Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.05 No.08(2017), Article ID:78657,8 pages
10.4236/jamp.2017.58126
L(2,1)-Labeling of the Brick Product Graphs
Xiujun Zhang1,2, Hong Yang2, Hong Li2
1School of Information Science and Engineering, Chengdu University, Chengdu, China
2Key Laboratory of Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Information Processing, Institutions of Higher Education of Sichuan Province, Chengdu University, Chengdu, China

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: July 15, 2017; Accepted: August 19, 2017; Published: August 23, 2017
ABSTRACT
A k-L(2,1)-labeling for a graph G is a function 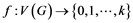 such that
such that  whenever
whenever 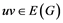 and
and 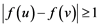 when- ever u and v are at distance two apart. The λ-number for G, denoted by
when- ever u and v are at distance two apart. The λ-number for G, denoted by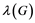 , is the minimum k over all k-L(2,1)-labelings of G. In this paper, we show that
, is the minimum k over all k-L(2,1)-labelings of G. In this paper, we show that 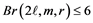 for
for 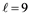 or 11, which confirms Conjecture 6.1 stated in [X. Li, V. Mak-Hau, S. Zhou, The L(2,1)-labelling problem for cubic Cayley graphs on dihedral groups, J. Comb. Optim. (2013) 25: 716-736] in the case when
or 11, which confirms Conjecture 6.1 stated in [X. Li, V. Mak-Hau, S. Zhou, The L(2,1)-labelling problem for cubic Cayley graphs on dihedral groups, J. Comb. Optim. (2013) 25: 716-736] in the case when 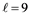 or 11. Moreover, we show that
or 11. Moreover, we show that 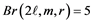 if 1) either
if 1) either 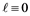 (mod 6), m is odd,
(mod 6), m is odd, 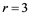 , or 2)
, or 2) 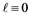 (mod 3), m is even (mod 2),
(mod 3), m is even (mod 2),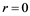 .
.
Keywords:
Graph Labeling, Brick Product Graph, L(2,1)-Labeling, Frequency Assignment Problem

1. Introduction
Let 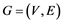 be a graph. For two vertices u and v in G, the distance between u and v is the number of the edges of the shortest path between u and v. A k-L(2,1)-labeling for a graph G is a function
be a graph. For two vertices u and v in G, the distance between u and v is the number of the edges of the shortest path between u and v. A k-L(2,1)-labeling for a graph G is a function  such that
such that 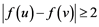 whenever
whenever 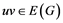 and
and  whenever u and v are at distance two apart. The λ-number for G, denoted by
whenever u and v are at distance two apart. The λ-number for G, denoted by
The L(2,1)-labeling problem was studied very extensively in the literature and has attracted much attention. Griggs and Yeh [6] proposed a conjecture, which is called the 








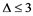



Let



















Next, for each pair 






Li et al. [10] proposed the following conjecture:
Conjecture 1. [10] 


Shao et al. [11] confirmed the above conjecture, i.e. it was proved that
Theorem 1. [11] 



Therefore, Conjecture 1 is still open for odd 

In this paper, we show that 







2. Main Results
From the definition of the brick product graph, it is clear that
Fact 1. 

2.1. Some Results on the Upper Bound 6 of l-Number
In [6] , it was shown that
Lemma 1. [6] The λ-number of any connected cubic graph is at least 5.
Proposition 1. Let


By Theorem 1, we have 



We use the pattern 





Now, we consider the case











Proposition 2. Let


Similar to Proposition 1, we only need to consider the case 
Case 1:
We use the following pattern 

















Figure 1. The 6-L(2,1)-labeling of 

Case 2:
We use the following pattern 

















From Propositions 1 and 2, we have
Theorem 2. Let


2.2. Brick Product Graphs with l-Number 5
In [10] , it was proved that
Theorem 3. Let 



Moreover, 
1) 3 divides 
2) 6 divides 
Furthermore, if neither 1) nor 2) is satisfied, then 



However, Theorem 3 consider the condition that


Theorem 4. Let




Let







Proposition 3. Let



Let


induces a 5-L(2,1)-labeling of

Proposition 4. Let



Let


Then Q induces a 5-L(2,1)-labeling of

Proposition 5. Let



Let

times. Then Q induces a 5-L(2,1)-labeling of

Proposition 6. Let

Let




By observing the results of Propositions 3 - 6, we propose the following con- jecture:
Conjecture 2. Let



Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Applied Basic Research (Key Project) of Sichuan Province under grant 2017JY0095, Key Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Education under grant 17ZA0079 and Automotive Creative Design Pilot Area of Chengdu University and Longquanyi District under grant 2015-CX00- 00010-ZF.
Cite this paper
Zhang, X.J., Yang, H. and Li, H. (2017) L(2,1)-Labeling of the Brick Product Graphs. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 5, 1529-1536. https://doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2017.58126
References
- 1. Roberts, F.S. (1988) Private Communication to J. R. Griggs.
- 2. Hale, W.K. (1980) Frequency Assignment: Theory and Applications. Annals of Operations Research, 76, 73-93.
https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1980.11899 - 3. Whittlesey, M.A., Georges, J.P. and Mauro, D.W. (1995) On the λ number of Qn and related graphs. SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 8, 499-506.
https://doi.org/10.1137/S0895480192242821 - 4. Shao, Z. and Vesel, A. (2014) L(2,1)-Labeling of the Strong Product of Paths and Cycles. The Scientific World Journal, 2014, 12.
- 5. Georges, J.P., Mauro, D.W. and Whittlesey, M.A. (1994) Relating Path Coverings to Vertex Labellings with a Condition at Distance Two. Discrete Mathematics, 135, 103-111.
- 6. Griggs, J.R. and Yeh, R.K. (1992) Labelling Graphs with a Condition at Distance Two. SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 5, 586-595.
https://doi.org/10.1137/0405048 - 7. Chang, G.J. and Kuo, D. (1996) The L(2,1)-Labeling Problem on Graphs. SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 9, 309-316.
https://doi.org/10.1137/S0895480193245339 - 8. Král', D. and Skrekovski, R. (2003) A Theorem about Channel Assignment Problem. SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 16, 426-437.
https://doi.org/10.1137/S0895480101399449 - 9. Goncalves, D. (2008) On the L( p,1)-Labelling of Graphs. Discrete Mathematics, 308, 1405-1414.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disc.2007.07.075 - 10. Li, X., Mak-Hau, V. and Zhou, S. (2013) The L(2,1)-Labelling Problem for Cubic Cayley Graphs on Dihedral Groups. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 25, 716-736.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-012-9525-4 - 11. Shao, Z., Xu, J. and Yeh, R.K. (2016) L(2,1)-Labeling for Brick Product Graphs. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 31, 447-462.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-014-9763-8








