Advances in Infectious Diseases Vol.05 No.01(2015), Article ID:54208,15
pages
10.4236/aid.2015.51003
Temporal Model for Dengue Disease with Treatment
Laurencia Ndelamo Massawe1*, Estomih S. Massawe1, Oluwole D. Makinde2
1Mathematics Department, University of Dar es Salaam, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
2Faculty of Military Science, Stellenbosch University, Saldanha, South Africa
Email: *lndelamo@yahoo.com, estomihmassawe@yahoo.com, dmakinde@yahoo.com
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 24 January 2015; accepted 15 February 2015; published 25 February 2015
ABSTRACT
This paper examines the effect of treatment of Dengue fever disease. A non linear
mathematical model for the problem is proposed and analysed quantitatively using
the stability theory of the differential equations. The results show that the disease-free
equilibrium point is locally andglobally asymptotically stable if the reproduction
number
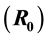 is less than unity. The additive compound matrices approach is used to show that
the dengue fever model’s endemic equilibrium point is locally asymptotically stable
when trace, determinant and determinant of second additive compound matrix of the
Jacobian matrix are all negative. However, treatment will have a control of dengue
fever disease. Numerical simulation of the model is implemented to investigate the
sensitivity of certain key parameters on the dengue fever disease with treatment.
is less than unity. The additive compound matrices approach is used to show that
the dengue fever model’s endemic equilibrium point is locally asymptotically stable
when trace, determinant and determinant of second additive compound matrix of the
Jacobian matrix are all negative. However, treatment will have a control of dengue
fever disease. Numerical simulation of the model is implemented to investigate the
sensitivity of certain key parameters on the dengue fever disease with treatment.
Keywords:
Dengue Fever Disease, Treatment of Dengue Fever Disease, Equilibrium Stability, Reproduction Number, Sensitivity Index

1. Introduction
Dengue is a vector borne disease transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected
female Aedes mosquito [1] . Dengue fever (DF) also known as break-born fever is
a mosquito born infection that causes a severe flu-like illness, caused by any one
of the four closed related dengue viruses transmitted by female mosquitoes, i.e.
DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3 and DEN-4. The first recognized Dengue epidemics occurred almost
simultaneously in Asia, Africa, and North America in the 1780s, shortly after the
identification and naming of the disease in 1779. It has spread especially in the
tropical and sub tropical regions around the world, and nowadays is a disease widely
found in urban and semi-urban areas, ([2] ). Mathematical modelling is the interesting
tool for understanding epidemiological diseases and for proposing effective strategies
to fight them ([3] ). The mathematical model of dengue transmission is a multi-population
model that captures the transmission dynamics between host (human) and vector (mosquito)
taking into account the four strains of dengue virus and the cross infections. Various
models have been proposed to study factors on the transmission dynamics and control
the spread of dengue fever disease ([2] -[10] , studied a dengue model by evaluating
and analysing the sensitivity indices of the reproduction number
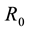 in order to determine the relative importance of the model parameters in the disease
transmission. So far no one considered a dynamical system that incorporates the
effects of treatment in dengue fever disease model. In this paper, it is therefore
intended to analyse a model which will include treatment. Thus, we study and analyse
a non linear mathematical model showing the effect of treatment on the transmission
of dengue fever disease in the population.
in order to determine the relative importance of the model parameters in the disease
transmission. So far no one considered a dynamical system that incorporates the
effects of treatment in dengue fever disease model. In this paper, it is therefore
intended to analyse a model which will include treatment. Thus, we study and analyse
a non linear mathematical model showing the effect of treatment on the transmission
of dengue fever disease in the population.
2. Model Formulation
A non linear mathematical model is formulated and analysed showing the effect of
treatment of Dengue fever disease. The basic reproduction number and stability of
equilibrium points are analysed qualitatively. Sensitivity analysis of parameters
and numerical simulations are performed. The total human population at any time
t will be denoted by
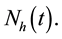 The total population is subdivided into four sub-populations namely; Susceptibles
The total population is subdivided into four sub-populations namely; Susceptibles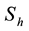 , Infectives
, Infectives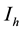 , Treated
, Treated
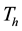 and Resistant
and Resistant .
.
Thus
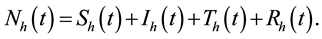
where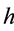 ―represent
human population.
―represent
human population.
There are three other state variables, related to the female mosquitoes, indexed
by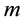 :
:
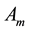 ―Aquatic phase
(that includes the egg, larva and pupa stages);
―Aquatic phase
(that includes the egg, larva and pupa stages);
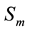 ―Susceptibles
(mosquitoes that are able to contract the disease);
―Susceptibles
(mosquitoes that are able to contract the disease);
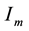 ―Infectives
(mosquitoes capable of transmitting the disease to human).
―Infectives
(mosquitoes capable of transmitting the disease to human).
In formulating the model, the following assumptions are considered:
i) Total human population
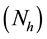 is constant at any time t, i.e.
is constant at any time t, i.e.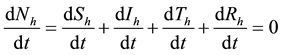 ,
,
ii) The population is homogeneous, which means that every individual of a compartment is homogeneously mixed with the other individuals,
iii) Immigration and emigration are not considered,
iv) Each vector has an equal probability to bite any host,
v) Humans and mosquitoes are assumed to be born susceptible i.e. there is no natural protection,
vi) The coefficient of transmission of the disease is fixed and does not vary seasonally,
vii) For the mosquito there is no resistant phase, due to its short lifetime, ([10] ).
Considering the above assumptions, we then have the following
Schematic model flow diagram for dengue fever disease with treatment:
From Figure 1 flow diagram, the model will be governed by the following equations:
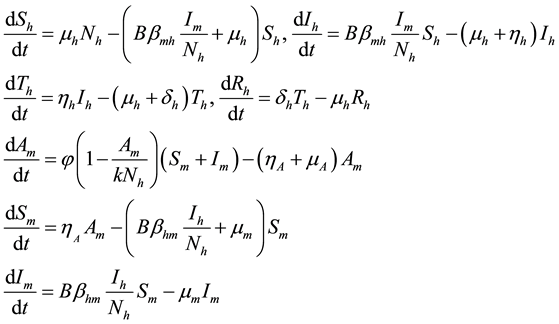 (1)
(1)
where
Figure 1. Model flow diagram for dengue fever disease with treatment.








3. Model Analysis
The model system of Equation (1) will be analysed qualitatively to get a better
understanding of the effects of treatment of Dengue fever disease. The basic Reproduction
number

3.1. Disease Free Equilibrium (DFE)
For the disease free equilibrium, it is assumed that there is no infection for both
populations of human and mosquitoes i.e.





3.2. The Basic Reproduction Number, “R0”
The basic reproduction number, denoted by
The basic reproduction number of the model (1)


where,





Using the linearization method, the associated matrix at DFE is given by
This implies that
With

or
The transfer of individuals out of the compartment

Using the linearization method, the associated matrix at DFE is given by
This gives

Therefore

The eigenvalues of the Equation (3) are given by
This gives
It follows that the Reproductive number which is given by the largest eigenvalue
for model system (1) with treatment denoted by


where
If


3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Model Parameters
In order to determine how best human mortality due to dengue fever is reduced, we
calculate the sensitivity indices of the reproduction number


Definition 1: The normalized forward sensitivity index of “


As we have an explicit formula for



























The parameters are ordered from most sensitive to the least.
Interpretation of Sensitivity Indices
From Table 1 generally it shows that the parameters











But individually, the most sensitive parameter is the average daily biting (per
day)











3.4. Local Stability of Disease Free Equilibrium Point
To determine the local stability of the disease free equilibrium, the variation
matrix



where
Therefore the stability of the disease free equilibrium point can be clarified by
studying the behaviour of


Table 1. Sensitivity Indices
of model parameters to
when

The other eigenvalues are given as
when

when

when

Hence under certain conditions the system is stable since all the seven eigenvalues
are negative. These imply that at

3.5. Global Stability of Disease Free Equilibrium Point
In this subsection, we analyse the global behaviour of the equilibria for system
(1). The following theorem provides the global property of the disease free equilibrium

Theorem 1: If

Proof:
To establish the global stability of the disease-free equilibrium, we construct the following Lyapunov function:

Calculating the time derivative of

Then substituting


where
It follows that
or
which is equivalent to
But
or

Substituting (9) into (8) yields
Therefore
Thus,









3.6. Existence and Local Asymptotic Stability of Endemic Equilibrium
Since we are dealing with presence of dengue fever disease in human population,
we can reduce system (1) to a 3-dimensional system by eliminating







The endemic equilibrium of the system (10) is given by




3.6.1. Existence of Endemic Equilibrium
For the existence and uniqueness of endemic equilibrium





Adding Equations (11)-(13) above, we have
or
But from (13) above
It follows that
or
Consequently
Then
This imply that
and
meaning that
Thus, the endemicity of the disease exists since



3.6.2. Local Stability of the Endemic Equilibrium
In order to analyse the stability of the endemic equilibrium, the additive compound matrices approach is used, using the idea of ([16] ).
If






Local stability of the endemic equilibrium point is determined by the variational
matrix



The following lemma was stated and proved by [17] , to demonstrate the local stability
of endemic equilibrium point
Lemma 1: Let






Using the above Lemma, we will study the stability of the endemic equilibrium.
Theorem 2: If



Proof:
From the Jacobian matrix

Thus,
Using Mathematica software, we get
Hence trace and determinant of the Jacobian matrix

The second additive compound matrix is obtained from the following lemma.
Lemma 2: Let









Proof:
The sub matrix of

The sub matrix of


The coefficient of





Other entries were done following the same method and to obtain
Thus
Using Mathematica software, we get
Therefore
Thus, from the lemma 1, the endemic equilibrium


4. Numerical Simulations
Here, we illustrate the analytical results of the study by carrying out numerical simulations of the model system (1) using the set of estimated parameter values given as shown below.

Figure 2 shows that the proportion of Dengue fever disease infectives, treated and recovery proportion of Dengue fever disease all plotted against the proportion of susceptible population. This shows the dynamic behaviour of the endemic equilibrium of the model system (1) using the parameter values in (18) for different initial
Figure 2. Variation of proportion of Dengue fever disease infective population, treated population and recovery population of Dengue fever disease against proportion of susceptibles population.
starting values in three cases as shown below [12] .
The equilibrium point of the endemic equilibrium

It is observed from Figure 2 that for any starting
initial value, the solution curves tend to the equilibrium

Figures 3(a)-(d) show the variation of population in different classes, human susceptibles,
treated human infective, dengue fever patient for different values of

From Figure 3(a), it is observed that proportion of susceptible human population decreases in time slightly before reaching its equilibrium position due to treatment. Therefore, infection becomes less endemic in the pop-




Figure 3. Distribution of population with time in all classes of human and mosquito, Variation of proportion of dengue fever disease infected population ,treated human population and Dengue Fever Patient for different values of (b) (average daily biting (per day)).
ulation. The proportion of Dengue fever disease infectives decreases in time then reaches equilibrium due to the increase in the number of population getting treatment. Moreover treated infectives increase and then decrease due to infected population moving to other classes, and then also recovery population increases in time as more population are treated. Furthermore infected mosquitoes decrease when the recovery population increases. Mosquito susceptible and aquatics increase with time and reaches its equilibrium point due to its short life span.
From Figure 3(b), it is observed that there is
increase in population of dengue fever disease infectives as the value of

From Figure 3(c), it is seen that when biting rate increases, the proportional of treated infectives increases and reaches its equilibrium point.
From Figure 3(d), it is observed that when biting rate increase, the proportion of Dengue fever disease increases with time. Therefore protective measures should be taken on board.
Figure 4(a) and Figure
4(b) shows the variation of proportion of dengue fever treated population
and recovery population for different values of

From Figure 4(a), it is observed that when treatment is increased, the treated proportion decreases due to treated individuals leaving the class. Moreover when there is no treatment, treated infectives increase and reaches equilibrium due to the decrease of population implying that death rate is high due to lack of treatment.
From Figure 4(b), it is observed that when there
is no treatment, i.e.


Figure 4. Variation of
proportion of dengue fever treated population and recovery population for different
values of

patients get treatment which prolongs their lives.
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Discussion
A nonlinear mathematical model has been analysed to study the effect of treatment
on the dengue fever disease. The analysis of the model shows that the disease-free
equilibrium is locally asymptotically stable by next generation method, which involves
the computation of basic reproduction number









Numerical results are provided to illustrate the analytical results. Sensitivity
analysis shows that the average daily biting (per day)



In numerical simulation it is observed that the increase of average daily biting (per day), tends to increase the number of infectious individual in the population. But the absence of average daily biting (per day), the infectious population is lowered and the disease can be eradicated. Moreover the increase of treatment will result the reduction of infected proportion as infected proportion population will move to other class, on the other hand when treatment is applied majority of infectious will be observed, as treatment will prolong the life of individual, but with no treatment infectious will be reduced because majority will die and will reach at equilibrium point. From this indicate that there is much work to be done to eradicate the disease by driving reproduction number to be less than unity. Thus the best thing to do is spraying pesticides to kill mosquitoes or sterile male mosquitoes as biological control.
5.2. Conclusion
A compartmental model for Dengue fever disease was presented, a model based on two populations, humans and mosquitoes with treatment. Simulation shows that on the application of treatment, the number of death is reduced. It has been proved algebraically that, if a constant minimum level of a treatment is applied, it is possible to maintain the basic reproduction number below unity, and the infected humans were smaller.
References
- Semenza, J.C. and Menne, B.B. (2009) Climate Change and Infectious Diseases in Europe. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 9, 365-375. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70104-5
- Rodrigues, H.S., Monteiro, M.T.T., Torres, D.F.M and Zinober, A. (2011) Dengue Disease, Basic Reproduction Number and Control. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, 1-13.
- Lenhart, S. and Workman, J.T. (2007) Optimal Control Applied to Biological Models. Chapman& Hall/CRC Mathematical and Computational Biology Series, Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton.
- Chikaki, E. and Ishikawa, H. (2009) A Dengue Transmission Model in Thailand Considering Sequential Infections with All Four Serotypes. J Infect Devctries, 3, 711-722.
- Thome, R.C., Yang, H.M. and Esteva, L. (2010) Optimal Control of Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes by the Sterile Insect Technique and Insecticide. Mathematical Biosciences, 223, 12-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mbs.2009.08.009
- Rodrigues, H.S., Monteiro, M.T.T. and Torres, D.F.M. (2010) Insecticide Control in a Dengue Epidemics Model. In: Simos, T., Ed., AIP Conference of Proceedings of the Numerical Analysis and Applied Mathematics, 1281, 979-982.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2011) Division of Vector Borne and Infectious Diseases, Prevention, How to Reduce Your Risk of Dengue Infection. http://www.cdc.gov/Dengue/prevention/index.html.
- Rodrigues, H.S., Monteiro, M.T.T. and Torres, D.F.M. (2012) Modeling and Optimal Control Applied to a Vector Borne Disease. International Conference on Computational and Mathematical Methods in Science and Engineering, CMMSE, 2012, 1063-1070.
- Rodrigues, H.S., Monteiro, M.T.T. and Torres, D.F.M. (2013) Bioeconomic Perspectives to an Optimal Control Dengue Model. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, 2013.
- Rodrigues, H.S., Monteiro, M.T.T. and Torres, D.F.M. (2013) Sensitivity Analysis in a Dengue Epidemiological Model. Conference Papers in Mathematics, 2013.
- van den Driessche, P. and Watmough, J. (2002) Reproduction Numbers and Sub-Threshold Endemic Equilibria for Compartmental Models of Disease Transmission. Mathematical Biosciences, 180, 29-48. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5564(02)00108-6
- Ratera, S., Massawe, E.S. and Makinde, O.D. (2012) Modelling the Effect of Screening and Treatment on Transmission of HIV/AIDS Infection in Population. American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, 2, 75-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.5923/j.ajms.20120204.03
- Ozair, M., Lashari, A.A., Jung, I.H., Seo, Y.I. and Kim, B.N. (2013) Stability Analysis of a Vector-Borne Disease with Variable Human Population. Research Article Stability, 2013, 1-12
- LaSalle, J.P. (1976) The Stability of Dynamical Systems. Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics, SIAM, Philadelphia.
- Tumwiine, J., Mugisha, J.Y.T. and Luboobi, L.S. (2007) A Mathematical Model for the Dynamics of Malaria in a Human Host and Mosquito Vector with Temporary Immunity. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 189, 1953-1965. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.12.084
- Lee, K.S. and Lashari, A.A. (2014) Global Stability of a Host-Vector Model for Pine Wilt Disease with Nonlinear Incidence Rate. Abstract and Applied Analysis, 2014, 1-11
- McCluskey, C.C. and van den Driessche, P. (2004) Global Analysis of Two Tuberculosis Models. Journal of Differential Equations, 16, 139-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:JODY.0000041283.66784.3e
NOTES
*Corresponding author.



























































