Open Journal of Applied Sciences
Vol.05 No.08(2015), Article ID:58735,6 pages
10.4236/ojapps.2015.58044
An Interval Matrix Based Generalized Newton Method for Linear Complementarity Problems
Hai-Shan Han, Lan-Ying
College of Mathematics, Inner Mongolia University for the Nationalities, Tongliao, China
Email: haishanhan@sohu.com
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 6 July 2015; accepted 9 August 2015; published 12 August 2015
ABSTRACT
The penalty equation of LCP is transformed into the absolute value equation, and then the existence of solutions for the penalty equation is proved by the regularity of the interval matrix. We propose a generalized Newton method for solving the linear complementarity problem with the regular interval matrix based on the nonlinear penalized equation. Further, we prove that this method is convergent. Numerical experiments are presented to show that the generalized Newton method is effective.
Keywords:
Linear Complementarity Problem, Nonlinear Penalized Equation, Interval Matrix, Generalized Newton Method

1. Introduction
The linear complementarity problem, denoted by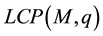 , is to find a vector
, is to find a vector  such that
such that
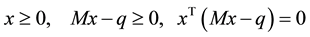 (1.1)
(1.1)
where 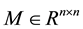 is a given matrix and
is a given matrix and 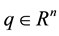 is a given vector. This problem serves as a unified formulation of linear and quadratic programming problems as well as of two-person (noncooperative) matrix-games, and has several important applications in economics and engineering sciences; see Cottle, Pang, and Stone [1] and its references.
is a given vector. This problem serves as a unified formulation of linear and quadratic programming problems as well as of two-person (noncooperative) matrix-games, and has several important applications in economics and engineering sciences; see Cottle, Pang, and Stone [1] and its references.
There exist several methods for solving , such as projection method, multi splitting method, interior point method, and the nonsmooth Newton method, smoothing Newton method, homotopy method etc. See [1] - [6] and its references.
, such as projection method, multi splitting method, interior point method, and the nonsmooth Newton method, smoothing Newton method, homotopy method etc. See [1] - [6] and its references.
In [7] , it given a nonlinear penalized Equation (1.2) corresponding to linear complementarity problem (1.1).
Find 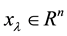 such that
such that
 (1.2)
(1.2)
where 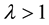 is the penalized parameter,
is the penalized parameter, 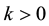 ,
, 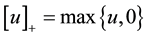 and
and 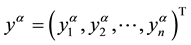 for any
for any  .
.
The nonlinear penalized problems (1.2) corresponding to the linear complementarity problem (1.1), which its research has achieved good results. In 1984, Glowinski [1] studied nonlinear penalized Equation (1.2) in , and proved the convergence of penalized equation that matrix
, and proved the convergence of penalized equation that matrix 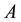 was symmetric positive definite. In 2006, Wang et al. [8] presented a power penalty function approach to the linear complementarity problem arising from pricing American options. It is shown that the solution to the penalized equation converges to that of the linear complementarity problem with matrix is positive definite. In 2008, Yang [7] proved that solution to this penalized Equations (1.2) converged to that of the LCP at an exponential rate for a positive definite matrix case where the diagonal entries were positive and off-diagonal entries were not greater than zero. The same year, Wang and Huang [9] presented a penalty method for solving a complementarity problem involving a second- order nonlinear parabolic differential operator, and defined a nonlinear parabolic partial differential equation (PDE) approximating the variational inequality using a power penalty term with a penalty constant
was symmetric positive definite. In 2006, Wang et al. [8] presented a power penalty function approach to the linear complementarity problem arising from pricing American options. It is shown that the solution to the penalized equation converges to that of the linear complementarity problem with matrix is positive definite. In 2008, Yang [7] proved that solution to this penalized Equations (1.2) converged to that of the LCP at an exponential rate for a positive definite matrix case where the diagonal entries were positive and off-diagonal entries were not greater than zero. The same year, Wang and Huang [9] presented a penalty method for solving a complementarity problem involving a second- order nonlinear parabolic differential operator, and defined a nonlinear parabolic partial differential equation (PDE) approximating the variational inequality using a power penalty term with a penalty constant , a power parameter k >0 and a smoothing parameter
, a power parameter k >0 and a smoothing parameter


Although the studies solving for the linear complementarity problem based on the nonlinear penalized equation have good results. But there is no method that is given for solving the nonlinear penalized equation. Throughout the paper, we propose a generalized Newton method for solving the nonlinear penalized equation with under the suppose 
2. Preliminaries
Some words about our notation: 









The definition of interval matrix arises from the linear interval equations [12] , given two matrices 







Lemma 1: Assume that interval matrix 



Proof: By definition of

By the assumptions, we have 
Lemma 2: Let
Definition 1 [1] : A matrix 
Lemma 3 [1] : A matrix 


3. Generalized Newton Method
In this section, we will propose that a new generalized Newton method based on the nonlinear penalized equation for solving the linear complementarity problem. Because when


These case penalty problems for the continuous Variational Inequality and the linear complementarity problems are discussed in [2] [13] .
Let us note

Thus, nonlinear penalized equation (3.1) is equivalent to the equation
A generalized Jacobian 

where 
depending on whether the corresponding component of 


Then
Since

Proposition 1 

Proof: Since

By [14] , its equivalent to

Let 

Proposition 2 

Proof: Since



lation between the (3.1) and the LCP (3.5), we can easily deduce that the (3.1) is uniquely solvable for any
Algorithm 3
Step 1: Choose an arbitrary initial point





Step 2: for the


Step 3: If


Step4: If 





4. The Convergence of the Algorithm
We will show that the sequence 




Theorem 3: Suppose that the interval matrix 



Proof: Suppose that sequence 

where 

We know subsequence 

Letting 
Since 








Under a somewhat restrictive assumption we can establish finite termination of the generalized Newton iteration at a penalized equation solution as follows.
Theorem 4: Suppose that the interval matrix 




Proof: Suppose that 







since 

Letting 
So the iteration (3.6) linearly converges to a solution 
In here, we will focus on the convergence of Algorithm 3.
Theorem 5: Suppose M is P-Matrix and that the interval matrix 




Proof: Since M is P-Matrix, then the 


let
we have 
5. Numerical Experiments
In this section, we give some numerical results in order to show the practical performance of Algorithm 2.1. Numerical results were obtained by using Matlab R2007 (b) on a



Example 1: The matrix 

The computational results are shown in Table 1. This 



Example 2: The matrix 

The computational results are shown in Table 2. This 



Table 1. Result from example 1.
Table 2. Result from example 2.
Supported
This work supported by the Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia in China (2011MS0114)
Cite this paper
Hai-ShanHan,Lan-Ying , (2015) An Interval Matrix Based Generalized Newton Method for Linear Complementarity Problems. Open Journal of Applied Sciences,05,443-449. doi: 10.4236/ojapps.2015.58044
References
- 1. Cottle, R.W., Pang, J.-S. and Stone, R.E. (1992) The Linear Complementarity Problem. Academic Press, San Diego
- 2. Glowinski, R. (1984) Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Variational Problems. Springer-Verlag, New York. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-12613-4
- 3. Kanzow, C. (1996) Some Non-Interior Continuation Methods for Linear Complementarity Problem. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 17, 851-868.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/S0895479894273134 - 4. Facchinei, F. and Pang, J.S. (2003) Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems. Springer, New York.
- 5. Han, J.Y., Xiu, N.H. and Qi, H.D. (2006) Nonlinear Complementarity Theory and Algorithms. Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House, Shanghai. (In Chinese)
- 6. Murty, K.G. (1988) Linear Complementarity, Linear and Nonlinear Programming. Heldermann, Berlin.
- 7. Wang, S. and Yang, X.Q. (2008) Power Penalty Method for Linear Complementarity Problems. Operations Research Letters, 36, 211-214.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.orl.2007.06.006 - 8. Wang, S., Yang, X.Q. and Teo, K.L. (2006) Power Penalty Method for a Linear Complementarity Problems Arising from American Option Valuation. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 129, 227-254. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10957-006-9062-3
- 9. Wang, S. and Huang, C.S. (2008) A Power Penalty Method for Solving a Nonlinear Parabolic Complementarity Problem. Nonlinear Analysis, 69, 1125-1137.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2007.06.014 - 10. Li, Y., Han, H.S., Li, Y.M. and Wu, M.H. (2009) Convergence Analysis of Power Penalty Method for Three Dimensional Linear Complementarity Problem. Intelligent Information Management Systems and Technologies, 5, 191-198.
- 11. Li, Y., Yang, D.D. and Han, H.S. (2012) Analysis to the Convergence of the Penalty Method for Linear Complementarity Problems. Operations Research and Management Science, 21, 129-134. (In Chinese)
- 12. Rohn, J. (1989) Systems of Linear Interval Equation. Linear Algebra and its Application, 126, 39-78.
- 13. Bensoussan, A. and Lions, J.L. (1978) Applications of Variational Inequalities in Stochastic Control. North-Holland, Amsterdam, New York, Oxford.
- 14. Mangasarian, O.L. and Meyer, R.R. (2006) Absolute Value Equations. Linear Algebra and Its Applications, 419, 359-367. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.laa.2006.05.004
- 15. Geiger, C. and Kanzow, C. (1996) On the Resolution of Monotone Complementarity Problems. Computational Optimization and Applications, 5, 155-173.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00249054 - 16. Jiang, H.Y. and Qi, L.Q. (1997) A New Nonsmooth Equations Approach to Nonlinear Complementarity Problems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 45, 178-193.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1137/S0363012994276494 - 17. Yong, L.Q., Deng, F.A. and Chen, T. (2009) An Interior Point Method for Solving Monotone Linear Complementarity Problem. Journal of Mathematics, 29, 681-686. (In Chinese)























