Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 Creative Education 2012. Vol.3, Supplement, 126-129 Published Online December 2012 in SciRes (http://www.SciRP.org/journal/ce) DOI:10.4236/ce.2012.37B033 Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 126 Conflict Balanced Design for the Evaluation System of University Research Achievements Hongzhuan Chen, Liangliang Shu College of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing China Email: Chz-hhu@163.com, shuliangliang@163.com Received 2012 Scientific research evaluation has an important guiding significance to university scientific research work. Based on conflict analysis model, it studies the strategies and preferences among the government, univer- sities and scientists in the scientific research evaluation mechanism. It builds a conflict analysis model of three players and gives all possible equilibrium situations. The paper also analyzes the characteristics analysis of each equilibrium situation, it finds out the Pareto optimal situation of scientific research eval- uation. The article provides guidance for the establishment of the evaluation system of university re- search. Keywords: Scientific Research Eval uat i on; Confict; Equilibrium Introduction In our country, the group of researchers such as teachers in many research universities is one of the important subjects to undertake development and research of the social academy. Therefore, academy naturally becomes a key factor and the core of the university. Academic evaluation is the judgment and affirmation of the intrinsic value of the academic achievements. For universities, it is the wind vane of academic development direction. It directly determines the value orientation and working key for researchers. With the increase of researchers and institutions, our country invests huge amounts of money for scientific research every year. However, it is hard to evaluate the academic level and quality of scientific research (Wei Zhang, 2007), as we investing huge scientific research funds. In the universities of our country, a large number of scientific and technological achievements pass the assessment every year. However, the achievements of scientific research which meet the needs of the community and can be translated into pract ical productive forces and products are insufficienct. To sum up, through continuous reform, the evaluation index system, means and ways of scientific research achievement obtained compre- hensive progress than before, starting from the system envi- ronment to specific systems and measures, and even legal pro- tection, the implementation process, being more comprehensive, systemic. These methods provide the basis and norms for us to make some evaluation. They also provide a platform for the evaluation of academy achievements (Yuqing Ceng, 2006). During the process university research evaluation system, there are varying degrees of judgment and understanding of conflicts among various interest groups in some aspects such as the qual- ity of the research results, quantity and efficiency. It is difficult to meet the requirement of suitability, fairness, impartiality in the evaluation system of university research achievements. It affects the stability and development of scientific research in universities (Ying Zhou, 2003). To resolve conflict, ensuring the overall interests and long-term stability of universities, we use the conflict analysis theory to analyze the conflict in the university research evaluation system and its stability to pro- vide a useful reference for the evaluation system of university research. Theory of Conflict Analysis Conflict analysis is a conflict analysis strategy presented by Fraser and Hipel in 1980s. It is a decision analysis method which focuses on solving social disputes. Conflict analysis aims to coordinate the contradiction of each participant in the con- flict and put forward finally expedient solution. Conflict analy- sis model can be abbreviated as: G = {N, Q, V, UI}. N is the player, namely the conflict subject. Q is all possible situations set under the current conflict model. They are represented by 0-1 sequence and changed a binary number which corresponded by each situation into a decimal. V is the order set which represented player’s preference to feasible situation. It is the optimal vector. UI is the set of unilateral improvements for all the players on their respective preference order of each element. The process of conflict analysis method is formed by two components modeling and stability analysis. Its processes are as follows: Conflict analysis method starts from the analysis of the situa- tion’s stability. For a conflict situation, we need to consider whether multiple players in a pass to leave the current scheme can achieve better situation; Whether the last project cooperat- ing with other players and partners to benefit is worth; How will the other players face the council of human movement and anti-movement in the conflict; All above information will be examined as the results of a conflict. Establishing of the Conflict Model Conflict Players The evaluation system of university scientific research achievement contains two kinds of stakeholders, universities and researchers. However, the government also playes a great role in China’s current of university research evaluation syst em  H. Z. CHEN, L. L. SHU Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 127 guided by the government. The relationship among these three game subjects shown in Figure 2. It can be seen from Figure 2, the government research de- partment’s encouragement to the researchers is a strong incen- tive, and the university’s encouragement to the researchers is a weak incentive. This double game equilibrium is favorable for the dedication and diligence of researchers. It is necessary for the government research department reforms the current re- search project funding management system and achievements assessment system, in order to mobilize the enthusiasm of the researchers and stimulate the creativity of researchers. There- fore, in the conflict model of university research evaluation system, there are three major decision makers, namely, re- searcher, university and government. Strategy of Playerss The current studies of college scientific research achieve- ment evaluation are mainly focused on the importance of qual- ity and quantity in college scientific achievements evaluation. The results of these studies are mainly embodied in the scien- tific research achievement evaluation index system, as well as the qualitative evaluation and quantitative evaluation of re- search. Quite a few scholars advocate that the evaluation of university scientific research achievement should emphasize on quality of the achievement, and support qualitative evaluation. Qualitative evaluation seems to be more close to the characte- ristics of evaluation objects, and can reveal the value scientific research achievements better. The evaluation based on univer- sity scientific research achievement evaluation criteria seems to put emphasize on both the output of scientific research activi- ties and its quality superficially. In fact the evaluation of scien- tific research achievements biases the pursuit of quantity, and ignore the quality. It makes scientific research activities more and more away from its own laws, which pushes academic morality level falling, and academic value depreciated causing certain impact on teaching level in universities. However, the humanities and social sciences can't provide the identification methods as clear as natural science. Even in the presence of social effect, it is difficult to use digital display. Along with the reform of evaluation system of scientific research, a simple method of quantification evaluation attracts considerable atten- tion. As Deng Yi said in "Analysis of the university research quantitive evaluation" that academic quantization is not only possible but also necessary. The fundamental purpose of aca- demic quantization is not a ' final judgment' of the academic research ability of an individual or a group, but an opportunity for potential researchers standing out (Yi Deng, 2006). Quantit- ative evaluation method has great practical value because it is flexible, objective, easy to be operated and it can get an objec- tive outcome based on the statistics, metrology ,the given pa- rameters and other software, The index system of university scientific research achieve- ment evaluation is a wind vane for wind researchers in univer- sities (Junping Qiu, 2007). The operability of qualitative evalu- ation is not strong, and the subjectivity is outstanding. Although the quantity is important, the quality is more important. The quality can easily be ignored once the quantity is pushed to the top position. As the objective data cannot reflect the abstraction of scientific research, quantitative evaluation cannot guarantee that the data is effective to scientific research evaluation. In order to compensate evaluation problems, appropriate quantita- tive indicators should be introduced in the index system scien- tific research achievement evaluation. It plays a role of supple- ment and supervision in qualitative evaluation, so that the ef- fectiveness of the scientific research evaluation index system can be improved and perfected. In addition, the economic benefit of scientific research is an important indicator of universities and its research outcome. At present, university scientific research evaluation system focus on the pursuit of academic benefit, pays little attention to the actual benefit, especially the transformation from intellectual property to economic achievements. With the further develop- ment of economy, science and technology system reform, con- sidering the economic benefit of scientific research when de- signing the evaluation system of college scientific research achievemenst is not only beneficial to the improvement of scientific research management, but also conducive to the ac- celeration of the popularization and application of research results, promoting the rapid transformation into enormous ma- terial strength, which can improve the scientific research work efficiency. Therefore, the conflict strategies of the three main decision makers are respectively: Researcher: A-- focus on the quality of scientific research; B-- focus on the quantity of scientific research ; C--focus on the social benefits of scientific research. Researcher 1 Researcher n Government adjustment whe n the equilibrium is non-existent Nash balance Core solution University University Researcher 1 Researcher 1 University 1 University 1 Government Government Government adjustment whe n the equilibrium is non-existent Figure 2. The game rel at ionship among st akeholders in uni versity research evaluation system. 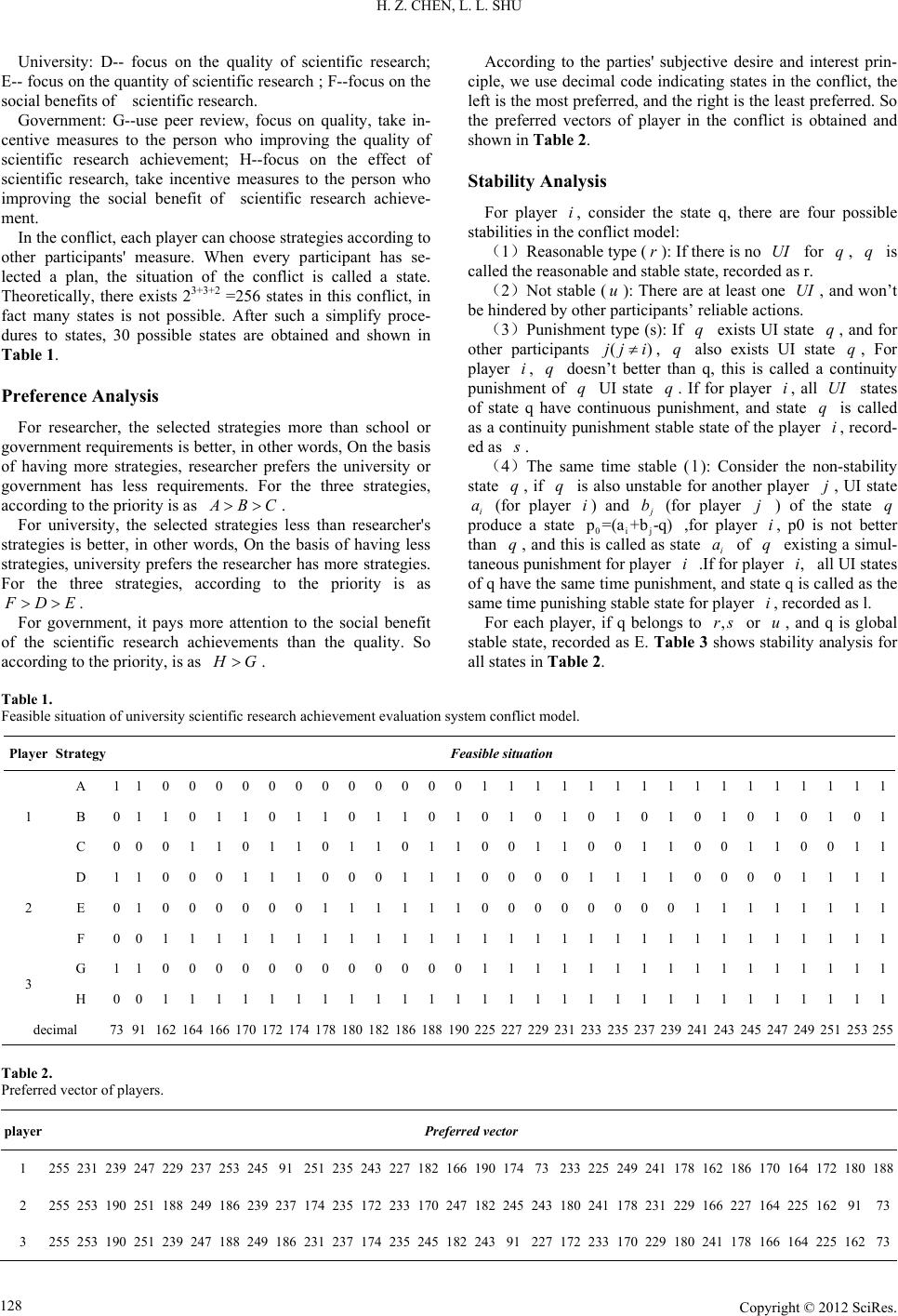 H. Z. CHEN, L. L. SHU Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 128 University: D-- focus on the quality of scientific research; E-- foc us on the quantity of scientific research ; F--focus on the social benefits of scientific research. Government: G--use peer review, focus on quality, take in- centive measures to the person who improving the quality of scientific research achievement; H--focus on the effect of scientific research, take incentive measures to the person who improving the social benefit of scientific research achieve- ment. In the conflict, each player can choose strategies according to other participants' measure. When every participant has se- lected a plan, the situation of the conflict is called a state. Theoretically, there exists 23+3+2 =256 states in this conflict, in fact many states is not possible. After such a simplify proce- dures to states, 30 possible states are obtained and shown in Table 1. Preference Analysis For researcher, the selected strategies more than school or government requirements is better, in other words, On the basis of having more strategies, researcher prefers the university or government has less requirements. For the three strategies, according to the priority is as ABC>> . For university, the selected strategies less than researcher's strategies is better, in other words, On the basis of having less strategies, university prefers the researcher has more strategies. For the three strategies, according to the priority is as FDE>> . For government, it pays more attention to the social benefit of the scientific research achievements than the quality. So according to the priority, is as HG> . According to the parties' subjective desire and interest prin- ciple, we use decimal code indicating states in the conflict, the left is the most preferred, and the right is the least preferred. So the preferred vectors of player in the conflict is obtained and shown in Table 2. Stability Analysis For player i , consider the state q, there are four possible stabilities in the conflict model: (1)Reasonable type ( r ): If there is no UI for q , q is called the reasonable and stable state, recorded as r. (2)Not stable ( u ): There are at least one UI , and won’t be hindered by other participants’ reliable actions. (3)Punishment type (s): If q exists UI state q , and for other participants () jj i≠, q also exists UI state q , For player i , q doesn’t better than q, this is called a continuity punishment of q UI state q . If for player i , all UI states of state q have continuous punishment, and state q is called as a continuity punishment stable state of the player i , record- ed as s . (4)The same time stable ( l ): Consider the non-stability state q , if q is also unstable for another player j , UI state i a (for player i ) and j b (for player j ) of the state q produce a state 0 ij p=(a +b -q) ,for player i , p0 is not better than q , and this is called as state i a of q existing a simul- taneous punishment for player i .If for player ,i all UI states of q have the same time punishment, and state q is called as the same time punishing stable state for player i , recorded as l. For each player, if q belongs to ,rs or u , and q is global stable state, recorded as E. Table 3 shows stability analysis for all states in Table 2. Table 1. Feasible situation of university scientific research achievement evaluation system conflict model. Player Strategy Feasible situation 1 A 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 B 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 C 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 2 D 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 E 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 F 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 G 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 H 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 decimal 73 91 162 164 166 170 172 174 178 180 182 186 188 190 225 227 229 231 233 235 237 239 241 243 245 247 249 251 253 255 Table 2. Preferred vector of players. player Preferred vector 1 255 231 239 247 229 237 253 245 91 251 235 243 227 182 166 190 174 73 233 225 249 241 178 162 186 170 164 172 180 188 2 255 253 190 251 188 249 186 239 237 174 235 172 233 170 247 182 245 243 180 241 178 231 229 166 227 164 225 162 91 73 3 255 253 190 251 239 247 188 249 186 231 237 174 235 245 182 243 91 227 172 233 170 229 180 241 178 166 164 225 162 73  H. Z. CHEN, L. L. SHU Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 129 Table 3. Stability analysis table. player N N E N N N N N E N N N N N N E N E N N N N N N N N N N N N 1 a r r r r u u u s r u u u u r r r r r u u u u u u u u u u u u b 231 239 255 247 229 237 253 245 91 251 235 243 227 182 166 190 174 73 233 225 249 241 178 162 186 170 164 172 180 188 c 231 239 255 247 255 239 247 231 235 229 255 247 182 166 190 174 166 174 182 190 2 a r r r r r r r u s u u s s s u s s u s u s u s s u s s s r r b 255 253 190 251 188 249 186 239 237 174 235 172 233 170 247 182 245 243 180 241 178 231 229 166 227 164 225 162 91 73 c 255 253 190 251 188 249 186 255 190 253 251 188 249 186 255 253 190 251 188 249 186 3 a r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r b 255 253 190 251 239 247 188 249 186 231 237 174 235 245 182 243 91 227 172 233 170 229 180 241 178 166 164 225 162 73 c (Here a represents policymakers stability, b represents the prefer red vector of players ( suppliers ), c represe nts unilatera l improvement.) Result An alysis From Table 3, we can see this conflict model has four stable solutions. The situation 255 shows that considering the quality, quantity of scientific research and social benefits caused by the quality and quantity, government will take positive incentives for researchers and schools. When researchers, schools and government build evaluation system of university research achievements, this is the Pareto equilibrium solution estab- lished by three sides. The situation 91 has the following mean- ings. When researchers, schools and government build evalua- tion system of university research achievements, not consider- ing social benefits, government only encouraging the quality of scientific research can promote researchers and schools consi- dering scientific research to consider the quality of the scientif- ic achievement and efficiency. The situation 190 shows that besides considering social benefits ,researchers and schools still need to consider the quantity of the scientific research without considering the quality of the scientific research. Currently the status of university research evaluation is the stable situation 190. The equilibrium of the situation 73 shows only consider- ing the quality of the scientific research, researchers, schools and government can reach the equilibrium. From the above analysis, we know that the situation 255 is the Pareto of evaluation system of university scientific achievements, and the situation 190 mostly conforms the equi- librium status of university research evaluation. To make the conflict equilibrium situation of university research evaluation sys tem turn the situation 91, 190 and 73 to the situation 255, scientific researchers, schools and government must constantly improve and perfectly develop the important role of the evalua- tion system in practice. Acknowledgment s This papaert is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(71002046) ; Post doctoral degrees funds of China and Jiangsu province (NO: 20100481135, 1001051C);Jiangsu Social Science Foundation (11GLA003) and Basic scientific research expenses special research project of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (NJ20120011). REFERENCES Zhang Wei. Frequently Met Problems in Evaluation on Scientific Reaearch in Higher Education al Institutions and Innovation of Eval- uation System [J]. Journal of Taiyuan Normal University(SOCIAL SCIENCES EDITION),2007,(0 4 ). Ceng Yuqing. Evaluatio n method and ap plication of u niversity research outputs [J]. Hunan social sci ence, 2006,(04). Zhou Ying, Wang Pu sh eng .Conf lict of in terests in p ee r revie w, an alysis and treatment [J].Science research. 2003,(03). Deng Yi. Quantitative evaluation of scientific research in universities [J].Modern e ducation, 2006,48(4). Qiu Junping, Tan Chunhui. Significances, System and Practices of Evaluation of Humanities and So cial Science in China [J]. Journal of Chongqing University(SOCIAL SCIENCE S E DI TION), 2007,(05). |

