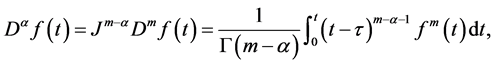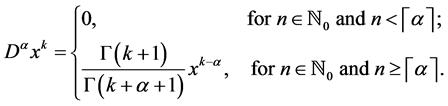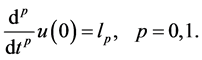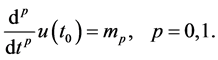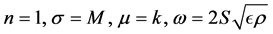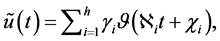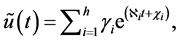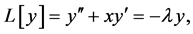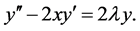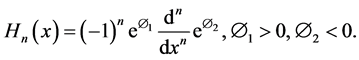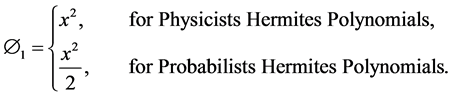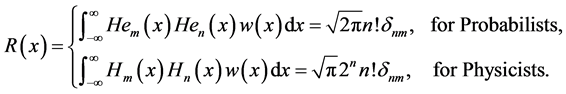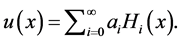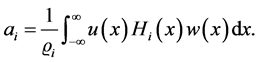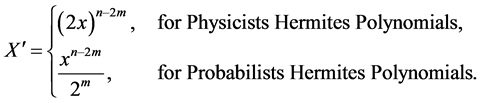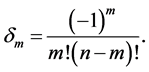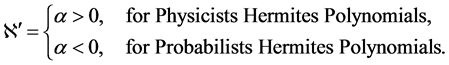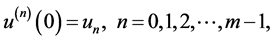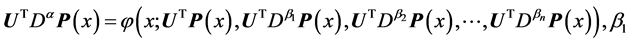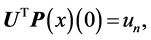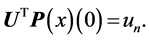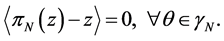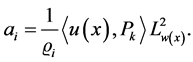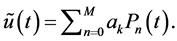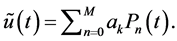International Journal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Application
Vol.06 No.03(2017), Article ID:78406,15 pages
10.4236/ijmnta.2017.63010
Hermite Solution of Bagley-Torvik Equation of Fractional Order
Tamour Zubair1,2*, Marriam Sajjad3, Rehmatullah Madni2, Amna Shabir2
1Department of Applied Mathematics and Statics, Institute of Space and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
2Department of Mathematics, University of Sargodah, Lyallpur Campus, Faisalabad, Pakistan
3Department of Mathematics, University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: May 8, 2017; Accepted: August 11, 2017; Published: August 14, 2017
ABSTRACT
In this paper, a new methodology of fractional derivatives based upon Hermite polynomial is projected. The fractional derivatives are demonstrated according to Caputo sense. Hermite collocation technique is introduced to express the definite results of Bagley-Torvik Equations. The appropriateness and straightforwardness of numerical plan is presented by graphs and error tables.
Keywords:
MAPLE 13, Bagley-Torvik Equations, Hermite Polynomials, Fractional Calculus

1. Introduction
Numerical analysis is the study of set of rules that use numerical estimation for the problems of mathematical analysis as distinguished from discrete mathematics. Fractional differential equations are operational and most effective tool to describe different physical phenomena such as rheology, diffusion processes, damping laws, and so on. Many technics have been delegated to solve differential equation of fractional order. Different structures are used to resolve the issues of nonlinear physical models of fractional orders like Finite element method [1] , Finite difference method [2] , differential transformation method [3] [4] , Adomian’s decomposition method [5] [6] [7] , variational iteration method [8] [9] [10] , Homotopy perturbation technique [11] , Zubair decomposition method (ZDM) [12] , (G’/G)-expansion method [13] , (U’/U)-expansion method [14] , U- expansion method [15] , Fractional sub numerical announcement method [16] [17] , Legendre wavelets technique [18] , Chebyshev wavelets framework [19] [20] [21] , Haar wavelets schema [22] , Legendre Method [23] , Chebyshev strategy [24] , Jacobi polynomial scheme [25] and collocation scheme [26] [27] [28] [29] . All the mentioned approaches have certain limitations like excessive computational work, less efficiency to tackle nonlinearity and divergent solution due to which many issues arise. All these disputes can be fixed with the help of orthogonal polynomials, which is a vital thought in close estimation and structures. These orthogonal polynomials are the reason of powerful strategies of spectral methods [30] [31] [32] . Starting late, Khader [33] displayed a capable numerical procedure for enlightening the fractional order physical problems using the Chebyshev polynomials. In the [34] two Chebyshev spectral frameworks for measuring multi-term fractional problems are displayed. The author (Tamour Zubair) devolve a new wavelets algorithm to construct the numerical solution of nonlinear Bagley-Torvik equation of fractional order which will have less computational works, straight forward and better accuracy as compare to the existing technique. It is to be emphasized that proposed algorithm is tremendously simple but highly effective Moreover, this new pattern is proficient for reducing the computational work to a tangible level while still retaining a very high level of accuracy.
2. Basic Definitions
Fractional Calculus [35] - [40]
We give some basic definitions and properties of the fractional calculus theory which are used further in this paper.
Definition 1. A real function  is said to be in the space
is said to be in the space  if there exists a real number
if there exists a real number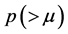 , such that
, such that , where
, where 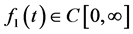 , and it is said to be in the space
, and it is said to be in the space 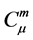 iff
iff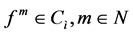 .
.
Definition 2. The Riemann-Liouville fractional integral operator of order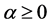 , of a function
, of a function  is defined as
is defined as
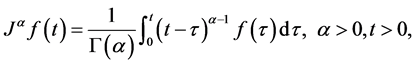
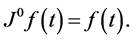
Properties of the operator 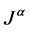 can be found in literature, we mention only the following: For
can be found in literature, we mention only the following: For 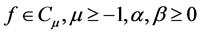 and
and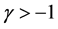 :
:
1) 
2) 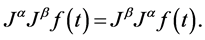
3) 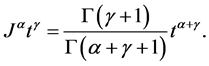
The Riemann-Liouville derivative has certain drawbacks when trying to model real-world processes with fractional differential equations. Therefore, we shall introduce a improved fractional differential operator 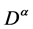 proposed by
proposed by
Definition 3. The fractional derivative of 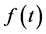
for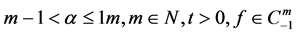

We use the ceiling function 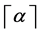
3. Bagley-Torvik Equations
Bagley-Torvik equation assumes an extremely vital part to study the performance of different material by application of fractional calculus [40] [41] . It has increased its significance in many fields of industrial and applied sciences. Precisely, the equation with 1/2 order derivative or 3/2 order derivative can be model the frequency dependent damping materials. The summed up form of Bagley-Torvik equation is given
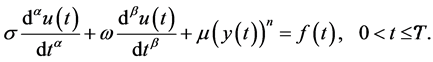
with initial condition
with boundary condition at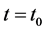
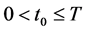
where 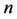
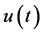


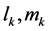
where 
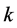
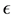
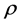
has the fraction derivative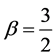
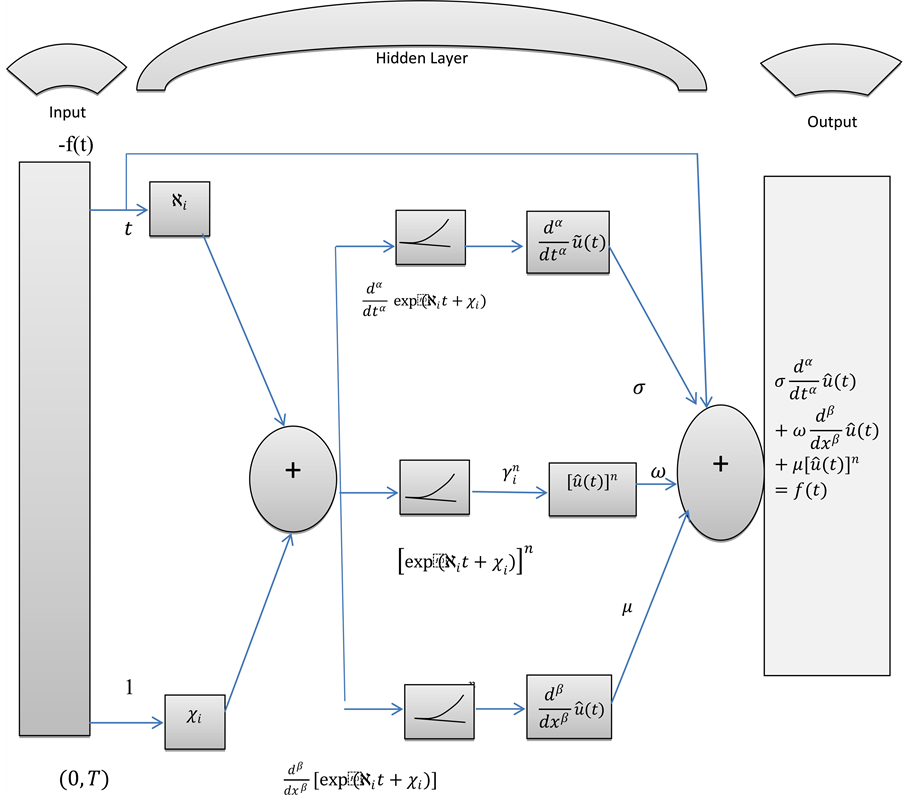
Further, we will discuss mathematical modeling of BT equation with feed-for- ward artificial neural network. The solution 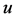
tion along with its
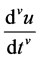
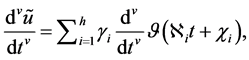
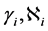
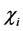

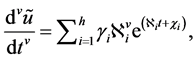

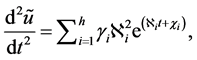
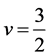
Figure 1. FDE-NN architecture of Bagley-Torvik equation.
The mathematical model can be the linear combinations of the networks represented above. The FDE-NN architecture formulated for Bagley-Torvik equation can be seen in Figure 1. It is clear that the solution 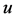
4. Hermite Polynomials [45]
It is classical orthogonal polynomials play very important role in probability. It has wide applications in numerical analysis as finite element methods as shape functions for beams. They are also applicable in physical quantum theory. Hermite polynomials are categorized into two kinds
The Probabilists Hermite polynomials are the solutions of
where 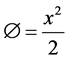
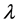
should be polynomially bounded at infinity. The above equation can be written in the form of eigen value problem
solutions are the Eigen functions of the differential operator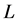
whose solutions are the Physicists Hermites Polynomials, which is the second kind of Hermite polynomials.
The Hermite polynomials is given by
where
and also
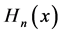
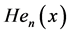
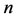
Here we have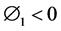
Further we have orthogonality 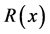
A function 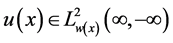
where 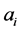
where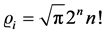
5. Fractional Form of Hermite Polynomials [35] - [40]
The explicit formula of Hermites polynomials is
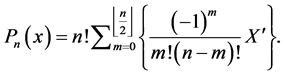
where 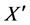
Further we have
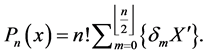
where 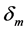
A function 
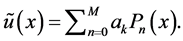
where 
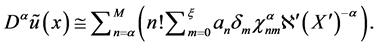
where 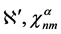
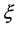
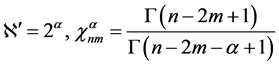
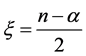
Note that only for
a) Methodology
Consider the multi order fractional differential equation (1) as
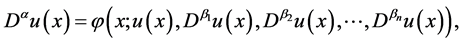
where 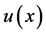
Step 1: According to the proposed algorithm we assume the following trial solution
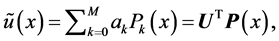
where 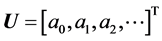
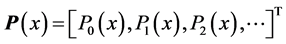
where 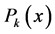
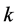
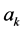
Step 2: Substituting Equation (6) into Equation (5), we get
Using (4) we have
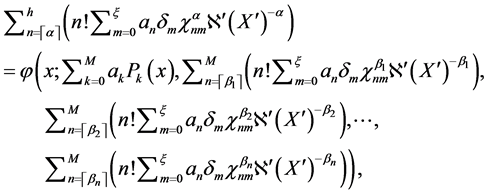
Step 3: Further we Assume suitable collocation point for Equation (7). There- fore, we obtained system has 

b) Approximation by Hermite Polynomials [45]
Let us define 

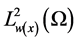
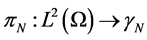
Due to the orthogonality property, we can write it as
where 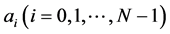
6. Numerical Simulation
In this section, we apply new algorithm to construct approximate/exact solutions fractional differential equation. Numerical results are very encouraging.
Case 1 In Equation (1), we take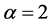
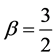

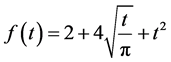
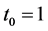
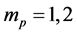
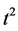
Consider the trial solutions for 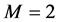
Using the trail solution into Equation (1) and proceed it according to Step 1 and Step 2, then we collocate it further to generate the system of equations. Solve the system of equations along with initial conditions, we get the values of constants
Finally, we get the approximate solution
which is exact solution.
Case 2 In Equation (1), we take
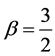
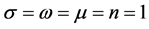
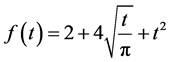
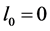
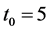
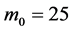

Consider the trial solutions for 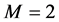
Using the trail solution into Equation (1) and proceed it according to Step 1 and Step 2, then we collocate it further to generate the system of equations. Solve the system of equations along with initial conditions, we get the values of constants
Finally, we get the approximate solution
which is exact solution.
Case 3 In Equation (1), we take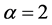
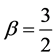
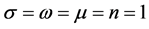
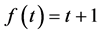
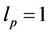
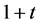
This equation can be simplify by using
Consider the trial solutions for 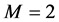
Using the trail solution into Equation (1) and proceed it according to Step 1 and Step 2, then we collocate it further to generate the system of equations. Solve the system of equations along with initial conditions, we get the values of constants
Finally, we get the approximate solution
which is exact solution.
Case 4 In Equation (1), we take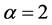

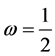
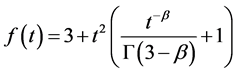

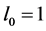
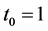
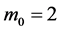
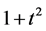
Using the trail solution into Equation (1) and proceed it according to Step 1 and Step 2, then we collocate it further to generate the system of equations. Solve the system of equations along with initial conditions, we get the values of constants
Finally, we get the approximate solution
which is exact solution.
Case 5. In Equation (1), we take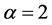
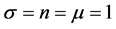
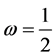
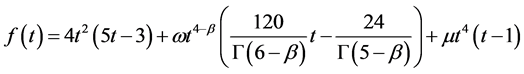
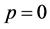
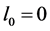
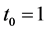
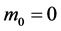
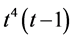
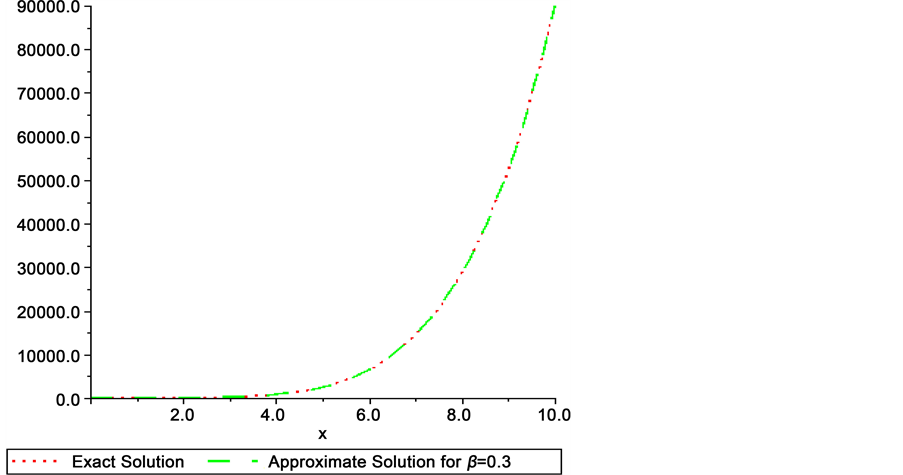
The numerical solution is represented in Table 1 in case of 
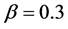
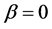
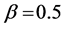
Table 1. Numerical comparison between exact and approximate solution for deferent values of
Table 2. Numerical comparison between exact approximate solutions for different values of 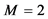
Figure 2. Graphysical comparision between exact and approximted solution.
7. Conclusions
All the facts and findings of the paper are summarized as follow:
・ This paper provides novel study of Bagley-Torvik equations of fractional order in different situations by using newly suggested Hermite Polynomial scheme.
・ Implementation of this methodology is moderately relaxed and with the help of this suggested algorithm, complicated problems can be tackled.
・ It is to be highlighted that the suggested comparison gives attentive respond regarding some particular issues for values of M, which demonstrates viability of the proposed framework. Likewise, the reliability of the application provided this technique a more comprehensive suitability.
Cite this paper
Zubair, T., Sajjad, M., Madni, R. and Shabir, A. (2017) Hermite Solution of Bagley-Torvik Equation of Fractional Order. International Journal of Modern Nonlinear Theory and Application, 6, 104-118. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijmnta.2017.63010
References
- 1. Deng, W. (2008) Finite Element Method for the Space and Time Fractional Fokker-Planck Equation. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 47, 204-226.
http://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/080714130
https://doi.org/10.1137/080714130 - 2. Gao, G.H., Sun, Z.Z. and Zhang, Y.N. (2012) A Finite Difference Scheme for Fractional Sub-Diffusion Equations on an Unbounded Domain Using Artificial Boundary Conditions. Journal of Computational Physics, 231, 2865-2879.
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/mpe/2012/924956/
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2011.12.028 - 3. Momani, S., Odibat, Z. and Erturk, V.S. (2007) Generalized Differential Transform Method for Solving a Space- and Time-Fractional Diffusion-Wave Equation. Physics Letters A, 370, 379-387.
https://www.mutah.edu.jo/userhomepages/shmomani/public.htm https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2007.05.083 - 4. Odibat, Z. and Momani, S. (2008) A Generalized Differential Transform Method for Linear Partial Differential Equations of Fractional Order. Applied Mathematics Letters, 21, 194-199.
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/7250/38695674846cdbb7c5f5d2d9cbcb5f4e0fc9.pdf
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2007.02.022 - 5. Hu, Y., Luo, Y. and Lu, Z. (2008) Analytical Solution of the Linear Fractional Differential Equation by Adomian Decomposition Method. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 215, 220-229.
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/58a6/966afe30ccc2f7bbc6b17319d6a3d1a663ba.pdf
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2007.04.005 - 6. El-Sayed, A.M.A. and Gaber, M. (2006) The Adomian Decomposition Method for Solving Partial Differential Equations of Fractal Order in Finite Domains. Physics Letters A, 359, 175-182.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223114291_The_Adomian_decomposition_method_for_solving_partial_differential_equations_of_fractal_order_in_finite_domains
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2006.06.024 - 7. El-Sayed, A.M.A., Behiry, S.H. and Raslan, W.E. (2010) Adomian’s Decomposition Method for Solving an Intermediate Fractional Advection-Dispersion Equation. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 59, 1759-1765.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0898122109005537
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2009.08.065 - 8. Inc, M. (2008) The Approximate and Exact Solutions of the Space- and Time-Fractional Burgers Equations with Initial Conditions by Variational Iteration Method. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 345, 476-484.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022247X08003739
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2008.04.007 - 9. Odibat, Z. and Momani, S. (2009) The Variational Iteration Method: An Efficient Scheme for Handling Fractional Partial Differential Equations in Fluid Mechanics. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 58, 2199-2208.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0898122109001436
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2009.03.009 - 10. Wu, G.C. and Lee, E.W.M. (2010) Fractional Variational Iteration Method and Its Application. Physics Letters A, 374, 2506-2509.
https://zulfahmed.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/2010-physics-letters-section-a-general-atomic-and-solid-state-physics-37425.pdf
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2010.04.034 - 11. He, J.H. (2003) Homotopy Perturbation Method: A New Nonlinear Analytical Technique. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 135, 73-79.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242791050_Homotopy_perturbation_method_A_new_nonlinear_analytical_technique
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0096-3003(01)00312-5 - 12. Zubair, T., Hamid, M., Saleem, M. and Mohyud-Din, S.T. (2015) Numerical Solution of Infinite Boundary Integral Equations. International Journal of Modern Applied Physics, 5, 18-25.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311202189_Numerical_Solution_of_Infinite_Boundary_Integral_Equations - 13. Bin, Z. (2012) (G’/G)-Expansion Method for Solving Fractional Partial Differential Equations in the Theory of Mathematical Physics. Communications in Theoretical Physics, 58, 623-630.
http://ctp.itp.ac.cn/EN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=15873
https://doi.org/10.1088/0253-6102/58/5/02 - 14. Usman, M. and Mohyud-Din, S.T. (2013) Traveling Wave Solutions of 7th Order Kaup Kuperschmidt and Lax Equations of Fractional-Order. International Journal of Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1, 17-34.
http://www.ijaamm.com/uploads/2/1/4/8/21481830/paper_2_sayed.pdf - 15. Usman, M. and Mohyud-Din, S.T. (2014) U-Expansion Method for 5th Order Kaup Kuperschmidt and Lax Equation of Fractional Order. International Journal of Modern Mathematical Sciences, 9, 63-81.
http://www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ViewArticle.aspx?XBq7Uu+HD/8eRjFUGMqlRUFMGJSojFCd8JeYyjsMmViTRlEyTDVgYMCmavqTokhF - 16. Alzaidy, J.F. (2013) Fractional Sub-Equation Method and Its Applications to the Space-Time Fractional Differential Equations in Mathematical Physics. British Journal of Mathematics & Computer Science, 3, 153-163.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271263179_Fractional_Sub-Equation_Method_and_its_Applications_to_the_Space-Time_Fractional_Differential_Equations_in_Mathematical_Physics
https://doi.org/10.9734/BJMCS/2013/2908 - 17. Alzaidy, J.F. (2013) The Fractional Sub-Equation Method and Exact Analytical Solutions for Some Nonlinear Fractional PDEs. American Journal of Mathematical Analysis, 1, 14-19.
http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajma/1/1/3/ - 18. Jafari, H., Yousefi, S.A., Firoozjaee, M.A., Momani, S. and Khalique, C.M. (2011) Application of Legendre Wavelets for Solving Fractional Differential Equations. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 62, 1038-1045.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0898122111003257
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2011.04.024 - 19. Khader, M.M., El Danaf, T.S. and Hendy, A.S. (2013) A Computational Matrix Method for Solving Systems of High Order Fractional Differential Equations. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37, 4035-4050.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235916821_A_computational_matrix_method_for_solving_systems_of_high_order_fractional_differential_equations
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2012.08.009 - 20. Zhu, L. and Fan, Q.B. (2012) Solving Fractional Nonlinear Fredholm Integro-Differential Equations by the Second Kind Chebyshev Wavelet. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 17, 2333-2341.
https://advancesindifferenceequations.springeropen.com.previewlive.oscarjournals.springer.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s13662-017-10856?site=advancesindifferenceequations.springeropen.com.previewlive.oscarjournals.springer.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.10.014 - 21. Agarwal, N. (1953) A Propos d’unc Note de H4. Pierre Humbert, C. R. Se’ances Acad. Sci., 236, 2031-2032.
http://jnus.org/pdf/1/2014/1/1038.pdf - 22. Li, Y. and Zhao, W. (2010) Haar Wavelets Operational Matrix of Fractional Order Integration and Its Applications in Solving the Fractional Order Differential Equations. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 216, 2276-2285.
http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2641414
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2010.03.063 - 23. Khader, M.M. and Hendy, A.S. (2012) The Approximate and Exact Solutions of the Fractional-Order Delay Differential Equations Using Legendre Pseudo Spectral Method. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 74, 287-297.
http://www.ijpam.eu/contents/2012-74-3/1/1.pdf - 24. Sweilam, N.H. and Khader, M.M. (2010) A Chebyshev Pseudo-Spectral Method for Solving Fractional Integro-Differential Equations. The ANZIAM Journal, 51, 464-475.
https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/anziam-journal/article/div-classtitlea-chebyshev-pseudo-spectral-method-for-solving-fractional-order-integro-differential-equationsdiv/D54540C52DE837C74F79EDB24A32FE71
https://doi.org/10.1017/S1446181110000830 - 25. Beheshti, S., Khosravian-Arab, H. and Zare, I. (2012) Numerical Solution of Fractional Differential Equations by Using the Jacobi Polynomials. Bulletin of the Iran Mathematical Society, 39, 6461-6470.
http://bims.iranjournals.ir/article_947_b3ed3a5b2e22cf9386624a6699f3ff0d.pdf - 26. Xu, C.-L. and Guo, B.-Y. (2002) Laguerre Pseudospectral Method for Non-Linear Partial Differential Equations. Journal of Computational Mathematics-International Edition, 20, 413-428.
http://dergi.cumhuriyet.edu.tr/cumuscij/article/view/5000118841 - 27. Razzaghi, M. and Yousefi, S. (2001) Legendre Wavelets Method for the Solution of Nonlinear Problems in the Calculus of Variations. Mathematical and Computing Modelling, 34, 45-54.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895717701000486 - 28. Khader, M.M. (2012) Introducing an Efficient Modification of the Homotopy Perturbation Method by Using Chebyshev Polynomials. Arab Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 18, 61-71.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S131951661100051X
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajmsc.2011.09.001 - 29. Khader, M.M., Sweilam, N.H. and Mahdy, A.M.S. (2011) An Efficient Numerical Method for Solving the Fractional Diffusion Equation. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Bioinformatics, 1, 1-12.
http://www.scienpress.com/upload/JAMB/Vol%201_2_1.pdf - 30. Hussaini, M.Y. and Zang, T.A. (1987) Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 19, 339-367.
http://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.fl.19.010187.002011
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fl.19.010187.002011 - 31. Funaro, D. (1992) Polynomial Approximation of Differential Equations. Springer Verlag, New York, 8.
http://www.springer.com/gb/book/9783662138786 - 32. Khader, M.M., El Danaf, T.S. and Hendy, A.S. (2012) Efficient Spectral Collocation Method for Solving Multi-Term Fractional Differential Equations Based on the Generalized Laguerre Polynomials. Fractional Calculus Application, 3, 1-14.
http://naturalspublishing.net/files/published/vk2130l11wp11o.pdf - 33. Khader, M.M. (2011) On the Numerical Solutions for the Fractional Diffusion Equation. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulations, 16, 2535-2542.
http://www.ijpam.eu/contents/2013-84-4/1/1.pdf - 34. Doha, E.H., Bahrawy, A.H. and Ezz-Eldien, S.S. (2011) Efficient Chebyshev Spectral Methods for Solving Multi-Term Fractional Orders Differential Equations. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 35, 5662-5672.
http://naturalspublishing.net/files/published/vk2130l11wp11o.pdf
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2011.05.011 - 35. Dalir, M. and Bashour, M. (2010) Applications of Fractional Calculus. Applied Mathematical Sciences, 4, 1021-1032.
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/b9f3/cebf62c66c7bc06eab009aa1d60d70a19312.pdf - 36. Schneider, K., Kevlahan, N.K.R. and Farge, M. (1997) Comparison of an Adaptive Wavelet Method and Nonlinearly Filtered Pseudospectral Methods for Two-Dimensional Turbulence. Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics, 9, 919-206.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s001620050040 - 37. Erdelyi, A. (1955) Higher Transcendental Functions, McGrawHill, New York.
http://apps.nrbook.com/bateman/Vol3.pdf - 38. Bagley, R.L. and Torvik, P.J. (1983) Fractional Calculus—A Different Approach to the Analysis of Viscoelastically Damped Structures. AIAA Journal, 21, 741-748.
https://arc.aiaa.org/doi/abs/10.2514/3.8142
https://doi.org/10.2514/3.8142 - 39. Podlubny, I. (1999) Fractional Differential Equations, vol. 198 of Mathematics in Science and Engineering, Academic Press, San Diego.
http://www.sciepub.com/reference/3051 - 40. Bagley, R.L. and Torvik, P.J. (1984) On the Appearance of the Fractional Derivative in the Behavior of Real Materials. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 51, 294-298.
http://appliedmechanics.asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/article.aspx?articleid=1407517
https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3167615 - 41. Zahoor, M.A., Khan Raja, J.A. and Qureshi, I.M. (2010) Heuristic Computational Approach Using Swarm Intelligence in Solving Fractional Differential Equations. Proceedings of the 12th Annual Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, Portland, 2023-2026.
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2012/721867/ref/ - 42. Ray, S.S. and Bera, R.K. (2005) Analytical Solution of the Bagley Torvik Equation by Adomian Decomposition Method. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 168, 398-410.
http://www.ijpam.eu/contents/2016-110-2/3/ - 43. Zahoor, R.M.A., Khan, J.A. and Qureshi, I.M. (2009) Evolutionary Computation Technique for Solving Riccati Differential Equation of Arbitrary Order. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 58, 531-536.
https://scholar.google.com.pk/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=z9xwIcMAAAAJ&citation_for_view=z9xwIcMAAAAJ:WF5omc3nYNoC - 44. Raja, M.A.Z., Khan, J.A. and Qureshi, I.M. (2010) Evolutionary Computational Intelligence in Solving the Fractional Differential Equations. Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems, Hue City, 24-26 March 2010, 231-240.
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-12145-6_24
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12145-6_24 - 45. Bojdi, Z.K., Ahmadi-Asland, S. and Aminataei, A. (2013) Operational Matrices with Respect to Hermite Polynomials and Their Applications in Solving Linear Differential Equations with Variable Coefficients. Journal of Linear and Topological Algebra, 2, 91-103.
https://doaj.org/toc/2345-5934