Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.14(2015), Article ID:62450,9 pages
10.4236/am.2015.614198
Four Nontrivial Solutions for Kirchhoff Problems with Critical Potential, Critical Exponent and a Concave Term
Mohammed El Mokhtar Ould El Mokhtar
Departement of Mathematics, College of Science, Qassim University, Buraidah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2015 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 13 November 2015; accepted 27 December 2015; published 30 December 2015
ABSTRACT
In this paper, we consider the existence of multiple solutions to the Kirchhoff problems with critical potential, critical exponent and a concave term. Our main tools are the Nehari manifold and mountain pass theorem.
Keywords:
Kirchhoff Problems, Critical Potential, Concave term, Nehari Manifold, Mountain Pass Theorem

1. Introduction
In this paper, we consider the multiplicity results of nontrivial solutions of the following Kirchhoff problem
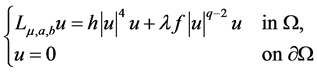 (1.1)
(1.1)
where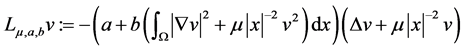 , Ω is a smooth bounded domain of
, Ω is a smooth bounded domain of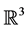 ,
, 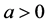 ,
,
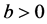 ,
, 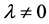 ,
, 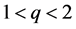 ,
, 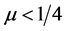 ,
, 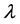 is a real parameter,
is a real parameter, 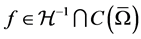 with
with 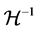 is the topological dual of
is the topological dual of 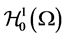 satisfying suitable conditions, h is a bounded positive function on Ω.
satisfying suitable conditions, h is a bounded positive function on Ω.
The original one-dimensional Kirchhoff equation was introduced by Kirchhoff [1] in 1883. His model takes into account the changes in length of the strings produced by transverse vibrations.
In recent years, the existence and multiplicity of solutions to the nonlocal problem
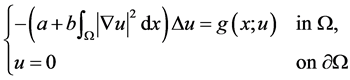 (1.2)
(1.2)
has been studied by various researchers and many interesting and important results can be found. For instance, positive solutions could be obtained in [2] -[4] . Especially, Chen et al. [5] discussed a Kirchhoff type problem when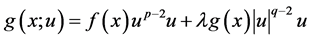 , where
, where 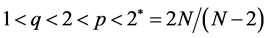 if
if






Researchers, such as Mao and Zhang [6] , Mao and Luan [7] , found sign-changing solutions. As for in nitely many solutions, we refer readers to [8] [9] . He and Zou [10] considered the class of Kirchhoff type problem when 

In the case of a bounded domain of 

the existence of at least two solutions to (1.2) for


Before formulating our results, we give some definitions and notation.
The space 
wich equivalent to the norm
with
for all


Let 

Since our approach is variational, we define the functional 


A point 



Throughout this work, we consider the following assumptions:
(F) There exist 



(H)
Here, 
In our work, we research the critical points as the minimizers of the energy functional associated to the problem (1.1) on the constraint defined by the Nehari manifold, which are solutions of our system.
Let 
where
Now we can state our main results.
Theorem 1. Assume that



Theorem 2. In addition to the assumptions of the Theorem 1, if (H) hold and 



Theorem 3. In addition to the assumptions of the Theorem 2, assuming 
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we give some preliminaries. Section 3 and 4 are devoted to the proofs of Theorems 1 and 2. In the last Section, we prove the Theorem 3.
2. Preliminaries
Definition 1. Let 

i) 

where 
ii) We say that I satisfies the 

Lemma 1. Let X Banach space, and 

i) there exist


ii) there exist 

let 
then c is critical value of J such that
Nehari Manifold
It is well known that the functional 




Thus, 

Define
Then, for

Now, we split 
Note that 
Lemma 2. 

Proof. If
Thus, 

We have the following results.
Lemma 3. Suppose that 





Proof. If 



Hence, there exists a Lagrange multipliers 
Thus,
But


Lemma 4. There exists a positive number 


Proof. Let us reason by contradiction.
Suppose 

and
with
From (2.5) and (2.6), we obtain
Thus
For the sequel, we need the following Lemma.
Lemma 5. i) For all 


ii) There exists 

Proof. i) Let
and so
We conclude that
ii) Let
Thus, for all 


For each 

Lemma 6. Let 








Proof. With minor modifications, we refer to [11] .
Proposition 1. (see [11] )
i) For all 



ii) For all 



3. Proof of Theorem 1
Now, taking as a starting point the work of Tarantello [8] , we establish the existence of a local minimum for 

Proposition 2. For all 



i)
ii) 
Proof. If






Thus, by (3.1), 


in

We get a contradiction. Therefore, 








there exists 

which contradicts the fact that





4. Proof of Theorem 2
Next, we establish the existence of a local minimum for 

Lemma 7. Assume that 





i)
ii) 

Proof. If





This implies that
Moreover, by (H) and (2.4) we obtain
if 

This implies that
Now, we prove that 





we have
and this is a contradiction. Hence,
Thus,
Since 



Now, we complete the proof of Theorem 2. By Propositions 2 and Lemma 7, we obtain that (1.1) has two positive solutions 




5. Proof of Theorem 3
In this section, we consider the following Nehari submanifold of
Thus, 
Firsly, we need the following Lemmas.
Lemma 8. Under the hypothesis of theorem 3, there exist 



Proof. Fix 
Clearly 


If 






Lemma 9. There exist M positive real such that
for 
Proof. Let 
Thus, if 

Lemma 10. There exist r and 
i) we have
ii) there exists 



Proof. We can suppose that the minima of 


i) By (2.4), (5.1), the Holder inequality and the fact that
Thus, for 

ii) Let
Letting 


Let 
and
Proof of Theorem 3.
If 



Thus 



Cite this paper
Mohammed El Mokhtar Ould ElMokhtar, (2015) Four Nontrivial Solutions for Kirchhoff Problems with Critical Potential, Critical Exponent and a Concave Term. Applied Mathematics,06,2248-2256. doi: 10.4236/am.2015.614198
References
- 1. Kirchhoff, G.R. (1883) Vorlesungen über mathematische Physik—Mechanik. 3 Edition. Teubner, Leipzig.
- 2. Alves, C.O., Correa, F.J.S.A. and Ma, T.F. (2005) Positive Solutions for a Quasilinear Elliptic Equation of Kirchhoff type. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 49, 85-93.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2005.01.008 - 3. Cheng, C.T. and Wu, X. (2009) Existence Results of Positive Solutions of Kirchhoff Type Problems. Nonlinear Analysis, 71, 4883-4892.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2009.03.065 - 4. Ma, T.F. and Rivera, J.E.M. (2003) Positive Solutions for a Nonlinear Nonlocal Elliptic Transmission Problem. Applied Mathematics Letters, 16, 243-248.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0893-9659(03)80038-1 - 5. Chen, C., Kuo, Y. and Wu, T. (2011) The Nehari Manifold for a Kirchhoff Type Problem Involving Sign Changing Weight Functions. Journal of Differential Equations, 250, 1876-1908.
- 6. Mao, A.M. and Zhang, Z.T. (2009) Sign-Changing and Multiple Solutions of Kirchhoff Type Problems without the P.S. Condition. Nonlinear Analysis, 70, 1275-1287.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2008.02.011 - 7. Mao, A.M. and Luan, S.X. (2011) Sign-Changing Solutions of a Class of Nonlocal Quasilinear Elliptic Boundary Value Problems. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 383, 239-243.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2011.05.021 - 8. Jin, J.H. and Wu, X. (2010) Infinitely Many Radial Solutions for Kirchhoff-Type Problems in RN. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 369, 564-574.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2010.03.059 - 9. Wei, L. and He, X.M. (2012) Multiplicity of High Energy Solutions for Superlinear Kirchho Equations. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computing, 39, 473-487.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12190-012-0536-1 - 10. He, X.M. and Zou, W.M. (2009) Infinitely Many Positive Solutions for Kirchhoff-Type Problems. Nonlinear Analysis, 70, 1407-1414.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2008.02.021 - 11. Brown, K.J. and Zhang, Y. (2003) The Nehari Manifold for a Semilinear Elliptic Equation with a Sign Changing Weight Function. Journal of Differential Equations, 2, 481-499.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0396(03)00121-9 - 12. Drabek, P., Kufner, A. and Nicolosi, F. (1997) Quasilinear Elliptic Equations with Degenerations and Singularities, Walter de Gruyter Series in Nonlinear Analysis and Applications Vol. 5. New York.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/9783110804775






























































