Open Journal of Nursing
Vol.3 No.1(2013), Article ID:29577,9 pages DOI:10.4236/ojn.2013.31020
The effect of protective genital care protocol on preventing diaper dermatit development in 0 - 18 month old children using antibiotics
![]()
1Pediatric Nursing Deparment, Faculty of Health Sciences, Atatürk University, Erzurum, Turkey
2Pediatric Nursing Deparment, Practical and Research Hospital, Dokuz Eylül University, İzmir, Turkey
Email: rozbaran@gmail.com
Received 29 January 2013; revised 5 March 2013; accepted 14 March 2013
Keywords: Diaper Dermatit; Vaseline; 0 - 18 Month Old Children; Antibiotic; Protective Genital Care
ABSTRACT
Diaper dermatit is among the widely seen inflamatory skin diseases in neonatals and small 0 - 18 month old children. Control of causative agents as well as providing good genital care may prevent or reduce the risk of the disease. The aim of this study is find out the effect of protective genital care on reducing the diaper dermatit development in 0 - 18 months old inpatient 0 - 18 month old children who are using antibiotic. The study was conducted as prospective halfexperimetal using control-experimental groups. Our samples comprise of 0 - 18 month old children admitted at Dokuz Eylul University Practical and Research Hospital, pediatric clinic between January and May 2009, 41 0 - 18 month old children as a control group were not under protective genital care, and 42 0 - 18 month old children as an experimental group were under the protecion and using vaseline. The mothers of the experimental group 0 - 18 month old children were given education. All 0 - 18 month old children were followed-up 3 - 7 days and the collected data were evaluated in computer using Pearson’s chisquare, Fisher’s exact chi-square and Yatest-corrected chi-square tests. The diaper dermatit development ratio was 34.1% in the control group and 7.1% in the experimental group (p < 0.05). The rash disease in most of the control group 0 - 18 month old children developed in 2 - 3 days earlier than those in experimental group which appeared after the fourth day of study. All the 0 - 18 month old children with diaper dermatit in the experimental group were found to be with first grade diaper dermatit while those with diaper dermatit in the control group were found to be with second and third grade diaper dermatit. The Diaper dermatit development ratio between the experiment group who were given the protective genital care and vaseline was meaningfully low in comparison to the control group who were not given any care. And those who acquired diaper dermatit disease among experiment group 0 - 18 month old children the disease appeared in late days and was rather mild. As the diaper dermatit was found to be more frequent in 0 - 18 month old children on antibiotics, to prevent the occurence of the disease proper protective genital care, vaseline use whenever the diaper is changed and giving education to mothers on the subject concerned is advised.
1. INTRODUCTION
Diaper dermatit in among the widely seen inflamatory skin disease in babes as well as neonatals [1-3]. As most of the parent does not see the diaper dermatit as a disease, and most of the 0 - 18 month old 0 - 18 month old children are treated at homes the proper prevalence is unknown [4,5]. In different researches done in other countries the diaper dermatit prevalence is changes between 15.2% and 60.3% [1,6,7] In our country (Turkey) the prevalence is between 23.9% and 61.5% [8,9].
For years it has been believed that amonium the product of bacterial breakdown of urea in the child’s urine to be the cause of diaper dermatit, but nowadays the concesus show that among the main causes are excessive moisture, friction, excessive hydration from long time contact of skin with urine and feces, fungus infections, bacterial infections, the type of diaper used, skin damage from the orally taken drugs which pass unabsorbed through the intestines, feeding style and skin Ph. [3,10, 11].
The thinness of the 0 - 18 month old children’s skin compared to adults [3,12], frequent appearence of diarhoea as well as frequent use of antibiotic because of infections lead to an increased risk of the diaper dermatit diease in 0 - 18 month old children [3,11]. Also in other studies it has bee shown that skin disease history is one of the risk factor for the diaper dermatit development [1,7], however in one of the study negative results were found [9].
The diaper dermatit occurs equally in both sexes. According to various studies the meaningful diferrence between disease prevalence was not found [1,7-9]. Because of the reduced diaper use after 18 - 20 months the disease prevalence decrease. Althought it is generally known most frequently that the disease appears between 6 - 12 months, other studies shows variations [7,13,14]. In 3 - 24 months children it has been shown more meanigfuly that oftenly diaper dermatit appears between 3 - 6 [7]. In Çimen et al. study (2007), 6 - 27 month group showed more diaper dermatit and this statistical difference was found meaningful [11]. There was not meaningful difference between prevalence of diaper dermatit and age groups in Kırcuval study (2001). Also in Çimen et al. study mother’s educational status and 0 - 18 month old children’s age diferrence in the family affect the occurence of the diaper dermatit, that is, high educational level mothers and the first new born babe were found with low rate of diaper dermatit develeopment [8]. It is expressed that 0 - 18 month old children on brestfeed in comparison to those on artifial food have lower chance of getting diaper dermatit. Brestfed babes have very low amount of microorganismas with urease enzyme. Babes who are fed with lower Ph and mother’s milk which contains fecal enzyme are difficulty to have perianal damage [15]. However according to various studies feeding style has no important significant effect on the development of diaper dermatit [1,8,9]. In one of the study the effect of mother’s milk on the severity of diaper dermatit was found [16]. Frequent diarrhea in small 0 - 18 month old children increases the development of diaper dermatit [3]. According to researches diarrhoeic babes compared to those without diarroea an increased risk of the diaper dermatit was found [1,7-9]. Diarrhoeic condition leads to increase speed of intestine and therefore feces with large amount of digestive enzymes. 0 - 18 month old children’s skin contact with the feces increase accordingly and thereby fecal enzymes such as protease and lipase lead to destruction of skin’s stratum corneum and therefore diaper dermatit development risk easily occurs [3].
Other important factor which play an important role on diaper dermatit development is the use of antibiotics. In this study 0 - 18 month old children on antibiotics were taken into consideration. Other study groups with the same feature were considered. Infectous disease is frequent in 0 - 18 month old children, especially in our country (Turkey) mostly upper respiratory infection, gastroenteritis and bronchopneumonia [17].
Also in our country because of frequent infections, among the most used drugs are the antibiotics. If 0 - 18 month old children take antiobitic or take milk from a mother using antibiotic normal intestine floras is destroyed and therefore easier is fungus colonisation. So the intestine regions with decreased resistance become easier to be infected by fungi. The best examples of fungus colonisation are mouth fungus infection (oral thrush) as well as diarrhoea from the disturbed intestine function [3].
Microorganisms were found to play role on the diaper dermatit development. Ferrazzini et al researched on 77 0 - 18 month old children and found that diaper dermatit 0 - 18 month old children in their diapers were significant amount of candinda colonies. According to other studies 0 - 18 month old children with aphthous in comparison with those without aphthous statically diaper dermatit was significantly increased [1,8,18]. However Kırçuval’s studies showed no relationship between aphthous and diaper dermatit ratio [9]. Increased diarrhoea increase the development of diaper dermatit because of increase contact of feces with the 0 - 18 month old children’s skin. Also other many studies show that 0 - 18 month old childrens using antibiotic in comparison to those not using antibiotic have increaed risk of diaper dermatit [7-9]. Adalat et al. didn’t found any relationship between the use of antibiotics and frequency of diaper dermatit [1].
After every diaper change skin cleanness should be done with mild warm water or with the cotton wet with mild warm water two times a day on the diaper region. Normal soaps having high Ph they should be used twice a day as soon after applied to the skin they should be cleaned immediately. There is no need of washing with soaps everytime and soft soaps should be prefered. Most of the wet paper used for genital parts cleaning when they destroy the general skin structure they should be used [3]. Researches have proved that diaper region cleaning style as well as cleaning by wet napkins are effectıve in diaper dermatit development [1,8]. Because of the destructive properties as well as danger of aspiration powder should be used [5]. In one of the study by Adalat et al. there was no significant difference between the use of powder and the diaper dermatit disease frequency [1].
After every diaper change the cleaned skin should be applied with protective creams (i.e. olive oil vasseline, linoline or baby oil) [3]. Nowadays more than half of mothers use olive oil to remove diaper rash. In the study by Adalat et al. (2007) those who used diaper dermatit protective creams appeared to have significantly high incidence of the disease the reaseon was that beacause of the cream preference. In one of the study there was a significant different between the use of protective material every after diaper change in the incidence of the diaper dermatit, [9] whereas in another study there was no such a relationship [8]. Very tightly diaper babes compared to those with lightly tightened diapers were found to have more increased risk of diaper dermatit development. Very tightening leads to diaper diare on baby’s buttocks because of airlesness.
In the study by Çimen et al. show that there are no programmed and continuous use of protective cream. Most used protective products are zinc oxide and vaseline. Protective creams such as vaseline zinc oxide dimetikon as well as lanoline make a lipid layer on the skin and therefore prevent the skin from the irritants and microorganisms. Some of the protective creams contain good smell ingredients such as aloe vera vitamins and plants and because of this property they have been found to be allergens or potentially skin destructive. If there are any infections the protective creams may intensify the clinical feature [10]. One of the most used creams, vaseline which is a long chaın aliphatic hydrocarbon mixture (petrolatum) being hydrofobic may be a skin protector [5,10]. Other frequently used creams contaıng zinc oxide they have barrier making capacity but very hard to be removed from the skin. In addition to its protective ability zinc oxide helps in healing the destructed skin and it has low toxicity [10]. Most of the artificial protective creams contain zinc oxide as well or vaseline. Also finally in the diaper produaction the inner part of diaper is made with zinc oxide/vaseline/sterile alcohol compounds. Diapers containg zinc oxide/Vaseline [19] and those containg only Vaseline has been shown to reduce the diaper dermatit rate and severity [20]. Because of its side effects such as skin atrophy and cushing syndrome too much use of corticosteroid is not advised [21]. Vaseline (white) known being with moisturising as well as water impermeability (waterproof barrier) properties protect the skin.
According to nurses situations quality care can be provided. If nurses and families know the general diaper dermatit criteria the disease development can be diagnosed earlier. They especially have to be aware of the the disease etiologic features, protection as well as alternative treatment measures to prevent the disease. Firstly the nurses goal should be on preventing the disease development as well as giving education to parents [1,10].
Both our country and worldwide diaper dermatit causative agents and frequency related researches are available however there are not preventive measure researches on the diaper dermatit.
The aim of this study is find out the effect of protective genital care on reducing the diaper dermatit development in 0 - 18 months old inpatient children who are using antibiotic.
Hypothesis 1: In 0 - 18 month old childrens on antibiotic those who were provided with the diaper dermatit prevention measures appeared to be very few compared to those not provided with care.
Hypothesis 2: In 0 - 18 month old childrens on antibiotic there appeared to be difference in diaper dermatit starting time between those who were provided with the diaper dermatit prevention measures and these not provided with care.
Hypothesis 3: In 0 - 18 month old childrens on antibiotic those who were provided with the diaper dermatit prevention measures appeared have different severity of the diaper dermatit.
2. METHODS
2.1. Research Type
The study was conducted as prospective half-experimetal using control-experimental groups.
2.2. Research Cases
Our examples comprise of 0 - 18 month old childrens admitted at Dokuz Eylul University Practical and Research Hospital, pediatric clinic between January and May 2009. There were 41 0 - 18 month old children as contol group and 42 0 - 18 month old children as experimental group. In the previously conducted researches it has been show the prevalence of diaper dermatit disease to be in a ratio of 61.5% - 69.2%, take averagely to be 67.5% [12,22]. At the end this ratio was aimed to be reduced to 50%. According to these data (67.50% - 33.75%) the Alpha security level 95%, and the experimental power as 80 in power analysis example taken to every group were shown to be at least 26. At the end of the study; control and experimental group data were n: 41/n: 42, diaper dermatit development ratio were 34.1%/ 7.1% and the alpha security level was 95%, respectively and in the conducted power analysis, power of the test found to be 93.1 (DSS research, 2009). Experimental and control groups in terms of factors that affect the occurrence of diaper rash were paired. The groups were compared by chi-square analysis, there was no significant statistical difference between the group (p > 0.05, Table 1). According to SPPS 15 package program the finding of the study are meaningful when p < 0.05 (95% confidence interval) and according to the same program the finding are not meaningful p > 0.05.
2.3. Example Selecting Criteria
The study was taken the first day since the 0 - 18 month old children start antibiotic and followed-up between 3 - 7th day. Those who were discharged out of the hospital three days before were not concluded in the study. The diaper dermatit generally developed second and third day. 0 - 18 month old children were observed between 37 day because the number of 0 - 18 month old children using antibiotic more than seven day decrease. Only those who
Table 1. Comparison of the features affecting development of diaper dermatit in control and experimental group.
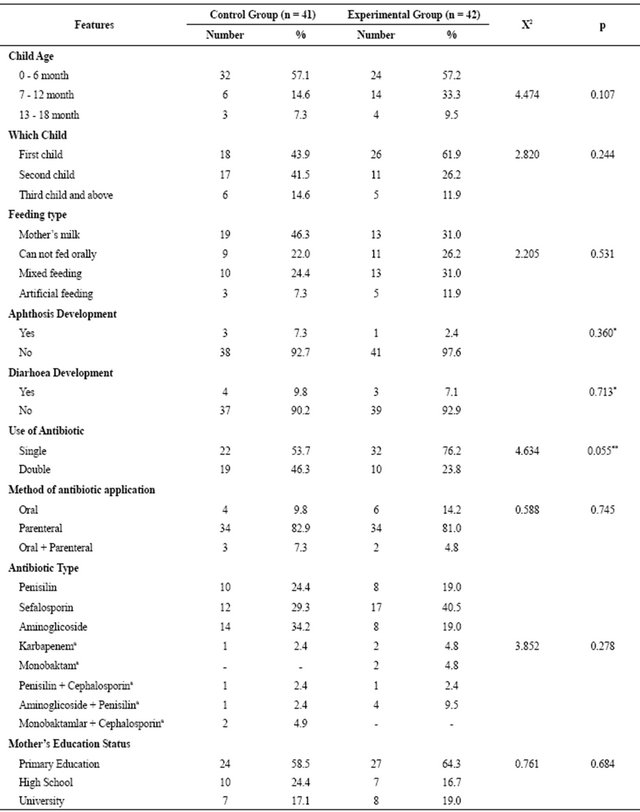
*Because the expected number was less than 5, Fisher’s exact chi-square analysis was done; **Because the expected number was less than 25, Correcting Yates Chi-square analysis was done; aBecause of less numbers groups were combined and analyses; Not allowed to be used is the same in both groups of antibiotics did not make the difference.
were using the disposable diaper were considered in this study. The following 0 - 18 month old children were not considered into the study; those who could control their toilet behaviour, premature and low birth weight babies, 0 - 18 month old children previously had a history of diaper dermatit, diarhea, aphthosis, eczema, allergic diseases and skin diseases such as seborhoiec dermatitis, 0 - 18 month old children on antimycotic drugs (amphoterisin etc.), meningomyelocele, those with urinary incontinance because of reasons such as cerebral palsy etc., and those 0 - 18 month old children who would develop genital iritation or redness from long-time use of urinary bag.
Children in the control group did not considered differently. The control group included 0 - 18 month old children using antibaotic, and were not provided with special education and protective care from the diaper dermatit during the antiaiotic using period. Firstly the control group data and then experimental group’s data were collected since there was not diaper dermatit protective care education in the routine clinic.
The experimental group icluded 0 - 18 month old children on antibiotic treatment for the diaper dermatit from the first day. 0 - 18 month old children using antibiotic together with their mothers were given one-to-one education on the diaper dermatit through genital region care as well as protective cream such as using vaseline and during the treatment period all the 0 - 18 month old children were made sure they get proper protective care. The protective care includes; frequent diaper changing (at least 5 times), genital region cleaning (with soap), infruquent use of diaper, and use of protective cream such as vaseline(white vaseline) after changing dipaer. In this study because of its hydrophobic feature vaseline was prefered [5,19] and the specialist consultation was taken on protective care content and the education brochure.
2.4. The Definitive Features for Control and Experimental Group
When the Nondefinitive features in the development of diaper dermatit of the 0 - 18 month old children included in the study were carefully studied and 61% of 0 - 18 month old children in the control group, 61.9% of the experimental group were boys, the care-givers in the control group were all the mother of those 0 - 18 month old children but in the expeimental group just 90.5% of the care givers were mothers of the 0 - 18 month old children others were family relatives such as grandmother etc. were found. The average ages of the care givers were 28.8 ± 5.0, in the control group and 26.9 ± 5.0 in the experimental group. The reason of hospital admission for all the 0 - 18 month old children was mostly respiratory pathway infections (C: %58.6, E: %45.2). Among other reasons for hospital admission included urinary system and other system’s infections. Other known effective definitive features which belonged to the 0 - 18 month old children for diaper dermatit development are given in the Table 1.
Factors affecting development of diaper dermatit in the control as well as experimental group were studied. The factors affecting diaper dermatit development, included in the Table 1, to show their similarities between the two groups, the groups were compared by chi-square analysis, there was no significant statistical difference between the group (p > 0.05, Table 1). There was no changes made on the 0 - 18 month old children genital caring practices in the control group. And the genital caring condition in this group is given in the table below (Table 2).
Mothers of the 0 - 18 month old children in the control group were provided with diaper dermatit protection care practicals. While the number of diaper changing per day to every child in the experimental group were at least 5, this number was more less in the control group. While diaper region wiping with water or cleaning and ventilation were done in all the 0 - 18 month old children in the experiment group, this practices were less given. Diaper tightening condition was done to no child in the experimental group but some 0 - 18 month old children in the control group seen to be tightened tightly.
2.5. Dependent and Independent Variables
2.5.1. Dependent Variables
Diaper dermatit development condition and severityTable 2. Protective genital care practices in control group children (N = 41).
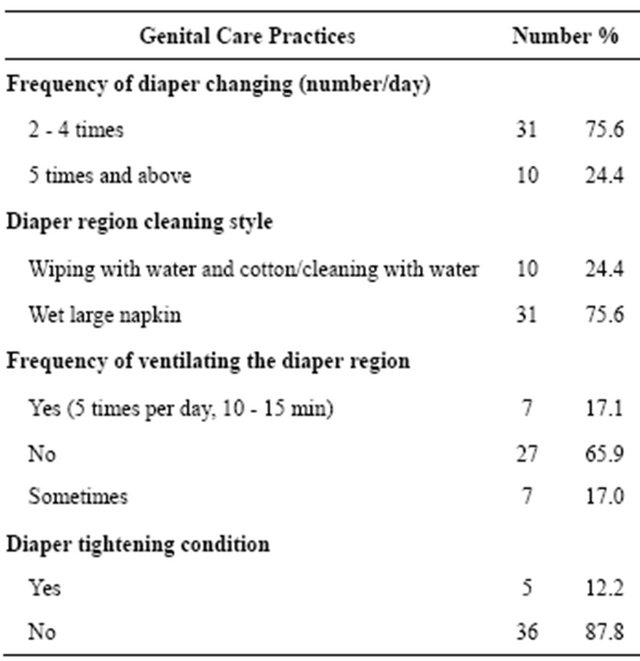
development day.
2.5.2. Independent Variables
Diaper dermatit protective care education as well as care provision condition.
2.5.3. Data Collection Mediator
In the study 0 - 18 month old 0 - 18 month old children, according to their social-demographic features 10 questions, according to genital caring 10 questions were prepared in a data collecting form and by using the diaper dermatit degree Classification developed by Kırçuval (2001), diaper dermatit Region Evaluating Form planned by Çimen et al. was used.
2.5.4. Diaper Dermatit Evaluation
Place-Diameter
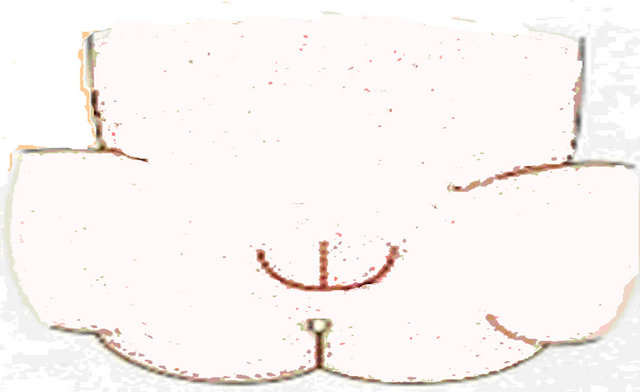
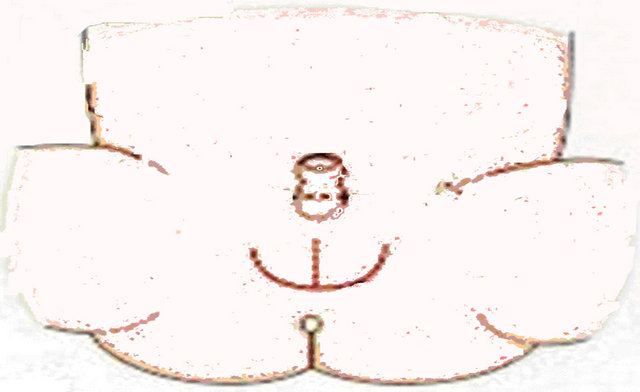
Diaper dermatit degree in the diaper dermatit 0 - 18 month old children would be categorised according to the diaper dermatit region signs.
1) Degree: Mild redness limited to only diaper region.
2) Degree: Evident redness, lesion or desquamation limited to the diaper region.
3) Degree: Redness spread from diaper region to medial part of thighs and abdomen.
4) Degree: Evident Redness, erosion and pustules spread from diaper region to medial part of thighs and abdomen.
2.5.5. Data Collection
The data were collected by the researchers in the hospital environment through face to face talking with mothers and the 0 - 18 month old children’s skin was observed 24 hours and data was filled in the data collecting form. Also when the diaper dermatit appears the child was observed by two observers (researcher and clinic’s nurse) an evaluated. Nurses who joined in the observation were given informations one by one about the diaper dermatit definition by the researchers. 0 - 18 month old children were observed 3 - 7 day. Control group were observed in an average of 5.3 ± 1.5 days, experiment group averagely 4.5 ± 1.7 days (t = 2.23, p = 0.150).
2.5.6. Data Evaluation
The research data were evaluated through computer by using Pearson chi-square, Fisher’s exact chi-square and Yatest-corrected chi-square tests.
2.5.7. Research Ethic
The permission of conducting the study was officially given by Dokuz Eylul University Nursing Highschool Ethic cabinet. Mothers who participated to the study were given informations on the aim of the study as well as about what were going to be done and verbal permissions were given from them and therefore those who decided to volunteer to the study were taken into consideration. Since she decided not to participate, one of the mothers who was considered in the experimental group did no participate in the study. During the study time when diaper dermatit appears in both groups doctor was consulted for treatment.
3. RESULTS
The diaper dermatit development ratio between the control group and experiment group was statistically very significantly high in control group compared to experiment group (control group: 34.1%; experiment group: 7.1%, p < 0.01, Figure 1).
More than half of 0 - 18 month old children in the control group were seen with diaper dermatit (57.1%) in the second and third day and the remaining were seen with the disease after the fourth day. 0 - 18 month old children in the experiment group (n: 2; 66.7%) developed diaper dermatit in fourth and fifth day, one child in 6 - 7th day (n: 1; 7.1%) diaper dermatit developed in the control group 0 - 18 month old children 85.8% were first degree and 14.2% were second and third degree while diaper dermatit developed in the experiment group 0 - 18 month old children were all (n: 3) first degree diaper dermatit (p < 0.05) (Figures 2 and 3).
4. DISCUSSION
It is possible to control frequently seen problems such as diaper dermatit and its facilitating factors in 0 - 18 month old children by providing good genital care and controlling the facilitating factors for the diaper dermatit. In this study protective genital care practices against diaper dermatit were studied. Both in our country and in the world the studies about diaper dermatit treatment and etiologic features are frequent, however there are no studies about protective genital care against the diaper dermatit and by this reason our discussion is very limited. In this study programmed protective genital care given by educated mothers and vaseline used in the experimental group 0 - 18 month old children (7.1%), those who were not provided with the programmed care (34.1%) when compared significantly diaper dermatit was seen in the later. The first research hypothesis was agreed. It is advised to

Figure 1. Diaper dermatit development ratio comparison between control group and experiment group.
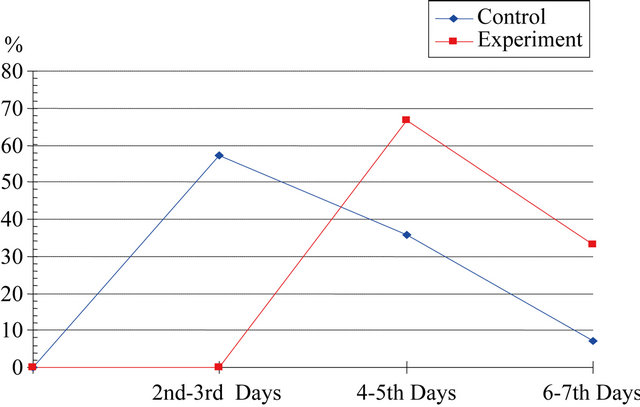
Figure 2. Diaper dermatit development day comparison between control and experimental group.
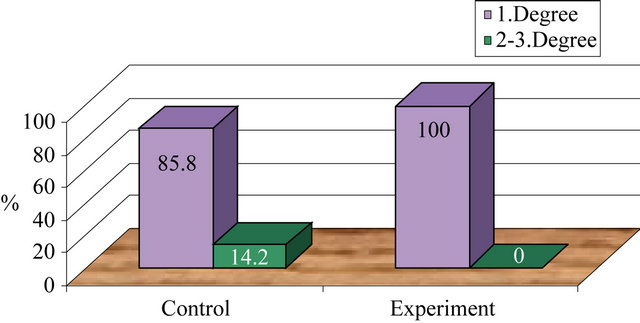
Figure 3. Diaper dermatit severity comparison between control group and experiment group.
prevent diaper dermatit by ensuring the following measures; diaper region dryness, diaper changing after every defecation and changing diaper at least 5 times a day, ventilating the diaper region every after cleaning, lightly tightening the diaper, not frequently using tight clothes, optimum room temperature and without moisture, the use of effective materials and frequent ventilation [5,23]. In other studies changing diaper at least five times a day, [9,16]. Lightly tightening of the diaper [8] was seen with decreased ratio of diaper dermatit.
Antibiotic use increases the risk of diaper development. In this study 0 - 18 month old children on antibiotic and who were in the experiment group, their mothers provided with the education on how to reduce the diaper dermatit and the use of vaseline however in clinic standards protective care being not programingly given to the control group would lead to the development of diaper dermatit (Figure 1). Most of the 0 - 18 month old children in the control group used nonalcoholoc wet napkins for the region cleanness however in various studies wet napkins were seen not be effective on the diaper dermatit development [1,8,20]. In this study it was mostly suggested that diaper changing frequency, ventilation as well as lightly tightening of diaper being very effective in diaper dermatit development.
The reason for the less frequently seen diaper dermatit in the experiment group was related not only to protective genital care practices but also the use of vaseline every after the diaper. It is advised to moisturise the diaper region, to prevent the contaction of urine and feces from skin so as to prevent the diaper dermatit. In our study vaseline was used as the protective material. Vaseline known being with moisturising as well as water impermeability properties protect the skin [5,10]. In one study, 0 - 18 month old children with diaper dermatit were also treated with zinc oxide/vaseline containing diaper as decreased the ratio and severity of diaper dermatit [19,24,25]. In other study diaper containing vaseline was seen to reduce the severity and redness in the 0 - 18 month old children with diaper dermatit [20].
Definitively in various studies, in 0 - 18 month old children on antibiotic and who were not provided with the protective genital care the diaper dermatit frequency was 61.5% - 69.2% [8,9]. In this study 0 - 18 month old children who were not provided with special protective care the development of diaper dermatit was found to be about half of the ratio seen in other studies. And it was related to the fact that even if protective care was not given, a 3 - 7 day observation increased the awareness of mother and they would have been giving their 0 - 18 month old children good care during the observation period. In Çimen et al. study the condition between the diaper dermatit incidency and protective materila use was not of significant difference [8]. In Kırçuval’s those who study protective material when compared to those who did not use, the less diaper dermatit frequency was observed in those who did not use protective material. Also in Kırcuval study when comparing among the protective materials zinc oxide, dexpantenol, cosmetic creams and vaseline containing creams there was a closely relation on the diaper dermatit ratio. While it was expected the use of protective material to reduce the diaper dermatit, in definitive and cross-section studies it was not fond to be effective in reducing diaper dermatit. The reason for inharmony between the results and this study were thought to be improper use of the products and especially according to mothers testimonies, mothers of 0 - 18 month old children with diaper dermatit preference of using protective material [1,9].
The diaper dermatit developing day and severity difference among groups with the study’s second and third hypothesis did not tested because of the low number of diaper dermatit development in the experiment group. In order to reach these data in the future it clearly that larger number of examples are needed. In this study, the diaper dermatit appeared earlier (most of them being 2nd and 3rd day) than in the experiment group (after 4th day).
Those who developed diaper dermatit in experimental group were also rather mild. While most of the control group 85.7% developed first degree diaper dermatit all the experiment group developed first degree diaper dermatit. It was suggested that the apperance of diaper dermatit in late days in experiment group and unprogressive diaper dermatit severity related to the effectiveness of the protective genital care and moisturising and hydrophobic property of the vaseline [5,10]. Vaseline is thought to protect skin from contact with the urine and feces and therefore reduced skin damage, by forming a lipid layer on the skin. Also in other study it was found that the diaper dermatit severity was significantly reduced in 0 - 18 month old children used zinc oxide/vaseline as the protective material compared to those who used normal diaper [19,20,26-29]. In this study also, vaseline skin protective effect is the matter of subject.
5. CONCLUSIONS
In this study 0 - 18 month inpatient on antibiotic were considered and the comparison between those provided with protective genital care and those who were not provided were done experiment group which provided with the protective genital care had a diaper dermatit development ratio of 7.1% less than those in the control group who were not provided with the protective genital care having a diaper dermatit development ratio of 34.1% (p < 0.05). Diaper dermatit seen in control group 0 - 18 month old children appeared in 2nd - 3rd day earlier than experiment group 0 - 18 month old children which appeared in 4th day and above, and the being very few cases the data could not be tested. Diaper dermatit in experiment group 0 - 18 month old children was very mildly. All the experiment group 0 - 18 month old children with diaper dermatit appeared to have first degree while those in the control group had 2nd and 3rd degree diaper dermatit and the numbers being very few, could not be tested.
Since diaper dermatit have been seen frequently in 0 - 18 month old children using antibiotic programmed protective genital care (every after defecation and more than five times a day diaper changing, cleaning/wiping with warm water, frequent ventilation, the use of effective protective material like vaseline, lightly tightening of the diaper) is needed to protect 0 - 18 month old children from diaper dermatit every after changing diaper protective cream like vaseline should be applied and care giver such as mother or baby-sitters should be advised likewise. To prevent or reduce development of diaper dermatit in 0 - 18 month old children using. Genital diaper brochures about the subject concerned should be given to mothers to provide genital care education. To prevent or protect 0 - 18 month old children from diaper dermatit different products should be used and then the studies about their effectivity comparisons should be done and repeated with larger number of examples.
![]()
![]()
REFERENCES
- Adalat, S., Wall, D. and Goodyear, H. (2007) Diaper dermatitis-frequency and contributory factors in hospital attending 0 - 18 month old children. Pediatric Dermatology, 24, 483-488. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00499.x
- Adherton, D.J. (2001) The aetiology and management of irritant diaper dermatitis. European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 15, 1-4. doi:10.1046/j.0926-9959.2001.00001.x
- Akin, F., Spraker, M., Aly, R., Leyden, J., Raynor, W. and Landin, W. (2001) Effects of breathable disposable diapers: Reduced prevalence of candida and common diaper dermatitis. Pediatric Dermatology, 18, 282-290. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1470.2001.01929.x
- Akkaya, S. (1990) Diaper döküntüler “Diaper dermatit”. Katkı Pediatri Dergisi, 11, 41-44.
- Al-Waili, N.S. (2005) Clinical and mycological benefits of topical application of honey, olive oil and beeswax in diaper dermatitis. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 11, 141-163. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01013.x
- Baldwin, S., Odio, M.R., Haines, S.L., Connor, R.J., Englehart, J.S. and Lane, A.T. (2001) Skin benefits from continuous topical administration of a zincoxide/petrolatum formulation by a novel disposable diaper. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 15, 5-11. doi:10.1046/j.0926-9959.2001.00002.x
- Biltekin, Ö., Boran, Ö.D., Denkli, M.D. and Yalçınkaya, S. (2004) Naldöken sağlık ocağı bölgesinde 0 - 11 aylık bebeği olan annelerin doğum öncesi dönem ve bebek bakımında geleneksel uygulamaları. Sürekli Tıp Dergisi, 13, 166-168.
- Borkowksi, S. (2004) Diaper rash care and management. Pediatric Nursing, 30, 467-470.
- Campell, R.L., Bartlett, A.F., Sarbaugh, F.C. and Pickering, L.K. (1988) Effects of diaper types on diaper dermatitis associated with diarrhea and antibiotic use in 0 - 18 month old children in day-care centers (Abstract). Petiatric Dermatology, 5, 83-87. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1988.tb01143.x
- Concannon, P., Gisoldi, E., Phillips, S. and Grossman, R. (2001) Diaper dermatitis: A therapeutic dilemma. Results of a double-blind placebo controlled trial of miconazole nitrate 0.25%. Pediatric Dermatology, 18, 149-155. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1470.2001.018002149.x
- Çimen, S., Aslan, G. and Yaprak, E. (2007) Hastanede yatan 0 - 24 aylık bebeklerde pişik görülme durumu ve etkileyen etmenlerin incelenmesi. Ege University School of Nursing Pediatric Nursing 1st National Congress Abstract Book, 100.
- Daniel, B.W., Alan, B.F., Steven, R.F. and Daniel, P.K. (2000) Characterization of diaper dermatitis in the United States. Archive Pediatric Adolescent Medicine, 15, 943- 946.
- Davies, M.W., Dore, A.J. and Perissinotto, K.L. (2008) Topical Vitamin A, or its derivatives, for treating and preventing napkin dermatitis in infants (Review). The Cochrane Library, 4, 1-11.
- DSS Research (2009) Researcher’s toolkit. http://www.dssresearch.com/toolkit/sscalc/size_p2.asp
- Ehretsmann, C., Schaefer, P. and Adam, R. (2001) Cutaneous tolerance of baby wipes by infants with atopic dermatitis, and comparison of the mildness of baby wipe and water in infant skin. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 5, 16-21. doi:10.1046/j.0926-9959.2001.00004.x
- Ferrazzini, G., Kaiser, R.R., Cheng, S.K.H., Wehrli, M., Casa, V.D., Pohlig, G., Gonser, S., Graf, F. and Jörg, W. (2003) Microbiological aspects of diaper dermatitis. Dermatology (Basel), 206, 136-141.
- Fiorillo, L. (2004) Therapy of pediatric genital diseases. Dermatology Therapy, 7, 117-128. doi:10.1111/j.1396-0296.2004.04012.x
- Görak G. (2002) Yenidoğanın deri hastalıkları. In: Türkan Dağoğlu, T. and Görak, G., Eds., Temel Neonataloji ve Hemşirelik İlkeleri, Nobel Tıp Kitabevleri, 3rd Edition, Nobel Matbaacılık, İstanbul, 649-650.
- Gupta, A. and Skinner, A. (2004) Management of diaper dermatitis. International Journal of Dermatology, 43, 830- 834. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02405.x
- Hatipoğlu, N., Kurtoğlu, S., Keskin, M. and Kendirci, M. (2007) Topikal steroid kullanımına bağlı iyatrojenik cushing sendromu. A case rapors. Erciyes Medical Journal, 29, 155-158.
- Honig, P.J., Gribetz, B. and Leyden, J.L. (1988) Amoxicillin and diaper dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 19, 275-279. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(88)70171-1
- Kırçuval, D. (2001) 0 - 2 yaş çocuklarda diaper dermatiti sıklığı, klinik özellikleri ve etyolojik faktörlerin değerlendirilmesi. University of Trakya, Edirne, 43-60.
- Odio, M.R., Scot, J.S. and Hansen, R.C. (2001) Disposable baby wipes: Efficacy and skin mildness. Dermatology Nursing, 13, 107-121.
- Odio, M.R. and Fallon, F.S. (2000) Diaper dermatitis and advances in diaper technology. Current Opinion Pediatrics, 12, 342-346. doi:10.1097/00008480-200008000-00011
- Odio, M.R., Oconnor, R.J., Sarbaugh, F. and Baldwin, S. (2000) Continous topical administration of a petrolatum formulation by a novel disposable diaper. Dermatology, 200, 238-243. doi:10.1159/000018366
- İşgüven, P., Yıldız, M., Ergüven, M., Malçok, M. and Güven, A. (2007) Bez dermatiti nedeniyle kullanılan topikal steroide bağlı cushing sendromu: A case rapor. Güncel Pediatri, 5, 35-37.
- Kimberly, A.H. (2009) Patient information: Diaper rash in infants and 0 - 18 month old children. http://www.uptodate.com/patients/content/topic.do?topicKey=~xrAHHNqmCOJqF1t
- Longhi, F., Garluccı, G., Bellucci, R., Gırolamo, D.I. and Palumbo, G. (1992) Amerıo P. Diaper dermatitis: A study of contributing factor. Contact Dermatitis, 26, 248-252. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb00237.x
- Mandleco, B.L. (2002) Theoretical approaches to the growth and development of 0 - 18 month old children. In: Micki, L.P., Ed., Pediatric Nursing Caring for 0 - 18 Month Old Children and Their Families, 4th Edition, Delmar Thomson Learning, Albany, 182.

