obtain

where 

And so on,

Substituting (45) into (44) and using the recurrence relation we have 
Therefore, the solution is 
5. Comparison
In this section, we use the Adomian decomposition method to obtain the solution of (1) and (2). and discuss the comparison between the reduced differential transform method and the Adomian decomposition method.
With reference to the article [7] - [9] , (1) can be rewritten In an operator form as:

where

The inverse operators 


By applying 



Adomian method admits the use of recursive relation


where

We applying adomian decomposition method to examples (3) and (6) to illustrate the comparison between the two method.
Following the pervious discussion and using (49) Equations (27) and (28) gives

This gives

This result is again identical to the one obtained by the RDTM example (3).
Again applying pervious discussion and using (49) Equations (42) and (43) gives

where 

Then the closed form solution is giving by

This result is again identical to the one obtained by RDTM in example (6).
We have carried out the comparative study between the reduced differential transform method and the Adomian decomposition method by handling the Goursat problem, Two numerical examples have shown that the reduced differential transform method is a very simple technique to handle linear and nonlinear Goursat problem than the Adomian decomposition method, and also, it is demonstrated that the reduced differential transform method solves linear and nonlinear Goursat problem without using any complicated polynomials like as the Adomian polynomials.
In addition, the obtained series solution by the reduced differential transform method converges faster than those obtained by the Adomian decomposition method. It is concluded that this simple reduced differential transform method is a powerful technique to handle linear and nonlinear initial value problems.
6. Conclusion
The Goursat problem has been analyzed using reduced differential transform method. All the illustrative examples have shown that the reduced differential transform method is powerful mathematical tool to solving Goursat problem. It is also a promising method to solve other nonlinear equations, the presented method reduces the computational difficulties existing in the other traditional methods and all the calculations can be done by simple manipulations.
Cite this paper
Sharaf Mohmoud,Mohamed Gubara, (2016) Reduced Differential Transform Method for Solving Linear and Nonlinear Goursat Problem. Applied Mathematics,07,1049-1056. doi: 10.4236/am.2016.710092
References
- 1. Zhou, J.K. (1986) Differential Transform and Its Applications for Electrical Circuits. Huazhong University Press, Wuhan.
- 2. Wazwaz, A.M. (1993) On the Numerical Solution of the Goursat Problem. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 59, 89-95.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0096-3003(93)90036-e - 3. Keskin, Y., Caglar, I. and Koc, A.B. (2011) Numaerical Solution of Sine-Gordon Equation by Reduced Differential Transform Method. WEC, 1, 6-8.
- 4. Day, J.T. (1966) A Runge-Kutta Method for the Numerical Solution of the Goursat Problem in Hyperbolic Partial Differential Equations. The Computer Journal, 9, 81-83.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/9.1.81 - 5. Evans, D.J. and Sanugi, B.B. (1988) Numerical Solution of the Goursat Problem by a Nonlinear Trapezoidal Formula. Applied Mathematics Letters, 1, 221-223.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0893-9659(88)90080-8 - 6. Wazwaz, A.M. (2007) The Variational Iteration Method for a Reliable Treatment of the Linear and the Nonlinear Goursat Problem. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 193, 455-462.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2007.03.083 - 7. Wazwaz, A.M. (1995) The Decomposition Method for Approximate Solution to the Goursat Problem. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 69, 299-311.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0096-3003(94)00137-s - 8. Wazwaz, A.M. (2002) Partial Differential Equations: Methods and Applications. Balkema Publishers, The Netherlands.
- 9. Adomian, G. (1994) Solving Frontier Problems of Physics: The Decomposition Method. Kluwer, Boston.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-8289-6











