Advances in Pure Mathematics
Vol.05 No.14(2015), Article ID:61843,7 pages
10.4236/apm.2015.514077
Lp Polyharmonic Dirichlet Problems in the Upper Half Plane
Kanda Pan
Department of Mathematics, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China

Copyright © 2015 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 11 November 2015; accepted 8 December 2015; published 11 December 2015
ABSTRACT
In this article, a class of Dirichlet problem with Lp boundary data for polyharmonic function in the upper half plane is mainly investigated. By introducing a sequence of kernel functions called higher order Poisson kernels and a hierarchy of integral operators called higher order Pompeiu operators, we obtain a main result on integral representation solution as well as the uniqueness of the polyharmonic Dirichlet problem under a certain estimate.
Keywords:
Dirichlet Problem, Polyharmonic Function, Higher Order Poisson Kernels, Higher Order Pompeiu Operators, Non-Tangential Maximal Function, Uniqueness

1. Introduction
Usually harmonic functions are defined by Laplace operator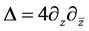 , where
, where 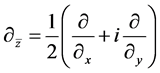 is the Cauchy-Riemann operator and
is the Cauchy-Riemann operator and 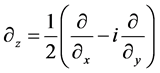 is the adjoint operator of C-R operator. By iterating the
is the adjoint operator of C-R operator. By iterating the
Laplace operator, one can define the so-called polyharmonic functions by  [1] . In [2] , Goursat obtained his decomposition formula, in [3] , Vekua developed one method to construct an approximative solution of the biharmonic Dirichlet problem in a simply connected domain. In recent years, the study of explicit solution of BVPS (boundary value problems) has undergone a new phase of development [4] - [6] . There are Dirichlet, Neumann and Robin boundary value problems in regular domain (in the disc [4] ; and in the upper half plane [5] ) and in irregular domains (Lipschitz domains [6] ). Although, there are many marked works about the BVPS, few of them give a certain estimate about the uniqueness of the solution. Thus, the purpose of this article is devoted to solving the unique solution of the following polyharmonic Dirichlet problems (for short, PHD) for
[1] . In [2] , Goursat obtained his decomposition formula, in [3] , Vekua developed one method to construct an approximative solution of the biharmonic Dirichlet problem in a simply connected domain. In recent years, the study of explicit solution of BVPS (boundary value problems) has undergone a new phase of development [4] - [6] . There are Dirichlet, Neumann and Robin boundary value problems in regular domain (in the disc [4] ; and in the upper half plane [5] ) and in irregular domains (Lipschitz domains [6] ). Although, there are many marked works about the BVPS, few of them give a certain estimate about the uniqueness of the solution. Thus, the purpose of this article is devoted to solving the unique solution of the following polyharmonic Dirichlet problems (for short, PHD) for 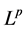 data in the upper half plane, H, i.e.
data in the upper half plane, H, i.e.
 (1.1)
(1.1)
with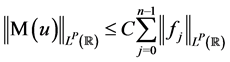 , where
, where  is the Laplacian, and
is the Laplacian, and 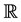 is the real axis,
is the real axis,  for some
for some
suitable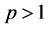 ,
, 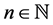 ,
, 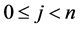 ,
, 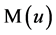 is the non-tangential maximal function of u, which is defined by
is the non-tangential maximal function of u, which is defined by
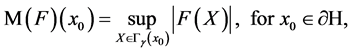
where 
where
It is clear that all the boundary data in BVPs (1.1) are non-tangential.
2. Preliminary and Some Lemmas
Definition 2.1. If a real valued function 

We use the notation 

Lemma 2.2. [7] Let D be a simply connected (bounded or unbounded) domain in the complex plane with smooth boundary





where 



Corollary 2.3. If the sequence of functions 
(1)
(2) 

Then 


where 


Definition 2.4. A sequence of real-valued functions of two variables 


(1) For all




exists for all t and



(2) 


uniformly on 




(3) 


(4)

(5)

where all limits are non-tangential.
Definition 2.5. Let D be a simply connected (bounded or unbounded) domain in the plane with smooth boundary










Lemma 2.6. [8] If 






with

for

for 


Moreover,

is the classical Poisson kernel for the upper half plane. All of the above

exists on



can be continuously extended to 


uniformly on 



Moreover,

for any 

Remark 2.7. Lemma 2.6 provides a algorithm to obtain all explicit expressions of higher order Poisson kernels appeared in [8] .
3. Homogeneous PHD Problem in the Upper Half Plane
In order to solve the homogeneous PHD problems (1.1) and get the uniqueness of its solution, we need the following lemmas.
Lemma 3.1. [8] Let D be a simply connected unbounded domain in the plane with smooth boundless boundary



uniformly on 



Lemma 3.2. [8] Let 

for any 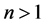


Lemma 3.3. [9] Let





where 










Lemma 3.4. (Hardy-Littlewood maximal theorem, see [10] ) Let



(1) If



(2) If


where 
Corollary 3.5. 





for any






Theorem 1. Let 



is the unique solution of PHD problem (1.1)
Proof. Since the higher order Poisson kernels possess the inductive property as stated in Definition 2.4. Act on the two sides of (3.9) with the polyharmonic operator


since the Laplace operator is


follow from Lemma 2.6 and the nice property of G, i.e.,

for any
Similarly, letting the polyharmonic operator 


Next we turn to the estimate and uniqueness of the solution. By Definition 2.4 and Corollary 3.5, we have
As discussed above, the uniqueness of solution follows.
4. Inhomogeneous PHD Problem in the Upper Plane
Due to the limited knowledge of the author, at this section, we only consider the bounded domain D for in- homogeneous PHD problem in the upper half-plane, i.e.

where





Definition 4.1. [11] Let kernels

where m and n are integer, with 



The following properties of 
Lemma 4.2. Assume


Then, the integral 


Proof. See Corollary 4.6 in [11] .
Lemma 4.3. Assume



(a) If 




(b) If 




are valid in 

Proof. See Corollary 5.4 in [11] .
Theorem 2. The problem of (4.1) is solvable and its unique solution is

where 



Proof. Through Lemma 4.2 and Lemma 4.3, we get
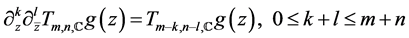
in the Sobolev sense. Moreover,

Noting (4.9) we know that 
and for some

By the aforementioned, the problem (4.1) is equivalent to the PHD problem of simplified form
So, through Theorem 1 as well as the estimate of the solution, we complete the proof of Theorem 2.
Cite this paper
Kanda Pan, (2015) Lp Polyharmonic Dirichlet Problems in the Upper Half Plane. Advances in Pure Mathematics,05,828-834. doi: 10.4236/apm.2015.514077
References
- 1. Aronszajn, N., Cresse, T. and Lipkin, L. (1983) Polyharmonic Functions, Oxford Math. Clarendon, Oxford.
- 2. Goursat, E. (1898) Sur I’équation ΔΔu = 0. Bulletin de la Société Mathématique de France, 26, 236-237.
- 3. Vekua, I.N. (1976) On One Method of Solving the First Biharmonic Boundary Value Problem and the Dirichlet Problem. American Mathematical Society Translations, 104, 104-111.
- 4. Begehr, H., Du, J. and Wang, Y. (2008) A Dirichlet Problem for Polyharmonic Functions. Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata, 187, 435-457.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10231-007-0050-5 - 5. Begehr, H. and Gaertner, E. (2007) A Dirichlet Problem for the Inhomogeneous Polyharmonic Equations in the Upper Half Plane. Georgian Mathematical Journal, 14, 33-52.
- 6. Verchota, G.C. (2005) The Biharmonic Neumann Problem in Lipschitz Domain. Acta Mathematica, 194, 217-279.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02393222 - 7. Du, Z. (2008) Boundary Value Problems for Higher Order Complex Differential Equations. Doctoral Dissertation, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin.
- 8. Du, Z., Qian, T. and Wang, J.X. (2012) Polyharmonic Dirichlet Problem in Regular Domain: The Upper Half Plane. Journal of Differential Equations, 252, 1789-1812.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jde.2011.08.024 - 9. Stein, E.M. and Weiss, G. (1971) Introduction to Fourier Analysis on Euclidean Spaces. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey.
- 10. Garnett, J. (2007) Bounded Analytic Functions. Springer, New York.
- 11. Begehr, H. and Hile, G.N. (1997) A Hierarchy of Integral Operators. Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics, 27, 669-706.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1216/rmjm/1181071888












