Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 Creative Education 2013. Vol.4, No.5, 348-356 Published Online May 2013 in SciRes (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ce) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ce.2013.45051 Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 348 Factor Analysis of Competency of Computer Teacher at Vocational Certificate Level Punnee Leekitchwatana, Paitoon Pimdee, Sangutai Moto Faculty of Industrial Education, King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, Bangkok, Thailand Email: klpunnee@kmitl.ac.th Received February 27th, 2013; revised March 28th, 2013; accepted April 12th, 2013 Copyright © 2013 Punnee Leekitchwatana et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. The research objectives were to analysis the factor and construct the questionnaire on competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level of educational institute under Office of Vocational Educa- tion Commission (OVEC). The descriptive research and structural relationship model were used for the study. Sample groups comprised of 1) 90 experts and 2) 200 educational institutes under OVEC. Research instruments were questionnaires on competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level for: 1) experts and 2) educational institutes. Data analysis were conducted with: 1) Exploratory factor analysis by using SPSS for Windows for data from experts, 2) The second order confirmatory factor analysis with LISREL 8.72 program and Cronbach’s α formula for data from educational institutes. Research results revealed that competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level composed of 12 components from 62 variables covered 3 domains of knowledge, skill, and affection. Those 12 components were gen- eral knowledge about education, knowledge about curriculum, knowledge about teaching, knowledge about e-Learning and e-Media, knowledge about IT support, knowledge about computer use, teaching skill, skill about e-Learning and e-Media, skill about IT support, skill for using computer, supportive af- fection to be a teacher and affection in IT. The questionnaire on competency of computer teacher had good quality with good construct validity and high reliability in 2 dimensions of intent and actual compe- tencies. Keywords: Factor Analysis; Competency of Computer Teacher; Vocational Certificate Level Introduction The rapid growth of global economic and technology af- fected to Thailand, therefore Thai government had policy to mobilize the country and Thai society to new economic system based on knowledge development to increase competency com- petition. Readiness preparation of man power to face with new economic with attributes of physical infrastructure and effective technology are very important and essential issues (OVEC, 2005). Computerized technology is a very important tool for work implementation in different occupations, therefore the voca- tional certificate curriculum of every program has computer subject for vocation as fundamental subject for every student to take course. If the student at vocational certificate level fully obtains computer subject for vocation according to curriculum, it would be beneficial for student to apply to use in his career effectively and it provides high advantage for various work units and work places. Educational management with good quality in accordance with curriculum, teacher is the most important factor to aid for learning, therefore the teacher should fully manage learning and teaching for student according to aim of curriculum. Conse- quently, he needs to have proper competency to take responsi- bility and readiness of competency of knowledge, skill, and affection. Management of learning and teaching computer sub- ject for vocation, it also needs the teacher who owns covering 3 domains as mentioned. However, at present, it is not obvious evident to point clearly whether components are important for better competency of computer teacher for vocation at voca- tional certificate level and how much competency he has, and what part that it needs to be developed. Therefore, researchers are interested in studying the component of competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level and construct the questionnaire of competency of computer teacher at voca- tional certificate level for educational institute to use for need assessment and for development of competency of computer teacher further. Objectives 1) To analysis the factor of competency of computer teacher for vocation at vocational certificate level. 2) To construct the questionnaire of competency of computer teacher for vocation at vocational certificate level. Hypotheses 1) The studied variables were able to be in components of competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level.  P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. 2) The questionnaire of competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level had good construct validity and high reliability. Conceptual Framework Prototype components of competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level composed of 3 domains that were knowledge, skill and affection. Each domain composed of 2 components therefore there were 6 components that were ap- plied from 6 prototype components of competency of IT teacher of Leekitchwatana (2010) in Table 1. Research Scope Population Scope 1) Population for the factor analysis were experts in teaching computer subject/IT subject. 2) Population for the examination the quality of question- naire were 414 educational institutes where open vocational certificate level under Office of Vocational Education Commis- sion (OVEC) in academic year of 2011 (OVEC, 2011). Content Scope Content scope of competency of computer teacher for voca- tion covered 3 domains. Each domain had 2 components and total were 6 components as mentioned in Table 1. Research Implementation Research Steps Research methodology was descriptive research composed of 2 parts as the followings. 1) Factor analysis of competency of computer teacher for vocation by constructing prototype components from docu- ments and related literatures to be the questionnaire for data collection from experts sample group, then data was analyzed with exploratory factor analysis (EFA). 2) Examination the quality of questionnaire on competency of computer teacher for vocation for educational institute by using component that was results of exploratory factor analysis mentioned in item 1) to construct the questionnaire and use it to collect data from the education institute sample group, then data analysis was done with statistics of second order confirmatory factor analysis (2nd order CFA) and calculated the reliability with α formula of Cronbach. Sample Groups 1) Sample group used for the factor analysis of competency Table 1. Prototype components of competency of computer teacher. Domain Component 1. Knowledge 1. Knowledge in teacher professional 2. Knowledge in computer subject for vocation 2. Skill 3. Skill in teacher professional 4. Skill in computer subject for vocation 3. Affection 5. Supportive affection to be a teacher 6. Affection in IT was 100 experts who teach computer subject/IT subject. They were selected by using network pattern. 2) Sample group used for the examination the quality of questionnaire was 200 educational institutes. The sample size was determined by using table of Krejcie and Morgan (1970) and the samples were selected by using multi-stage random sampling from population of 414 educational institutes under OVEC nationwide in academic year of 2011. Research Instruments 1) Expert questionnaire was opinion toward the list of vari- ables about competency of computer teacher for vocation at vocational certificate level covering 3 domains of knowledge, skill, and affection that was improved from questionnaire of Leekitchwatana (2010). It was classified as 6 prototype com- ponents from 62 variables. The attribute question was rating scale with 5 levels. The quality was content validity between 0.66 - 1.00 and reliability in terms of domain between 0.91 - 0.95 and reliability in terms of component were 0.88 - 0.94. 2) Educational institute questionnaire was opinion about competency of computer teacher for vocation at vocational cer- tificate level in 2 dimensions of intent and actual competencies covering of 3 domains of knowledge, skill, and affection. It was classified as 12 components from 62 variables resulted from EFA in item 1). The question attribute was rating scale with 5 levels. The validity was at good level in both dimensions from the 2nd order CFA with reliability in dimension of intent com- petency in terms of each domain between 0.96 - 0.97 and in terms of component were 0.85 - 0.98 and reliability of actual competency in terms of 3 domains were 0.95 equally and as each component between 0.78 - 0.95. Data Collection 1) The expert data were collected from expert sample group by bringing questionnaire to them and receiving back directly from 90 experts. It was 90 percents back from 100 experts set- ting. 2) The education institute data were collected from education institute sample group by mailing questionnaire to 200 educa- tional institutes and received back by mailing from 200 educa- tional institutes. It was 100 percents back from 200 sample setting. Data Analysis 1) Factor analysis of competency from expert data with sta- tistics EFA by extracting component with principal component analysis and orthogonal rotation with varimax method by using SPSS for Windows program, and using criteria consideration for component and variable to be used as the followings. a) Component with eigenvalue more than 1.00. b) Variable with factor loading initiation of 0.40. 2) Examination the quality of questionnaire from educational institute data as the followings. a) Analysis the construct validity with 2nd order CFA by us- ing LISREL 8.72 program and using criteria consideration for model confirmation with empirical data that applied from some part of Wiruchchai (1995) and Ungsuchote et al. (2008) as the Chi-square has no statistical significance at level of 0.05 (p > 0.05), RMSEA < 0.05, GFI > 0.90, AGFI > 0.90, RMR < 0.05 Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 349  P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 350 and SRMR < 0.05 b) Calculate the reliability with α formula of Cronbach and using criterion at good level with initiation of 0.80. Research Results Results of Factor Analysis of Competency of Computer Teacher for Vocation 1) KMO or MSA equaled to 0.693, it indicated that this set of variables was proper for factor analysis at moderate level according to criteria of Hair et al. (1998). The result of Bart- lett’s test of sphericity, it was found that variables were related with statistically significant at 0.000. These illustrated that various variables were related and were able to use for factor analysis. 2) Result of extraction with principal component analysis, communality was found in 62 variables that were used for fac- tor analysis of competency between 0.430 - 0.902 as moderate to more size. The tendency was able to classify into component. 3) Result of orthogonal rotation with varimax method show- ed in Table 2. From Table 2, it was found that 62 variables were used to analyze, these were grouped to be 14 components with eigen- value more than 1.00. It indicated that each component was able to explain the variation of 62 variables more than 1.00. The whole 14 components were able to explain variation of 62 variables with 81.719 percents. In order to group various variables to be in only one compo- nent with the highest factor loading, it was found that the 62 variables were able to be grouped into 13 components, there- fore each component composed of 2 - 11 variables. Each vari- able was grouped into component would have factor loading between 0.430 to 0.902. Result of grouping as mentioned above, it was found that some component composed of 11 variables and they were in the different domains while some component composed of only 2 variables. Therefore, it was minor adjusted structure of compo- nent in order to group by letting the each component composed of the variable from the same domain and the numbers of vari- ables were not much different, then there were 12 components from 62 variables. The adjusted components were named to give meaning with congruence to cover all variables in each component. 4) Result of adjust variable grouped and named the compo- nent showed in Table 3. Results of Examination the Quality of Questionnaire Competency of Computer Teacher for Vocation Results of Construct Validation with Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) Results of the 2nd order CFA of intent and actual competen- cies as showed in Figures 1 and 2 and Tables 4 and 5. From Figure 1 and Table 4, it was found that the model of intent competency of computer teacher for vocation at voca- tional certificate level was congruent to empirical data of edu- cational institutes under OVEC at good level because every statistic value to measure the confirmation passed every crite- rion. It illustrated that model with good validity and it illus- trated the structure of content in questionnaire had good valid- ity and it confirmed that teacher competency composed of 3 factors from 12 sub-factors. The important sequences of factors were knowledge, skill, and affection respectively. Moreover, the important sequences of sub-factors in each factor, the factor of knowledge were knowledge about teaching, knowledge Table 2. Orthogonal rotation with varimax method. Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings Component Total (Eigenvalue) % of Variance Cumulative % Total (Eigenvalue) % of Variance Cumulative % 1 22.323 36.005 36.005 7.852 12.664 12.664 2 5.768 9.303 45.308 6.753 10.891 23.555 3 4.039 6.515 51.824 4.692 7.567 31.122 4 2.742 4.423 56.246 4.295 6.927 38.050 5 2.392 3.859 60.105 3.983 6.425 44.474 6 2.139 3.450 63.555 3.736 6.027 50.501 7 2.109 3.401 66.956 3.555 5.734 56.235 8 1.912 3.084 70.040 3.551 5.727 61.962 9 1.555 2.508 72.548 3.046 4.913 66.874 10 1.325 2.137 74.685 2.443 3.940 70.814 11 1.191 1.921 76.606 2.208 3.562 74.376 12 1.096 1.768 78.374 1.913 3.086 77.462 13 1.067 1.721 80.095 1.419 2.289 79.751 14 1.007 1.624 81.719 1.220 1.967 81.719  P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. Table 3. Structure and name of components of competency of computer teacher for vocation at vocational certificate level after adjust. Domain Component Variable 1. Knowledge about Act of National Education 2. Knowledge about learning reform 3. Knowledge about educational philosophy 4. Knowledge about standard of teacher professional 1. Knowledge 1. General knowledge about education 5. Knowledge about teacher ethics 6. Knowledge about curriculum of vocational certificate 2. Knowledge about curriculum 7. Knowledge about curriculum of computer subject for vocation 8. Knowledge about curriculum development 9. Knowledge about teaching planning 10. Knowledge about teaching model as learner centered 11. Knowledge about various teaching forms 12. Knowledge about developmental psychology (teenage) 13. Knowledge about learning psychology 14. Knowledge about test construction 3. Knowledge about teaching 15. Knowledge about learning evaluation 16. Knowledge about teaching form with e-Learning 4. Knowledge about e-Learning and e-Media 17. Knowledge about various electronic media for instruction such as Computer Aid Instruction (CAI), and Web Based Instruction (WBI) for instance 18. Knowledge about development of various electronic media for instruction such as Computer Aid Instruction (CAI), and Web Based Instruction (WBI) for instance 19. Knowledge about assembling and installing computer 20. Knowledge about equipment with driver such as printer and scanner for instance 2 5. Knowledge about IT support 1. Knowledge about basic computer software installing such as Microsoft Office and OpenOffice.org for instance 22. Knowledge about installing operation system (OS) such as Microsoft Windows and Linux for instance 23. Knowledge about computer network system 24. Knowledge about computer maintenance 25. Basic knowledge about computer 26. Knowledge about principles of work, role and benefit of computer 27. Knowledge about using word compilation to prepare document for vocation such as Microsoft Word, and OpenOffice.org Writer for instance 28. Knowledge about using program, and table program for vocation by emphasizing such as Microsoft Excel and OpenOffice.org Calc for instance 5. Knowledge about IT support 29. Knowledge about program utilization of presentation for vocation such as Microsoft PowerPoint, OpenOffice.org Impress for instance 30. Knowledge about internet use to search information and communicate for vocation 31. Knowledge about principles and methods to solve problem with information technology process 6. Knowledge about computer use 32. Knowledge about computer law and related law 33. Skill about teaching planning 34. Skill about instructional management as learner centered 35. Skill about selection of teaching method 36. Skill about application for developmental psychology (teenage) 37. Skill about application for learning psychology 38. Skill about test construction 7. Teaching skill 2. Skill 39. Skill about learning evaluation 40. Skill about instructional management e-Learning 8. Skill about e-Learning and e-Media 41. Skill about selection of electronic media for instruction 42. Skill about electronic media development for instruction Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 351  P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 352 Continued Domain Component Variable 43. Skill about assembling and installing computer 44. Skill about installing equipment with driver 45. Skill about installing basic computer software 46. Skill about installing operational system (OS) 9. Skill about IT Support 47. Skill about computer maintenance 48. Skill for using word compilation program to prepare document for vocation 49. Skill for using program and table program for vocation 50. Skill for using presentation program for vocation. 51. Skill for using internet to search information and communicate for vocation 10. Skill for using computer 52. Skill for problem solving with IT process 53. Ethics of teacher professional 54. To be a person of learning 55. Achievement motive 56. Future oriented and self of control 11. Supportive Affection to be a Teacher 57. Attitude toward electronic media use for instruction 58. Attitude toward computer 59. Attitude toward internet 60. Attitude toward IT media 3. Affection 12. Affection in IT 61. Ethics in IT use 62. Readiness for change Affect Know Skill Com Kno w1 Kno w2 Kno w3 Kno w4 Kno w5 Kno w6 Skill1 Skill2 Skill3 Skill4 Aff e c t 1 Aff e c t 2 1.000 0.983 0.855 0.653 0.681 0.838 0.794 0.760 0.791 0.876 0.809 0.836 0.718 0.939 0.877 Chi-Square = 30.542, df = 29, P-value = 0.387, RMSEA = 0.016 Chi-Square = 38.990, df = 28, P-value = 0.081, RMSEA = 0.044 Affec t Know Skill Com Know1 Know2 Know3 Know4 Know5 Know6 Skill1 Skill2 Skill3 Skill4 Affect1 Affect2 1.000 0.991 0.819 0.626 0.557 0.689 0.644 0.753 0.843 0.746 0.701 0.743 0.806 0.938 0.864 Figure 1. Intent Competency Model. Figure 2. Actual Competency Model. about e-Learning and e-Media, knowledge about computer use, knowledge about IT Support, knowledge about curriculum and general knowledge about education respectively. The factor of skill were teaching skill, skill about IT Support, skill about e-Learning and e-Media, and skill for using computer respec- tively. The factor of affection were supportive affection to be a teacher and affection in IT respectively. From Figure 2 and Table 5, it was found that the model of actual competency of computer teacher for vocation at vocational certificate level was Congruent to empirical data of educational institutes under OVEC at good level because every statistic value to measure the confirmation passed every criterion. It illustrated that model with good validity and it illustrated the structure of content in questionnaire had good validity and it confirmed that teacher competency composed of 3 factors from 12 sub-factors. The important sequences of factors were knowledge, skill, and af- fection respectively. Moreover, the important sequences of sub-factors in each factor, the factor of knowledge were knowl- 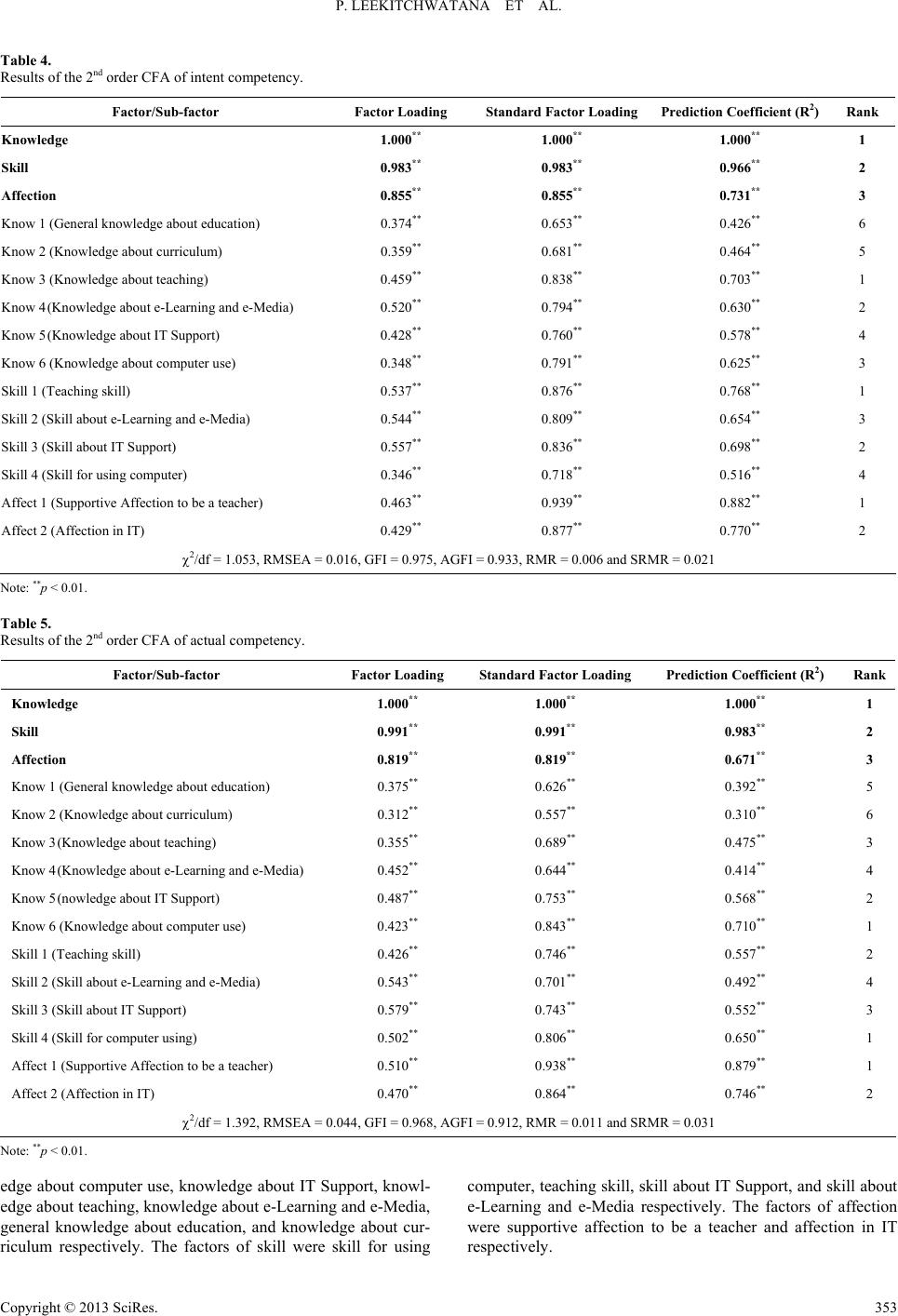 P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. Table 4. Results of the 2nd order CFA of intent competency. Factor/Sub-factor Factor Loading Standard Factor Loading Prediction Coefficient (R2)Rank Knowledge 1.000** 1.000** 1.000** 1 Skill 0.983** 0.983** 0.966** 2 Affection 0.855** 0.855** 0.731** 3 Know 1 (General knowledge about education) 0.374** 0.653** 0.426** 6 Know 2 (Knowledge about curriculum) 0.359** 0.681** 0.464** 5 Know 3 (Knowledge about teaching) 0.459** 0.838** 0.703** 1 Know 4 (Knowledge about e-Learning and e-Media) 0.520** 0.794** 0.630** 2 Know 5 (Knowledge about IT Support) 0.428** 0.760** 0.578** 4 Know 6 (Knowledge about computer use) 0.348** 0.791** 0.625** 3 Skill 1 (Teaching skill) 0.537** 0.876** 0.768** 1 Skill 2 (Skill about e-Learning and e-Media) 0.544** 0.809** 0.654** 3 Skill 3 (Skill about IT Support) 0.557** 0.836** 0.698** 2 Skill 4 (Skill for using computer) 0.346** 0.718** 0.516** 4 Affect 1 (Supportive Affection to be a teacher) 0.463** 0.939** 0.882** 1 Affect 2 (Affection in IT) 0.429** 0.877** 0.770** 2 2/df = 1.053, RMSEA = 0.016, GFI = 0.975, AGFI = 0.933, RMR = 0.006 and SRMR = 0.021 Note: **p < 0.01. Table 5. Results of the 2nd order CFA of actual competency. Factor/Sub-factor Factor Loading Standard Factor Loading Prediction Coefficient (R2) Rank Knowledge 1.000** 1.000** 1.000** 1 Skill 0.991** 0.991** 0.983** 2 Affection 0.819** 0.819** 0.671** 3 Know 1 (General knowledge about education) 0.375** 0.626** 0.392** 5 Know 2 (Knowledge about curriculum) 0.312** 0.557** 0.310** 6 Know 3 (Knowledge about teaching) 0.355** 0.689** 0.475** 3 Know 4 (Knowledge about e-Learning and e-Media) 0.452** 0.644** 0.414** 4 Know 5 (nowledge about IT Support) 0.487** 0.753** 0.568** 2 Know 6 (Knowledge about computer use) 0.423** 0.843** 0.710** 1 Skill 1 (Teaching skill) 0.426** 0.746** 0.557** 2 Skill 2 (Skill about e-Learning and e-Media) 0.543** 0.701** 0.492** 4 Skill 3 (Skill about IT Support) 0.579** 0.743** 0.552** 3 Skill 4 (Skill for computer using) 0.502** 0.806** 0.650** 1 Affect 1 (Supportive Affection to be a teacher) 0.510** 0.938** 0.879** 1 Affect 2 (Affection in IT) 0.470** 0.864** 0.746** 2 2/df = 1.392, RMSEA = 0.044, GFI = 0.968, AGFI = 0.912, RMR = 0.011 and SRMR = 0.031 Note: **p < 0.01. edge about computer use, knowledge about IT Support, knowl- edge about teaching, knowledge about e-Learning and e-Media, general knowledge about education, and knowledge about cur- riculum respectively. The factors of skill were skill for using computer, teaching skill, skill about IT Support, and skill about e-Learning and e-Media respectively. The factors of affection were supportive affection to be a teacher and affection in IT respectively. Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 353  P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. Results of Calculation of Reliability with α Formula of Cronbach The intent competency of knowledge, skill, and affection were 0.96, 0.97 and 0.96 and actual competency were 0.95, 0.95 and 0.95 respectively as shown in Table 6. Conclusion Results of factor analysis of competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level from expert data with EFA, it was found that the 62 studied variables from 6 prototype compo- nents covering in 3 domains, that were able to group as com- ponent with eigenvalue more than 1.000 with 14 components and the whole components were able to explain the whole variables with 81.719 percents and factor loading of each vari- able between 0.430 to 0.902. Afterward, 62 variables were minor adjusted the new structure component to be 12 compo- nents in the same 3 domains that were knowledge, skill and affection. Those 12 components were general knowledge about education, knowledge about curriculum, knowledge about teaching, knowledge about e-Learning and e-Media, knowledge about IT support, knowledge about computer use, teaching skill, skill about e-Learning and e-Media, skill about IT support, skill for using computer, supportive affection to be a teacher and affection in IT. Results of examination the quality of questionnaire on com- petency of computer teacher for vocation at vocational certifi- cate level from educational institute data. 1) It was found that the 12 competency components covering 3 competency domains including knowledge, skill and affection obtained from EFA in term 7.1, these had good construct valid- ity because the model was congruent to empirical data at good level in both dimensions of intent and actual competencies with statistical value passed as the followings. a) Model of intent competency had Chi-square value with no statistical significance (p = 0.387), RMSEA = 0.016, GFI = 0.975, AGFI = 0.933, RMR = 0.006, and SRMR = 0.021. The important sequence of factors from most to less were knowl- edge, skill and affection respectively. b) Model of actual competency had Chi-square value with no statistical significance (p = 0.081), RMSEA = 0.044, GFI = 0.968, AGFI = 0.912, RMR = 0.011, and SRMR = 0.031. The important sequence of factors from most to less were knowl- edge, skill and affection respectively. 2) Moreover, it was found that the questionnaire had high re- liability in both dimensions as the followings. a) Reliability of intent competency in terms of factors with initiation 0.96 - 0.97 and in terms of sub-factor with initiation 0.85 - 0.98. b) Reliability of actual competency in terms of factors with 0.95 in 3 domains and in terms of sub-factor with initiation 0.78 - 0.95. Discussion Results of factor analysis of competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level, it was found that the 62 studied variables were able to be grouped into 14 components and each component had eigenvalue more than 1. Moreover, the whole components were able to explain the variation of whole vari- able with 81.719 and factor loading of each variable had value with initiation 0.430 to 0.902. This indicated that the variables are able to use for studying competency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level since these variables had document and research support. The documents and related literatures were wide reviewed therefore the important variables was ob- tained with congruence and covering large structure of 3 com- petency domains included document and research. The whole 62 variables are able to group into 14 components, then there is minor structural component adjusted for more Table 6. Results of calculation of reliability of questionnaire classified by dimension in terms of factors and sub-factors. Reliability (α) Factor/Sub-factor Intent Competency Actual Competency Knowledge 0.96 0.95 Skill 0.97 0.95 Affection 0.96 0.95 Know 1 (General Knowledge about education) 0.91 0.87 Know 2 (Knowledge about curriculum) 0.85 0.78 Know 3 (Knowledge about teaching) 0.92 0.88 Know 4 (Knowledge about e-Learning and e-Media) 0.94 0.90 Know 5 (Knowledge about IT Support) 0.94 0.91 Know 6 (Knowledge about computer use) 0.92 0.89 Skill 1 (Teaching skill) 0.96 0.92 Skill 2 (Skill about e-Learning and e-Media) 0.91 0.92 Skill 3 (Skill about IT Support) 0.98 0.95 Skill 4 (Skill for computer using) 0.94 0.94 Affect 1 (Supportive Affection to be a teacher) 0.94 0.90 Affect 2 (Affection in IT) 0.96 0.92 Total 0.98 0.98 Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 354  P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. proper to be 12 components from the whole 62 variables cov- ering 3 domains. Afterward these components and variables were used for constructing the questionnaire on teacher compe- tency for educational institute and these were examined for construct validity with the 2nd order CFA to confirm 2 issues as the followings. 1) To confirm 12 adjusted components, these were arranged into 12 sub-factors in 3 factors. 2) To confirm 3 factors, these composed to be the whole competency. Results of examination the quality of questionnaire on com- petency of computer teacher at vocational certificate level for educational institute; it was found that questionnaire had good construct validity and high reliability. The 2nd order CFA of competency composed of 12 sub-factors and 12 sub-factors were grouped into 3 factors included knowledge, skill and af- fection. These were factor of competency since the model was congruent to empirical data of educational institutes at good level both intent and actual competencies. Owing to the vari- ables and factor were introduced to construct questionnaire had documents and related literature support and it was analyze with EFA, therefore when these were used to analyze with 2nd order CFA, then it was found that construct validity was at good level. Considering the importance of 3 factors, it is obviously seen that competency in domains of knowledge and skill are very important as the first and the second orders with factor loading almost similar. This is congruent to the importance of knowl- edge and skill for IT use in accordance with objective of train- ing in model of professional teacher skill development in aspect of IT use of Downes et al. (2002). The factor in this research is congruent to the research results of Leekitchwatana (2010) who studied on factor of competency of IT teacher at lower secondary school level and found 3 do- mains of knowledge, skill, and affection. The sub-factor in this research were found 12 sub-factors but she found 10 sub-fac- tors with differences in factor of knowledge and skill of subject teaching but at vocational certificate level would have more sub-factors than lower secondary school level. Furthermore, it is also go along with research results of Ju- lachoo (2005) who studied competency tendency of IT teacher by using Delphi technique and found that the competency ten- dency of IT teacher at third level in 3 domains included knowl- edge, practice skill and attitude. In addition, it is congruent to study of Boonserm (2003) who studied factor of competency of art teacher at primary school level by the 2nd order CFA and found 2 principal factors and 7 sub-factors. The congruent fac- tors are academic, teaching skill, moral and ethic aspect, art knowledge aspect, and art skill aspect. The two last factors are knowledge and skill that are the same as this research results. Recommendations Recommendations from the Research Results Factor of competency of computer teacher for vocation from this research results had the document and related literature support and was examined the validity by factor analysis 2 times that were EFA and the 2nd order CFA. It was found that there was content validity therefore, it is able to study compe- tency of computer teacher for vocation both intent and actual competencies. Questionnaire on competency of computer teacher for voca- tion construct had good quality since it had good construct va- lidity and high reliability, therefore, it is able to study compe- tency of computer teacher for vocation both intent and actual competencies. Recommendations for Further Research Factor of competency of computer teacher for vocation from this research results was emphasized to be proper for teacher who is teaching if one wants to use the component regarding to extensive role of teacher or more complex role than this, it might be added competency of teacher in other domains such as researcher and head of work unit of computer/ IT for instance, therefore in order to congruent and cover with role and function of information technology teacher who has higher position and/or more responsibility, the adjusted component might use to examine the new construct validity by using EFA and/or CFA. The variables and factors of competency of computer teacher in this research is proper for study competency of computer teacher for vocation, therefore if one wants to study compe- tency of computer teacher in other subjects or other levels, it needs to adjust the variables and factors to be proper with con- tent or context of that educational level, particularly variables and factors in domains of computer knowledge and skill be- cause different subjects or different education levels of learner and different roles and functions of teacher, therefore the ad- justed variables and factors can be used by examining the new construct validity and analyzing with EFA and/or CFA. Acknowledgements The researchers would like to express gratitude to the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research Univer- sities, Office of the Higher Education Commission, Thailand for supporting this study. In addition, We are deeply indebted to the Faculty of Industrial Education and King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang (KMITL) for giving us the opportunity to complete this study. Finally, we would like to give our special thanks to all the experts and educational insti- tutes which were a part in this study and enabled us to complete this work. REFERENCES Boonserm, P. (2003). Analysis of component and study of background related to competency of art teacher at primary school level. Master Thesis, Chulalongkorn: Chulalongkorn University. Downes, T., Khun, T., Scott, D., Leonard, R., & Warhurst, J. (2002). Preservice Teacher Training and Teacher Professional Development in the Use of ICTs in the Teaching of Mathematics and Science in Participating SEAMEO Countries. Report Submitted to SEAMEO HOM, Bangkok, 2002. Hair Jr., J. E., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1998). Multivariate data analysis. 5th Edition, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc. Julachoo, S. (2005). Competency tendency of information technology teacher in content group of occupation and technology in school under the office of educational area of Nakorn Nayok. Master Thesis, Kasetsart: Kasetsart University. Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Journal of Educational and Psychological Meas- urement, 30, 607-610. Leekitchwatana, P. (2010). Development of competency of information technology teacher at lower secondary school. Khon Kaen Research Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 355  P. LEEKITCHWATANA ET AL. Journal, 15, 1101-1114. Office of Vocational Education Commission (OVEC) (2011). Educa- tion institute under office of vocational education commission. http://www.vec.go.th/Default.aspx?tabid=113 Office of Vocational Education Commission (OVEC) (2005). Principle theory and policy of vocational education reform. http://www.vec.go.th/ Ungsuchote, S. et al. (2008). Statistical Analysis for Research in Social Science and Behavioral Science: Technique of LISREL Program. Bangkok: Mission Media. Wiruchchai, N. (1995). Linear structural equation relationship model (LISREL). 2nd Edition, Bangkok: Chulalongkorn Press. Copyright © 2013 SciRes. 356 |

