Applied Mathematics
Vol.05 No.20(2014), Article ID:51587,6 pages
10.4236/am.2014.520305
The best piecewise linearization of nonlinear functions
Mohammad Mehdi Mazarei*, Ali Asghar Behroozpoor, Ali Vahidian Kamyad
Department of Applied Mathematics, School of Mathematical Sciences, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, International Campus, Mashhad, Iran
Email: *mm.mazarei@pgstp.ir
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 11 August 2014; revised 12 September 2014; accepted 8 October 2014
ABSTRACT
In this paper, we propose a method for finding the best piecewise linearization of nonlinear functions. For this aim, we try to obtain the best approximation of a nonlinear function as a piecewise linear function. Our method is based on an optimization problem. The optimal solution of this optimization problem is the best piecewise linear approximation of nonlinear function. Finally, we examine our method to some examples.
Keywords:
Nonlinear systems, Piecewise linearization, Optimization problem, Linear programming

1. Introduction
The linearization of nonlinear systems is an efficient tool for finding approximate solutions and treatment analysis of these systems, especially in application [1] -[3] . Some researchers have used some methods based on the optimization problem [4] . But in many applications for nonlinear and nonsmooth functions, we are faced to some problems. In fact, piecewise linearization is a more efficient tool for finding approximate solutions. Some researchers have used piecewise linearization in applications [5] [6] . Also, some researchers have used piecewise linearization to solve ODEs and PDEs [7] .
First, we consider a nonlinear function. Let 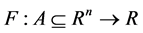 be a nonlinear function. We suppose that
be a nonlinear function. We suppose that
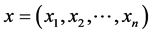 varies in a subset of
varies in a subset of 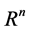 as
as  and this subset is compact. Our aim is to approximate the
and this subset is compact. Our aim is to approximate the
nonlinear function  by a piecewise linear function as follows:
by a piecewise linear function as follows:
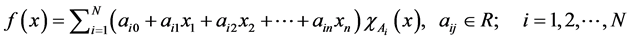 (1)
(1)
where 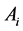 is
is  th subset in partitioning of
th subset in partitioning of  as
as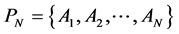 . As we know, this partitioning has bel-
. As we know, this partitioning has bel-
low properties:
1) 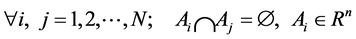
2) 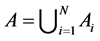
Also, 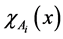 is a characteristic function on
is a characteristic function on 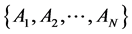 such that:
such that:
 (2)
(2)
Now, let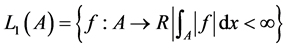 . As we know
. As we know 

ing inner product:

and

Definition 1. We define 


Definition 2. If 



Theorem. The subset 

Proof. Suppose that 

Definition 3. We call 

we have

In fact, by above definition 

Obviously, because
2. Approach
At first, we consider a nonlinear function


1) Let to consider the bellow optimization problem
where, 



Now, we decompose interval 


Since, 
Figure 1. Partitioning 


Our objective function is a functional. Now, we reduce this functional to a summation as follows:

So, the optimization problem (8) is as follows:

But, the optimization problem (9) is a nonlinear programming problem. We reduce this problem to a linear programming problem by relation 


2) Second, we consider a nonlinear function

where 





where 



3) Third, we consider a nonlinear function
Figure 2. Partitioning 

lows:

As, we explained in sections 1) and 2) this optimization problem will be reduced to a linear programming problem as follows:

where 

3. Examples
In this section, we show efficiency of our approach by several examples. Also, we define the root mean squared error by follow relation:

Example 1. We consider nonlinear nonsmooth function 

As we explained in section 1), the linear programming corresponding to this function is as follows:

The optimal solution of linear programming problem (16) is the best piecewise linearization of the function 





Example 2. We consider nonlinear function 

As we explained in section 1), the linear programming corresponding to this function is as follows:

Figure 3. The figure of piecewise function approximation of nonlinear function 

Figure 4. The figure of piecewise function approximation of nonlinear function 

The optimal solution of linear programming problem (17) is the best piecewise linearization of the function 





Example 3. We consider nonlinear non smooth function 

As we explained in section 2), the linear programming corresponding to this function is as follows:

The optimal solution of linear programming problem (18) is the best piecewise linearization of the function




Figure 5. The figure of piecewise function approximation of nonlinear function 

Figure 6. The figure of piecewise function approximation of nonlinear function 

Figure 7. The figure of piecewise function approximation of nonlinear function 

we have 

4. Conclusion
Our method for piecewise linearization of nonlinear functions is extensible to 

References
- Aranda-Bricaire, E., Kotta, U. and Moog, C. (1996) Linearization of Discrete-Time Systems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 34, 1999-2023. http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/S0363012994267315
- Jouan, P. (2003) Immersion of Nonlinear Systems into Linear Systems Modulo Output Injection. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 41, 1756-1778. http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/S0363012901391706
- Sladeček, L. (2003) Exact Linearization of Stochastic Dynamical Systems by State Space Coordinate Transformation and Feedback Ig-Linearization. Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 3, 99-106.
- Vahidian Kamyad, A., Hashemi Mehne, H. and Hashemi Borzabadi, A. (2005) The Best Linear Approximation for Nonlinear Systems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 167, 1041-1061. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2004.08.002
- Herdem, S. and Koksal, M. (2002) A Fast Algorithm to Compute Steady-State Solution of Nonlinear Circuits by Piecewise Linearization. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 28, 91-101.
- Gunnerud, V., Foss, B.A., Mckinnon, K.I.M. and Nygreen, B. (2012) Oil Production Optimization Solved by Piecewise Linearization in a Branch and Price Framework. Computers and Operations Research, 39, 2469-2477. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2011.12.013
- Ramos, J.I. and Garcia-Lopez, C.M. (1997) Nonstandard Finite Difference Equations for ODEs and 1-D PDEs Based on Piecewise Linearization. Applied Mathematics and Computations, 86, 11-36.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.












