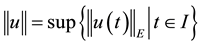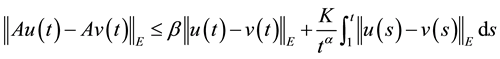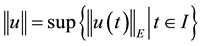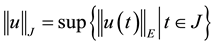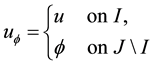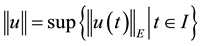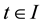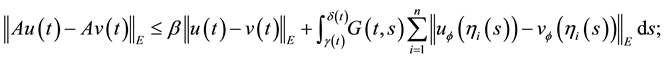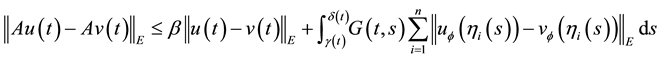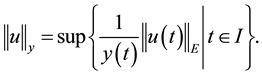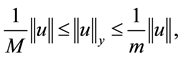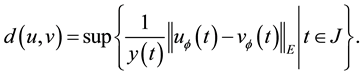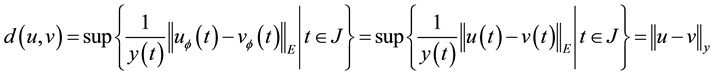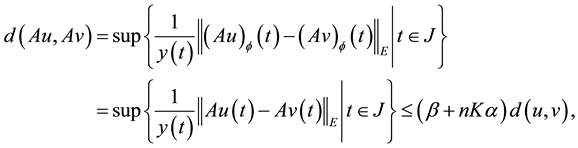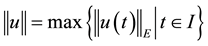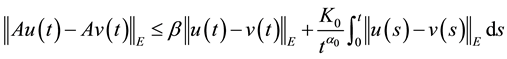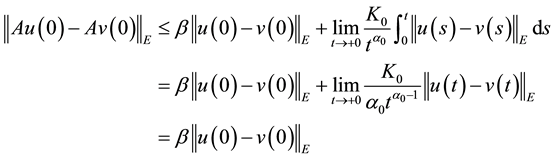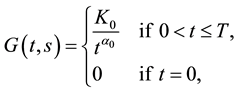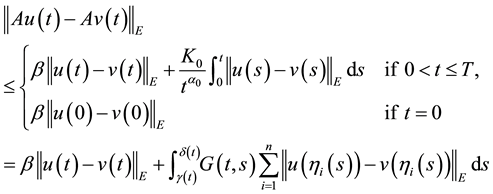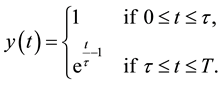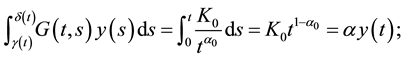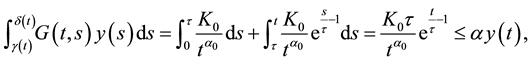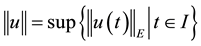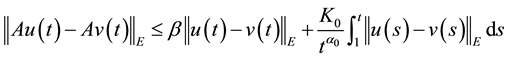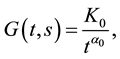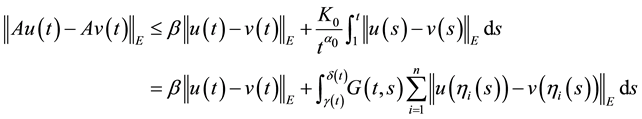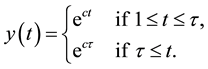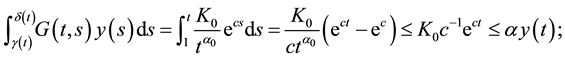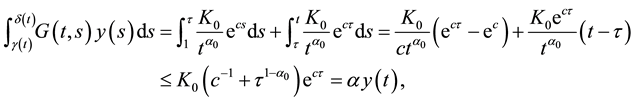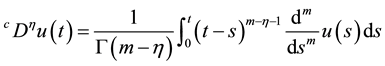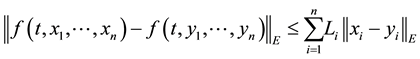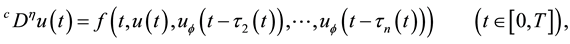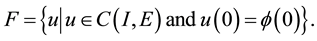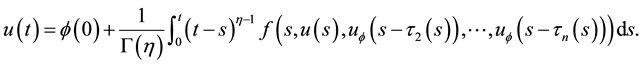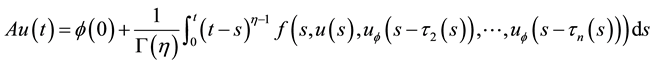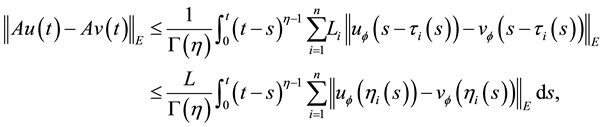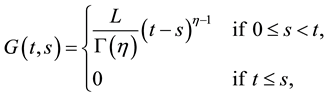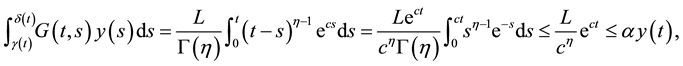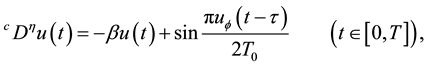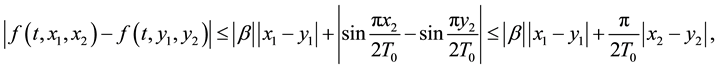Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.13(2015), Article ID:61592,7 pages
10.4236/am.2015.613192
Fixed Point Theorem and Fractional Differential Equations with Multiple Delays Related with Chaos Neuron Models
Toshiharu Kawasaki, Masashi Toyoda
Faculty of Engineering, Tamagawa University, Tokyo, Japan
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).


Received 9 July 2015; accepted 27 November 2015; published 30 November 2015

ABSTRACT
In this paper, we show a fixed point theorem which deduces to both of Lou’s fixed point theorem and de Pascale and de Pascale’s fixed point theorem. Moreover, our result can be applied to show the existence and uniqueness of solutions for fractional differential equations with multiple delays. Using the theorem, we discuss the fractional chaos neuron model.
Keywords:
Fixed Point Theorem, Ordinary Differential Equation, Delay Differential Equation, Fractional Differential Equation, Fractional Chaos Neuron Model

1. Introduction
The following was the famous fixed point theorem introduced by Banach in 1922.
The Banach contraction principle ([1] ). Let
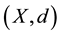 be a complete metric space, let F be a nonempty closed subset of X and let A be a mapping from F into itself. Suppose that there exist
be a complete metric space, let F be a nonempty closed subset of X and let A be a mapping from F into itself. Suppose that there exist
 such that
such that
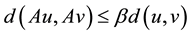
for any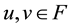 . Then A has a unique fixed point in F.
. Then A has a unique fixed point in F.
In 1999 Lou proved the following fixed point theorem.
Lou’s fixed point theorem ([2] ). Let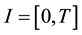 , let
, let
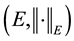 be a Banach space, let
be a Banach space, let
 be the Ba- nach space consisting of all continuous mappings from I into E with norm
be the Ba- nach space consisting of all continuous mappings from I into E with norm
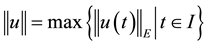
for any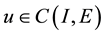 , let F be a nonempty closed subset of
, let F be a nonempty closed subset of
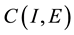 and let A be a mapping from F into itself. Suppose that there exist
and let A be a mapping from F into itself. Suppose that there exist
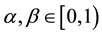 and
and
 such that
such that
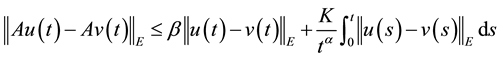
for any
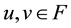 and for any
and for any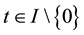 . Then A has a unique fixed point in F.
. Then A has a unique fixed point in F.
Moreover, in 2002 de Pascale and de Pascale proved the following fixed point theorem.
De Pascale-de Pascale’s fixed point theorem ( [3] ). Let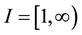
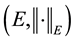
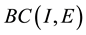
for any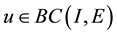
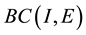
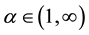
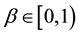

for any
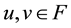
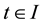
In this paper, using the Banach contraction principle, we show a fixed point theorem which deduces to both of Lou’s fixed point theorem and de Pascale and de Pascale’s fixed point theorem. Moreover, our results can be applied to show the existence and uniqueness of solutions for fractional differential equations with multiple delays. Using the theorem, we discuss the fractional chaos neuron model [4] .
2. Fixed Point Theorem
In this section, we show a fixed point theorem. It deduces to Lou’s fixed point theorem [2] and de Pascale and de Pascale’s fixed point theorem [3] .
Definition 1. Let I be an arbitrary finite or infinite interval, let J be an interval with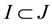
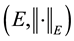
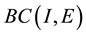
for any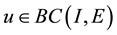
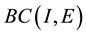
for any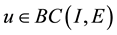
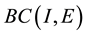
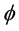
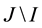
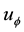
for any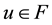
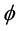
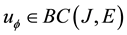
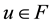
Theorem 1. Let I be an arbitrary finite or infinite interval, let
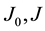
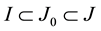
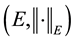
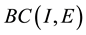
for any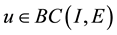
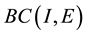
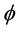
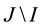
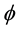
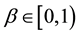
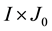
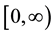
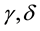
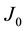

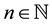
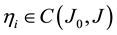
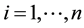
(H1) for any
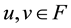
(H2) there exist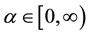


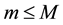
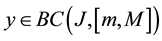
1)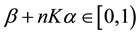
2)
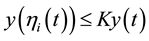
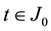
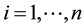
3)
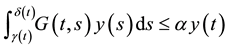
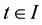
Then A has a unique fixed point in F.
Proof. By (H1) we obtain
for any
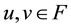
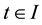
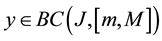
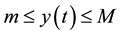
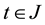
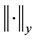
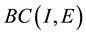
Since
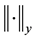

Since
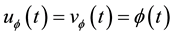
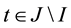
and hence
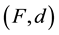
for any
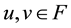
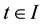
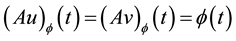
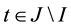
that is, A is a contraction mapping. By the Banach contraction principle A has a unique fixed point in F.
The following remarks show that our fixed point theorem derives Lou’s fixed point theorem [2] and de Pascale and de Pascale’s fixed point theorem [3] . The proofs are owed to [5] .
Remark 1. By Theorem 1 we can obtain Lou’s fixed point theorem [2] . Actually let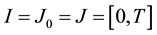
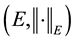
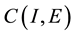
for any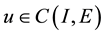
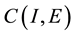
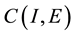
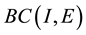
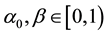
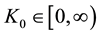
for any
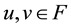
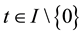
for any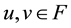
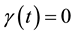
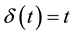
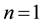
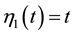
for any
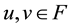
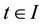
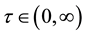
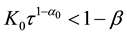
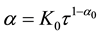
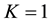

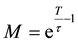
Then (1) and (2) of (H2) hold. Moreover, if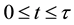
if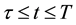
that is, (3) of (H2) holds. Therefore, by Theorem 1 A has a unique fixed point in F.
Remark 2. By Theorem 1 we can obtain de Pascale and de Pascale’s fixed point theorem [3] . Actually let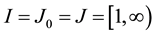
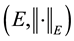
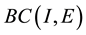
for any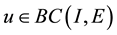
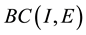
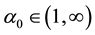
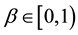
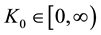
for any
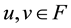
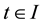
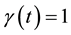
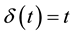
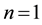
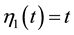
for any
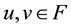
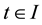
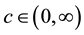
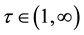
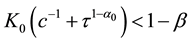
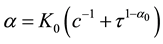
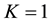
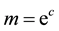
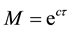
Then (1) and (2) of (H2) hold. Moreover, if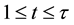
if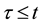
that is, (3) of (H2) holds. Therefore, by Theorem 1 A has a unique fixed point in F.
3. Fractional Differential Equations with Multiple Delays
In this section, by using Theorem 1, we show the existence and uniqueness of solutions for fractional differential equations with multiple delays. Throughout this paper, the fractional derivative means the Caputo-Riesz derivative
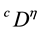
for any
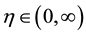
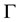
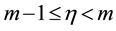
Theorem 2. Let
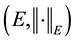
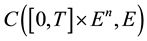
ous mappings from
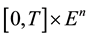
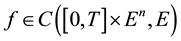
(Hf) there exist
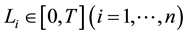
for any
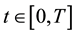
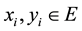
Let
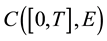
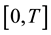
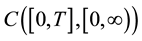
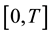
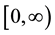
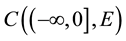
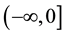
where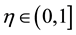
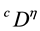
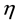
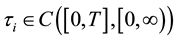
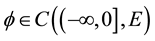
have a unique solution in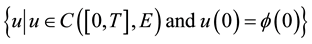
Proof. Put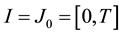
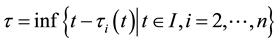
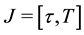
Then F is closed. Since
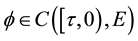
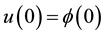
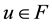
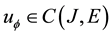
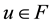
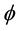
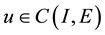
Define a mapping A by
for any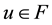
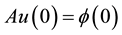
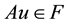
where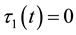
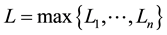
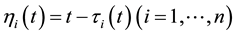
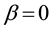
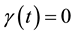
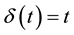
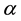
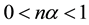
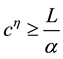
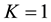
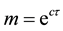
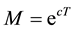
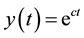
(3) of (H2) holds. Therefore, by Theorem 1 A has a unique fixed point in F.
By using Theorem 2, we discuss the fractional chaos neuron model [4] .
Example 1. We consider the following fractional differential equation with delay
where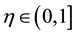
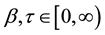
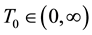
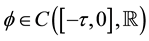
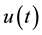
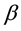
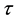
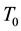
called the fractional chaos neuron model [4] . Put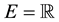
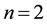
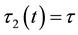
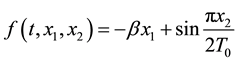
Since
f satisfies (Hf) for
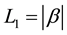
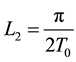
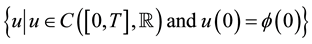
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the referee for valuable comments.
Cite this paper
ToshiharuKawasaki,MasashiToyoda, (2015) Fixed Point Theorem and Fractional Differential Equations with Multiple Delays Related with Chaos Neuron Models. Applied Mathematics,06,2192-2198. doi: 10.4236/am.2015.613192
References
- 1. Banach, S. (1922) Sur les opérations dans les ensembles abstraits et leur application aux équations integrals. Fundamenta Mathematicae, 3, 133-181.
- 2. Lou, B. (1999) Fixed Points for Operators in a Space of Continuous Functions and Applications. Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, 127, 1159-2264.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1090/S0002-9939-99-05211-9 - 3. de Pascale, E. and de Pascale, L. (2002) Fixed Points for Some Non-Obviously Contractive Operators. Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, 130, 3249-3254.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1090/S0002-9939-02-06704-7 - 4. Matsuzaki, T. and Nakagawa, M. (2003) A Chaos Neuron Model with Fractional Differential Equation. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 72, 2678-2684.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.72.2678 - 5. Suzuki, T. (2006) Lou’s Fixed Point Theorem in a Space of Continuous Mappings. Journal of the Mathematical Society of Japan, 58, 769-774.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2969/jmsj/1156342037 - 6. Kilbas, A.A., Srivastava, H.M. and Trujillo, J.J. (2006) Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
- 7. Lai, X. and Zhang, Y. (2012) Fixed Point and Asymptotic Analysis of Cellular Neural Networks. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2012, Article ID: 689845.
- 8. Zhang, Y. and Luo, Q. (2013) Global Exponential Stability of Impulsive Cellular Neural Networks with Time-Varying Delays via Fixed Point Theory. Advances in Difference Equations, 2013, 2013:23.