Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 Creative Education 2012. Vol.3, Supplement, 100-103 Published Online December 2012 in SciRes (http://www.SciRP.org/journal/ce) DOI:10.4236/ce.2012.37B026 Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 100 Let Professional Degrees Graduate Education for Oil and Gas Engineering Become the Cradle for the Birth and Growth of Petroleum Engineers Zhibin Liu, Qingyou Liu Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, China Email: Liuzhibinswpi@vip.sina.com, liuqy66@swpu.edu.cn Received 2012 The demand of the talents in petroleum engineering of petroleum enterprises is analyzed in this paper ac- cording the current situation of the engineering education. The four levels of the professional talents needed by the petroleum enterprises are specified, which makes it clear that what the purpose and orienta- tion of the higher education in petroleum engineering should be. The qualities of the petroleum engineers are discussed specifically and it is pointed out that the training of the postgraduate for professional degree in oil and gas engineering should be the cradle of the petroleum engineers. A training schedule is listed in this paper based on the discussion, including curriculum provision, practice link, thesis and training mode, which will be a pathfinder of the education of the professional degree graduate student in oil and gas en- gineering. Keywords: Engineering Education; Petroleum Engineering; Professional Degree Graduate Students; Engineers Introduction Recently, the engineering education is developed rapidly in China and we have made a lot of achievements [1]. In 2010, there are 6.6 million students were enrolled in universities and colleges, 47% percent of which, 3.1 million, were higher voca- tional college students. About 470,000 graduate student were enrolled in this year, and there were 23%, 110,000, professional master degree candidates. There were 34,000 master degree candidates of engineering in these professional graduate stu- dents. Moreover, a pilot project of doctor of engineering has be launched. However, there is still a strange phenomenon in talents supply and demand, which is the contradiction between the employment difficulty of the graduates and the lack of tal- ents needed by enterprises. The direct reason of this situation is the mismatching of the supply of labor educated in school and the demand of the enterprises and markets. In the “Outline of the Plan of the Medium-long Term Na- tional Educational Reform and Development (2010-2012)”, the core mission of our higher education is to improve the quality of our graduates, which means the time is coming to an end that the number of college students increases extensively. Obviously the improvement of the quality of students contains the devel- oping direction of the engineering education, and the main mis- sion of the future postgraduate education is to adjust the educa- tional structure and develop the training of the professional degree graduate students. Like the other engineering fields, the key problem of oil and gas engineering is how to fulfill the demand of petroleum en- terprises. The difference of the normal graduate students and the students for professional master degree needs to be focused, and the different level of these two types of education needs to be specified. In 2010, there were 64 colleges and universities authorized by the ministry of education to make the experiment of the training of professional graduate students, including the Petroleum University (Beijing, Huadong) and Southwest Pe- troleum University. This experiment indicates the urgent de- mand of the petroleum enterprises for the talents and the mis- matching of the supply of labor educated by school and the demand of the enterprises. The Quality should be Processed by a Petroleum Engineer To solve the problems above, we should first make it clear that what kind and what level of the talent is demanded by the petroleum enterprises, and what quality they should process. There are mainly 4 levels of engineering and technical per- sonnel needed by the national petroleum enterprises. The first level is the normal skilled workers, i.e. the specific operators. The second level is the normal engineering and technical man- agers. The third level is the engineers, they are in charge of the engineering and technical affairs. The fourth level is the re- searchers of engineering and technology. According to the sta- tistic, the proportion of the demand is 60:28:10:2. The mis- matching of the supply and demand comes from the ignorance of this proportion and the inaccuracy of the education target. The difference between the third level, the petroleum engi- neers, and the normal technicians is that they have more broad and in-depth knowledge, and more experiences. Most of the engineers in China come from the normal technicians. However, we believe that although these technicians can exchange the time for engineering experiences, they may not get more broad and in-depth professional knowledge. This should be specified by the colleges and universities. The third level and the fourth level are obviously different,  Z. B. LIU, Q. Y. LIU Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 101 that is, the researchers mainly do not involve in the manufac- ture directly. However, the management mode of some enter- prises makes this difference vague. There are general engineer, senior engineer, and professor of engineering, in which the senior engineer seems to be researchers. There are 3 second disciplines under the first level discipline of oil and gas engineering, which are oil-gas well engineering, oil and gas field development engineering, oil and gas storage and transportation engineering. The petroleum engineers with more broad and in-depth knowledge should be the specialists of all these fields, otherwise, they can only be drilling engineers, reservoir engineers, or oil production engineers. The Training Schedule and Mode of the Postgraduate for Pro f essional Degrees in Oil and Gas Engineering The Purpose and Orientation Although there are differences between individual colleges and universities, their purpose and orientation of the education of postgraduate in oil and gas engineering are all to train high- level practical compound engineers and managers. Most of these schools focus on the word “high-level”, which will make some misunderstandings. We think that the division of four levels of talents demanded by petroleum enterprises will make it much clearer that what the purpose and orientation should be. The first level is the vocational or spec ialist education for general skilled workers. The second level is the undergraduate education for general technicians. The third level is the professional postgraduate education for engineers. The fourth level is training of the research postgraduate or doctor for researchers. The professional postgraduate education is the cradle of the petroleum engineers. The Training Schedule The training schedule of the postgraduate for professional degrees contains course learning, practice link and dissertation. Oil and gas engineering is to drill and probe the hydrocarbon resources underground with scientific theories and technologies efficiently, exploit maximum oil and gas to the surface eco- nomically, extract, store and transport the oil and gas safely. This field involves mineral survey and exploration, earth ex- ploration and information technology, mineral engineering, engineering mechanics, chemical engineering, mechanical en- gineering, and traffic and transportation engineering. The cur- riculum provision should take them into consideration. The curriculum of Southwest Petroleum University (SWPU) for the postgraduate for professional degrees is listed in Appendix I, and the practical link is listed in Appendix II. The topic of the dissertation of engineering masters should be derived from the actual project or have definite technical background, which means the research and composition should go along with the practice. The supervisors should be expe- rienced, conscientious, high level staffs with senior technical titles in campus or industrial establishments. The Training Mode Comparing with the training mode of the general academic postgraduates, the purse and methods of the education of engi- neering masters are very different, which makes us have to innovate to adapt the demand of the petroleum enterprises. In SWPU, we have established several types of training modes based on the disciplines of the education of postgraduate after several years of exploration. On-job postgraduate for professional degrees There are several training modes for the technicians in oil and gas enterprises and college teachers. The first mode is the cooperating training of the college and enterprises. This mode is mainly for the technicians in the pe- troleum enterprises, and it is some kind of customized training. The enterprises can set some courses based on their technical demands, and participate in the selection and management of the students. The enterprise should make the inspection and appraisal of the students’ degree dissertation and participate in their oral defenses. The second mode is the cooperating training of the colleges. For the convenience of the students and to make the most of the resources of the brother school, we have made agreements with several schools to cultivate postgraduates cooperatively such as Chonqing Institute of Technology. We take charge of the quali- fication examination of the supervisors, teaching materials and send teachers to give some core lessons. The whole training process is supervised by both schools. The third mode is fully released from work. To improve the theoretical level of the petroleum technicians, recent years we have accepted several consignments to train the engineering masters for the Xinjiang Oilfield Company of PetroChina, the Northwest Oil Marketing Company of PetroChina, Huabei Oilfield Company, etc. The students will spend 1 year in SWPU fully released from work, they can take different courses based on their own needs. The participation in the academic activities and the communication with the supervisors will help them finish their study successfully. Full-time postgraduate for professional degrees In SWPU, we began enrolling full-time postgraduates for professional degrees in since Sep. 2009, and were authorized to make experiments of the education reform of the training of postgraduates for professional degrees in Sep. 2010. There are 2 systems of our training mode in our exploration according to the training purposes and regulations, that is, the system of teaching in classroom and the system of engineering practice. The students are trained mainly by cooperation with the pe- troleum enterprises. They complete the theoretic courses in class to get enough credits in school. After that, they’ll be sent to different engineering practice bases. The practice link will help familiarize themselves with some engineering software and composite the opening report of their research projects, which is an efficient way to acquaint with the methods and ideas to solve the problems in the fields. There are 2 types of dissertations for their degrees. One is combined with the in-situ production, the format of which is not fixed and the topics mainly involve the actual engineering design, application of engineering software to solve production problems, analysis of engineering cases, feasibility study of engineering problems, study of one aspect of a large-scale engineering problems, etc. The other type is combined with the research of application projects of the supervisors, which is mainly to solve the actual engineering problems. The workstation for graduate students in our school has established a stable group of technologists, who have strong theoretical background and rich experience in pro- 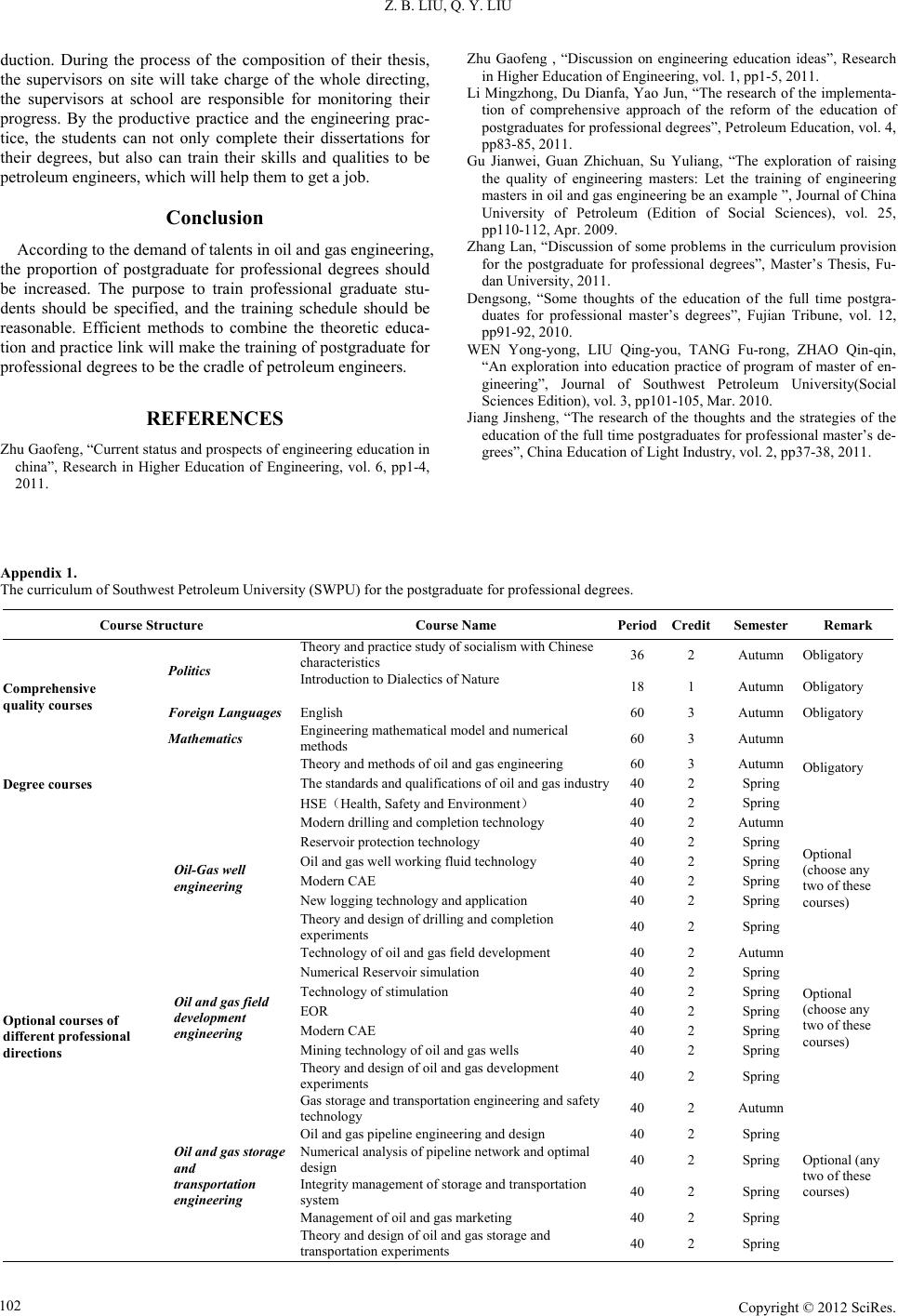 Z. B. LIU, Q. Y. LIU Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 102 duction. During the process of the composition of their thesis, the supervisors on site will take charge of the whole directing, the supervisors at school are responsible for monitoring their progress. By the productive practice and the engineering prac- tice, the students can not only complete their dissertations for their degrees, but also can train their skills and qualities to be petroleum engineers, which will help them to get a job. Conclusion According to the demand of talents in oil and gas engineering, the proportion of postgraduate for professional degrees should be increased. The purpose to train professional graduate stu- dents should be specified, and the training schedule should be reasonable. Efficient methods to combine the theoretic educa- tion and practice link will make the training of postgraduate for professional degrees to be the cradle of petroleum engineers. REFERENCES Zhu Gaofeng, “Current status and prospects of engineering education in china”, Research in Higher Education of Engineering, vol. 6, pp1-4, 2011. Zhu Gaofeng , “Discussion on engineering education ideas”, Research in Higher Educ ation of Engineer ing, vol. 1, pp1-5, 2011. Li Mingzhong, Du Dianfa, Yao Jun, “The research of the implementa- tion of comprehensive approach of the reform of the education of postgraduates for p rofessional d egrees”, Petroleu m Ed ucation , vol. 4 , pp83-85, 2011. Gu Jianwei, Guan Zhichuan, Su Yuliang, “The exploration of raising the quality of engineering masters: Let the training of engineering masters in oil and gas en gineering be an example ”, Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Social Sciences), vol. 25, pp110-112, Apr. 2009. Zhang Lan, “Discussion of some problems in the curriculum provision for the postgraduate for professional degrees”, Master’s Thesis, Fu- dan Universit y, 2011. Dengsong, “Some thoughts of the education of the full time postgra- duates for professional master’s degrees”, Fujian Tribune, vol. 12, pp91-92, 2010. WEN Yong-yong, LIU Qing-you, TANG Fu-rong, ZHAO Qin-qin, “An exploration into education practice of program of master of en- gineering”, Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Social Sciences Editi on), vol. 3, pp101-105, Mar. 2010. Jiang Jinsheng, “The research of the thoughts and the strategies of the education of the f ull time postgraduates f or professional master’s de- grees”, China Education of L ight Industr y, vol. 2, pp37-38, 2011. Appendix 1. The curriculum of Southwest Petroleum University (SWPU) for the postgraduate for professional degrees. Course Structure Course Name Period Credit Semester Remark Comprehensive quality courses Politics Theory and practice study of socialism with Chinese characteristics 36 2 Autumn Obligatory Introduction to Dialectics of Nature 18 1 Autumn Obligatory Foreign Languages English 60 3 Autumn Obligatory Mathematics Engineering mathematical model and numerical methods 60 3 Autumn Obligatory Degree courses Theory and methods of oil and gas engineering 60 3 Autumn The standards and qualifications of oil and gas industry 40 2 Spring HSE(Health, Safety and Environm ent) 40 2 Spring Optional courses of different professional directions Oil-Gas well engineering Modern dril l i ng and completion technology 40 2 Autumn Optional (choose any two of these courses) Reservoir protection technology 40 2 Spring Oil and gas well working fluid technology 40 2 Spring Modern CAE 40 2 Spring New logging t echnology and application 40 2 Spring Theory and design of drilling and completion experiments 40 2 Spring Oil and gas field development engineering Technology of oil and ga s field deve l opment 40 2 Autumn Optional (choose any two of these courses) Numerical Reservoi r simulation 40 2 Spring Technology of stimulation 40 2 Spring EOR 40 2 Spring Modern CAE 40 2 Spring Mining technology of oil and gas wells 40 2 Spring Theory a nd design of oil and gas development experiments 40 2 Spring Oil and gas storage and transportation engineering Gas storage and transportation engineering and safety technology 40 2 Autumn Optional (any two of these courses) Oil and gas pipeline engineering and design 40 2 Spring Numerical analysis of pipeline network and optimal design 40 2 Spring Integrity management of storage and transportation system 40 2 Spring Management of oi l and gas marketing 40 2 Spring Theory a nd design of oil and gas storage and transportation experiments 40 2 Spring 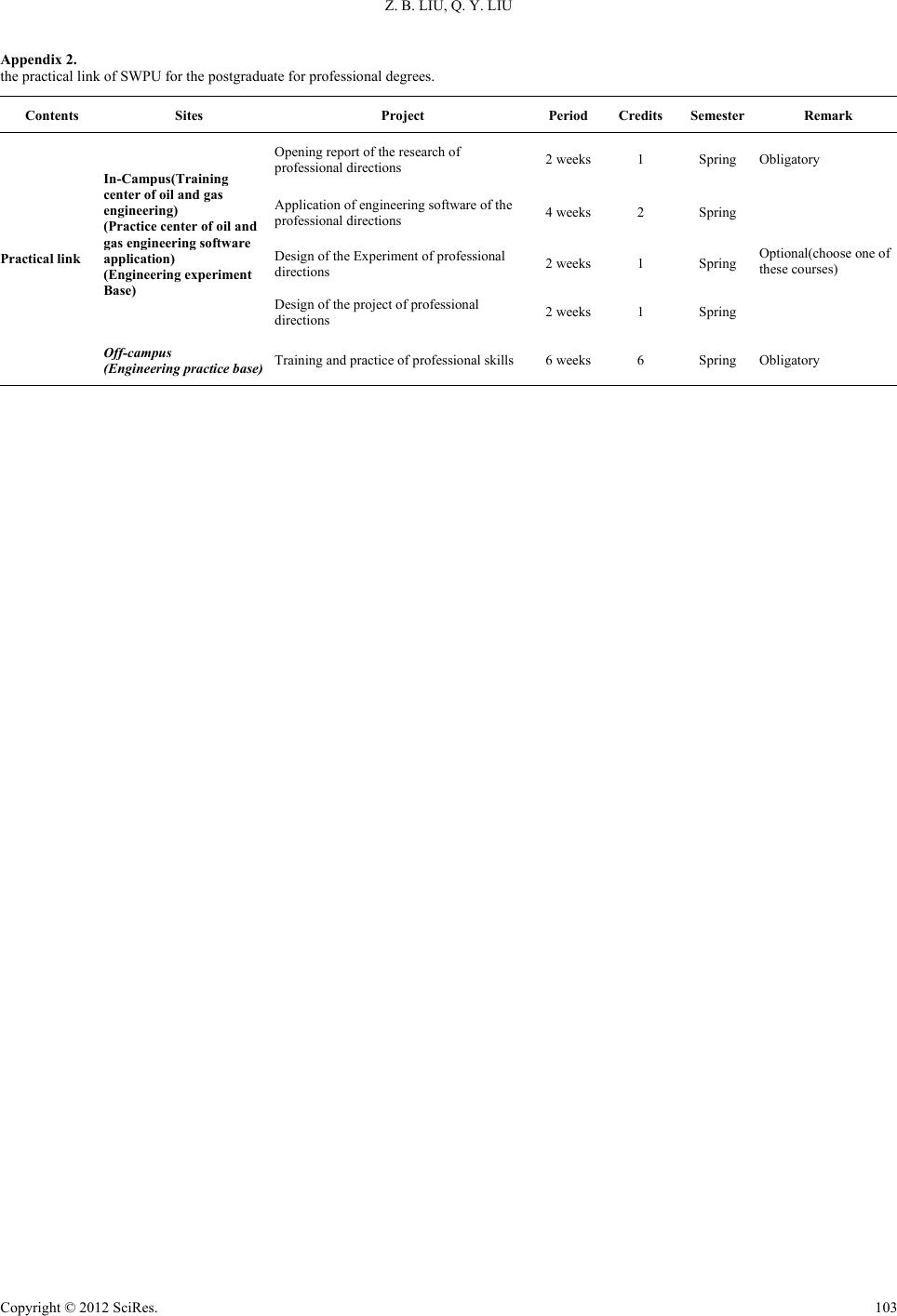 Z. B. LIU, Q. Y. LIU Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 103 Appendix 2. the practical link of SWPU for the postgraduate for professional degrees. Contents Sites Project Period Credits Semester Remark Practical link In-Campus(Training center of oil and gas engineering) (Practice center of oil and gas enginee ring software application) (Engineering experiment Base) Opening report of the research of professional directions 2 weeks 1 Spring Obligatory Application of engineering software of the professional directions 4 weeks 2 Spring Optional(choose one of these courses) Design of the Experiment of professional directions 2 weeks 1 Spring Design of the project of professional directions 2 weeks 1 Spring Off-campus (Enginee ring pr actice base) Training and practice of professional skills 6 weeks 6 Spring Obligatory |

