Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 iBusiness, 2013, 5, 54-57 doi:10.4236/ib.2013.51b012 Published Online March 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ib) Copyright © 2013 SciRes. IB Empirical Study on B-S Model Based Pricing of Warran t s in China ——With Calculation of Standard Deviation by Modified EMA Model Zhaoyuan Geng, Qi Ding, Junchi Zhang Department of Applied Economics, Business School of Zhejiang University City College, Hangzhou, China. Email: gengzy@zucc.edu.cn Received 2013 ABSTRACT This article valuated theoretical prices of covered warrants in china through fitting temporal series of target warrant prices and market information of corresponding underlying securities. Furthermore, the author surveyed the deviation between market price and theo retical price of warrant. In order to eliminate the inaccuracy caused by constant volatility assumption of B-S Model, the author creatively used Modified Exponentially Moving Average (Modified EMA) Model to calculate the historical volatility of market prices of warrants and fixed the best dilutio n factor through Grid Search Technique. Also, validities o f calculatio n of historical vo latilit y by Modified EMA Mod el and original EMA Model are compared. Original data came from market information during the period 2005-2008 supported by security trading software and calculatio n was d one via Excel. At the same time when Chinese government was going to revive covered warrant market, this article provided a more accurate method of pricing covered warrant, also known as modified B-S Model. Keywords: Warrant Pricing; Covered Warrant; B-S Model; EMA Model; Grid Search Technique 1. Introduction Pricing warrant has been researched a lot in abroad, which has perfect pricing theory system and with B-S model for the main body of the effective measurement method system [1]. Black-schoals (B-S) model over- comes the limitations of the study of early scholars, pro- viding the stock options and warrants pricing methods reliably. While the study in China is still developing, lacking correction of own assumptions of B-S model. In the background that Chinese government was going to revive covered warrant market, the author creatively puts forward Mod ified Exp onentia lly Movi ng Avera ge (Mod- ified EMA) Model to measure the volatility of the asset, fixed B-S model’s constant volatility assumptions, and get the more suitable model of pricing covered warrants for China. 2. Model Constru ction The article aims to construct an accurate pricing method of covered warrant, which essentiall y is a Mo d ified Black-Scholes (Mod ified B-S) Model. The formul a of Original Black-Scholes (Original B-S) Model as shown below: 12 (,)( )() rt e CSTSNdK Nd − = − (1) 2 1 11 ln (1) 2 S dT K T σ σ = ++ (2) 21 d dTt σ =−− (3) where C(S,T): the value of European call option; S: present price of underlying assert; T: Due date of warrant; K: striking pric e of option; r: he risk-free rate of rate of the inves tment due in T; σ : the annual volatility of the price of underlying a s- sert; N(x) means cumulative probability distribution func- tion of sta nd a rd normal distribution variab le [2]. The pricing object in this article is the C hinese covered warrant, which can be seen as a typical European call option, so it is reasonable to use the original B-S Model. However, the rigo rous limitati ons attached to the original B-S Model on the financial market, underlying asserts and the characteristics of the option have affected the accuracy of the pricing to different degrees [3]. Therefore, this article is to amend this model. Apart from the Behavioral Financial, almost all the pricing models in the spin-off pricing have included the perfect market hypothesis, so the improvement in terms  Empirical Study on B-S Model Based Pricing of Warrants in China opyright © 2013 SciRes. IB 55 of the prerequisite hypothesis of the financial market is impractical. Then the solely necessary and feasible amendment lies on the prerequisite hypothesis of the underlying assert. Evidences have accumulated to show that the deviation caused by the share profits prepayment hypothesis is not significant, and furthermore the covered warrant itself does not produce the shareholding dilution effect, so the amendment of the shareholding dilution effect can be excluded. Upon this, the article has finally chosen the constant volatility rates hypothesis as the breach to amend the original B-S Model. In order to amend the constant volatility hypothesis of B-S Model, the author creatively used Modified EMA Model to calculate the volatility of yield of underlying warrants. EMA (Exponentially Moving Average) is a dynamic s ta tistic,which esse ntially is a predictive value by adding observations in the past and giving longer value a lower weightings coefficients [4]. Original EM A Model supposes the yield of underlying assert obeying Gaussian distribution—t R ~ 2 (0, )N σ , the formula as sho wn blow 2 0 () 1 R n µ σ − =− ∑ (4) 2 22 11 1 (1 )() ttt t R σλµ µσ −− − =− −+ (5) where t σ : the volatility of the t; λ : dilution factor (0< λ <1); µ : average yield rate in sample periods; 1t R−: the yield r a te in the t-1 [5]. SIAH Continuous Information Connecting Hypothesis indicates that Volatility has a positive correlation with volume. Based on this hypothesis, Rong He amended EMA Model in 2009. The formula as shown bl ow: 2 22 11 1 (1 )() t Lttt VR σ γλµµσ −− − = +−−+ (6) where γ is constant coefficient; L V is the long-period volatility of the yield rate of warrant. According to the two theory models above, the author has deduced a more accurate pricing method of covered warrant used in this article, the modified B-S Model. Using the modified EMA Model to calculate t σ , and supposing n = 60, which mea ns usi ng the sta ndar d d evia- tion 60 trading days before the opening day of the sample term as the original volatility 0 σ , one can get the final σ used in the modified B-S Model. 3. Analysis of Chinese’s Data Warrants Based on Empirical 3.1. Data’s Selec tions This evidence in the article is used in Time-series data, including Angang JTC1, Wuliang YGC1 and Yage QCB1 three Covered Warrants’ price data from the opening to the delisting and the corresponding underly- ing stock price data. In addition to warrants and the price of the underlying asset, B-S Model also requires Risk-free Interest Rate over the same period. This article uses the 7-Day Bond Repurchase Rate instead of the Risk-free Interest Rate, the data logger for details sees appendix A. 3.2. Real Diagnosis Examination 1) Determination of Attenuation factor λ . In order to determine the best attenuatio n factor value, this article uses the Grid Search Technique, λ value is 0.1, 0.5, 0.8 and 0.95 carry on the pilot calculation sepa- rately. According to the definition, the best attenuation factor must make the theoretical price and the market price cumulative departure is smallest, also namely rea- lizes { } 2 1 min () T i ii CP = ∑− , i P is the market price, i C is the theoretical price. The result compiles see Table 1: λ = 0.95 2) Modified EMA Model validity examination In order to check the Modified EMA Model’s validity, this article has compared three sign stock income fluctu- ation rate separately under the Modified EMA Model and the Original EMA Model measurement cumulative de- parture. It compiles the result to reference Tables 1 and 2: The result demonstrates, in all four pricing of warrants estimate, uses the Modified EMA Model to measure the sign stoc k income fluctuation rate forms price accumula- tion deviation is smaller than EMA Model. Obviously, the Modified EMA Model has achieved the anticipated effect, this has a lso guara nteed this article validit y, which revises to the Modified B-S Model. Table 1. Modified EMA Model accumulation price devia- tion tabl e. λ =0.1 λ =0.5 λ =0.8 λ =0.95 Angang JTC 1 97.942 95.965 95.985 95.013* Wulian g YGC1 1595.977 1596.124 1595.823 1595.299* Yage QCB1 362.917 350.266 344.466 327.194* Note: *is the accumulation deviation the most minor term. Table 2 . Ori ginal EM A Model accumulati on price devi ation table. λ =0.1 λ =0.5 λ =0.8 λ =0.95 Angang JTC 1 369.924* 370.948 372.923 375.016 Wulian g YGC1 1791.567 1796.074 1784.153* 1809.885 Yage QCB1 553.957* 576.433 603.248 625.416 Note: *is the accumulation deviation the most minor term. 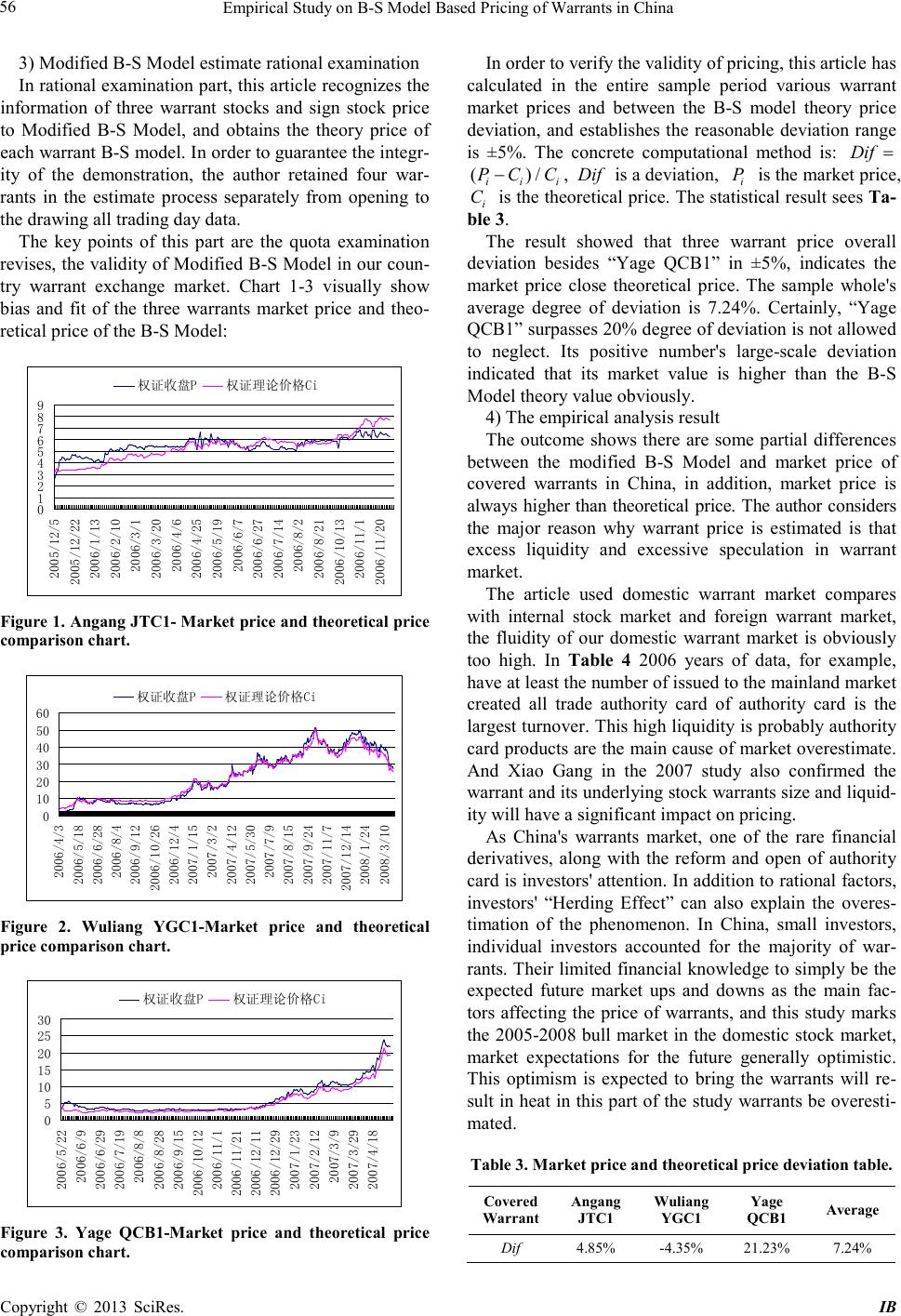 Empirical Study on B-S Model Based Pricing of Warrants in China Copyright © 2013 SciRes. IB 56 3) Modified B-S Model estimate rational examination In rational e xamination part, t his article rec ognizes the information of three warrant stocks and sign stock price to Modified B-S Model, and obtains the theory price of each warrant B-S model. In or de r to guar a nt ee t he integr- ity of the demonstration, the author retained four war- rants in the estimate process separately from opening to the drawing all trading day data. The key points of this part are the quota examination revises, the valid ity of Modified B-S Model in our coun- try warrant exchange market. Chart 1-3 visually show bias and fit of the three warrants market price and theo- retical price of the B-S Model: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2005/12/5 2005/12/22 2006/1/13 2006/2/10 2006/3/1 2006/3/20 2006/4/6 2006/4/25 2006/5/19 2006/6/7 2006/6/27 2006/7/14 2006/8/2 2006/8/21 2006/10/13 2006/11/1 2006/11/20 权证收盘P 权证理论价格Ci Figure 1 . Angang JTC1- M arket price an d theoretical pri ce comparison chart. 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 2006/4/3 2006/5/18 2006/6/28 2006/8/4 2006/9/12 2006/10/26 2006/12/4 2007/1/15 2007/3/2 2007/4/12 2007/5/30 2007/7/9 2007/8/15 2007/9/24 2007/11/7 2007/12/14 2008/1/24 2008/3/10 权证收盘P 权证理论价格Ci Figure 2. Wuliang YGC1-Market price and theoretical price compa rison cha rt . 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 2006/5/22 2006/6/9 2006/6/29 2006/7/19 2006/8/8 2006/8/28 2006/9/15 2006/10/12 2006/11/1 2006/11/21 2006/12/11 2006/12/29 2007/1/23 2007/2/12 2007/3/9 2007/3/29 2007/4/18 权证收盘P 权证理论价格Ci Figure 3. Yage QCB1-Market price and theoretical price comparison chart. In order to verify the validity of pricing, t his article has calculated in the entire sample period various warrant market prices and between the B-S model theory price deviation, and establishes the reasonable deviation range is ±5%. The concrete computational method is: Dif = ( )/ ii i PC C− , Dif is a deviation, i P is the market price, i C is the theoretica l price. T he statistical resul t sees Ta- ble 3. The result showed that three warrant price overall deviation besides “Yage QCB1” in ±5%, indicates the market price close theoretical price. The sample whole's average degree of deviation is 7.24%. Certainly, “Yage QCB1” surpasses 20% degree of deviation is not allo wed to neglect. Its positive number's large-scale deviation indicated that its market value is higher than the B-S Model theory value obviously. 4) The empirical analysis result The outcome shows there are some partial differences between the modified B-S Model and market price of covered warrants in China, in addition, market price is alwa ys higher than theoretical price. The author considers the major reason why warrant price is estimated is that excess liquidity and excessive speculation in warrant market. The article used domestic warrant market compares with internal stock market and foreign warrant market, the fluidity of our domestic warrant market is obviously too high. In Table 4 2006 years of data, for example, have at le ast the number of i s sued to the mainl and market created all trade authority card of authority card is the largest t urno ver. T his high liquidity is pr obably author ity card products are the main cause of market overestimate. And Xiao Gang in the 2007 study also confirmed the warra nt and its u nd er l yi ng s to ck war r ants s ize and l iquid- ity will have a significant impact on p ricing. As China's warrants market, one of the rare financial derivatives, along with the reform and open of authority card is investors ' attention. I n addition to rational facto rs, investors' “Herding Effect” can also explain the overes- timation of the phenomenon. In China, small investors, individual investors accounted for the majority of war- rants. Their limited financial kno wledge to simply be the expected future market ups and downs as the main fac- tors affecting the price of warrants, and this study marks the 2005-2008 bull market in the do mestic stock market, market expectations for the future generally optimistic. This optimism is expected to bring the warrants will re- sult in heat in this part of the study warrants be overesti- mated. Table 3. M arket price and theoretical price deviatio n table. Covered Warrant Angang JTC1 Wuliang YGC1 Yage QCB1 Average Dif 4.85% -4.35% 21.23% 7.24% 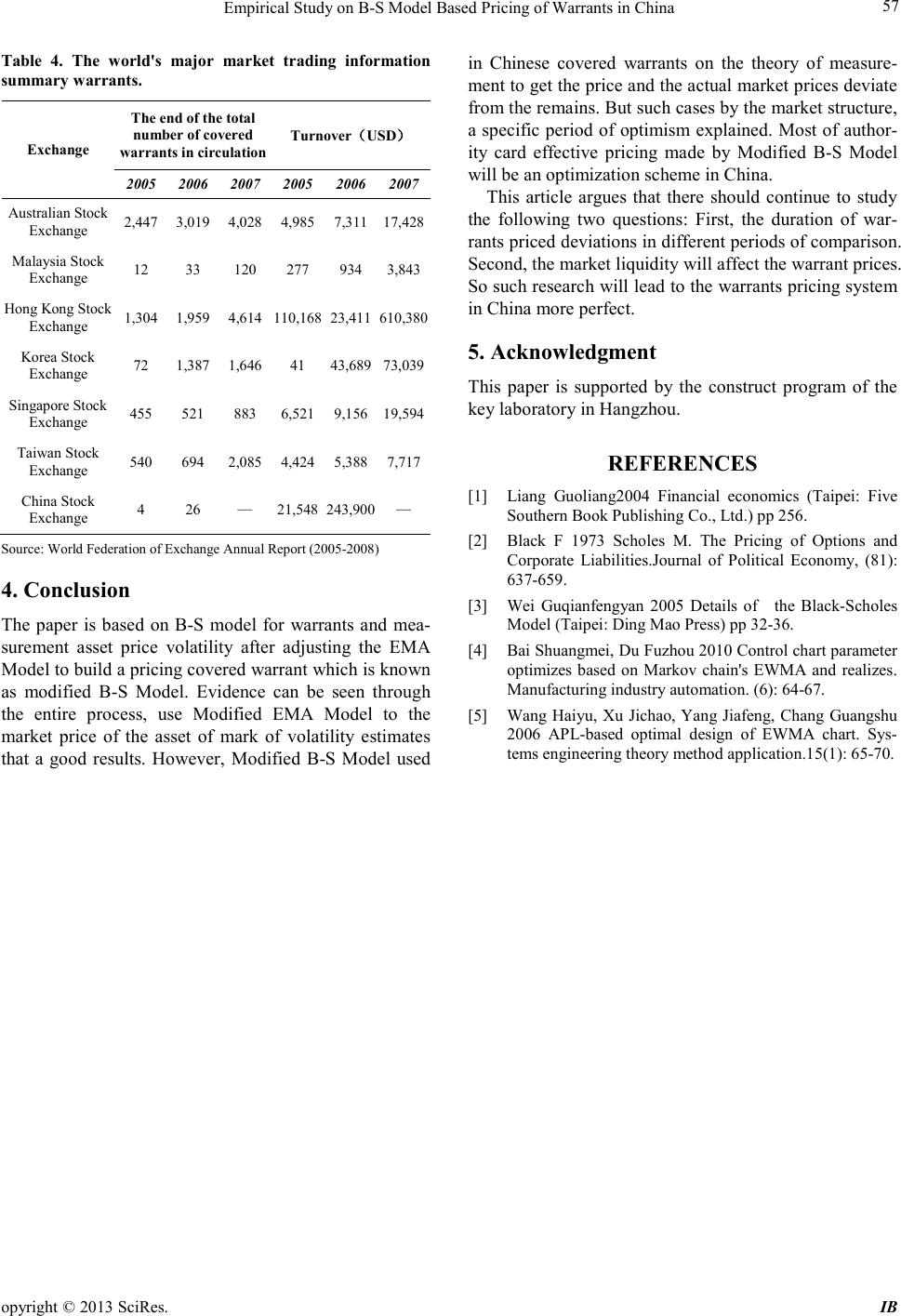 Empirical Study on B-S Model Based Pricing of Warrants in China opyright © 2013 SciRes. IB 57 Table 4. The world's major market trading information summary warrants. Exchange The end of the total num ber of covered warrants in circulat ion Turnover ( USD ) 2005 2006 2007 2005 2006 2007 Australian Stock Exchange 2,447 3,019 4,028 4,985 7,311 17,428 Malaysia Stock Exchange 12 33 120 277 934 3,843 Hong Kong Stock Exchange 1,304 1,959 4,614 110,168 23,411 610,380 Korea Stock Exchange 72 1,387 1,646 41 43,689 73,039 Singapore Stoc k Exchange 455 521 883 6,521 9,156 19,594 Taiwan Stock Exchange 540 694 2,085 4,424 5,388 7,717 China S tock Exchange 4 26 — 21,548 243,900 — Source: World Federation of Exchange Annual Report (2005-2008) 4. Conclusion The paper is based on B-S model for warrants and mea- surement asset price volatility after adjust ing the EMA Model to build a pricing covered warrant which is k nown as modified B-S Model. Evidence can be seen through the entire process, use Modified EMA Model to the market price of the asset of mark of volatility estimates that a good results. However, Modified B-S Model used in Chinese covered warrants on the theory of measure- ment to get the price and the actual market prices deviate fr om the r emain s. But s uch case s b y t he ma rke t struc tur e, a specific period of optimism explained. Most of aut hor- ity card effective pricing made by Modified B-S Model will be an optimization sc heme in China. This article argues that there should continue to study the following two questions: First, the duration of war- rants priced deviations in different periods of comparison. Second, the market liquidity will affect the warra nt prices. So such resear ch will lead to the warrants pricin g system in China more perfect. 5. Acknowledgment This paper is supported by the construct program of the key laborator y in Hangzhou. REFERENCES [1] Liang Guoliang2004 Financial economics (Taipei: Five Southern Book Publishing Co., Ltd.) pp 256. [2] Black F 1973 Scholes M. The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities.Journal of Political Economy, (81): 637-659. [3] Wei Guqianfengyan 2005 Details of the Black-Scholes Model (Taipei: Ding Mao Press ) pp 32-36. [4] Bai Shuangmei, Du Fuzhou 2010 Contr ol char t p arameter optimizes based on Markov chain's EWMA and realizes. Manufacturing industry automation. (6): 64-67. [5] Wang Haiyu, Xu Jichao, Yang Jiafeng, Chang Guangshu 2006 APL-based optimal design of EWMA chart. Sys- tems engineering theory method application.15(1): 65-70. |

