Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.13(2015), Article ID:61605,12 pages
10.4236/am.2015.613193
Lebesgues-Stieltjes Integrals of Fuzzy Stochastic Processes with Respect to Finite Variation Processes
Jinping Zhang, Lingli Luo, Xingmei Li, Xiaoying Wang
Department of Mathematics and Physics, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China

Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).


Received 28 September 2015; accepted 27 November 2015; published 30 November 2015

ABSTRACT
Let 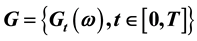 be a fuzzy stochastic process and
be a fuzzy stochastic process and 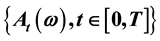 be a real valued finite variation process. We define the Lebesgue-Stieltjes integral denoted by
be a real valued finite variation process. We define the Lebesgue-Stieltjes integral denoted by 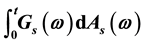 for each
for each 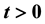 by using the selection method, which is direct, nature and different from the indirect definition appearing in some references. We shall show that this kind of integral is also measurable, continuous in time t and bounded a.s. under the Hausdorff metric.
by using the selection method, which is direct, nature and different from the indirect definition appearing in some references. We shall show that this kind of integral is also measurable, continuous in time t and bounded a.s. under the Hausdorff metric.
Keywords:
Fuzzy Stochastic Process, Finite Variation Process, Fuzzy Stochastic Lebesgue-Stieltjes Integral, Measurability

1. Introduction
Recently, the theory of fuzzy functions has been developed quickly due to the measurements of various uncertainties arising not only from the randomness but also from the vagueness in some situations. For example, when considering wave height at time t denoted by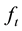 , due to the influence of random factors and the limitations of the measurement tools and methods, we may not precisely know the height
, due to the influence of random factors and the limitations of the measurement tools and methods, we may not precisely know the height . It is reasonable to consider the wave height as a fuzzy random variable on a probability space
. It is reasonable to consider the wave height as a fuzzy random variable on a probability space .
.
Since Puri and Ralescu [1] (1986) defined fuzzy random variable, there had been many further topics such as expectations of fuzzy random variables, fuzzy stochastic processes, integrals of fuzzy stochastic processes, fuzzy stochastic differential equations etc. In order to study a fuzzy function u, it is natural and equivalent to study its 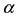 -level set
-level set  for any
for any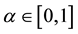 , where
, where  is a set-valued function. Therefore, as usual, in order to explore the integrals of fuzzy stochastic processes, at first we can study the integrals of set-valued stochastic processes. Kisielewicz (1997) [2] used all selections to define the integral of a set-valued process as a nonempty closed subset of
is a set-valued function. Therefore, as usual, in order to explore the integrals of fuzzy stochastic processes, at first we can study the integrals of set-valued stochastic processes. Kisielewicz (1997) [2] used all selections to define the integral of a set-valued process as a nonempty closed subset of , but did not consider its measurability. Based on Kisielewicz’s work (1997) [2] , Kim and Kim (1999) [3] studied some properties of this kind of integral. Jung and Kim (2003) [4] modified the definition in 1-dimensional Euclidean space R so that the integral became a set-valued random variable. After the work [4] , there are some references on set-valued integrals and fuzzy integrals. One may refer to papers such as [5] -[13] etc. and references therein. Zhang and Qi [14] (2013) considered the set-valued integral with respect to a finite variation process directly instead of taking the decomposable closure appearing in [4] [6] and other references. As a further work of [14] , here we shall explore the integrals of fuzzy stochastic processes with respect to finite variation processes and prove the measurability and boundedness of this kind of integral, the continuity with respect to t under the Hausdorff metric and its representation theorem.
, but did not consider its measurability. Based on Kisielewicz’s work (1997) [2] , Kim and Kim (1999) [3] studied some properties of this kind of integral. Jung and Kim (2003) [4] modified the definition in 1-dimensional Euclidean space R so that the integral became a set-valued random variable. After the work [4] , there are some references on set-valued integrals and fuzzy integrals. One may refer to papers such as [5] -[13] etc. and references therein. Zhang and Qi [14] (2013) considered the set-valued integral with respect to a finite variation process directly instead of taking the decomposable closure appearing in [4] [6] and other references. As a further work of [14] , here we shall explore the integrals of fuzzy stochastic processes with respect to finite variation processes and prove the measurability and boundedness of this kind of integral, the continuity with respect to t under the Hausdorff metric and its representation theorem.
This paper is organized as follows: in Section 2, we present some notions on set-valued random variables and fuzzy set-valued random variables; in Section 3, we shall give the definition of integral of fuzzy set-valued stochastic processes with respect to finite variation process and prove the measurability and  -boundedness which are necessary to our future work on fuzzy stochastic differential equations.
-boundedness which are necessary to our future work on fuzzy stochastic differential equations.
2. Preliminaries
We denote N the set of all natural numbers, R the set of all real numbers,  the d-dimensional Euclidean space with the usual norm
the d-dimensional Euclidean space with the usual norm ,
, 






Let 





is finite. f is called 

Let 








Denote
For
A set-valued function 



Let 











In the following, 

A set-valued random variable F is said to be integrable if 




An 




















In a fashion similar to the 
















Let 

1) The level set
2) Each v is upper semi-continuous function, i.e. for each


Let 

3) The support set 
A fuzzy set v is convex if
It is know that v is convex if and only if, for any





sets in

We know that 



Lemma 1. (cf. [16] ) Let B be a set and 
1)
2) 

3)


Then the function 



A mapping 





















A fuzzy stochastic process G is called 





Let 









Let 

1)
2)
3)
We define 






3. Lebesgue-Stieltjes Integrals with Respect to Finite Variation Processes
Let 






is finite and 





where 



In the product space
For




For



For any 





Lemma 2. (cf. [8] ) Let 








From now on, we always assume the sigma-field 
Let 


where
For any

Definition 1. (cf. [7] ) For a set-valued stochastic process 

For some fuzzy stochastic process
Let 



where
For a fuzzy stochastic process

Set

for all
Definition 2. For a fuzzy stochastic process 



by


Theorem 1. ([12] ) For




Lemma 3. (cf. [18] ) Let 




Lemma 4. (cf. [14] ) Let 


1)
2)
Lemma 5. (cf. [18] ) Let 



1) 
2) for any
We obtain that F is a set-valued random variable.
From Lemma 3 and Lemma 5, when





Lemma 6. (cf. [19] ) Let 







Theorem 2. Let





Proof. Taking

















Theorem 3. Let


Proof. By Theorem 2, for any





For any

Then
Hence,

which means
Theorem 4. Let



Proof. Let

Then

For any
Then for all






Lemma 7. Let fuzzy stochastic process



where the closure is taken in
Proof. Since 









Theorem 5. For a fuzzy set-valued stochastic process 


and for each t
where “cl” denotes the closure in
Proof. For each

where the closure is taken in
For each

At first we will show that
In fact, taking

then there exists a subsequence 
Therefore
On the other hand
since 

Since
is closed and

For any

Then for each t,
which means

(7) together with (8) yields
Lemma 8. (cf. [15] ) Let








Theorem 6. Let

Proof. Let





and
Therefore

By Lemma 8, we have

Then

Then
Similarly, we have
Then for each
Therefore
Hence
Theorem 7. Let

Proof. For any

by Lemma 8, we have

Then

Then
Similarly, we have
Then for each
Moreover
Hence
Remark 1. In Theorem 6 and Theorem 7, the inequalities hold too if we take the expectation on both sides.
4. Conclusion
In [21] , the author studied the Lebesgue-Stieltjes integral of real stochastic processes with respect to fuzzy valued stochastic processes. In some references such as [5] [6] , the integrals of fuzzy stochastic processes with respect to time t and Brownian motion were studied. In order to guarantee measurability of the integral, Kim (2005) Li and Ren (2007) defined the integral indirectly by taking the decomposable closure. Here, when the integrand taked value in compact and convex subsets of


Acknowledgements
We thank the editor and the referees for their comments. This work is partly supported by NSFC (No. 11371135).
Cite this paper
JinpingZhang,LingliLuo,XingmeiLi,XiaoyingWang, (2015) Lebesgues-Stieltjes Integrals of Fuzzy Stochastic Processes with Respect to Finite Variation Processes. Applied Mathematics,06,2199-2210. doi: 10.4236/am.2015.613193
References
- 1. Puri, M.L. and Ralescu, D.A. (1986) Fuzzy Random Variables. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 114, 409-422.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-247X(86)90093-4 - 2. Kisielewicz, M. (1997) Set-Valued Stochastic Integrals and Stochastic Inclusions. Stochastic Analysis and Applications, 15, 780-800.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/07362999708809507 - 3. Kim, B.K. and Kim, J.H. (1999) Stochastic Integrals of Set-Valued Processes and Fuzzy Processes. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 236, 480-502.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmaa.1999.6461 - 4. Jung, E.J. and Kim, J.H. (2003) On Set-Valued Stochastic Integrals. Stochastic Analysis and Applications, 21, 401-418.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1081/SAP-120019292 - 5. Kim, J.H. (2005) On Fuzzy Stochastic Differentials Equations. Journal of the Korean Mathematical Society, 42, 153-169.
http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/JKMS.2005.42.1.153 - 6. Li, S. and Ren, A. (2007) Representation Theorems, Set-Valued and Fuzzy Set-Valued ITO Integral. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 158, 949-962.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2006.12.004 - 7. Malionwski, M.T. and Michta, M. (2011) On Set-Valued Stochastic Integrals and Fuzzy Stochastic Equations. Fuzzy Sets Systems, 177, 1-19.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2011.01.007 - 8. Zhang, J., Li, S., Mitoma, I. and Okazaki, Y. (2009) On Set-Valued Stochastic Integrals in an M-Type 2 Banach Space. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 350, 216-233.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2008.09.017 - 9. Zhang, J., Li, S., Mitoma, I. and Okazaki, Y. (2009) On the Solution of Set-Valued Stochastic Differential Equations in M-Type 2 Banach Space. Tohoku Mathematical Journal, 61, 417-440.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2748/tmj/1255700202 - 10. Li, J. and Wang, J. (2012) Fuzzy Set-Valued Stochastic Lebesgue Integral. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 200, 48-64.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2012.01.021 - 11. Mitoma, I., Okazaki, Y. and Zhang, J. (2010) Set-Valued Stochastic Differential Equations in M-Type 2 Banach Space. Communications on Stochastic Analysis, 4, 215-237.
- 12. Zhang, J., Mitoma, I. and Okazaki, Y. (2013) Set-Valued Stochastic Integral with Respect to Poisson Process in a Banach Space. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 54, 404-417.
- 13. Fei, W. (2013) Existence and Uniquess for Solutions to Fuzzy Stochastic Differential Equations Driven by Local Martingales under the Non-Lipschtiz Condition. Nolinear Analysis, 76, 202-214.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2012.08.015 - 14. Zhang, J. and Qi, J. (2013) Set-Valued Stochastic Integrals with Respect to Finite Variation Processes. Advances in Pure Mathematics, 3, 15-19.
http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/apm.2013.39A1003 - 15. Hu, S. and Papageorgiou, N. (1997) Handbook of Multivalued Analysis, Volume I: Theory. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston.
- 16. Negoito, C. and Ralescu, D. (1975) Applications of Fuzzy Sets to Systems Analysis. Wiley, New York.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-5921-9 - 17. Kwakernaak, H. (1987) Fuzzy Random Variables, Definition and Theoroems. Information Sciences, 15, 1-29.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-0255(78)90019-1 - 18. Zhang, W., Li, S. and Wang, Z. (2007) Set-Valued Stochastic Process Introduction. Science Press, Beijing. (In Chinese)
- 19. Charalambos, D.A. and Kim, C.B. (1994) Infinite Dimensional Analysis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- 20. Li, S., Ogura, Y. and Kreinovich, Y. (2002) Limit Theorems and Applications of Set-valued and Fuzzy Set-Valued Random Variables. 43rd Edition, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9932-0 - 21. Feng, Y. (2001) Fuzzy-Valued Mappings with Finite Variation, Fuzzy-Valued Measures and Fuzzy-Valued Lebesgue-Stieltjes Integrals. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2, 227-236.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(99)00178-5




















































