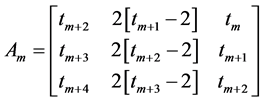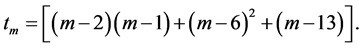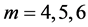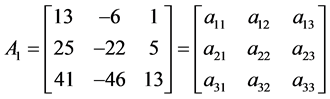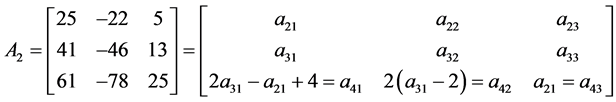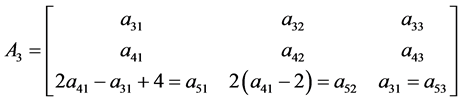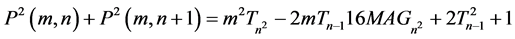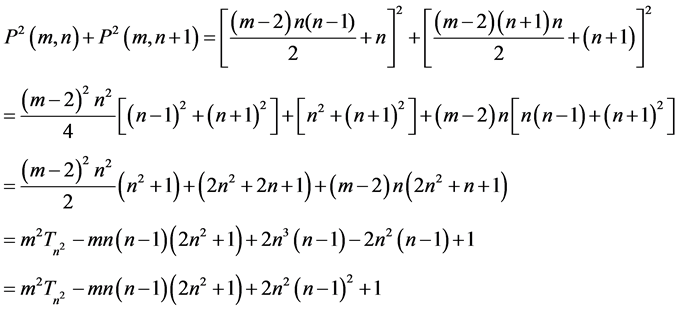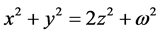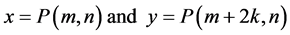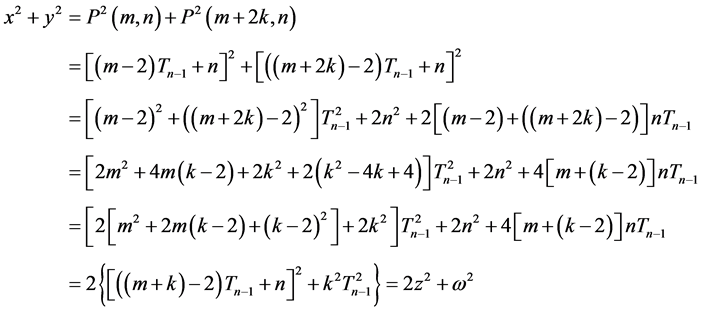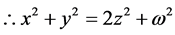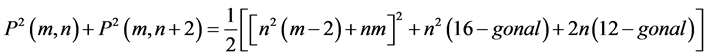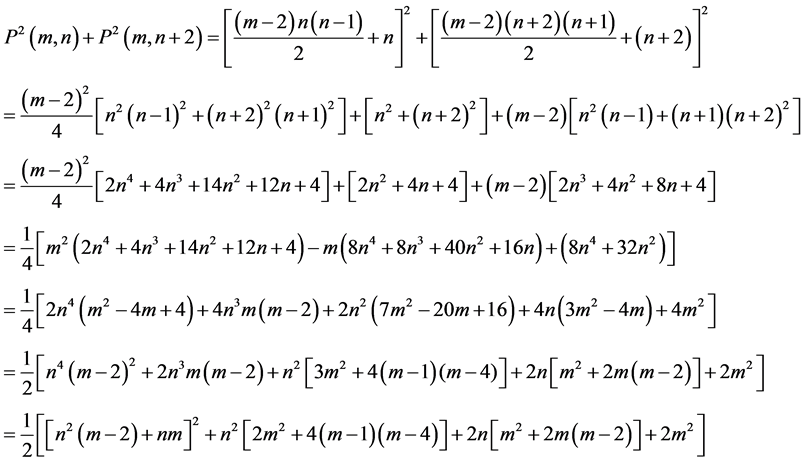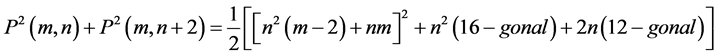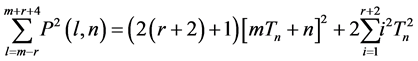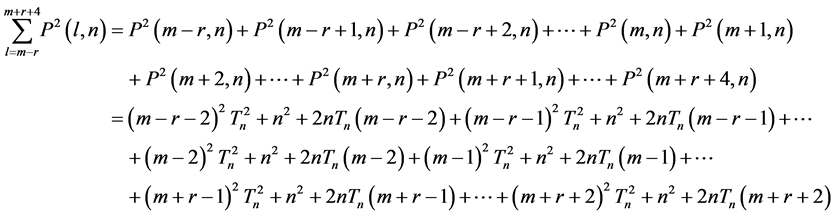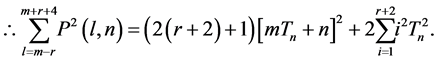Advances in Pure Mathematics
Vol.06 No.04(2016), Article ID:65099,5 pages
10.4236/apm.2016.64019
Sums of Squares of Polygonal Numbers
A. Gnanam, B. Anitha
Department of Mathematics, Government Arts College, Tiruchirappalli, India
Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 6 February 2016; accepted 26 March 2016; published 29 March 2016
ABSTRACT
Polygonal numbers and sums of squares of primes are distinct fields of number theory. Here we consider sums of squares of consecutive (of order and rank) polygonal numbers. We try to express sums of squares of polygonal numbers of consecutive orders in matrix form. We also try to find the solution of a Diophantine equation 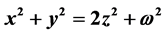 in terms of polygonal numbers.
in terms of polygonal numbers.
Keywords:
Polygonal Numbers, Sums of Squares, Triangular Numbers

1. Introduction [1]
Polygonal numbers have been meticulously studied since their very beginnings in ancient Greece. Numerous discoveries stemmed from these peculiar numbers can be seen in the basic fundamental group work of number theory today with finding such as pascal’s triangle and Fermat triangular number theorem. It becomes a popular field of research for mathematicians. The concept of polygonal numbers was first defined by the Greek Mathematical hypsicles in the year 170 BC. If the polygonal numbers are divided successively into triangles it will ultimately end up with right triangle. The right triangles immediately remind us of Pythagorean property. This leads to the idea of finding sums of squares of consecutive polygonal numbers. In this paper we calculate sums of squares polygonal numbers of consecutive orders. We also calculate the sums of squares of m-gonal numbers of consecutive ranks. We analyze some properties of the above.
2. Polygonal Number
2.1. Definition
For 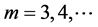
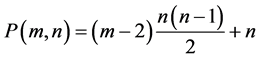 with
with 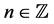
are called generalized m-gonal numbers.
Also 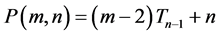
where
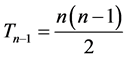 with
with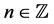 , a triangular number of rank
, a triangular number of rank 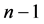
Sums of Squares of Polygonal numbers of Consecutive Orders of Same Rank
2.2. Proposition
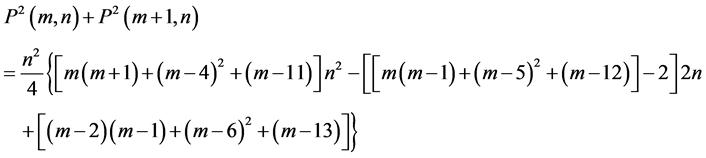
Proof
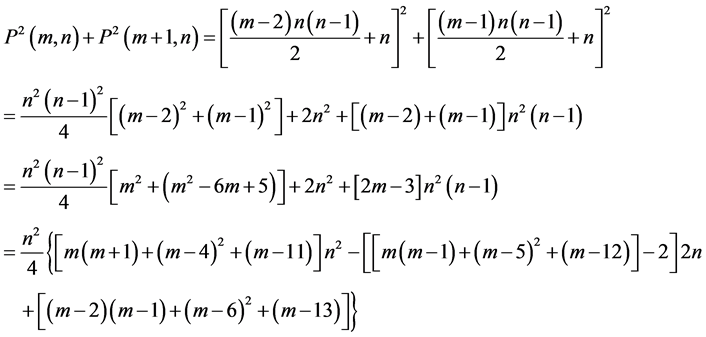
Sums of squares of Polygonal numbers of Consecutive Orders in Matrix Form [2]
Expressing the coefficients of 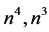 and
and 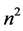 for 3 consecutive sums of squares in a
for 3 consecutive sums of squares in a 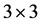 matrix the coefficients of sums of squares of any three consecutive terms of higher order can be obtained.
matrix the coefficients of sums of squares of any three consecutive terms of higher order can be obtained.
The coefficient matrix 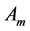 of sums of squares polygonal numbers is
of sums of squares polygonal numbers is
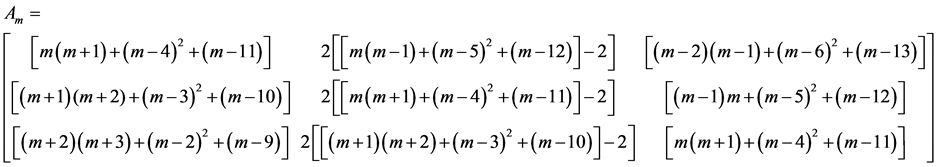
for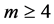
In general,
where
Recursive matrix form
Consider the initial matrix as the coefficients of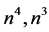
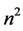
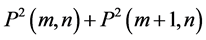
The elements of next order 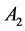
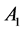
The first two rows elements of 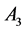
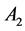
In general, the matrix of order 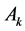
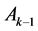
Sums of squares of Polygonal Numbers with Consecutive ranks n, n+1.
2.3. Proposition [3]
Proof
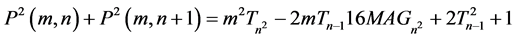
2.4. Proposition
The Triple 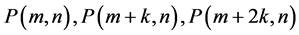
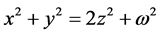
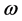
Proof
Consider the Diophantine equation
We try for the solution in polygonal numbers.
Take
Taking 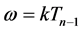
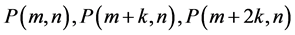
2.5. Proposition
Proof
2.6. Proposition
Proof
3. Conclusion
It is observed that the polygonal numbers of consecutive ranks constitute the solution of the Diophantine equation 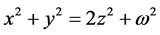
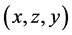
Cite this paper
A. Gnanam,B. Anitha, (2016) Sums of Squares of Polygonal Numbers. Advances in Pure Mathematics,06,297-301. doi: 10.4236/apm.2016.64019
References
Notations
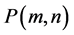
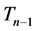
16MAGn: Magna Number order n.