Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 The foundation of “The Max Area Pattern” and Its Training Significance Yi Xu Dept. of Physical EducationNanjing Normal College, Sichuan Neijiang Abstract- by reference and simplifying the volume expressions of Barrel Theory, this paper puts forward the Double Bottleneck Concept, the Weights of plate as well as the K-value concept on the flex coefficient of the items reflecting the comparative needing of the factors. It also advances the automatic arrangement on the position of each item and the Max Area Pattern representing the athletic diathesis and ability. It also analysis training pattern in different time-limitation by the Max Area Pattern based on the concept of Balanced-Development. Keywords- the Max Area Pattern; the Double Bottleneck Concept; the flex coefficient; the Balanced-Development; time-limitation Introduction After "barrel theory”, rooted in Japan's Toyota on corporate management experience, was introduced in the sports community; the "bucket model" was used to express the image of the sport quality and the relationship between exercise capacity. Although Professor Feng Yan [1], Donghua Qu, Youkuan Shi [2], Kai Li [3] have put forward different views, they simply point out the relationship of the sport quality and sport performance from the way of concept, and failure to provide an operational methods to quantify and evaluate their relationship.Given this situation, this paper attempts to establish a model of "maximum acreage" to quantify and analysis relationship between the sport quality and sport performance, and then discuss training mode choice under the different aging. 2. The foundation of "maximum area" model A.Introduction of "bucket model" simplified expressions. Simplifying the "bucket model" volume expression to "area model" expression can more easily quantify the relationship between the performance determinants and overall athletic performance. Expanding the barrel and array the wood boards constituting a barrel in turn and then making a straight line XY to mark the water level height, the acreage of quadrilateral XOZY (seeing Figure 1) is the bucket volume, and that is the collectivity sport level. For the mode of "barrel reasonable place" (oblique), the area expression can also be simplified as "area model": arrange the wood boards from high to low and mark a water height through making a horizontal straight line XY, to round the boards with O as the original point to make the line XY rise until getting a maximum area of quadrilateral XOZY. Here the area of quadrilateral XOZY (seeing Figure 2) is the bucket volume of reasonable placing barrel, that is, the overall athletic performance. B.The factor analysis of "maximum area" model Some factors that influence its overall athletic performance is an effect of corresponding to a single, and having no impact on athletic performance with other interrelated factors. Such as the reaction of starting sprint and the height of high jump athletes, their impact on athletic performance has nothing to do with other factors. This type of factor is called constant factor, the corresponding, a class of factors of mutual influence and mutual restriction that have an impact on athletic performance are known as variable factors. "The biggest Open Journal of Applied Sciences Supplement:2012 world Congress on Engineering and Technology Cop y ri g ht © 2012 SciRes.159  area" model is discussing the relationship between the variable factors and athletic performance. C. The introduction of weight values A variety of variable factors have different impacts on athletic performance, and some impacts are great and some impacts are minimal. Taking the sprint for an example, strength of speed and strength absolute has a great impact, and technology is on the lesser of its impact, but relatively tactical awareness has much smaller impact; the mastery of knowledge like sports bio-mechanics and aerodynamics theory has smaller impact; while as to the pingpong, relative to the strength of speed and strength, the technical and tactical awareness have a much greater impact. It is clear that a same kind of factor in different sports weights differently; and in the same sport, different factors weights differently. "Barrel theory" incorrectly set an equal of determinants impacting on the overall athletic performance (seeing Figure 1); the "maximum area" model has designed to introduce a weight value to accurately reflect the weights of determinants impacting on the overall athletic performance, by way of the corresponding weights size of each element as plate width (seeing Figure 3). There are already many reports in the literature [4] [5]of corresponding studies on a single degree of correlation between a variety of factors and overall athletic performance, and its findings can be used as reference data of the weight value of each factor plates when establishing the mode of "maximum area". D. Multi-criteria of evaluating plate height Different projects require different standards on the quality development of various levels. For example, a people with a normal development level of physical and intellectual, weighting the needing-standard of chess athletes, certainty has a higher development degree of physical plates in the mode of “maximum area” than the development degree of intellectual quality plates; while weighting the one in the standard of sprinter, he certainly has a lack of physical plate development in “maximum area” mode and has a higher development degree in the intellectual quality. It can be seen that a factor in an absolute level of development has different relative level of development in different sports, that is, the height of reflected plates are different. Clearly, each value of plates tested from the normal standard of requirement must be amended through some kind of mathematical treatment and then can be used as the height of mode plate. The multiple relationships between the normal standard of requirements and the standard of items on each factor is called the scalable coefficient K. K = the average of mass demand ÷the average of relative project demand, Namely: plate height = scalable coefficient K ×measured standards of the mass For example, the speed plate is respectively 0.5 and 1 by the way of the normal requirements of standards for an ordinary people and relative demand of standards for sprint, and the scalable coefficient of speed factor in sprint K = 0.5 ÷ 1 = 0.5. The factor plate K of different project can be found in mathematical statistical methods. The plate height corrected by the K value is truly reflecting the relative level of development of various factor plates in the project. At present the theories of training are still using the general-purpose calculations of normal requirements standards when assessing the development level of each quality plates, and fail to take into account of the particular nature of different projects for the needs of various quality development levels, as a result, some level value of quality plates, that the relative development is well above the needed in the project, has been valued too low, and wrongly making a long board as a short board. E.Method of founding the "maximum area" model The development level of each variable factor is the plate height of a single element, and the weight of that impacting on the overall athletic performance is the plate width of a single factor. Arrange the plates from high to low and make a straight line XY within the plate, maximizing the area of quadrilateral XOZY under this line, and the maximum area is the overall level of the sport (seeing Figure 3). It can be found in Figure 3 that, in the particular oblique state, if putting one plate or few plates after the point U1, even if it is not the lowest one piece of wood, the capacity may be increased. For example, in Figure 3 after raising the height of plate g to a height more than plate d, the capacity increases (seeing Figure 4). 160 Cop y ri g ht © 2012 SciRes. 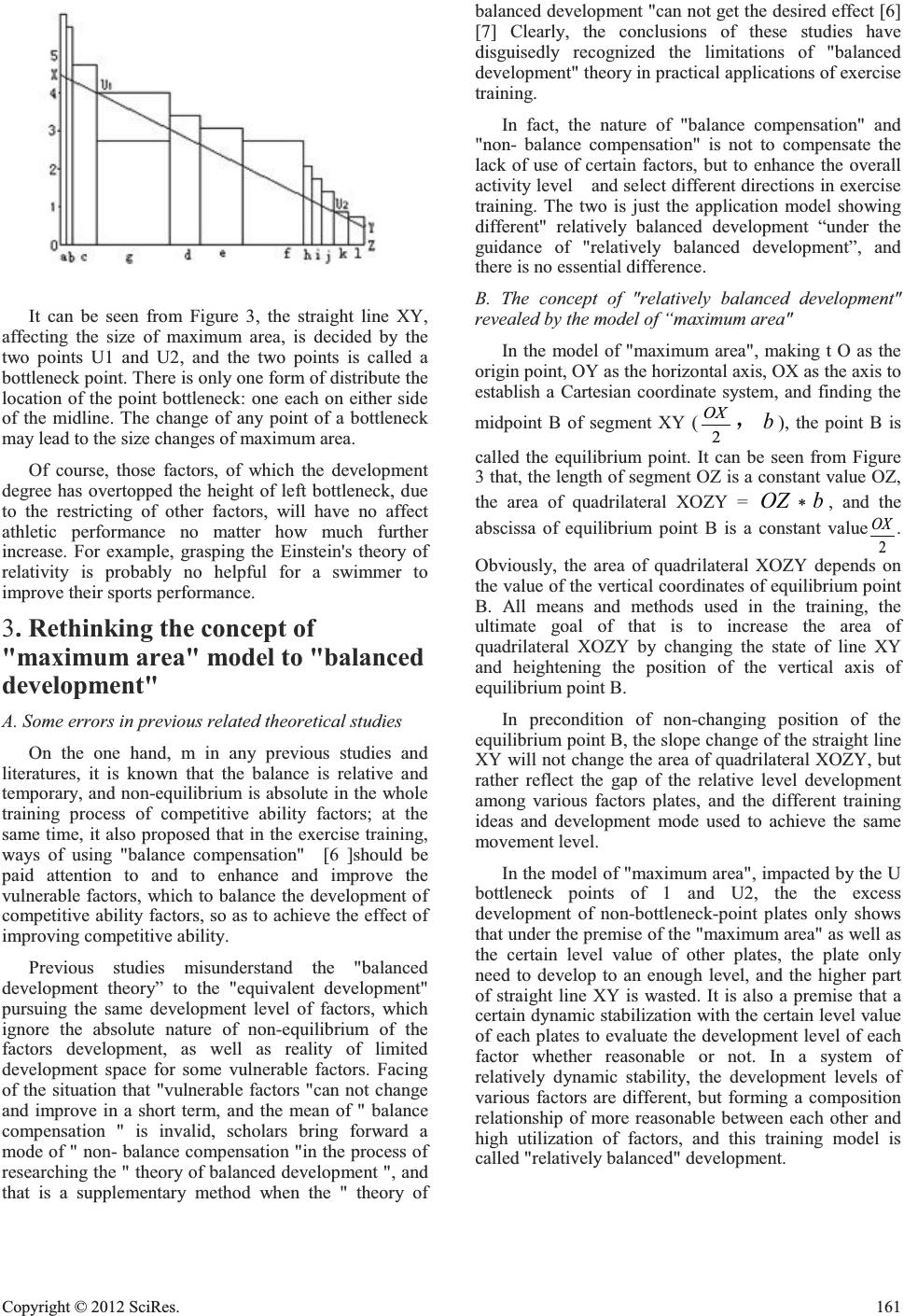 It can be seen from Figure 3, the straight line XY, affecting the size of maximum area, is decided by the two points U1 and U2, and the two points is called a bottleneck point. There is only one form of distribute the location of the point bottleneck: one each on either side of the midline. The change of any point of a bottleneck may lead to the size changes of maximum area. Of course, those factors, of which the development degree has overtopped the height of left bottleneck, due to the restricting of other factors, will have no affect athletic performance no matter how much further increase. For example, grasping the Einstein's theory of relativity is probably no helpful for a swimmer to improve their sports performance. 3. Rethinking the concept of "maximum area" model to "balanced development" A. Some errors in previous related theoretical studies On the one hand, m in any previous studies and literatures, it is known that the balance is relative and temporary, and non-equilibrium is absolute in the whole training process of competitive ability factors; at the same time, it also proposed that in the exercise training, ways of using "balance compensation" [6 ]should be paid attention to and to enhance and improve the vulnerable factors, which to balance the development of competitive ability factors, so as to achieve the effect of improving competitive ability. Previous studies misunderstand the "balanced development theory” to the "equivalent development" pursuing the same development level of factors, which ignore the absolute nature of non-equilibrium of the factors development, as well as reality of limited development space for some vulnerable factors. Facing of the situation that "vulnerable factors "can not change and improve in a short term, and the mean of " balance compensation " is invalid, scholars bring forward a mode of " non- balance compensation "in the process of researching the " theory of balanced development ", and that is a supplementary method when the " theory of balanced development "can not get the desired effect [6] [7] Clearly, the conclusions of these studies have disguisedly recognized the limitations of "balanced development" theory in practical applications of exercise traini ng. In fact, the nature of "balance compensation" and "non- balance compensation" is not to compensate the lack of use of certain factors, but to enhance the overall activity level and select different directions in exercise training. The two is just the application model showing different" relatively balanced development “under the guidance of "relatively balanced development”, and there is no essential difference. B. The concept of "relatively balanced development" revealed by the model of “maximum area" In the model of "maximum area", making t O as the origin point, OY as the horizontal axis, OX as the axis to establish a Cartesian coordinate system, and finding the midpoint B of segment XY ( 2 OX ˈ b ), the point B is called the equilibrium point. It can be seen from Figure 3 that, the length of segment OZ is a constant value OZ, the area of quadrilateral XOZY = OZ b , and the abscissa of equilibrium point B is a constant value 2 OX . Obviously, the area of quadrilateral XOZY depends on the value of the vertical coordinates of equilibrium point B. All means and methods used in the training, the ultimate goal of that is to increase the area of quadrilateral XOZY by changing the state of line XY and heightening the position of the vertical axis of equilibrium point B. In precondition of non-changing position of the equilibrium point B, the slope change of the straight line XY will not change the area of quadrilateral XOZY, but rather reflect the gap of the relative level development among various factors plates, and the different training ideas and development mode used to achieve the same movement level. In the model of "maximum area", impacted by the U bottleneck points of 1 and U2, the the excess development of non-bottleneck-point plates only shows that under the premise of the "maximum area" as well as the certain level value of other plates, the plate only need to develop to an enough level, and the higher part of straight line XY is wasted. It is also a premise that a certain dynamic stabilization with the certain level value of each plates to evaluate the development level of each factor whether reasonable or not. In a system of relatively dynamic stability, the development levels of various factors are different, but forming a composition relationship of more reasonable between each other and high utilization of factors, and this training model is called "relatively balanced" development. Cop y ri g ht © 2012 SciRes.161  From the model of "maximum area", it can be seen that to there is not only one way to increase the "maximum area" by heightening the plate with bottleneck point, yet no necessary to raise the lowest plate. To develop the plate of non-bottleneck and change the position of sorting plates can also increase the "maximum area." The change (change of line XY) of "the maximum area" and the level value of other plates, and the plate position can be automatically change the sort, and then the plate relatively developed surplus before can also become lack. For example, the more development level of plate g 3 from Figure3 of low sport level becomes lack in Figure 4 of the high sport level. The actual development level of the plates of bottleneck points U1 and U2, which show a relative lack of development, is not lack of U1 and U2 section, the actual level of development is not dropped behind. Bottleneck point just reminds us that in the current relatively stable system, if the bottleneck point plate may be raised, benefits can be immediately got. But it does not mean the best option is to enhance the bottleneck point. In fact, at a training phase of high level, the development of certain factors (especially physical factor) has tended to a limit, even if devoting an amount quantity to its training, the level of the factor is difficult to improve and the increase range of athletic performance is minimal, obviously which is not worth the candle. At this time even if the factor is the one shorter and wide plate, it can not get a lot of training. Here, it is naturally become a more reasonable choice to explore the potential of other plate factors (these factors can be theoretically increased unlimitedly), even if it is one longer and narrower plate, the overall athletic performance can be improved by making it longer. Similarly, the development level of the bottleneck points U1 and to the right plate are both absolutely in a lack state, but in the current state of the stable development, based on the function of "maximum area" model automatic sorting, it is expressed relatively surplus. If the rule of automatic compositor is not followed, and putting these plates forward, a lack state of development of restraining “the greatest area" increase will also be shown. Clearly, the bottleneck points U1 and the right section both have a two-side nature of development level of absolute lack and absolute spare, as well as a two-side nature of relative shortage and relative spare. To determine a development level of one factor is to put it in a dynamic stabilization system within a certain value of development level of the other factors, and to get a conclusion of relative shortage, appropriate and spare, of which the absolute gap is nothing to do with the development level of this plate relatively in this system. C. The utilization of the plate is the standard to evaluate the equilibrium level "The maximum area" model can clearly reflect the status and role of various factors placed when determining the overall athletic performance by dint of the weights and the area ratio of plates in the quadrilateral XOZY. As "the greatest area" model can automatically sort, the level that plates are higher than the position of XY, has intuitively and accurately show the relative-balance development level of various plates. Seeing from the Figure 3, the development of blocks a, b, c is relatively advanced, while the plate of d, e, k, is relatively lagging behind. The overall balance of plate development can be better reflected by using the overall utilization ratio of the "maximum area" model. For example, the maximum area of the development model of Figure 3 and Figure2 are the same, but the overall utilization rate in Figure 1 is 76.4% and the overall utilization rate in Figure 5 is 79.2%. So, the relatively balanced development of various factors in Figure 5 better than that in Figure1. The utilization of other plates is improved by the way of "Balance compensation" theory using an approach of "same development", the results of that is unsatisfactory in the training practice of high level athletes. It is not the best way of improving utilization to develop disadvantaged sections. The utilization of other plate can be better improved by changing the bottlenecks points to tend a balanced development. When setting the training programs, the training efficiency of training imputing and producing has to be fully calculated, and to get the maximum training returns with the minimum investment in the principle of effectiveness and economy. The theory of non-balanced-compensation emphasizes the role of compensation for advantaged factor to disadvantaged factor, but in practice, by nature it has achieved the purpose of increasing the maximum area through development of excellent plates, changes of the straight line XY, and increasing the utilized area of the excellent plate, ignoring the training effectiveness. 4. The significance of sports training of "maximum area" model 162 Cop y ri g ht © 2012 SciRes.  A. accurately reflecting the role of timing 1) The upper limit of the training inputs Many physical factors, such as strength, endurance, etc., because of physical constraints, need to be restored and recovered excess, so the. Skills factors, constrained by physical ability and time, the amount of training imputed once or within a certain period of time also has a certain limit. Intelligence factors, especially the game experience gained, due to the constraints of events arranged, the training in a certain period of time is much limited. Even in the training arrangement is very scientific and rational, but after all, there is a certain limit for people’s time and energy. Therefore, the upper limit of the training inputs must exist as it is restricted by the timing of completing the training objectives. The different training objectives will also constraint the amount of training inputs. For example, as a professional athlete, he had to take the limit of impacting sport as a target, and the training inputs must be fully excavated, so as to tend closely to a endurance limit of personal physical and psychological; while the training mode of making sport as a hobby can only improve their athletic ability at the premise of non-affecting work and study, and the training inputs will certainly be much smaller. 2) The impact of time on the plate height There is a purpose in exercise training. No matter the short-term goal and the long-term goal, as long as the target exists, there is bounded a time stamp. Therefore, any setting of the training program must have a limit of specific length of time for completion. There are mainly two aspects of the time factor impacting on the training effect. First, in a certain length of time, there is a upper amount limit of investment of the overall training of various factors. Second, many physiological factors, over time, the level of which will naturally reduce, and the investment in the training of these factors can only play a role slowing the reducing speed level. 3) The role of the effect of aging on evaluating the training effect "Barrel theory" fails to consider the timeliness of exercise training; it ignores the time length needed to improve some low-level factors and features of development of certain factors inevitable drooping after the development and maintenance of a certain length of time. "The maximum area" model can not only reflect the result of increased levels of factors, but also may reflect the results of factors reducing level. For example, over time, as the improvement of the technical level and abundant experienced competition for a table tennis player, the height of corresponding plate will increase, while the decline level in physical fitness, the height of corresponding plate will reduce. "The biggest area" model can bring the positive effects which produced from upgrading skills and enriching extensive competition experience and the negative impact resulted in the decline level of fitness, and then accurately reflect the final result. B The effect of "double choke points" in the selection process of exercise training There must be a change of the plate height in the maximum area model or sorting turns when raising the height of one or more plate after a certain point to the above height, and which will increase the horizontal or vertical axis value and lead to a maximum area increase. (seeing Figure 3, Figure 4). Similarly, the plate height in the maximum area mode or the sorting turns will change if one of more factor levels in front of the bottleneck point is lower than the one. it will definitely lead to the reduction of maximum area as well as the value of bottleneck point of horizontal or vertical coordinate. In the new model, the factors that constituted a bottleneck point may be the original factors and maybe the other factors of which the level of development is lower or higher than the original factors. For example, raising the height of plate g in Figure 3 above the height of plate g, the sort of plate changes and the bottleneck point U1 also changes from the plate d to plate g. (seeing Figure 4). C.The determination of training inputs the direction and movement training Enhancing the plate g in Figure 3, of which affect the weight value greater and plate l , of which affect the weight value smaller respectively to a same height, the maximum area will increase 13.85% (Figure 4) when enhancing the plate g, while to enhance the plate 1 can only increase the maximum area of 3.08% (Figure 6). In the initial training phase, a variety of factors are easier to be improved, obviously, the factor g, which to invest the same amount of training into effect on athletic performance factor weights greater, can achieve a much better actual result compared with the factor 1, of which the weight value of the direction impacting athletic performance smaller. (Especially in order to obtain significant results in a short term). At a high level training phase, certain factors (especially physical factor) has developed to a limit, even if a large amount of training is invested in, the factor levels are difficult to improve, and the increase of Cop y ri g ht © 2012 SciRes.163  athletic performance is minimal, which is obviously not worth the candle. Then even if the factor plate is shorter and wider, no more training will be put in, but to explore the potential of other factors (these factors can be unlimitedly enhanced theoretically). At this time, even if it is a longer and narrower one, it can also become longer to improve the overall athletic performance to some extent. This can be verified from the psychological, technical movements, tactical awareness of the world's best players and that occupies a large proportion training.Take Figure 7 as an example, it reflects the development of all aspects of a high quality high jump athlete, the development of the leg explosive g, technology development f have been closer to the limit, and there is a certain improvement room for psychological e.At this point, to enhance the psychological e, the game experience, d, and the other plate h and i impacting small on weight but can be enhanced to the height above point U1, also have an effective for improving the of athletic performance (seeing Figure 8). In this upgrade process, even if the level of legs explosive g decreases in certain, the improvement and maintain of the athletic performance it will not be affected (seeing Figure 8). Of course, as to those factors, the development of which is higher than the height of the left bottleneck, due to the restrictions by other factors, no matter how much further increased, will not affect athletic performance. For example, grasping the Einstein's theory of relativity is probably no helpful for a swimmer to improve their sports performance. D. Choice of "relatively balanced development" concept and the training mode 1) different combination of training under the modes of "relatively balanced development" Seeing the Figure 3 and Figure 5, the height of four plates corresponding d, e, f, g in the two models are different, but the "maximum area" are equal. Therefore, each factor of "the largest area" model can have a relatively different balanced combination mode and getting the same value of "maximum area", that is the athletic performance is equal. In other words, all roads lead to Rome, different development paths and models can achieve the same training objectives. It full obeys the principle of giving priority to efficiency and purpose when choosing these different development model. E. The timing effect and training mode under the concept of "relatively balanced development" 1) Selection of Short-term training mode In the initial training phase, a variety of factors are easier to be improved, obviously, comparing with the investments to factors weighting small impact on athletic performance, to invest the same amount of training into factor, of which weights greater on will obtain actual much better results (especially in the short term in order to obtain significant results.) At this time, the training mode shown is naturally inclined to the approach of "balance compensation". 2) Selection of long-term training mode When making the long-term training programs, the balanced development of high level sport often require non-balanced development in low-level campaign, that the advance development is basic. This development mode, even though in the short term can improve athletic performance to maximization, but will prevent the development of movement to a certain extent level, and a plate can not be enhanced with an appropriate speed. The formed bottleneck point will restrict the utilization of other plates in a long term, which will cause a serious imbalance in the actual development, and has seriously hampered the situation of improving sport level, and so as to achieve the maximization of final training effect. At the high level training phase, certain factors (especially physical factor) has tended to a limited development, and the potential factors is focused to improve, and then the training model clearly demonstrated is the "non-value-compensation" approach, namely: developing the skills of players, making the formatting of individual technical and tactical style consistent. 164 Cop y ri g ht © 2012 SciRes.  5. Steps of evaluating training program with application of "maximum area" model Follow the steps should be followed when quantitatively evaluating the training program. First, the length time of training must be determined. Secondly, according to a given time, and fully taking into account the training purpose, the restore speed of body, training time, space, climate, and many other factors, to establish different training distribution inputs program, and correctly assess each program element of the plate probably obtaining the maximum amount training of investment. Third, to determine the changes that maybe produced under the program of different distribution training inputs, including the rise and fall changes caused of time factors. Fourth, to establish the "maximum area" model with training effect of different training inputs distribution program. Fifth, to compare and analys the "maximum area" model got in step four, and to choose the optimized solution. 6. Conclusions For the studies of degree of correlation between non-physiological factors and the athletic performance, there is no specific result to refer to; as to the calculation of specific values of scalable coefficient K, it has not yet been carried out; what factors should be included of the composition of the "maximum area" model has yet to be explored. Therefore, although the "maximum size" model can explain some phenomenon in the exercise training in a reasonable way, and provide a reference and theoretical basis for the training mode selection, but there is still some distance away from practical application, which is still in the conceptual stage. This article discusses the "maximum size" model established by the structure of "double choke point". The possibility of establishing "Maximum size" model" with “three bottleneck point", "four choke point" and "multi-choke point", and what the requirements of the abscissa range for "choke point" are stille to be further explored. REFERENCES [1] Yan Feng. The adaptive analysis of "barrel theory" in the high-level athletes training [J]. Beijing Physical Education Teachers College, 1999,11 (4) :61-64 [2] QuDonghua, Shi Youkuan. Brief discussion of the practicability of "barrel theory" in the exercise training [J]. Liaoning Sports Technology, 2002,22 (3) :1-2 [3] Li Kai. Study of "Alloy theory" [J]. Shandong Institute of Physical Education, 2000,11 (1): 1 ~ 5 [4] LIANG Jingquan. The effect of swing on the swing leg on long jump [J]. Youth Sports Training 2005, (3): 30 [5] Mi Weiguo, and so on. view the swinging leg techniques from knee angle of different levels of long jump athlete [J]. Shanghai Institute of Physical Research, 2003,24 (2), 33 [6] Zhang Long. The application of balanced development and training of non-value-structure theory in practice [J]. Taiyuan Teachers College, 2006,3 (1) :127-130 [7] Zheng Wei. The study and analysis On the "principle of balanced development of athletic ability," [J]. Shandong Institute of Physical Education, 2005,8 (4) :95-96 Cop y ri g ht © 2012 SciRes.165 |

